Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Well Drilling, Mud and Casing
Uploaded by
Rizwan FaridOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Well Drilling, Mud and Casing
Uploaded by
Rizwan FaridCopyright:
Available Formats
Knowledge interrelated with well testing
Well Drilling, Mud
and Casing
Well Testing Co.
GWDC
2013-4
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Fixed rigs
Jack up rig Land rig
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Floating rigs
Semi-Submersible rig Drillship
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Water Depth vs. Rig Types
Onshore Bottom-supported Jack ups Semi-Submersible Drill Ship
(caisson)
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
4 categories of well: Vertical, Deviated, Horizontal and Slant.
Vertical
Deviated
Horizontal
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Land
Rig
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Rig Hoisting System
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Rig Floor
draw works
dog house
drive
mouse hole
rat hole
driller’s console
door ramp
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Rotary
System
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
In the Rotary
Table
Bushings
Slips
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Rotating Systems
– Kelly & Rotary Table drill 1 joint at a
time.
– Power swivel(top drive) drills in
stands (3 x 30’/2 x 45’)
– Down hole motor does not require
string rotation.
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
BOP stack Location
All Fixed Rigs All Floating Rigs
Just Bellow Rig Floor
Sea level
Ground level
BOP stack
Sea bed
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Why do we need a BOP stack ?
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Blow Out Preventers
Main Components
–Wellhead Connector
–Pipe Rams
–Shear Rams
–Blind Rams
–Annular Preventers
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
BOP stack
(drilling)
(drilling)
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
BOP stack / Pipe
Rams
•Fit a specific pipe size
•Need pipe to make a
seal
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
BOP stack / Shear Rams
•Both shears drill pipe and seals the hole
•Capacity to cut through 6-5/8” drill pipe
•Emergency equipment
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
BOP stack
Hydrill-type
Annular Preventer
Close/seal on
any object
in the wellbore
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
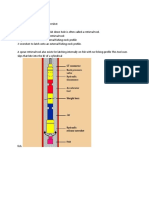
Drill Tubular
(from surface
to bit)
• Kelly stem,
• Drill pipe,
• Heavy wall
drill pipe,
• Drill collar
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Drill Tubular CONNECTIONS
Connection
type Male/female note
IF 211/210, 311/310, 411/410……
Drill FH 221/220,321/320,421/420……
Tubular REG 231/230,331/330,431/430……
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Rig
Circulating
System
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Drilling Fluids
The drilling fluid, popular named mud, is an essential
part of the drilling and well control system.
It is the blood of the drilling.
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Mud is used to:
• Cool, wash & lubricate the bit,
• Wash bottom, carry & suspend debris,
• Help to break up the rock in jet drilling,
• Provides a pressure to overcome that of the
formation,
• Makes a mud cake on well bore to seal
permeable formation,
• Drive down hole motor / turbine.
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Requirement of mud:
• Low damage to person & environment,
• Low influence to reservoir interpretation
& evaluation,
• Low damage to reservoir,
• Low erodibility to drilling equipment &
Tubular
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Variety of drilling fluid
Liquid Gas
Gas-liquid
mixture
Water-base Oil-base Aerated Foam Air Natural
mud mud mud gas
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Variety of drilling fluid
Water-base mud:
• Fresh water mud,
• Salt water mud,
• Sea water mud used on offshore, one of salt water muds
• Saturated salt-water mud,
• Calcium treated mud,
• Low solids mud,
• Emulsion mud (oil emulsion mud, oil-in-water)
……
Oil-base mud:
• Common Oil-base, water<10%,
• Water-in-oil emulsion, 10%<water<50%(60%),
Foam & air used in very low formation pressure
especially gas well.
