Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth and Life Science G11 Q1 W8 HydrometeorologicalHazards
Uploaded by
Ana CristinoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Earth and Life Science G11 Q1 W8 HydrometeorologicalHazards
Uploaded by
Ana CristinoCopyright:
Available Formats
EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE
QUARTER 1 HYDROMETEOROLOGICAL HAZARDS MODULE 7
MELC 18 Week No. 8 Code: S11/12ES-Ig-36: Using hazard maps, identify areas prone to hazards
brought about by tropical cyclones, monsoons, floods, or ipo -ipo.
MELC 19 Week No. 8 Code: S11/12ES-Ih-38: Describe how coastal processes result in coastal
erosion, submersion, and saltwater intrusion.
MELC 20 Week No. 8 Code: S11/12ES-Ii-41: cite ways to prevent or mitigate the impact of land
development, waste disposal, and construction of structures on control coastal processes
Earth and Life Science – Grade 11
Supplementary Learning Material
Republic Act 8293, section 176 states that: No copyright shall subsist in any
work of the Government of the Philippines. However, prior approval of the
government agency or office wherein the work is created shall be necessary for
exploitation of such work for profit. Such agency or office may, among other things,
impose as a condition the payment of royalties.
Borrowed materials (i.e., songs, stories, poems, pictures, photos, brand
names, trademarks, etc.) included in this module are owned by their respective
copyright holders. Every effort has been exerted to locate and seek permission to use
these materials from their respective copyright owners. The publisher and authors
do not represent nor claim ownership over them.
DEVELOPMENT TEAM OF THE MODULE
Writer: Henrick C. Bajo
Content Editor: Agnes A. Alegre, PhD
Language Editor: Roxane S. Villanueva
Layout and Design Editor: Henrick C. Bajo
Illustrator: Henrick C. Bajo
Cover Layout Artist: Nemesio S. Cancan Jr.
MANAGEMENT TEAM
OIC-SDS: Romela M. Cruz, CESE
CID Chief: Alyn G. Mendoza, PhDTE
SGOD Chief: Emma G. Arrubio
EPS-in-Charge: Restituto I. Rodelas
EPS-LRMS: Ruby E. Baniqued, EDD
Department of Education – Schools Division Office, Mandaluyong
Office Address: Calbayog St. Highway Hills, Mandaluyong City
Telephone number: CID- 79552557
E-mail Address:sdo.mandaluyong@deped.gov.ph ● www.depedmandaluyong.org
The following are some reminders in using this module:
1. Handle this module with care. Use a separate sheet in answering the
exercises.
2. Read the directions carefully before doing each task.
3. Activities in this module can be done individually or with the help of your
teacher, home learning partner or knowledge source partner.
4. Finish this module for the intended week.
5. Return this module to the authorize person in charge of retrieval.
1. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ig-36 2. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ih-38 3. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ii-41
Earth & Life
Science
NAME SECTION SCORE
TEACHER DATE
OBJECTIVES Af ter you have f inished working on this module, you are expected to:
After you have finished
1. Determine areas that are prone to various hydrometeorological hazards.
2. Analyze how hydrometeorological hazard maps work.
3. Describe the different coastal processes and their influence and hazards on coastal
landforms.
4. Explain the different ways to cope with coastal hazards, particularly on coastal
erosion, submersion and saltwater intrusion.
5. Evaluate the appropriateness and effectivity of the different mitigation measures to
minimize or prevent various coastal hazards .
PRETEST Answer this to determine how much you already know about the lessons.
TRUE OR FALSE. Identify which of the following statements is correct by writing
TRUE on the space before each item. Otherwise, write FALSE
_____1. Hazard maps does not rely on historical data.
_____2. Project NOAH main focuses is on typhoon data
_____3. Project NOAH helps us assessing national hazards.
_____4. Topographic features are typically removed in hazard maps.
_____5. The process of accretion is identical to how reclamation is done.
_____6. The deposition may result from the action of constructive waves.
_____7. Backwash and swash are actions associated with destructive waves.
_____8. The different hazards related to topography are also included in Project NOAH.
_____9. Submersion attributed to global warming can cause lowland areas to disappear.
_____10. Saltwater intrusion will most likely occur when waves enter an area of shallow
water.
REVIEW How can you relate the lessons in this module to your prior knowledge?
Recall the different names of tropical cyclone depending on the location where they are
formed.
