Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Structure and Functions
Uploaded by
Jen Laurine CosicolOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Structure and Functions
Uploaded by
Jen Laurine CosicolCopyright:
Available Formats
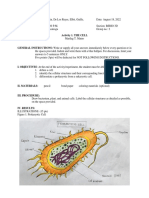
CELL THEORY Cell Structure and Functions
- giving facts and characteristics of cells
1. Cell wall – maintains cell shape
Robert Hooke – first described what the cells look like in his book
2. Plasma membrane – regulates what enters and goes out from
“Micrographia”
the cell.
1600s – start of using microscopes
3. Cytoplasm – liquid-like are in the cell
Cell Theory – Theodor Schwann (1839)
4. Nucleiod – the DNA of a prokaryotic organism is one big loop or
All organisms are made of cell a circular, which is located inside the nucleiod.
Cell is the basic unit of life. (Schwann, Schleide, 1938)
5. Ribosome – synthesizes protein
Cells form by free-cell formation, similar to the formation of
crystals (spontaneous generation) *now debunked* 6. Cytoskeleton – compose of filaments and microtubules; secures
organelles in specific positions
MODERN CELL THEORY
7. Flagella – facilitate cellular locomotion
1. All organisms are made of cells
8. Cillia – cellular locomotion; it is the small tail
2. The cell is the basic unit of life
9. Endoplasmic reticulum – modifies proteins and synthesizes
3. Cells come from pre-existing cells (Rudolf Virchow, 1858) lipids
4. Cells contain hereditary information which is passed from cell to cell Rough Er
during cell division – attached ribosomes
5. Cells of all organisms within a similar species are mostly the same, – helps in aiming protein
both structurally and chemically Smooth ER
– for lipids metabolism
6. Energy flow occurs within cells
10. Mitochondria – energy producing of the cell
CELL
11. Golgi apparatus – helps in packaging and transporting the
A. Prokaryotic Cell protein and li[ids into the other part of the cell
single-celled (unicellular) organism that lacks nucleus, or any 12. Vacuole – storage and transport
other membrane-bound organelle
Central vacuole – found in the center part
B. Eukaryotic Cell Contractile vacuole – present in marine unicellular
These organisms have membrane bound nucleus with many organism
cell organelles to perform several cellular functions within the 13. Nucleus – cell organelle that houses DNA; directs synthesis of
system ribosomes and proteins
1. Plant Cell chromatin
2. Animal Cell chromosome
14. Centrosome – maintain the distribution of chromosome Parts of Plant Cell
15. Peroxisome – for enzyme activities; metabolizes waste 1. Cell Membrane
16. Chloroplast – contains chlorophyll 2. Cytoplasm
3. Ribosome
17. Fimbriae – longer; only seen in gram- 4. Smooth and Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
for attachment
18. Pili – seen in gram+ and gram- and conjugation 5. Mitochondrion
6. Golgi Apparatus
19. Plasmodesmata – signaling between two signal junction 7. Central Vacuole
8. Nucleus
20. Microvilli – expansion and absorption of surface area of a cell
9. Centrosome
10. Cytoskeleton
11. Cell wall (called cellulose)
Parts of Prokaryotic Cell 12. Perixosome
1. Cell Membrane 13. Chloroplast
2. Cytoplasm 14. Plasmodesmata
3. Ribosome
4. Nucleoid
5. Capsule CELL CYCLE
6. Cell Wall (called peptidoglycan)
7. Flagella and cilia (some) CELL DIVISION
8. Fimbriae (for gram positive and gram negative) - Mitosis (Somatic cells, produces 2 daughter cells)
9. Pili (for gram negative)
- Meiosis (Gametes cells, produces 4 unique daughter cells)
Importance of Cell Division
Parts of Animal Cell (1) Reproduction
(2) Growth Development
1. Cell Membrane (3) Tissue Renewal
2. Cytoplasm
3. Ribosome Process of Mitosis
4. Rough and Smooth Endpolasmic Reticulum 1. Interphase – longest stage in the eukaryotic cell cycle
5. Mitochondrion a. Gap 1 - half set of chromosome
6. Golgi Apparatus b. Synthesis Phase - replication
7. Vacuole c. Gap 2 - complete set of chromosome
8. Nucleus 2. Prophase
9. Centrosome -nucleoli disappear
10. Cytoskeleton -centrosomes move away from each other
11. Perixosome
-mitotic spindle forms
12. Flagella and cilia (some)
13. Microvili
3. Prometaphase 6. Prophase 2
- preparation for metaphase - spindle apparatus form
-nuclear envelope fragments 7. Metaphase 2