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Oil-base mud
Advantages
• Caving inhibition
• Lubrication action prevent sticking
• Protect reservoir
• Good heat stability
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Mud properties
• Weight (density) ρ,
• Viscosity η: apparent viscosity η(Marsh funnel
viscosity) & plastic viscosity η,
• Shear forceτ: gel strength τs, yield value τo,
• Filtration (API, HTHP)
• Filter cake thickness,
• pH and alkalinity,
• Sand content,
• Solids content,
• Bentonite content,
• Inorganic ion contents
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Mud weight
•The mud density is kept at a level to overcome expected
reservoir pressures and keep the well at a positive
“overpressure”.
•It should be not too heavy or it will crack the formation,
resulting in “lost circulation”.
•Mud weight can be used in predicting the formation pressure
before carrying a well testing.
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Equivalent circulating density(ECD) =
Equivalent mud density (EMD)
ECD:
Sum of mud density and additive density converted by flow
resistance in bottoms up
ECD=EMD=mud density + head loss in bottoms up/depth
Note:
Usually the ECD in reverse circulation is bigger than ECD in
direct circulation
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Mud flow models
Shear
rate Newtonian
Dilatant fluid
fluid Pseudoplastic fluid
Bingham fluid
Casson fluid
s 0 Shear
stress
赫切尔—巴尔克莱流体
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Gel strength τs & Yield value τo
Bingham fluid
Shear rate γ
Bingham fluid
s 0 Shear stress
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Apparent viscosity ηe & Plastic viscosityηp
Bingham fluid
Shear rate γ
Bingham fluid
s 0 Shear stress
Model: = o+p ηe = τ/γ = (τo+ηpγ)/γ = τo /γ+ηp= ηs+ηp
:Shear stress (YP), Pa
o:Yield value (YP), Pa ηe: Apparent viscosity,
p:Plastic viscosity (PV), cP
:Shear rate, s-1 ηs: Structure viscosity
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Filtration & wall building effect
cake
Hydrostatic
column Static filtration Dynamic filtration
pressure
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Mud Cake
Good cake:
• Thin,
• Compact,
• Good toughness
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Categories of solids in mud
Function: Granularity:
• Useful solids • Clay: d<2m
– Clay • Silt: 2m< d<74m
– Barite • Sand: d>74 m
• Useless solids
– Debris(cuttings)
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Casing
Casing is seamless steel pipe string to be run
in hole to protect the wellbore from caving
after drilling a well or one stage of drilling.
After running in hole the casing the annular
space between bore hole face and casing will
be bonded through well cementing. When
produce the well a perforating job will be
usually needed to make holes on the casing
as passes between reservoir and well bore.
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Varieties of casing
• Conductor casing
• Surface casing: seal the shallow layer and fix
up the well head.
• Protection casing or intermediate casing. 1, 2
or 3 layers of protection casing depending on
well depth and formation badness.
• Production casing and/or liner
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Current Casing program
•Casings start large and
gradually become smaller
•Casing sizes are always
given as Outside Diameter
•The Inner Diameter
depends on the weight or
wall thickness
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Casing
Liner 5-1/2”
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
Cementing
•Cementing is used to fix the casing in place and provide
mechanical strength to the system.
•The most essential use of cementing is to seal one zone
from another.
•If the cement is found poor, a squeeze has to be made to
repair the deficit.
