Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To PPE
Uploaded by
SHAIK NOOR AHAMED0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views10 pagesThe document discusses different power sources used in India. It mentions that power plant engineering deals with studying different types of power plants. Sources are divided into conventional (non-renewable) and non-conventional (renewable). In India, major sources of power generation include water/hydroelectric, coal, diesel, nuclear materials, and non-conventional sources like solar and wind. Hydel power plays a vital role as it is a perennial source, but developing hydroelectric projects requires long investigations. Nuclear power is an option for states with limited conventional resources, but developing nuclear plants requires technical capability and foreign exchange.
Original Description:
Original Title
1. Introduction to PPE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses different power sources used in India. It mentions that power plant engineering deals with studying different types of power plants. Sources are divided into conventional (non-renewable) and non-conventional (renewable). In India, major sources of power generation include water/hydroelectric, coal, diesel, nuclear materials, and non-conventional sources like solar and wind. Hydel power plays a vital role as it is a perennial source, but developing hydroelectric projects requires long investigations. Nuclear power is an option for states with limited conventional resources, but developing nuclear plants requires technical capability and foreign exchange.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views10 pagesIntroduction To PPE
Uploaded by
SHAIK NOOR AHAMEDThe document discusses different power sources used in India. It mentions that power plant engineering deals with studying different types of power plants. Sources are divided into conventional (non-renewable) and non-conventional (renewable). In India, major sources of power generation include water/hydroelectric, coal, diesel, nuclear materials, and non-conventional sources like solar and wind. Hydel power plays a vital role as it is a perennial source, but developing hydroelectric projects requires long investigations. Nuclear power is an option for states with limited conventional resources, but developing nuclear plants requires technical capability and foreign exchange.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Introduction
• Power Plant Engineering is a science, which deals
with the complete study of different types of
power plant. Sources are divided into two types
• 1. Conventional sources (Non-Renewable
Sources)-these are consumable sources.
– Ex: Coal, Diesel, Nuclear activity materials etc.
• 2. Non-conventional sources (Renewable Sources)
-these are non-consumable sources
– Ex: Solar, Wind, Tidal, Water etc.
Power Plant Engineering (PPE)
Power Plant Engineering is a science, which deals
with the complete study of different types of power
plant. Sources are divided into two types
1. Conventional sources (Non-Renewable Sources)-
these are consumable sources.
Ex: Coal, Diesel, Nuclear activity materials etc.
2. Non-conventional sources (Renewable Sources) -
these are non-consumable sources
Ex: Solar, Wind, Tidal, Water etc.
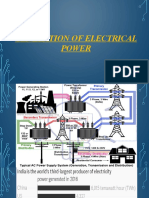
RESOURCES OF POWER IN INDIA
In India, the following sources are used to generate the
power.
1. Water energy – It is used in Hydro-Electric Power
Plant
2. Coal- It is used in Steam Plant
3. Diesel- It is used in I.C Engine plant
4. Nuclear activity materials- It is used in Nuclear Power
Plant
5. Non-conventional sources- These are used in Solar,
Wind & tidal power plant
Hydel Power
• The hydel power source plays a vital role in the
generation of power, as it is a non- conventional
perennial source of energy.
Hydel Power
• The world‘s total waterpower potential is estimated
as 1500 million kW at mean flow.
• Quantity equivalent to 3750 million tonnes of coal at
20% efficiency.
• India‘s total mean annual river flows are about 1675
thousand million cubic meters of which the usable
resources are 555 thousand million cubic meters.
• India‘s power potential from hydel source as per the
recent estimate is 41500 mW while its present hydel
capacity is only 32000 mW
Hydel Power
• The major difficulty in the development of
hydroelectric projects is the relatively longer time
required for its hydrological, topographical and
geological investigations. Lack of suitable. Site is an
added problem.
• It was less costly per mW to build a single 1000 mW
thermal plant than 20 small hydro plants.
• Small hydro-projects ranging from 10 to 1500 kW are
becoming more feasible as standardization of major
equipment reduces costs.