-kinetochore microtubules - chromosomes are not genetically identical
4. Metaphase 8. Anaphase 2
- chromosomes convene at metaphase plate - breakdown of proteins
5. Anaphase - chromatids move toward opposite poles
- shortest stage 9. Telophase 2 and Cytokinesis
- daughter cells begin moving towards the opposite ends of the - four unique daughter cell (haploid set)
cell - chromosome condense
- cell elongates
6. Telophase CELL MEMBRANE – selective permeable
- 2 daughter nuclei form
- microtubules are depolymerized Primary Functions
- Nuceloli reappear (1) Keep substances out of the cell
- nuclear envelope arise from the fragments (2) Contain receptors and channels that allow specific molecules
- chromosomes become less condensed between organelles and between the cell and outside
7. Cytokinesis environment
- formation of cleavage furrow (3) Separate vital but incompatible metabolic process conducted
- division of cytoplasm is complete within organelles
Process of Meiosis Membrane Models
1. Anaphase 1. Sandwich Model
2. Prophase 1 - pospholipid bilayer (hydrophilic) between two layers of
- crossing over (exchange of genetic materials) protein (hydrophobic)
- synapsis/synaptomenal complex (site of crossing over) - Hugh Davson and James Danielle 1935
- chiasmata (area where crossing over took place 2. Fluid Mosaic Model
3. Metaphase 1 - plasma membrane of animal as a mosaic of components
- both chromatids of one homolog (homologous pair of Phospholipid Bilayer
chromosome) are attached to kinetochore - phosphate head (hydrophilic)
4. Anaphase 1 - glycerol backbone
- breakdown of proteins -fatty acid tails (hydrophobic)
- homologs move towards opposite poles Types of Phospholipid
5. Telophase 1 and Cytokinesis 1. Unsaturated (with double bond)
- each half of the cell has complete haploid set 2. Saturated (without double bond)
- cleavage furrow for animal cells, cell plate for plant cells
Freeze-Fructure Technique b. Exocytosis
- method where a membrane is frozen and cut to study and examine BIOMOLECULES
it
Types of Macromolecules
Type of Solvent 1. Carbohydrate
1. Non-polar (equal) 2. Lipids
2. Polar (unequal) 3. Protein
Fluidity of Membrane 4. Nucleic Acid
1. Lateral movement Two ways of binding
2. Flip-flopping 1. Hydrolisis
Six Major Functions of Membrane Protein 2. Dehydration
1. Transport Carbohydrates
2. Enzymatic activity -Binding: glycosidic
3. Signal transduction -Monomer: Monosaccharide
4. Cell-cell recognition -Function: Immediate source of energy
5. Intercellular joining Classification of Carbohydrates
6. Attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix 1. Based on location of carboxyl groups
i. Trioses
TRANSPORT ii. Pentoses
Types of Cell Transport iii. Hexoses
1. Active Transport - requires energy 2. Based on functions
2. Passive Transport - does not require energy a) Storage
Types of Passive Transport i. Starch (plants)
1. Diffusion - molecules spread evenly ii. Glycogen (animals) - contains amylose
2. Facilitated Diffusion - specific proteins b) Structure
3. Osmosis - water i. Cellulose (plants)
a. Osmolarity - capacity of the membrane to absorb water ii. Chitin (animals)
b. Tonicity - influence of outside environment Types of Carbohydrates
c. Hypotonic - lower concentration 1. Monosaccharide (1)
d. Hypertonic - higher concentration a. Glucose
e. Isotonic - equilibrium b. Galactose
Types of Active Transport c. Fructose
1. Primary Active Transport 2. Disaccharide (2)
2. Secondary Active Transport a. Lactose (glucose+galactose)
3. Bulk Transport b. Sucrose (glucose+fructose)
a. Endocytosis c. Maltose (glucose+glucose)
i. Phagocytosis ii. Pinocytosis iii. receptor-mediated 3. Polysaccharide (many)
5. Transmitting nerve impulse
Proteins Examples of Lipids
-Monomer: Amino Acids 1. Fats
Polymer of Amino Acids: Polypeptide (20 Amino Acids) 2. Phospholipids
-Binding: peptide 3. Steroids
Classification of Proteins 4. Oils
1. Based on Functions 5. Wax
a) Enzymatic proteins Nucleic Acid
i. Digestive enzymes -Monomers: Nucleotides
ii. Lactase - nucleosidde +phosphate groups (nucleotide without
b) Storage proteins phosphate group is called nuceloside)
i. Casein -Function: Genetic Information
c) Hormonal proteins -Polymers called polynucleotides
i. Insulin -consists:
d) Contractile and motor proteins Nitrogenous base
i. Motor proteins Pyrimidines[C,T,U]- six-membered ring
