Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Soft Skills 2 Unit 1 - LSRW Skills
Uploaded by
Satyajeet Kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views3 pagesSoft Skills 2 Unit 1 - LSRW Skills
Uploaded by
Satyajeet KumarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
1
UNIT 1: LSRW Skills
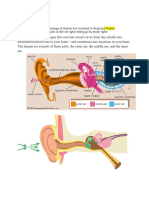
1.1 Listening How to Master the Art of Listening
Types of Listening 1. Make Eye Contact
2. Don’t Interrupt
1. Active Listening
3. Practice “Active Listening”
'Active listening' means, as its name suggests,
4. Show You Understand
actively listening. That is fully concentrating on what
5. Listen without Thinking
is being said rather than just passively ‘hearing’ the 6. Listen without Judgement
message of the speaker.
7. Listen to Non-Verbal Communication
Active listening involves listening with all senses. As 8. Create a Suitable Environment
well as giving full attention to the speaker, it is 9. Observe Other People
important that the ‘active listener’ is also ‘seen’ to
be listening - otherwise the speaker may conclude
Stages/Process of Listening
that what they are talking about is not interesting
1. Receiving: At this stage, we are still only hearing
to the listener.
the message.
Interest can be conveyed to the speaker by using
2. Understanding: At this stage, we attempt to learn
both verbal and non-verbal messages such as
the meaning of the message.
maintaining eye contact, nodding your head and
3. Remembering: Remembering begins with
smiling, agreeing by saying ‘Yes’ or simply ‘Mmm
listening; if you can’t remember something that
hmm’ to encourage them to continue. By providing
was said, you might not have been listening
this 'feedback' the person speaking will usually feel
effectively.
more at ease and therefore communicate more
4. Evaluating: The fourth stage in the listening
easily, openly and honestly.
process is evaluating, or judging the value of the
The meaning of passive listening is to listen without
message. Evaluations of the same message can
asking questions or interrupting the speaker. It may
vary widely from one listener to another.
even mean that you don’t really understand what’s
5. Feedback/Responding: The responding stage is
being said or you are not interested.
the stage of the listening process in which the
listener provides verbal and/or nonverbal
2. Passive listening
reactions.
The meaning of passive listening is to listen without
asking questions or interrupting the speaker. It may
even mean that you don’t really understand what’s 1.2 Speaking
being said or you are not interested. Pronunciation
Pronunciation is the way in which a word or a
The Art of Listening language is spoken. Pronunciation refers to the
Listening is an art. It requires us to be patient, ability to use the correct stress, rhythm, and
receptive, open-minded, and non-judgmental. It intonation of a word in a spoken language.
requires us not to put words in other people’s To pronounce words, we push air from our lungs up
mouths, fill in gaps, or presume to understand the through our throat and vocal chords, through our
other person fully. mouth, past our tongue and out between our teeth
Those who can listen to others well can listen to and lips. (Sometimes air also travels through our
themselves deeply. This is the foundation of self- nose.)
awareness, self-love, and self-knowledge. To change the sound that we are making, we mainly
In fact, the art of listening is central to practices use the muscles of our mouth, tongue and lips to
such as meditation and mindfulness. So why not control the shape of our mouth and the flow of air.
hone this skill with others each day, and make the Speakers of different languages tend to develop
best opportunity of every moment you get? different muscles of the mouth for pronunciation.
When we speak a foreign language, our muscles
may not be well developed for that language, and
we will find pronunciation more difficult.
Downloaded from: www.KKWorld.in Made By: YouTube.com/KrazyKaksha
2
Tongue-Twisters Words that end in -cy, -ty, -phy and -
Tongue twisters are a great way to practice and improve gy (examples: deMOCracy, unCERtainty,
pronunciation and fluency. They can also help to improve geOGraphy, radiOLogy)
accents by using alliteration, which is the repetition of Words that end in -al (examples: exCEPtional,
one sound. They help us to clear sound while speaking. CRItical)
If you can master them, you will be a much more
confident speaker. Keep these simple rules in mind and you will soon
find your pronunciation getting better and better!
Examples:
1. I scream, you scream, we all scream for ice cream.
2. I have got a date at a quarter to eight; I’ll see you 1.3 Reading
at the gate, so don’t be late. Reading Comprehension
3. Can you can a can as a canner can can a can? Reading comprehension is the understanding of what a
4. You know New York, you need New York, you particular text means and the ideas the author is
know you need unique New York. attempting to convey, both textual and sub-textual.