Nuclear Power
• The states which are poor in natural resources and
those which have little untapped conventional
resources for future development have to consider
the development of nuclear plants.
• The nuclear fuel which is commonly used for
nuclear power plants is uranium and thorium,
Nuclear Power
• Power source (thorium), which is abundant in this
country, estimated at 500,000 tonnes.
• The major hurdle in the development of nuclear
power in this country is lack of technical facility
and foreign exchange required to purchase the
main component of nuclear power plant.
You might also like
- Classification of Energy ResourcesDocument43 pagesClassification of Energy ResourcesAir SevakkNo ratings yet
- Power PlantsDocument12 pagesPower PlantsLinda Leon TomaNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy: Options, Capacity and InterventionsDocument50 pagesRenewable Energy: Options, Capacity and InterventionsMuhammad Salman ArshidNo ratings yet
- Power Generation BasicsDocument17 pagesPower Generation Basicsnavdeep kaurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3 PDFDocument47 pagesChapter 1-3 PDFdipeshNo ratings yet
- Non Conventional Energy SourcesDocument10 pagesNon Conventional Energy SourcesDivya Reddy SurkantiNo ratings yet
- Haramaya University: Haramaya Institute of TechnologyDocument25 pagesHaramaya University: Haramaya Institute of TechnologyFola BayanNo ratings yet
- Energy Management - Ivin & TeamDocument27 pagesEnergy Management - Ivin & TeamIvin MichaelNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Main Energy Resource and Energy Crises and SolutionDocument14 pagesPakistan Main Energy Resource and Energy Crises and SolutionTayyaub khalid79% (14)
- L-1 Energy ScenarioDocument67 pagesL-1 Energy Scenariomaliniguru2003No ratings yet
- STEMcrew LRF Energy Lesson2Document14 pagesSTEMcrew LRF Energy Lesson2Imran RafiqNo ratings yet
- LecPPT1 - Nuclear Engineering BasicsDocument41 pagesLecPPT1 - Nuclear Engineering BasicsVishal MeenaNo ratings yet
- Me8072-Renewable Energy Sources: Unit IDocument116 pagesMe8072-Renewable Energy Sources: Unit IradhaNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 Intro, Solar Rad & MeasDocument121 pagesMod 1 Intro, Solar Rad & MeasChandrashekar ByalyalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hydropower 1Document14 pagesIntroduction To Hydropower 1Hydropower NepalNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Natural ResourcesDocument71 pagesUnit 3 - Natural ResourcesKshitijNo ratings yet
- Renewable Sources of Energy1Document18 pagesRenewable Sources of Energy1Arpit KapoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-5Document397 pagesChapter 1-5shovonNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage Unit 4Document35 pagesEnergy Storage Unit 4VIJAYANAND.N NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Lec 2Document26 pagesChapter 1 - Lec 2Vinay PrakashNo ratings yet
- Hydropower 1Document30 pagesHydropower 1Asmita AryalNo ratings yet
- Generation of Electrical PowerDocument44 pagesGeneration of Electrical PowerMohanNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Non-Renewable Natural ResourcesDocument21 pagesRenewable and Non-Renewable Natural ResourcesKomal BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document77 pagesUnit 111209d008No ratings yet
- Aee Slides1Document46 pagesAee Slides1kannanNo ratings yet
- Status of Hydroelectricity in Nepal Potential and ChallengesDocument38 pagesStatus of Hydroelectricity in Nepal Potential and ChallengesSuraj RauniyarNo ratings yet
- Hydropower IntroductionDocument73 pagesHydropower IntroductionAvneesh Meena100% (1)
- Unit 1 The Energy Producing SourcesDocument45 pagesUnit 1 The Energy Producing Sourcesapi-241427002No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document29 pagesChapter 1Ranjan DhungelNo ratings yet