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
The END
2013 well testing training, Tarim, China
You might also like
- Shale Shaker and Drilling Fluids Systems:: Techniques and Technology for Improving Solids Control ManagementFrom EverandShale Shaker and Drilling Fluids Systems:: Techniques and Technology for Improving Solids Control ManagementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Orifice Meter & Barton RecorderDocument46 pagesOrifice Meter & Barton RecorderNoor AliNo ratings yet
- 05 - WC Fundamentals - How Do We Manage The Borehole - RUSDocument53 pages05 - WC Fundamentals - How Do We Manage The Borehole - RUSElnur AskerovNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 v1Document26 pagesLecture 2 v1Anwar Hossain PolasNo ratings yet
- Bored Piling: Products Design Pricing Production Rates New Features Contact Us CapabilitiesDocument7 pagesBored Piling: Products Design Pricing Production Rates New Features Contact Us CapabilitiesG-SamNo ratings yet
- Deva - Glide - Hydro - 2022-01 - EN PDFDocument21 pagesDeva - Glide - Hydro - 2022-01 - EN PDFMạnh Ngô VănNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument74 pagesBrochureBittu DubeyNo ratings yet
- Fracture Formation PressureDocument7 pagesFracture Formation Pressuredekra abdoNo ratings yet
- Terradrive: A Brief Guide To Pile TestingDocument4 pagesTerradrive: A Brief Guide To Pile TestingMars TinNo ratings yet
- IDPT - 05 - Casing Running & Cementing Volumes PDFDocument19 pagesIDPT - 05 - Casing Running & Cementing Volumes PDFMas KuncritNo ratings yet
- Aggregate-Fine and CoarseDocument37 pagesAggregate-Fine and CoarseDishit KalariyaNo ratings yet
- Rotoblast Barrels 12 15gnDocument2 pagesRotoblast Barrels 12 15gnBoanerges BritoNo ratings yet
- Clinker Coolers Part 1 & 2 96dpiDocument246 pagesClinker Coolers Part 1 & 2 96dpigustavo50% (2)
- Cementing Design - FinalDocument27 pagesCementing Design - FinalBIGBOAZ XX100% (1)
- Drilling Fluid PDFDocument68 pagesDrilling Fluid PDFShiela ONo ratings yet
- 13 AsAc - Site Considerations and CecklistsDocument35 pages13 AsAc - Site Considerations and CecklistsThabiso MotalingoaneNo ratings yet
- JDS - Drilling Fluid - 2021 - HandoutsDocument57 pagesJDS - Drilling Fluid - 2021 - Handoutsrainaldy sebastianNo ratings yet
- Company Profile-Rheem-23.3.23Document20 pagesCompany Profile-Rheem-23.3.23novi cmidNo ratings yet
- IDM Basic Training - EzCleanDocument22 pagesIDM Basic Training - EzCleanThomas DuNo ratings yet
- 001 - Perforating Gun TechnologyDocument98 pages001 - Perforating Gun TechnologyKARIMA BAUZIZNo ratings yet
- Tammsgrout Supreme FTDocument3 pagesTammsgrout Supreme FTHugo BlancoNo ratings yet
- Tension Test Specimen PDFDocument2 pagesTension Test Specimen PDFtushak mNo ratings yet
- Technical BookDocument36 pagesTechnical BookBorisvc8No ratings yet
- Plastic & Polymer Catalogue 2022Document20 pagesPlastic & Polymer Catalogue 2022Ramkrishna TalwadkerNo ratings yet
- XLW Ec Auto Tensile TesterDocument3 pagesXLW Ec Auto Tensile TesterTri AriadiNo ratings yet
- Kandhal Lecture 2 On Grading of Bitumen and Polymer Modified Bitumen (PMB) - Handouts OnlyDocument10 pagesKandhal Lecture 2 On Grading of Bitumen and Polymer Modified Bitumen (PMB) - Handouts OnlyProf. Prithvi Singh Kandhal100% (3)
- Bomba Peristalticas ABAQUE PSGDocument49 pagesBomba Peristalticas ABAQUE PSGGabrielNo ratings yet
- 04-Drilling& CompletionDocument123 pages04-Drilling& CompletionYoussef BarsoumNo ratings yet
- Ecs268: Structural & Material Laboratory: I. ObjectiveDocument7 pagesEcs268: Structural & Material Laboratory: I. ObjectiveMuhd MuqhreyNo ratings yet