5. I saw a kitten eating chicken in the kitchen.
In order to read any text, your brain must process not
6. She sells seashells by the seashore. only the literal words of the piece, but also their
7. How can a clam cram in a clean cream can? relationship with one another, the context behind the
8. If a dog chews shoes, whose shoes does he choose?
words, how subtle language and vocabulary usage can
9. I thought I thought of thinking of thanking you.
impact emotion and meaning behind the text, and how
10. I wish to wash my Irish wristwatch.
the text comes together as a larger, coherent whole.
11. I saw Susie sitting in a shoeshine shop.
12. Near an ear, a nearer ear, a nearly eerie ear.
Steps to improve Reading skills
13. A big black bear sat on a big black rug.
1. Read a variety of material and do not limit
yourself to textbooks only.
Stress in English Language
2. Circle unknown words and try to find its
To communicate clearly when you are speaking in
meaning.
English, it’s important to stress the correct syllables
3. After reading recall as much of information as
in each word. This is called word stress, which means
possible.
pronouncing one syllable of a multisyllabic word
4. Consider how interesting the subject matter and
with greater emphasis (stress) than the other
how much you already know about it.
syllables in the word.
Here are four general rules to keep in mind about Reading Style
word stress as you practice pronunciation: 1. Skimming
1. Stress the first syllable of: Skimming is one of the basic methods of reading
Most two-syllable nouns (examples: CLImate, comprehension. In this, the reader first quickly read the
KNOWledge) passage in order to get a preview of the whole
Most two-syllable adjectives (examples: passage/passages and tries to understand after having
FLIPpant, SPAcious) skimmed the text.
2. Stress the last syllable of: 2. Scanning
Most two-syllable verbs (examples: reQUIRE, Scanning is the act of searching particular information in
deCIDE) a text with a particular approach.
3. Stress the second-to-last syllable of: Purposes of Scanning
Words that end in -ic (examples: ecSTATic, To search for a word in a dictionary or index
geoGRAPHic) To find a phone number or an address in a
Words ending in -sion and -tion (examples: directory
exTENsion, retriBUtion) To check the time schedule of a program in an
agenda
4. Stress the third-from-last syllable of: To check the price of a specific item in a catalog
To know a particular information from a text
Downloaded from: www.KKWorld.in Made By: YouTube.com/KrazyKaksha
3
3. Churning the beginning, this method is adopted. In it, one
The process of churning and assimilation comes after starts with the topic sentence, and goes on to
the skimming part. The word churning means record the supporting facts.
contemplating, analysis of the ideas and information.
This churning and assimilation helps in understanding 3.Exposition Method: These paragraphs explain how
the inference and contextual meaning of the text. something works or what the reader is to do to
make it work. Such paragraphs demand certain
4. Assimilation
knowledge. Nevertheless, writing them is a great
Assimilation refers to comprehending the text so that
exercise to understand the material, because you
you can answer any question based on the text. It is the
keep learning when you teach. In expository
end product of skimming, scanning and churning
processes during the reading of a given text. writing, linking words like first, second, then, and
finally are usually used to help readers follow the
ideas. Exposition is explanatory writing. Exposition
1.4 Writing
can be an incidental part of a description or a
Basic three sections of a paragraph: narration, or it can be the heart of an article.
1.Beginning - Introduce your idea.
2.Middle - Explain your idea. 4.Linear Method: Linear means 'consisting of lines'
3. End - Make your point again, transition to next or 'one dimensional'. Each sentence leads to the
paragraph. next one in a paragraph, with the purpose of
maintaining a forward movement; and each
Principle of Paragraph Development paragraph can be a step to take us to a goal. A
1. Topic sentence: Topic sentence is a sentence that
logical series can be made even a consecutive
expresses the main idea of a paragraph. This is also
arrangement of information.
known as key sentence or theme sentence.
2. Coherence: Coherence refers to the clear and logical
thinking of ideas in a paragraph in such a way that a 5. Interrupted method: Whenever the writer gives a
thought expressed in a sentence easily leads to the break to the line of thought and gives a turn to the idea
thought in next sentence and so on. The word to produce the desired effect, he uses this method. The
coherence literary means Consistency. punctuation marks , ( ) _! (comma, parentheses, em
3. Unity- Unity refers to one as a whole or oneness. All dash, exclamation mark) serve as interrupters and add
the parts of a paragraph should contribute to one emphasis to the sentences. The interrupt the flow of
effect and lead to unified purpose. One idea should sentences by breaking chunks of ideas. Remember,
be expressed in one sentence and avoid too much interrupters can be words, phrases, or punctuation
lengthy sentences. marks.