- RE PPT - 1Document47 pagesRE PPT - 120-811 mohd AleemNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument29 pagesIntroductionAaqibRNo ratings yet
- EE1451 RES 2 Mark Q & ADocument34 pagesEE1451 RES 2 Mark Q & AKrishnaram Kaliaperumal91% (33)
- 17 - Renewable Non-Renewable Energy SourcesDocument24 pages17 - Renewable Non-Renewable Energy SourcesSohilNo ratings yet
- NCES Module-IDocument14 pagesNCES Module-IVINAY BONALANo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy: Presented By: Jatin Meghlan Piyush Singh ChiraghDocument26 pagesRenewable Energy: Presented By: Jatin Meghlan Piyush Singh Chiraghjaazsingh100% (1)
- All AES & SSHP PDFDocument56 pagesAll AES & SSHP PDFAL habeshaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document54 pagesUnit 1Vansh R.No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document43 pagesLecture 2shahzodrahmatillayev12No ratings yet
- Alternative Energy ResourcesDocument16 pagesAlternative Energy ResourcesSreenu R SNo ratings yet
- ET NotesDocument313 pagesET Notesblackbeauty14No ratings yet
- Infrastructure Operations Management - Session VIIDocument41 pagesInfrastructure Operations Management - Session VIISai Ujjwala VemuriNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2MarkAnthonyS.LopezNo ratings yet
- 19ges20 - Renewable Energy SourcesDocument49 pages19ges20 - Renewable Energy Sourcesbitseee RandDNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument23 pagesEnergy ResourcesQueen BlehNo ratings yet
- 4 HydropowerDocument36 pages4 HydropowerBreadNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy in Global PerspectiveDocument43 pagesRenewable Energy in Global PerspectiveKhalil RazaNo ratings yet
- Electric Power Generation PDFDocument86 pagesElectric Power Generation PDFHARI R 1760805No ratings yet
- Unit 3A BeeeDocument15 pagesUnit 3A Beeejvharsha.sNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hydropower Engineering: Group MembersDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Hydropower Engineering: Group Membersएषण दाहालNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion and Rural Electrification: by Jemal HDocument18 pagesEnergy Conversion and Rural Electrification: by Jemal Hkass00488_180852609No ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Energy Resourses and UtilizationDocument40 pagesLecture 2-Energy Resourses and UtilizationsamwelNo ratings yet
- Hydropower NoteDocument446 pagesHydropower NoteUmesh RegmiNo ratings yet
- EVScomplete 1 PDFDocument19 pagesEVScomplete 1 PDFPrateek BalchandaniNo ratings yet
- RE MergeDocument216 pagesRE Mergeurstranger0No ratings yet
- 1.introduction 1Document21 pages1.introduction 1saurabhpatel19082002No ratings yet
- Energy Physics: 03 March 2021Document48 pagesEnergy Physics: 03 March 2021Rendani MuvhaliNo ratings yet
- Nuclearenergy 1 210115153034Document29 pagesNuclearenergy 1 210115153034gaviNo ratings yet
- Generation of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Generation of Electrical Power CourseFrom EverandGeneration of Electrical Power: Lecture Notes of Generation of Electrical Power CourseNo ratings yet
- B.tech R09 Mech Engg SyllabusDocument167 pagesB.tech R09 Mech Engg SyllabusSHAIK NOOR AHAMEDNo ratings yet
- Combined Cycle Power PlantDocument4 pagesCombined Cycle Power PlantSHAIK NOOR AHAMEDNo ratings yet
- Economics of Power PlantDocument16 pagesEconomics of Power PlantSHAIK NOOR AHAMEDNo ratings yet
- Layout of Different Power PlantsDocument17 pagesLayout of Different Power PlantsSHAIK NOOR AHAMEDNo ratings yet
- Development of Power in IndiaDocument3 pagesDevelopment of Power in IndiaSHAIK NOOR AHAMEDNo ratings yet