- Strengthen Wellbores During DrillingDocument32 pagesStrengthen Wellbores During Drillingrıdvan duranNo ratings yet
- Basic Cementing - Customer PresentationDocument164 pagesBasic Cementing - Customer Presentationdanielmcae100% (1)
- Continuous Improvement in Grinding Process: Vaishali Auto IndustriesDocument17 pagesContinuous Improvement in Grinding Process: Vaishali Auto Industriesshivam daveNo ratings yet
- Sampling dan Preparasi BatubaraDocument32 pagesSampling dan Preparasi BatubaraogiNo ratings yet
- August 2015Document120 pagesAugust 2015Pumper MagazineNo ratings yet
- PDS Tammsgrout Supreme 4 July 2023 Replaces July 2022Document2 pagesPDS Tammsgrout Supreme 4 July 2023 Replaces July 2022Randy PolancoNo ratings yet
- Balaram IND PROJECT 2 (RANGE CERAMIC)Document42 pagesBalaram IND PROJECT 2 (RANGE CERAMIC)Abugajal SkNo ratings yet
- Drilling Rig Components and OperationsDocument67 pagesDrilling Rig Components and OperationsMohamed Kamal100% (1)
- TC Pump: The Total Slurry SolutionDocument4 pagesTC Pump: The Total Slurry SolutionDiego Mejia100% (1)
- Jinflex Hose CatalogueDocument17 pagesJinflex Hose Cataloguefater esmandarNo ratings yet
- BitumenDocument60 pagesBitumencdnaveen100% (6)
- Bit Running GuidelinesDocument39 pagesBit Running GuidelinesEmad Zaki100% (1)
- Fordia Drillers Guide To Diamond ToolsDocument20 pagesFordia Drillers Guide To Diamond ToolsNelson de la RosaNo ratings yet
- Roto PeenDocument12 pagesRoto Peenronbytom ronbytomNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - DrillingWellDocument38 pagesLecture 10 - DrillingWellJuwisa Diky PNo ratings yet
- Oil Well Cementing: A Concise GuideDocument51 pagesOil Well Cementing: A Concise GuideMohab AymanNo ratings yet
- Appendix ADocument18 pagesAppendix Asaras unggulNo ratings yet
- Param XLW (PC) Auto Tensile Tester: ProfessionalDocument3 pagesParam XLW (PC) Auto Tensile Tester: ProfessionalAamirMalik100% (1)
- MDM Slurry Seal Microsurfacing-Chip Seals-HandoutDocument47 pagesMDM Slurry Seal Microsurfacing-Chip Seals-HandoutMax CedNo ratings yet
- Drilling FluidDocument48 pagesDrilling FluidNasih AhmadNo ratings yet
- Aphron Fluids Study2 Ramzi AljadiDocument5 pagesAphron Fluids Study2 Ramzi AljadidrumilNo ratings yet
- Schlumberger - Bit Running GuidelinesDocument38 pagesSchlumberger - Bit Running Guidelinesmanuelperdomot100% (1)
- Solid Mechanics Lab: Description Experiment Performed QuantityDocument17 pagesSolid Mechanics Lab: Description Experiment Performed Quantityhmce kalyaniNo ratings yet
- Landmark - Halliburton Well Design SoftwareDocument3 pagesLandmark - Halliburton Well Design SoftwareAli AlakariNo ratings yet
- Technical training on rubber mixing and extrusion processesDocument32 pagesTechnical training on rubber mixing and extrusion processesShweta BagdiNo ratings yet
- Weekly Report Part 222Document38 pagesWeekly Report Part 222Julian Paul Villaruel QuerubinNo ratings yet
- Containment: Shell Technology IndiaDocument10 pagesContainment: Shell Technology IndiababscribdNo ratings yet
- Drilling Fluid - 2021 - Handouts - 16 September 2022Document87 pagesDrilling Fluid - 2021 - Handouts - 16 September 2022Egis KrismaNo ratings yet
- Equivallnt DensityDocument8 pagesEquivallnt DensityRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- C.5 Reservoir Saturation ToolDocument29 pagesC.5 Reservoir Saturation ToolTamer KoksalanNo ratings yet
- Pierre Lefoll - Frutos y Pernos de Las PruebasDocument14 pagesPierre Lefoll - Frutos y Pernos de Las PruebasVanessa Lema ZabalaNo ratings yet
- MinimumExpense 2Document4 pagesMinimumExpense 2Rizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Chapter 5-Formation EvaluationDocument38 pagesPresentation - Chapter 5-Formation EvaluationMazin AlfarsiNo ratings yet