e) Defense Proteins Purines [A,G]- six-membered ring fused to a
i. Anti-bodies five-
f) Transport protein membered ring
g) Receptor proteins Pentose sugar
h) Structural proteins Phosphate groups (one or more)
i. Collagen
ii. Keratin Example of Nucleic Acid
Structures of Proteins 1. DNA (2 polynucleotides and 2 backbones in opposite 5’ and 3’)
1. Ribbon Model a. Sugar: Deoxyribose
2. Space-filling Model b. Eukaryotes
Lipids c. Replicates on its own
-Hydrophobic groups d. Directs synthesis of mRNA and controls protein synthesis
-Non-molar covalent bonds (occurs on ribosomes)
-Monomers: phosphate groups and fatty acids 2. RNA
-Binding: Ester binding a. Sugar: Ribose
Functions of Lipids b. Prokaryotes
1. Energy source (long term)
a) Excess energy from food is stored as adipose tissue
2. Maintaining body temperature
3. Cushioning vital organs
4. Regulating hormones
b) Conformational change
ENZYMES
-catalyst
-processes their substrates
-Majority of the enzymes are protein but not all proteins are enzymes
-Name ends with -ase (International Union of Biochemistry and
Molecular Biology)
-Enzymes are dematured when pH and temperature is not ideal
Classifications of Enzymes
1. Oxidoreductases (oxygen-reduction process)
a. Dehydrogenases
b. Oxidases
c. Oxygenases
d. Hydroxylases
2. Transferases (transfer of groups)
a. Transaminases
b. Transcarboxylases
c. Transmethylases
3. Hydrolases (addition of water)
a. Esterases
b. Phosphotasses
c. Peptidases
4. Lysases (removal of double bond)
a. Decarboxylases
b. Hydrateses
c. Deaminases
d. Synthases
5. Isomerases (rearrangement within a molecule)
a. Epimerases
b. Mutases
6. Ligases (between to substrate molecules
a. Synthetase
Models of Enzyme
1. Lock and Key Method
a) Hermann Emil Fischer
b) Lock-enzymes; key-substrates
2. Induced Fit Model
a) Daniel Koshland
You might also like
- Gen Bio I - ReviewerDocument6 pagesGen Bio I - ReviewerJen Laurine CosicolNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 The Cell 1Document6 pagesExercise 1 The Cell 1MJMadlangbayan100% (1)
- NotesDocument4 pagesNotesChad Laurence Vinson CandelonNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesPlant and Animal Cell OrganellesGraceNo ratings yet
- The Beginning of CellDocument4 pagesThe Beginning of CellTrishia Lynn MaldiaNo ratings yet
- 9th Unit 1Document17 pages9th Unit 1[36] IX-B P.Vishnu Vardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Grade 12-General Biology (Cells)Document11 pagesGrade 12-General Biology (Cells)angeliaNo ratings yet
- Cells: The Basic Units of LifeDocument17 pagesCells: The Basic Units of LifeglezamaeNo ratings yet
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Document17 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Dette Dominic Ballano67% (3)
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 - Cell Structure And-FunctionsDocument23 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 - Cell Structure And-FunctionsEmer Perez50% (2)
- AP Biology Name - Chapter 6 Guided Reading AssignmentDocument6 pagesAP Biology Name - Chapter 6 Guided Reading AssignmentRobert Ladaga33% (3)
- m2 DraftDocument4 pagesm2 DraftMae lea AndoloyNo ratings yet
- APIADOP ANA PHY Lab Activity 2 The Function of Composite CellDocument4 pagesAPIADOP ANA PHY Lab Activity 2 The Function of Composite CellAj ApiadoNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell FeaturesDocument26 pagesEukaryotic Cell FeaturesHridyanshu Singh RoyNo ratings yet
- Cell (Lesson Plan)Document4 pagesCell (Lesson Plan)aiza.coltamaiNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesBiology ReviewerLycaNo ratings yet
- Cells Parts, Function and Cycles-BiologyDocument3 pagesCells Parts, Function and Cycles-BiologyLUKE ADAM CAYETANONo ratings yet
- Graziella Beatriz A. Cabuyadao Warm-UpDocument1 pageGraziella Beatriz A. Cabuyadao Warm-UpBeverly CabuyadaoNo ratings yet
- MLT 115 - Eukaryotic CellsDocument33 pagesMLT 115 - Eukaryotic Cellsattaadutwum3No ratings yet
- All Cells Have 3 Things in CommonDocument21 pagesAll Cells Have 3 Things in CommonJascha Isaac PangandianNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Transport LectureDocument9 pagesCell Membrane Transport LectureJanine LimjucoNo ratings yet
- Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesCell: The Basic Unit of LifePradyun DSNo ratings yet
