Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C4 Chemical Kinetics
Uploaded by
PARAMBATH ANUP KUMAROriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C4 Chemical Kinetics
Uploaded by
PARAMBATH ANUP KUMARCopyright:
Available Formats
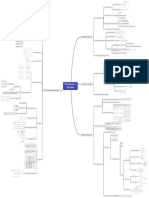
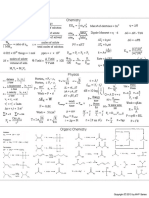
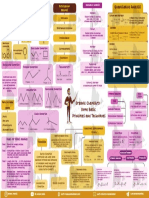
RATE OF REACTION
xX + yY
ORDER OF REACTION
for : aA + bB MOLECULARITY EFFECTIVE
Sum of powers of concentration Order of a COLLISION
• Number of reacting species
− 1 d[A] − 1 d[B] 1 d[x] 1 d[y] of reactants in the rate law. Molecular collide
rate = = = = reaction may taking part in an
a dt b dt x dt y dt be whole number elementary reaction
with sufficient
kinetic energy
or a fraction. • It cannot be zero or a and proper
fraction. ical orientation
A chem occurs
aA + bB → Pr oduct Molecularity = a + b n
reactiomolecules
INSTANTANEOUS when e with
RATE
AVERAGE RATE rate = k [A]x [B] y collid ient
suffic y.
order = x + y Energ
rate =
− d[R]
=
d[P]
rate =
−∆R −([R2 ] − [R 1])
=
cC + dD
aA + bB COLLISI
ON
dt dt NCY
∆t t 2 − t1
FREQUE ns
r of collisio
Numbe t volume of
i
per un n mixture.
RATE CONSTANT reactio
REACTION UNIT OF RATE CONSTANT (K) RATE
UNIT FOR nTH ORDER CONSTANT (k) ON
Zero Order mol L-1s-1
REACTION
RATE COLLISI FO R B I M OLECUL
AR
THEORY
ION
EXPRESSION REACT a/RT
First Order s-1 rate = k[A]x[B]y P z E-E
k = mol 1-n
Litren sec
-1 -1
rate =
rate ∝ A] x [B]y
A B
r
mol Ls ric facto
P → ste
-1 -1
Second Order
ollision
z AB → c cy
frequen
INTEGRATED RATE EQUATION
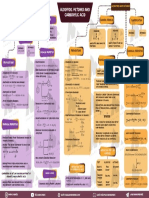
Reaction Differential Integrated Half life
rate law rate law -Ea
slope = R
d[R] kt = [R] − [R] [R] ln A
Zero Order =−k t 1/2 = °
ln k
dt ° 2k ARRHENIUS
First Order d[R]
= − k[R]
[R]
kt = ln °
t 1/2 =
0.693 EQUATION 1
temp.
dt [R] k
Radioactive
decay are first
order reaction.
k Ea T1 − T 2
log 1 =
ZERO ORDER FIRST ORDER k 2 2.303 T1 T2
Half life of nth
slope = -k order reaction
slope = -k
CHEMICAL KINETICS k = Ae-Ea/RT
Ea
ln (1/[R])
1− n
[R]
°
ln [R]
°
t1/2 ∝ [R° ] ln k = ln A −
[R]
time
RT
time
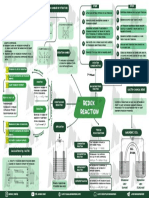
FACTORS INFLUENCING RATE
A .......B
PSEUDO FIRST ORDER (Activated complex without catalyst)
A B
REACTION
Ea(f) without X
catalyst
E’a(f) with
• are not truely first order PRESENCE OF catalyst E’a(b) without
CONCENTRATION TEMPERATURE SURFACE AREA E’a(b) with catalyst
Potential energy
reaction but in certain CATALYST catalyst
conditions behaves like those. Reactants
A+B
• hydrolysis of ethyl acetate in
Higher the concentration Rate of reaction
acidic medium` Greater is the surface Rate of reaction
of reactants, faster is increases with increases in presence Products
area, faster is the
the rate of reaction. increase in of a catalyst. AB + X
reaction rate.
temperature.