- Live Line Insulator WashingDocument8 pagesLive Line Insulator WashingWjdan Al ZwaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Bipv Introduction CourseDocument57 pagesLecture 1 Bipv Introduction CourseDaniel ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology of Non-SaccharomycesDocument15 pagesBiotechnology of Non-SaccharomycesIonuț NeaguNo ratings yet
- Subject 4. - Product Design OCW PDFDocument33 pagesSubject 4. - Product Design OCW PDFJose Luis BarradasNo ratings yet
- Bird On Fire Lessons From The World's Least Sustainable CityDocument310 pagesBird On Fire Lessons From The World's Least Sustainable CityDavidNo ratings yet
- Nova LiftDocument1 pageNova LiftFloorkitNo ratings yet
- Establishment of Standard X-Ray Qualities To Be Used in Diagnostic Level at SsdlsDocument50 pagesEstablishment of Standard X-Ray Qualities To Be Used in Diagnostic Level at SsdlsHoomi ShbNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating PumpDocument6 pagesReciprocating PumpManish SoniNo ratings yet
- An 571Document3 pagesAn 571shah435457No ratings yet
- Mvaw11 - 21 Brochure en 2018 12 Grid Ga 1657Document4 pagesMvaw11 - 21 Brochure en 2018 12 Grid Ga 1657selva rajaNo ratings yet
- Gas Welding NotesDocument5 pagesGas Welding NotesTanu RdNo ratings yet
- SMiRT-23 Paper107 RCCCW CourtoisClauzon-v1Document11 pagesSMiRT-23 Paper107 RCCCW CourtoisClauzon-v1CourtoisNo ratings yet
- Large Span Timber StructuresDocument34 pagesLarge Span Timber StructuresAnonymous 8f2veZf100% (1)
- ReneSola Micro Replus 250A 250BDocument2 pagesReneSola Micro Replus 250A 250BDario del AngelNo ratings yet
- CFD Analysis of An Annular Micro Gas Turbine Combustion Chamber Fuelled With Liquid Biofuels: Preliminary Results With BioethanolDocument10 pagesCFD Analysis of An Annular Micro Gas Turbine Combustion Chamber Fuelled With Liquid Biofuels: Preliminary Results With Bioethanolko koNo ratings yet
- Aqueous LiCl CaCl2 Solution Props UnlockedDocument31 pagesAqueous LiCl CaCl2 Solution Props UnlockedExal Eduardo Cabrera VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Durco IsoDocument28 pagesDurco Isomartin.rubenNo ratings yet
- Brodholt p1049-1053 97Document5 pagesBrodholt p1049-1053 97mauricio rojas alvarezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 PumpDocument63 pagesChapter 14 PumpRoque MoronNo ratings yet
- Power Supplies Module 02Document20 pagesPower Supplies Module 02Isabela Dos SantosNo ratings yet
- XS49281 4100XPC AC TrifoldDocument2 pagesXS49281 4100XPC AC TrifoldJuan Antonio TovarNo ratings yet
- RS6100004Document52 pagesRS6100004e_readingNo ratings yet
- SA08302002E - Control Panel Design GuideDocument37 pagesSA08302002E - Control Panel Design GuideDennis Codis100% (1)
- r050210801 Fluid Mechanics For Chemical EngineeringDocument7 pagesr050210801 Fluid Mechanics For Chemical EngineeringSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Industry Cables - General Catalogue - Prysmian Group 2016 - LR PDFDocument166 pagesIndustry Cables - General Catalogue - Prysmian Group 2016 - LR PDFEmre DalgicNo ratings yet
- Design of CFBC BoilerDocument86 pagesDesign of CFBC Boilerhalder.kalyan88% (8)
- Competency-Based Assessment Tool - CBAT V1 - 12!2!2020.-1Document44 pagesCompetency-Based Assessment Tool - CBAT V1 - 12!2!2020.-1humza sattiNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis of PSV Connected Piping Systems Using Caesar IIDocument6 pagesStress Analysis of PSV Connected Piping Systems Using Caesar IIwisesaNo ratings yet
- Offshore Pipe Line Design State of The ArtDocument33 pagesOffshore Pipe Line Design State of The ArtMvrnaidu MithraNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Performance Analysis of Francis HydDocument9 pagesA Study On The Performance Analysis of Francis HydAru Mithayatri RamlanNo ratings yet