- IIT-JAM Biotechnology (BT) Sample TheoryDocument55 pagesIIT-JAM Biotechnology (BT) Sample TheorysonamNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Biology 1Document6 pagesReviewer in Biology 1CameronNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2Document8 pagesKami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2bloomington369No ratings yet
- Cell Theory and StructureDocument5 pagesCell Theory and StructureScarlet VillamorNo ratings yet
- Historical Background:: Chapter 4: Cell StructureDocument6 pagesHistorical Background:: Chapter 4: Cell Structureanon_975930740No ratings yet
- Biology Y10 Ch2Document7 pagesBiology Y10 Ch2zuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Its BeginningDocument6 pagesThe Cell and Its BeginningZarc VenturaNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: Anatomy and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCells and Tissues: Anatomy and FunctionsAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- The Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesThe Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeCarlo Joseph MoskitoNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Cell 1. NucleusDocument2 pagesParts of A Cell 1. NucleusVon Lester SanchezNo ratings yet
- PDF Reference1-Lesson3-ProkaryotesvseukaryotesDocument3 pagesPDF Reference1-Lesson3-Prokaryotesvseukaryotesjg teNo ratings yet
- GEN. ZOO (Midterms)Document8 pagesGEN. ZOO (Midterms)mimiNo ratings yet
- General Biology-1: Senior High School Grade 12 GDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology-1: Senior High School Grade 12 GJackylyn Evangelista100% (2)
- Bio1 Lesson 1 NotesDocument7 pagesBio1 Lesson 1 Notesykanemoto81No ratings yet
- E1 2-CellsDocument7 pagesE1 2-CellshzntrpNo ratings yet
- Handout 2: Amity International School, Noida Class Ix Biology Chapter: The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument3 pagesHandout 2: Amity International School, Noida Class Ix Biology Chapter: The Fundamental Unit of LifeayaanNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument6 pagesCellsaryam aliNo ratings yet
- PACHECO - EXERCISE NO.1-The CellDocument3 pagesPACHECO - EXERCISE NO.1-The CellMaria Brooklyn PachecoNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGYDocument5 pagesMICROBIOLOGYCia RraNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument4 pagesCellsKristelle Dae PagunsanNo ratings yet
- Cl6001 Module 1Document11 pagesCl6001 Module 1reshalyavikaumadi19No ratings yet
- Ana CellsDocument4 pagesAna CellsDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument37 pagesCell StructureMARY ANN PANGANNo ratings yet
- Biology CellsDocument7 pagesBiology Cellsperaltasabina70No ratings yet
- Bio IpassDocument15 pagesBio IpassmonreNo ratings yet
- 2.1 A. Cell Theory B. Prokaryote Eukaryote 1Document24 pages2.1 A. Cell Theory B. Prokaryote Eukaryote 1saidatulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Structure of Cells and OrganellesDocument24 pagesChapter 2: Structure of Cells and OrganellesVassalyn Su ThatNo ratings yet
- Types of Cell PDFDocument20 pagesTypes of Cell PDFDave Billona100% (1)
- Bio 49 Activity 1Document6 pagesBio 49 Activity 1Theresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 Cell StructureDocument31 pagesCh.4 Cell StructureEmma WisemanNo ratings yet
- Week 1, LAS 1:: Structure/Function Cell PartDocument3 pagesWeek 1, LAS 1:: Structure/Function Cell PartKelly Misha NoolNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhysiologyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To PhysiologyMiaIsabelleAntonioNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle Review Worksheet Summer ValliniDocument3 pagesCell Organelle Review Worksheet Summer ValliniSummer ValliniNo ratings yet
- General Biology: System Consists of TheDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology: System Consists of ThePhilipp MendozaNo ratings yet
- Act 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5Document21 pagesAct 1. Physiology Lab. Group 5YEO, REGGIE ALBERT A.No ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Citizen JournalismDocument1 pageCitizen JournalismJen Laurine CosicolNo ratings yet
- WATCHAPPDocument9 pagesWATCHAPPJen Laurine CosicolNo ratings yet