Reaction Coordinate
anand_mani16 DR. Anand Mani https://www.anandmani.com/ https://discord.io/anandmani t.me/anandmani001
You might also like
- Hydrogen From BiomassDocument24 pagesHydrogen From BiomassDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENo ratings yet
- GOC AllenDocument33 pagesGOC AllenAshish Ranjan100% (5)
- Retaining Wall Construction WorkDocument12 pagesRetaining Wall Construction WorkRohit Singh90% (10)
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Class 11 Handwritten NotesDocument20 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry Class 11 Handwritten Notesnaveenrao800050% (2)
- Applied Mechanics FullDocument175 pagesApplied Mechanics FullZhongli MoraxNo ratings yet
- Design Project 2013Document154 pagesDesign Project 2013Fahad HussainNo ratings yet
- Thermal and Catalytic Processes in Petroleum RefiningDocument933 pagesThermal and Catalytic Processes in Petroleum RefiningSrihari Kodimela100% (7)
- AcetaldehydeDocument98 pagesAcetaldehydeKrishna DangiNo ratings yet
- A.2. Noncompetitive InhibitionDocument6 pagesA.2. Noncompetitive InhibitionFlorecita CabañogNo ratings yet
- Acetic Acid Production ReportDocument15 pagesAcetic Acid Production ReportArya Lodha100% (1)
- Chemical Kinetics: Aa BB CC DD + +Document1 pageChemical Kinetics: Aa BB CC DD + +Chandra Vamsi AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument1 pageChemical KineticsSamNo ratings yet
- Chem Ch6 NIE Premium NOtesDocument17 pagesChem Ch6 NIE Premium NOtessnigdhagulhane0922No ratings yet
- PHY3001 - 2022 Lecture 2Document10 pagesPHY3001 - 2022 Lecture 2Catherine GrivotNo ratings yet
- PHY3001 - 2022 Lecture 3 - CopieDocument11 pagesPHY3001 - 2022 Lecture 3 - CopieCatherine GrivotNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument651 pagesChemical Bonding Notesaaron hacNo ratings yet
- Handnotes Lecture41-42Document13 pagesHandnotes Lecture41-42Faheem ShanavasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: Col Lisi On Effective CollisDocument1 pageChemical Kinetics: Col Lisi On Effective ColliseliyachrisNo ratings yet
- Goc Revision ALpOMyojEgukEz4EDocument36 pagesGoc Revision ALpOMyojEgukEz4Eanmolsinha6157No ratings yet
- 2a REACTION RATEDocument17 pages2a REACTION RATEMinh ThànhNo ratings yet
- QSB 07 - Function of Proteins1Document29 pagesQSB 07 - Function of Proteins1fta2013No ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction: Appearance of Products (P) (P2) - (P1)Document3 pagesRate of Reaction: Appearance of Products (P) (P2) - (P1)Pardeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - Q&ADocument43 pagesTutorial 1 - Q&AHilb KelbNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 Notes - RxnsDocument39 pagesMidterm 1 Notes - RxnsNadineNo ratings yet
- 11.4 Review 11.4 Review: Knowledge and UnderstandingDocument1 page11.4 Review 11.4 Review: Knowledge and UnderstandingKapila NayananandaNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Physics I (PS417) : Jul - Dec 2019 Assignment 2Document2 pagesMathematical Physics I (PS417) : Jul - Dec 2019 Assignment 2Subhankar HowladerNo ratings yet
- 20190029657Document16 pages20190029657Jorge Luis CastilloNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Term 3 TopicsDocument10 pagesGrade 10 Term 3 TopicsOwamiirh RsaNo ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips Tablas GpsaDocument8 pagesQdoc - Tips Tablas GpsaDavid AL'varado ValenciaNo ratings yet
- The If: FingersDocument12 pagesThe If: FingersRiddhi SheteNo ratings yet
- Physic f5 Chap1Document10 pagesPhysic f5 Chap1Ev LamNo ratings yet
- TopicsDocument311 pagesTopicsRekha BhasinNo ratings yet
- Online Lecture 2: Understanding Chemical and Phase Equilibrium Through The Concept of Chemical PotentialDocument21 pagesOnline Lecture 2: Understanding Chemical and Phase Equilibrium Through The Concept of Chemical PotentialChegg BoltheNo ratings yet
- Cat ActivationDocument1 pageCat ActivationChandra HasNo ratings yet