- Control of Substances Hazardous To Health (COSHH) HSE Presentation HSE FormatsDocument39 pagesControl of Substances Hazardous To Health (COSHH) HSE Presentation HSE FormatsSyed Mustafa HussainNo ratings yet
- Instrument Air Supply SkidDocument7 pagesInstrument Air Supply SkidRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Office ContainersDocument6 pagesLaboratory and Office ContainersRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- PDC BitsDocument40 pagesPDC BitsRizwan Farid100% (1)
- UR Winter 2021 Int'l Student Fee ScheduleDocument2 pagesUR Winter 2021 Int'l Student Fee Schedulekarim alamiNo ratings yet
- H2S ScavengerDocument7 pagesH2S ScavengerRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- CALL 38 - PNRR - November - 2Document9 pagesCALL 38 - PNRR - November - 2Rizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- for Multiple Choice DocumentDocument7 pagesfor Multiple Choice DocumentRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- Glycol Dehydration UnitDocument9 pagesGlycol Dehydration UnitRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- English Language Proficiency Exempt Countries A I R: 2022-2023 Academic YearDocument1 pageEnglish Language Proficiency Exempt Countries A I R: 2022-2023 Academic YearKksbNo ratings yet
- NTS General Knowledge Questions - HamzaDocument13 pagesNTS General Knowledge Questions - HamzaRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- List 1: IELTS Academic WordlistDocument5 pagesList 1: IELTS Academic WordlistAnjana KumaraNo ratings yet
- Fishing retrieval tools: spears and overshotsDocument1 pageFishing retrieval tools: spears and overshotsRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- Jobs and NTS HelplineDocument52 pagesJobs and NTS HelplineRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- SNGPL+ GK + OverallDocument30 pagesSNGPL+ GK + OverallRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- FPSC GK by Web SiteDocument17 pagesFPSC GK by Web SiteRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- Best IELTS VocabularyDocument38 pagesBest IELTS VocabularyRizwan Farid100% (1)
- Analytical ReasoningDocument91 pagesAnalytical ReasoningRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- Punctuation PDFDocument13 pagesPunctuation PDFUsman AliNo ratings yet
- Remote SensingDocument172 pagesRemote SensingRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- Importan SynonymsDocument4 pagesImportan SynonymsRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- Gas lift valve failure analysisDocument10 pagesGas lift valve failure analysisRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- Fishing Operations EssentialsDocument24 pagesFishing Operations EssentialsRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- (IELTSMaterial - Com) 100 IELTS Speaking Part 2 Topics in 2016 & 2017 & Sample Answers PDFDocument135 pages(IELTSMaterial - Com) 100 IELTS Speaking Part 2 Topics in 2016 & 2017 & Sample Answers PDFUyenNo ratings yet
- Barrier Theory: Wellcontrolpreparation Live Course Comingon11 of March EnrollnowDocument11 pagesBarrier Theory: Wellcontrolpreparation Live Course Comingon11 of March EnrollnowRizwan FaridNo ratings yet
- Stas 8600-79Document2 pagesStas 8600-79joseNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document30 pagesLecture 7faiz alshammariNo ratings yet
- Foundation Design For Single PoleDocument3 pagesFoundation Design For Single PoleGururaj KanjikerNo ratings yet
- Sample Computation For FootingDocument3 pagesSample Computation For FootingDenice CastroNo ratings yet
- Marina Pier Repair Nasugbu BatangasDocument28 pagesMarina Pier Repair Nasugbu BatangasDennis SagaoNo ratings yet