1. A _____________is formed west of the Pacific Ocean.
2. A _____________ is formed in the Atlantic and Northeast Pacific.
3. A _____________ is formed in the Indian Ocean and South Pacific Ocean.
1. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ig-36 2. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ih-38 3. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ii-41
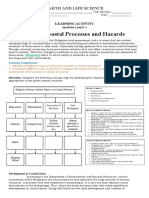
KEY CONCEPTS Af ter the end of this module, you should have learned that:
Coastal Processes
naturally-occurring human-induced
Waves and Tides Submersion Saltwater Intrusion
can cause
Accretion Attrition Bioerosion Corosion Abrasion
Hydrometeorological hazard maps shows the level of risk in an area due to floods,
tropical cyclones, monsoons, and tornadoes.
Project N.O.A.H. lead the creation of accurate and high resolution maps of Philippine
landscape and helps in hydrometeorological risk mitigation.
Infrastructures along coastline increases the incidents of sediment run-off that
contribute to coastal erosion.
PD 1586 has established the implementation of Philippine Environmental Impact
Assessment (EIA) pointing out the dangers before, during, and after development.
Environmental risk assessments (ERAs) help identify and evaluate the effects on the
ecosystem of any hazards caused by land development.
INTRODUCTION Get READY. SET yourself to #studymode. Here we GO !!!
Hydrometeorological hazard maps plot the levels of risk of an area. These maps may be in a local
area or the whole country. These assess potential damage due to floods, tropical cyclones, winds,
monsoons, and other hydrometeorological phenomena.
NOAH is an initiative that aims to reduce the damage caused by calamities to
properties and human life. The program led to the development of very high-resolution maps of
Philippine landscape. All maps are available in the Project NOAH website at http://noah.dost.gov.ph
and in the mobile app called ARKO .
Project NOAH’s website contains a large amount of valuable information. Some of these include the
following:
1. precipitation data;
2. real-time information about the changes in the water level of rivers and streams;
3. real-time information from rain gauges and sensors that may serve as early flood warnings;
4. flood hazard maps ;
5. hazard maps for the landslide-related phenomenon;
6. storm surge historical data; and many more.
ACTIVITY 1 GEOLOGICAL HAZARDS: Knowing & Coping
Objective: This is an activity that will allow you to familiarize with Project NOAH. Use the
diagram below to answer the following questions.
1. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ig-36 2. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ih-38 3. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ii-41
http://noah.up.edu.ph/#/section/geoserver/flood25
LEARNING TASK: List at least ten (10) areas in Metro Manila that you have been to or visited
because of family or friends living in those areas. Determine the risks of flood hazard of those
area using the above flood hazard map of Metro Manila. Fill up the table below.
AREA (Barangay, City) FLOOD HAZARD
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Guide Questions:
1. What could be the reason why some areas in Metro Manila have high risk of flooding?
____________________________________________________________________________________________
2. What is the general hazard risk of flooding for Mandaluyong City?
____________________________________________________________________________________________
3. What other examples of hazards can be assessed by Project NOAH?
____________________________________________________________________________________________
INTRODUCTION Get READY. SET yourself to #studymode. Here we GO !!!
Coastal zone or coast is the region where the land processes and the sea meet and interact. It is
constantly changing and is shaped by different natural and human processes.
Waves are undulations in the water surface as a result of wind. Wave action may result in erosion of
rocks or the deposition of sediments along coasts. Waves can be destructive or constructive.
Tides are the variations in the water level of oceans as a result of gravitational effects of the moon and
Sun in relation to Earth.
Storm surges are the production of exceptionally high levels of coast al water by strong onshore winds
and low barometric pressures caused by storms.
1. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ig-36 2. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ih-38 3. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ii-41
Coastal erosion involves processes causing debris and rock material along coasts to wear off and be
carried away. The main processes that cause coastal erosion are:
1. Accretion is the process of increasing the area of land along coasts as a result of
deposition and sedimentation.
2. Abrasion is a form of erosion on rocky shores resulting from waves hitting the coast or
windblown sand hitting rocks.
3. Attrition is the breaking and wearing down of debris from cliffs and rocky shores
because waves agitate the materials.
4. Corrosion occurs where acidic seawater dissolves the limestones or chalk
5. Bioerosion is erosion caused by the action of marine organisms like mollusks, sea
urchins, and coastal flora.