- PDP Math Revision WorsheetDocument1 pagePDP Math Revision WorsheetDaisyNo ratings yet
- Goc and Isomerism 1 YleLP2BEVwSg6aryDocument18 pagesGoc and Isomerism 1 YleLP2BEVwSg6aryzaviaisra1508No ratings yet
- Mind MapsDocument2 pagesMind Mapstobilobagee69No ratings yet
- Chemical Equilbrium 2Document4 pagesChemical Equilbrium 2bisenpallavi80No ratings yet
- 電動力學 L1Document18 pages電動力學 L1盧郁傑No ratings yet
- 1 26-Completed Rate Graph Notes 3Document15 pages1 26-Completed Rate Graph Notes 3api-336093393No ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument17 pagesChemical Kineticsabc defNo ratings yet
- Impact Actions Fundamentals 2019 1Document37 pagesImpact Actions Fundamentals 2019 1Zuhair NadeemNo ratings yet
- Algoritm of Solution Chem. Reaction Eng. (Intepretation of Batch Data) BatchDocument2 pagesAlgoritm of Solution Chem. Reaction Eng. (Intepretation of Batch Data) BatchXxxNo ratings yet
- Algoritm of Solution Chem. Reaction Eng. (Intepretation of Batch Data) BatchDocument3 pagesAlgoritm of Solution Chem. Reaction Eng. (Intepretation of Batch Data) BatchAnonymous pm9ApyB9MpNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Activity Based QuestionsDocument9 pagesCH 2 Activity Based QuestionsHamendra SahuNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument29 pagesChemical KineticsAditya PandeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 OkDocument17 pagesChapter 9 Okwaelabood51No ratings yet
- Matter WavesDocument5 pagesMatter Waveshtxpv4ccsyNo ratings yet
- RegletedDocument3 pagesRegletedYulia YuanNo ratings yet
- Checklist m2Document3 pagesChecklist m2Arwa HamdiNo ratings yet
- Amount of SubstanceDocument10 pagesAmount of SubstancelivvyridpNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics NotesDocument11 pagesNuclear Physics NotesMichelle nananaNo ratings yet
- Intro To RegressionDocument30 pagesIntro To RegressionShewakena GirmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry!: π ω Friction = F i Friction ≤ F i ΔL= αL ΔT ΔA= γ A ΔT P= Energy time I= Power SA Δf = v c Δ λ λ = v cDocument1 pageChemistry!: π ω Friction = F i Friction ≤ F i ΔL= αL ΔT ΔA= γ A ΔT P= Energy time I= Power SA Δf = v c Δ λ λ = v cjhhjjhNo ratings yet
- Mathematics AdvancedDocument19 pagesMathematics AdvancedCharu KansalNo ratings yet
- PHY SN M05 L01 685504 Digital TEDocument7 pagesPHY SN M05 L01 685504 Digital TERebeca RiveraNo ratings yet
- Natural ProductsDocument10 pagesNatural ProductsSony mulgundNo ratings yet
- Micom 30 Series Transformer Differential Protection Application GuideDocument30 pagesMicom 30 Series Transformer Differential Protection Application Guide1981todurkarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2:: Complex Reactions. Kinetic TreatmentDocument28 pagesUnit 2:: Complex Reactions. Kinetic TreatmentIrene Pardillo AhedoNo ratings yet
- 12 AtomsDocument7 pages12 Atomsshivammalik467xNo ratings yet
- Chemneet NCBDocument8 pagesChemneet NCBChirayuNo ratings yet
- RA01 Both E and B - Amit SharmaDocument21 pagesRA01 Both E and B - Amit SharmaPadam MantryNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Pre-Lab Question That I Got Wrong ExplanationDocument2 pagesWeek 6 Pre-Lab Question That I Got Wrong ExplanationAshley JoshiNo ratings yet
- Very Short Notes For Dual NatureDocument8 pagesVery Short Notes For Dual NatureAnkit RawaniNo ratings yet
- 7 EquilibriumDocument1 page7 EquilibriumPARAMBATH ANUP KUMARNo ratings yet
- A13 Hydrocarbons NewDocument1 pageA13 Hydrocarbons NewPARAMBATH ANUP KUMARNo ratings yet
- C6 ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageC6 ThermodynamicsPARAMBATH ANUP KUMARNo ratings yet
- C9 Coordination CompoundsDocument1 pageC9 Coordination CompoundsPARAMBATH ANUP KUMARNo ratings yet
- C13 AminesDocument1 pageC13 AminesPARAMBATH ANUP KUMARNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Basics Some PrincipleDocument1 pageOrganic Chemistry Basics Some PrinciplePARAMBATH ANUP KUMARNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDocument1 pageAldehyde Ketones and Carboxylic AcidPARAMBATH ANUP KUMARNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionDocument1 pageRedox ReactionPARAMBATH ANUP KUMARNo ratings yet