- Gas Spring Test Data Gas Spring Test DataDocument3 pagesGas Spring Test Data Gas Spring Test DataRaja Sekaran SajjaNo ratings yet
- Calculating UV Dose For UV/AOP Reactors Using Dose/Log As A Water-Quality MetricDocument6 pagesCalculating UV Dose For UV/AOP Reactors Using Dose/Log As A Water-Quality Metricchirag vyasNo ratings yet
- Transient Investigations On Lightning Overvoltages Applied On Oil Tanks RoofDocument11 pagesTransient Investigations On Lightning Overvoltages Applied On Oil Tanks Roofferdad4realNo ratings yet
- NDT Method: Month: YearDocument3 pagesNDT Method: Month: YearRajaNo ratings yet
- The Hylomorphic Doctrine of Presence by Powers and Its Relationship With Contemporary ScienceDocument110 pagesThe Hylomorphic Doctrine of Presence by Powers and Its Relationship With Contemporary ScienceDoctrix MetaphysicaeNo ratings yet
- Thermo1-Problem Set Part 1Document4 pagesThermo1-Problem Set Part 1Elisif DeFairNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering PDFDocument4 pagesSoil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering PDFDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Mat1033 4 3Document24 pagesMat1033 4 3jan lawrence panganibanNo ratings yet
- GIET UNIVERSITY PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS EXAMDocument2 pagesGIET UNIVERSITY PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS EXAMPritesh RayaguruNo ratings yet
- Pascua Project For Module 2 Problem Set With SolutionDocument14 pagesPascua Project For Module 2 Problem Set With SolutionDJ KillNo ratings yet
- ME-204 - Slides Set# 09 (Phase Changes-I)Document29 pagesME-204 - Slides Set# 09 (Phase Changes-I)mamoona noreenNo ratings yet
- IIT Jodhpur Recruitment 2023 PDFDocument7 pagesIIT Jodhpur Recruitment 2023 PDFHari Bhushan BazalaNo ratings yet
- Temperature PressureDocument2 pagesTemperature PressureMenasita MayantasariNo ratings yet
- F T ra n sf o rm Y er 2.0 Participant Examination on Basic Radio Propagation TheoryDocument100 pagesF T ra n sf o rm Y er 2.0 Participant Examination on Basic Radio Propagation Theorytrevor t.kNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials (SOM) Concept Inventory: Jim Morgan, Jim RichardsonDocument13 pagesStrength of Materials (SOM) Concept Inventory: Jim Morgan, Jim Richardsonbadboys123No ratings yet
- Thermal Bridge DisplacementsDocument18 pagesThermal Bridge DisplacementsAhmed KhalafNo ratings yet
- Day 3 - HW Test Review SOL G.14 Practice 3 - Similar SolidsDocument3 pagesDay 3 - HW Test Review SOL G.14 Practice 3 - Similar SolidsRyan AndersonNo ratings yet
- Triaxial Permeability 2023Document3 pagesTriaxial Permeability 2023Kim Yuen WongNo ratings yet
- The Ins and Outs of Human Cognition in The Construction of MeaningDocument11 pagesThe Ins and Outs of Human Cognition in The Construction of MeaningmarceloNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements and Instrumentation July 2023Document7 pagesElectrical Measurements and Instrumentation July 2023Shanmukh VegiNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Circuit Implementation of Demyelinated Human PDFDocument95 pagesEquivalent Circuit Implementation of Demyelinated Human PDFAndres PosadaNo ratings yet
- ICU Medical Gas NeedsDocument4 pagesICU Medical Gas NeedsGamerBro IDNo ratings yet
- Tuning of PID Controller: Dr. Sadeq Al-MajidiDocument11 pagesTuning of PID Controller: Dr. Sadeq Al-Majidijin kazamaNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment On WaeguideDocument2 pagesHome Assignment On WaeguideTsG gHoSt oP100% (1)
- IB Physics 7e AnswersDocument171 pagesIB Physics 7e Answersღ꧁Lizzy X Roxiie꧂ღ100% (1)