Submersion is when the sediment is submerged underwater and eventually replaced back to its
original location.
Saltwater intrusion is the movement of seawater into coastal freshwater aquifers. It is directly
affected by the water supply, and thus, happens naturally to a certain extent.
ACTIVITY 2 COASTAL PROCESSES
PART A. LEARNING TASK: Identify which type of coastal erosion processes is depicted by the
following images. Underline your answer.
1. Accretion OR Attrition 2. Abrasion OR Corrosion 3. Bioerosion OR Accretion
4. Abrasion OR Corrosion 5.Atrittion OR Bioerosion 6.Submersion OR Accretion
PART B. What are the environmental problems that concern Philippine coastal areas?
Problem:
Solution:
1. Manila de Bay
1. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ig-36 2. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ih-38 3. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ii-41
Problem:
Solution:
2. Boracay Island
CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING. Answer this bef ore proceeding to the next part.
What are the effects of coastal processes on the ecological conditions of
coastal areas?
WRAP-UP Great job! Now it’s time f or you to ref lect on what you have learned.
Write 3 coastal areas that is popular destination for ecotourism in the Philippines you wish to visit.
Explain why you select those areas.
POST TEST Answer this to determine how much you gained f rom the lessons.
1. Which of the following refers to the tool that shows the level of risk in an area due to
potential damage from floods, tropical cyclones, monsoons and other hydrometeorological
phenomena?
A. Biodiversity Map C. Hydrometeorological Map
B. Environment Disaster Map D. Richter Scale
2. Which of the following would you likely not encounter when looking at a hazard map?
A. It shows areas susceptible to hazard. C. It displays location of commercial areas.
B. It contains a base or a topographic map. D. It shows safe areas or possible evacuation centers.
3. Using the Hydrometeorological Map of Metro Manila, which of the following city is most
susceptible to high-height flood?
A. Makati B. Mandaluyong C. Marikina D. Pasig
4. Which of the following is produced when there is undulation in water surface caused by
strong wind?
A. tide B. tornado C. typhoon D. Waves
5. Which of the following would most likely to happen in an area that experiences continuous
surface erosion?
A. The area will remain intact despite of erosion.
B. Cliffs will form due to the erosion of the area.
C. Some points in the area will be submerged in seawater.
D. Constructive waves will bring back sediments to the area.
6. Which of the following is most likely to occur when there is a rise in sea level due to global
warming?
A. Abrasion B. Corrosion C. Saltwater Intrusion D. Submersion
7. The increase in demand for freshwater when a coast al area is developed will likely result
into what type of coastal hazards?
A. Abrasion B. Coastal Accretion C. Submersion D. Saltwater intrusion
8. Which type of erosion is caused by marine organisms?
A. Abrasion B. Bioerosion C. Corrosion D. Submersion
1. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ig-36 2. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ih-38 3. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ii-41
9. Which of the following best explains why construction of infrastructures must be done at a
“safe distance” from the coasts?
A. Construction does not pose dangers to the coasts.
B. It protects the infrastructure from coastal processes.
C. It protects the construction from the effects of high tides.
D. It provides the infrastructure with a better view of the coasts
10. Which of the following is being done in an ongoing infrastructural project as it used to
identify and evaluate the effects on the ecosystem?
A. blueprint C. preventive method
B. environmental risk assessment D. solid waste management
REFERENCES:
• Tarbuck, Edward J., and Lutgens, Frederick K. 2015. Earth Science. 14th edition. Pearson
Education Inc. USA.
• Columbia University in the City of New York. Coastal Processes. Accessed JUNE 20,2020.
http:// www.columbia.edu/~vjd1/coastal_basic.htm
• Quipper Teachers Guide Unit 13.2 Understanding Hydrometeorological Hazards. Accessed
June 12, 2020.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/115JWiKDuUQdCV0TlKhcilcbgfs3gqvmO/viewhttps://drive.