- Surface ChemistryDocument1 pageSurface ChemistryPARAMBATH ANUP KUMARNo ratings yet
- 5synthesis and Reactions of Unsaturated SugarsDocument65 pages5synthesis and Reactions of Unsaturated SugarsHung le VanNo ratings yet
- Experience Counts!: Modular Process SystemsDocument12 pagesExperience Counts!: Modular Process Systemsingegnere1234No ratings yet
- Mix Sulphuric AcidDocument69 pagesMix Sulphuric AcidjaiminNo ratings yet
- Activity No 8 Chemical KineticsDocument4 pagesActivity No 8 Chemical Kineticsshaneeee100% (1)
- To Study Reaction Kinetics of Acetic Acid - Methanol System and Determine ConveDocument7 pagesTo Study Reaction Kinetics of Acetic Acid - Methanol System and Determine ConveJuan ParisNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Grade 10 2019 (Autosaved)Document40 pagesEnzymes Grade 10 2019 (Autosaved)Asawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- PatentDocument7 pagesPatentAntonyHurtadoCristobalNo ratings yet
- Elsevier 1 N08Document270 pagesElsevier 1 N08criticald0% (1)
- Yoshimura 2001Document11 pagesYoshimura 2001Clive GriffithsNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Final Corrected 2016 PDFDocument128 pagesMechanical Final Corrected 2016 PDFiamrabiprakasNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Bio Lubricants With High Viscosity and High Oxidation StabilityDocument6 pagesSynthesis of Bio Lubricants With High Viscosity and High Oxidation StabilityDoris AngNo ratings yet
- PPChem2014 16276-93Document19 pagesPPChem2014 16276-93zeshan shanNo ratings yet
- Held Et Al-2008-Advanced Synthesis & CatalysisDocument10 pagesHeld Et Al-2008-Advanced Synthesis & CatalysisVikutoru KUnNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Enzyme ActionDocument4 pagesMechanism of Enzyme ActionrohiniNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Acetone Production Via The Dehydrogenation of IPADocument7 pagesGroup 3 - Acetone Production Via The Dehydrogenation of IPAQuỳnh Như PhạmNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For Master of Science in Chemistry: The Assam Kaziranga University, JorhatDocument52 pagesSyllabus For Master of Science in Chemistry: The Assam Kaziranga University, JorhatDibyajyoti SaikiaNo ratings yet
- AS Chemistry - Revision Notes Unit 2 - Foundation Physical and Inorganic ChemistryDocument10 pagesAS Chemistry - Revision Notes Unit 2 - Foundation Physical and Inorganic Chemistry24681097No ratings yet
- Study of The Rancimat Test Method in Measuring The Oxidation Stability of Biodiesel Ester and BlendsDocument37 pagesStudy of The Rancimat Test Method in Measuring The Oxidation Stability of Biodiesel Ester and BlendsHy TiongNo ratings yet
- (Green Alternative Energy Resources) Shurong Wang, Zhongyang Luo-Pyrolysis of Biomass PDFDocument268 pages(Green Alternative Energy Resources) Shurong Wang, Zhongyang Luo-Pyrolysis of Biomass PDFWilliam R Vargas ANo ratings yet
- Recovery of Platinum and Palladium From Scrap Automotive Catalytic ConvertersDocument11 pagesRecovery of Platinum and Palladium From Scrap Automotive Catalytic ConvertersMr RhodiumNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Chemical Equilibrium - HL - Paper 1 - 1.0 (Questions)Document3 pagesUnit 7 - Chemical Equilibrium - HL - Paper 1 - 1.0 (Questions)VedantNo ratings yet
- Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry: Antonio Tripodi, Matteo Compagnoni, Elnaz Bahadori, Ilenia RossettiDocument11 pagesJournal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry: Antonio Tripodi, Matteo Compagnoni, Elnaz Bahadori, Ilenia RossettiDarwin Alejandro Velasquez CastroNo ratings yet
- CV of Dr. T. SivakumarDocument9 pagesCV of Dr. T. SivakumarDwayne BrownNo ratings yet
- Principles of Chemical EquilibriumDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Chemical EquilibriumkaditasookdeoNo ratings yet