Writing Methods 6.Spatial Order Method: When the matter refers to
1.Inductive Order Method: When the matter certain areas, an area-wise arrangement of the
consists of some details or known facts, the matter must be preferred to present it
consideration of which leads to a conclusion, it is systematically. This method helps the reader to
desirable to adapt the inductive method. This is a visualize what he sees and, therefore, it is better
logical arrangement, beginning with the to understand the physical qualities of the subject
supporting information available and concluding matter.
with a topic sentence or a conclusion.
7. Chronological Method: When the matter refers to
2.Deductive Order Method: The deductive method some developments in terms of time, a
is the opposite of the inductive method. It reverses chronological order introduces system in its
the arrangement of matter prescribed in the presentation. This order is preferred in historical
inductive method. When a statement is made in narrations.
the beginning, and it is followed by the facts that
substantiate the assertion or suggestion made in
Downloaded from: www.KKWorld.in Made By: YouTube.com/KrazyKaksha
You might also like
- Essential Listening Skills for Effective CommunicationDocument26 pagesEssential Listening Skills for Effective CommunicationNarendra PatilNo ratings yet
- Oral Communications NotesDocument6 pagesOral Communications NotesSeraphina LopezzNo ratings yet
- Listening Skills Project ReportDocument12 pagesListening Skills Project Reportsarfraz_shahani88No ratings yet
- Active ListeningDocument22 pagesActive ListeningSameer ZabadiNo ratings yet
- What is Listening? The 11 Types ExplainedDocument6 pagesWhat is Listening? The 11 Types ExplainedMauhammad TaqiNo ratings yet
- Listening SkillsDocument6 pagesListening SkillsgodfreymshindiNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication SkillsDocument22 pagesEffective Communication SkillsSabir KhattakNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document26 pagesUnit 4Abhay kumarNo ratings yet
- Improve Communication Skills with Active ListeningDocument22 pagesImprove Communication Skills with Active ListeningkhanNo ratings yet
- Listening: What Is Listening? Quotation About ListeningDocument10 pagesListening: What Is Listening? Quotation About ListeningM.Shehroze RahilaNo ratings yet
- LSRWDocument126 pagesLSRWHariom JadonNo ratings yet
- Listening Skills and Techniques LessonDocument6 pagesListening Skills and Techniques LessonVwjaooNo ratings yet
- 11 - LN04 Active ListeningDocument8 pages11 - LN04 Active ListeningnarutoNo ratings yet
- Listening Skills - Lesson 5Document9 pagesListening Skills - Lesson 5Solomon Reuben IrmiyaNo ratings yet
- Improve Your Communication & Presentation SkillsDocument30 pagesImprove Your Communication & Presentation SkillskhanNo ratings yet
- Improve Listening Skills Through Understanding TypesDocument28 pagesImprove Listening Skills Through Understanding TypesthessianneNo ratings yet
- Listening Comprehension by Teaching English For Foreign LanguageDocument22 pagesListening Comprehension by Teaching English For Foreign LanguageZano ElfNo ratings yet
- Listening Skills: Dr. Deepa SethiDocument43 pagesListening Skills: Dr. Deepa SethimalhotramonikaNo ratings yet
- Bonga ExitDocument171 pagesBonga Exitbele yalewNo ratings yet
- Improve Listening SkillsDocument34 pagesImprove Listening SkillsGlorious PrinceNo ratings yet
- LSRWDocument124 pagesLSRWHarshit RaiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Listening Strategies and StylesDocument29 pagesModule 1 Listening Strategies and StylesFatima ButilNo ratings yet
- Listening in Communication: Tushar Gupta BBA - 1 Sem Mdu (Ii)Document18 pagesListening in Communication: Tushar Gupta BBA - 1 Sem Mdu (Ii)Tushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- LSRW Skills: A Way To Enhance CommunicationDocument4 pagesLSRW Skills: A Way To Enhance CommunicationIJELS Research JournalNo ratings yet
- Macro Skills ModuleDocument70 pagesMacro Skills ModuleJoefryQuanicoBarcebalNo ratings yet