- Essay - PhiloDocument1 pageEssay - PhiloJen Laurine CosicolNo ratings yet
- Philippines Mining Industry Adopts Environmentally Sustainable PracticesDocument1 pagePhilippines Mining Industry Adopts Environmentally Sustainable PracticesJen Laurine CosicolNo ratings yet
- Data Set 2Document2 pagesData Set 2Jen Laurine CosicolNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument3 pagesProblem SetJen Laurine CosicolNo ratings yet
- Data Set 1Document2 pagesData Set 1Jen Laurine CosicolNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - Long QuizDocument3 pagesEarth Science - Long QuizJen Laurine CosicolNo ratings yet
- Earth's characteristics necessary for lifeDocument6 pagesEarth's characteristics necessary for lifeJen Laurine CosicolNo ratings yet
- Eamcet 2.6.20Document201 pagesEamcet 2.6.20M JEEVARATHNAM NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Electrical Signals and Action PotentialsDocument20 pagesNervous System Electrical Signals and Action PotentialsAna G. VelascoNo ratings yet
- Chromosome AberrationDocument37 pagesChromosome AberrationAli Abbas AslamNo ratings yet
- Unique Properties of All Stem Cells PDFDocument1 pageUnique Properties of All Stem Cells PDFExicanLifeSciencesNo ratings yet
- Calbiochem InhibitorsDocument124 pagesCalbiochem InhibitorsChazMarloweNo ratings yet
- Abeloff Clinical Oncology 2020 (Part 1)Document22 pagesAbeloff Clinical Oncology 2020 (Part 1)Emiliana LarionesiNo ratings yet
- PIIS0896627316310078Document27 pagesPIIS0896627316310078Carolina RicárdezNo ratings yet
- 3 Enzymes As BiologyDocument35 pages3 Enzymes As BiologyADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- Use of PRP, PRF and CGF in Periodontal Regeneration andDocument23 pagesUse of PRP, PRF and CGF in Periodontal Regeneration andmaria teresa pertuz rondonNo ratings yet
- Rampado2022 - Lysis BufferDocument11 pagesRampado2022 - Lysis BufferRamonaTecucianuNo ratings yet
- The Golgi Apparatus and Centriole Functions, Interactions and Role in Disease (Malgorzata Kloc)Document530 pagesThe Golgi Apparatus and Centriole Functions, Interactions and Role in Disease (Malgorzata Kloc)Henrique AraujoNo ratings yet
- Coutu 2017Document12 pagesCoutu 2017ThunderslapNo ratings yet
- BoichemistryDocument20 pagesBoichemistrynishwa RajpootNo ratings yet
- F1 Is Language EX 0301Document3 pagesF1 Is Language EX 0301fgs101109No ratings yet
- Cell Model Project and RubricDocument2 pagesCell Model Project and Rubricapi-304326920100% (1)
- Aiims - Biochemistry Q&ADocument198 pagesAiims - Biochemistry Q&APrahladRao KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Hematology Book For PDF 1304281501 Phpapp02 PDFDocument260 pagesHematology Book For PDF 1304281501 Phpapp02 PDFAndrea Kocsis100% (1)
- BIO 001-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesBIO 001-WPS OfficeSam 9No ratings yet
- ECB3e Chapter 20Document80 pagesECB3e Chapter 20Sarifa Ghina RaquelleNo ratings yet
- (03241750 - Acta Medica Bulgarica) T Helper Cells in The Immunopathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis - Current TrendsDocument7 pages(03241750 - Acta Medica Bulgarica) T Helper Cells in The Immunopathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis - Current TrendsTeodorNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology PDFDocument28 pagesBiotechnology PDFCherry Lyn Belgira85% (13)
- Full Download Test Bank For Pathophysiology 8th Edition by Mccance PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Pathophysiology 8th Edition by Mccance PDF Full Chapterpicheywitlingaip34100% (21)
- Jurnal Metastasis TulangDocument16 pagesJurnal Metastasis TulangwidiastrikNo ratings yet
- Final Paper 1Document140 pagesFinal Paper 1Ramil LucasNo ratings yet
- Cellular Swelling Anand Jeughale VPPDocument42 pagesCellular Swelling Anand Jeughale VPPAnand JeughaleNo ratings yet
- SMK Petaling Test Specification Table (Jsu) Biology Form 4 Paper 2Document2 pagesSMK Petaling Test Specification Table (Jsu) Biology Form 4 Paper 2Raidah AdhamNo ratings yet
- SPM 4551 2006 Biology k2 BerjawapanDocument15 pagesSPM 4551 2006 Biology k2 Berjawapanpss smk selandarNo ratings yet
- Tri-Fold TemplateDocument2 pagesTri-Fold Templateapi-260948905No ratings yet
- What Is FertilizationDocument8 pagesWhat Is Fertilizationapi-303065931No ratings yet
- CH 05Document24 pagesCH 05filippo100% (3)