- Mendengarkan Aktif - Kul 3Document25 pagesMendengarkan Aktif - Kul 3Endah HutamiNo ratings yet
- 4 170502181330 PDFDocument9 pages4 170502181330 PDFRawand AwniNo ratings yet
- Listening SkillsDocument9 pagesListening SkillsRawand AwniNo ratings yet
- Week 18 - Listening SkillsDocument17 pagesWeek 18 - Listening Skillsjanani a/p ayaooNo ratings yet
- If Speaking Is Silver, Listening Is GoldDocument2 pagesIf Speaking Is Silver, Listening Is GoldIJELS Research JournalNo ratings yet
- EES 1 ListeningDocument4 pagesEES 1 ListeningShubham PatilNo ratings yet
- EL002 EscuchaActiva BasedelaComunicacion ENGDocument3 pagesEL002 EscuchaActiva BasedelaComunicacion ENGAsesoria SGSSTNo ratings yet
- Listening Vs HearingDocument24 pagesListening Vs HearingShiv Verdhan Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Listening SkillsDocument18 pagesListening SkillsFatima AslamNo ratings yet
- Aex 5Document7 pagesAex 5Muthu Krishnan MNo ratings yet
- Listening Is A Process of Receiving, InterpretingDocument25 pagesListening Is A Process of Receiving, Interpretingshafee ullahNo ratings yet
- Active Listening 1Document65 pagesActive Listening 1Richard PeterNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lab 2 Listening SkillDocument5 pagesModule 1 Lab 2 Listening SkillsachinpandhareNo ratings yet
- General English Listening Skills Materials 2020-2021Document99 pagesGeneral English Listening Skills Materials 2020-2021Bunny BaluNo ratings yet
- Listeningskills 120213044302 Phpapp01Document26 pagesListeningskills 120213044302 Phpapp01Deepak Oswal100% (4)
- Listening Skills (English For General Communication) 1Document26 pagesListening Skills (English For General Communication) 1al desmeNo ratings yet
- Levels of Listening Improve SkillDocument7 pagesLevels of Listening Improve SkillApenton MimiNo ratings yet
- Qtr1 - Eng - Activity Sheets 1 - Week 3Document3 pagesQtr1 - Eng - Activity Sheets 1 - Week 3Daniel AlonNo ratings yet
- Listening SkillsDocument25 pagesListening SkillsAhmad Sana FarooqNo ratings yet
- Draft (NHÓM 6) PSYCHOLOGY - LISTENINGDocument14 pagesDraft (NHÓM 6) PSYCHOLOGY - LISTENINGquynhanh5112No ratings yet
- Speaking SkillsDocument65 pagesSpeaking SkillsSrijana ShetNo ratings yet
- Listening SkillsDocument7 pagesListening SkillsTumpa GhoshNo ratings yet
- What is listening? Explained in detailDocument15 pagesWhat is listening? Explained in detailRoop KishorNo ratings yet
- English Grade-7 Q2 LP-1Document8 pagesEnglish Grade-7 Q2 LP-1Karen Creo BelchezNo ratings yet
- Makrong Ksanayang PangwikaDocument3 pagesMakrong Ksanayang PangwikaOdyssey Bunquin LaganNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm 2ND GradingDocument3 pagesOral Comm 2ND Gradingampineda4018pamNo ratings yet
- Full Notes Topic 4.1Document15 pagesFull Notes Topic 4.1renNo ratings yet
- Listening - BabitaDocument14 pagesListening - BabitaS ANo ratings yet
- Comm Arts (Listening)Document5 pagesComm Arts (Listening)Belle VillasinNo ratings yet
- LP1 Reviewer (English)Document2 pagesLP1 Reviewer (English)kjdobdin23No ratings yet
- Develop Effective Listening SkillsDocument6 pagesDevelop Effective Listening SkillsS Amit RaoNo ratings yet
- Master the Art of Effective ListeningDocument23 pagesMaster the Art of Effective ListeningPaula Cruz100% (6)
- Managerial Skill DevelopmentDocument121 pagesManagerial Skill DevelopmentSasi Kumar100% (2)
- College of Engineering, Architecture and Technology: Odule IN Nglish RoficiencyDocument11 pagesCollege of Engineering, Architecture and Technology: Odule IN Nglish RoficiencyMae Fundal FaeldinNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Notes CSSDocument12 pagesUNIT 2 Notes CSSSatyajeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Netflix Clone.9696881.PowerpointDocument3 pagesNetflix Clone.9696881.PowerpointSatyajeet KumarNo ratings yet
- 7 - Magnetic FieldDocument5 pages7 - Magnetic FieldSatyajeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Correct PPT Sequence and SeriesDocument36 pagesCorrect PPT Sequence and SeriesSatyajeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Cryptography: Techniques for Securing InformationDocument14 pagesCryptography: Techniques for Securing InformationSatyajeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Level B2 Portuguese ESL TeacherDocument30 pagesLevel B2 Portuguese ESL TeacherfelippeavlisNo ratings yet
- CodeDocument20 pagesCodeayu suhestiNo ratings yet
- Grammar English I OverviewDocument155 pagesGrammar English I OverviewANA ELENA TILLERO VALDIVIEZONo ratings yet
- Language Competence ... Hool.Document17 pagesLanguage Competence ... Hool.Son YongNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect SimpleDocument7 pagesPresent Perfect SimpleDalen NorwayNo ratings yet
- Drafting IMAS StandardsDocument32 pagesDrafting IMAS StandardsMelvin SmithNo ratings yet
- 5 класс 1 четвертьDocument57 pages5 класс 1 четвертьLorD SnowNo ratings yet
- Speech Analysis: What Can We Look For?Document16 pagesSpeech Analysis: What Can We Look For?dokifi6985nonicamy.comNo ratings yet
- 35 Deutsch Fünfunddreißigste LektionDocument4 pages35 Deutsch Fünfunddreißigste Lektionjohn roaNo ratings yet
- English the Easy Way Scope & SequenceDocument106 pagesEnglish the Easy Way Scope & SequenceSebas100% (2)
- Coherent and Cohesive Organization in Academic WritingDocument2 pagesCoherent and Cohesive Organization in Academic WritingJodelyn Mae ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Exercises Unit 1Document2 pagesExercises Unit 1María Jiménez CarreraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Week 42 Group AbDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Week 42 Group AbSyahira ShukriNo ratings yet
- Intermediate English Grammar "Summarize Chapter 13: Adjective Clause"Document20 pagesIntermediate English Grammar "Summarize Chapter 13: Adjective Clause"Arga SyahputraNo ratings yet
- 7 English For Journalism - Misspelling and StylesDocument18 pages7 English For Journalism - Misspelling and StylesSRI HARTINo ratings yet
- Introduction To Semantic ProcessingDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Semantic ProcessingRajat RaiNo ratings yet
- Copy of Strategy Implementation Report 6B Ratiocination.docxDocument3 pagesCopy of Strategy Implementation Report 6B Ratiocination.docxmfernstenNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning Foreign Languages in Uzbekistan. CEFR: Learning, Teaching and AssessmentDocument5 pagesTeaching and Learning Foreign Languages in Uzbekistan. CEFR: Learning, Teaching and AssessmentresearchparksNo ratings yet
- Learn Number Rules for Changing Singular to Plural NounsDocument6 pagesLearn Number Rules for Changing Singular to Plural Nounshemisphereph2981No ratings yet
- Lalñr&Foe'Kz%: JKF"V LalñrlalfkkueDocument158 pagesLalñr&Foe'Kz%: JKF"V LalñrlalfkkueSaurav ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Theoritical of Frameworks The Assimilation Anlysis On Meghan Trainor'S Singing Articulation Through Phonology ApproachDocument13 pagesTheoritical of Frameworks The Assimilation Anlysis On Meghan Trainor'S Singing Articulation Through Phonology ApproachClinton NyaoreNo ratings yet
- International Department of Beijing Bayi School 2020 2021 Semester Two Midterm ExamDocument6 pagesInternational Department of Beijing Bayi School 2020 2021 Semester Two Midterm ExamFrazNo ratings yet
- LISTENINGDocument30 pagesLISTENINGHazel Martinii PanganibanNo ratings yet
- White Stephen A Activities For English Language Learners AcrDocument136 pagesWhite Stephen A Activities For English Language Learners AcrВладлена0% (1)
- Mathematics in The Modern World-Lesson4Document27 pagesMathematics in The Modern World-Lesson4LharvaeNo ratings yet
- Qnet 261 Quieter LondonDocument4 pagesQnet 261 Quieter Londons.belkaNo ratings yet
- Headway Elementary Unit 11Document70 pagesHeadway Elementary Unit 11Công-65XD13 Phương Hữu100% (2)
- LESSON PLAN Personal PronounsDocument14 pagesLESSON PLAN Personal Pronounsmardaniaty rahmiNo ratings yet
- Maths Topic - Ordinary Level - Functions and GraphsDocument22 pagesMaths Topic - Ordinary Level - Functions and GraphsT SolomonNo ratings yet
- PhD Associate Professor Sentence ClassificationDocument22 pagesPhD Associate Professor Sentence ClassificationCristina Mihaela BurlicaNo ratings yet