google.com/file/d/115JWiKDuUQdCV0TlKhcilcbgfs3gqvmO/view
• Quipper Teachers Guide Unit 14.1 Coastal Processes. Accessed June 12, 2020.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1VBRZ6Cm-F_vvvGfVJh1gwRbClh7r0pUj/view
• Quipper Teachers Guide Unit 14.2 Mitigation of Impacts of Land Development and Waste
Disposal on Coast. Accessed June 12, 2020.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/14Dp2rZIJcrfPhYWWLF3v8zvwro7MtAYK/view
PHOTO CREDITS:
https://www.nps.gov/articles/coastal-processes-erosion.htm
https://www.nps.gov/articles/effects-of-grain-size-and-slope.htm
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Haast_River_18.jpg
https://www.flickr.com/photos/jsjgeology/15814993988
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:BeachErosionTP.jpg
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Varing_Osmussaar.JPG
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Roxas_blvd.__along_Manila_Bay;_aerial_shot_from_Legaspi
_Towers.jpg
https://www.flickr.com/photos/ashleyt/13354142693
For inquiries or feedback, please write or call:
Department of Education – Schools Division Office-Mandaluyong
Calbayog Street, Highway Hills, Mandaluyong City 1500
Telefax: (632) 79552557
Email Address: sdo.mandaluyong@deped.gov.ph www.depedmandaluyong.org
1. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ig-36 2. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ih-38 3. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ii-41
1. MELC Code: S11/12ES-If-30 2. MELC Code: S11/12ES-If-31 3. MELC Code: S11/12ES-If-33
1. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ig-36 2. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ih-38 3. MELC Code: S11/12ES-Ii-41
You might also like
- Tsunamis: Detection, Monitoring, and Early-Warning TechnologiesFrom EverandTsunamis: Detection, Monitoring, and Early-Warning TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Module 8Document11 pagesEarth and Life Science Module 8Perry FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Module in Earth and Life Science: What Is ItDocument8 pagesModule in Earth and Life Science: What Is ItKenjieNo ratings yet
- SLK 3Document21 pagesSLK 3Fame EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Response and Risk Reduction - q4 - Slm7Document15 pagesDisaster Response and Risk Reduction - q4 - Slm7Jimmie KitNo ratings yet
- 20 Core Subject Science 11 Earthn - Nlife Science Q1 Module 20Document17 pages20 Core Subject Science 11 Earthn - Nlife Science Q1 Module 20Winsear VardeNo ratings yet
- 16 Core Subject Science 11 Earth - Lide Science Q1 Module 16Document18 pages16 Core Subject Science 11 Earth - Lide Science Q1 Module 16Winsear VardeNo ratings yet
- DRRR11 Q2 Mod9Document25 pagesDRRR11 Q2 Mod9Rommel HapitaNo ratings yet
- 18-Core Subject-Science 11-Earth - Life Science-Q1-Module 18Document25 pages18-Core Subject-Science 11-Earth - Life Science-Q1-Module 18BruceNo ratings yet
- Flood Monitor Baby ThesisDocument23 pagesFlood Monitor Baby ThesisPaula Jane100% (2)
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 2: Natural HazardsDocument23 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 2: Natural HazardsRachel Ann CanlasNo ratings yet
- SLK 2Document25 pagesSLK 2Fame EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Docu 1Document34 pagesDocu 1Franco Cerna CuevaNo ratings yet
- DRRR - LAS Quarter 4Document8 pagesDRRR - LAS Quarter 4Jabez Flores Natividad0% (1)
- Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level in Geography SCHEME OF WORK: Unit 1: Global ChallengesDocument13 pagesPearson Edexcel International Advanced Level in Geography SCHEME OF WORK: Unit 1: Global ChallengesEnriqueMinhazNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Flood Risk ManagementDocument8 pagesThesis On Flood Risk Managementdebradavisneworleans100% (2)
- Responding To Climate Change in MozambiqDocument263 pagesResponding To Climate Change in MozambiqDinar IstiyantoNo ratings yet
- 18 Core Subject Science 11 Earth - Life Science Q1 Module 18Document23 pages18 Core Subject Science 11 Earth - Life Science Q1 Module 18Winsear VardeNo ratings yet
- 16-Core Subject-Science 11-Earth - Lide Science-Q1-Module 16Document23 pages16-Core Subject-Science 11-Earth - Lide Science-Q1-Module 16BruceNo ratings yet
- SLK 1Document24 pagesSLK 1Fame EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Coastal Hazards Mitigation MethodsDocument3 pagesCoastal Hazards Mitigation Methodsbernadeth barajasNo ratings yet
- Rapid Extreme Tropical Precipitation and Flood Inundation Mapping Framework (RETRACE) : Initial Testing For The 2021-2022 Malaysia FloodDocument24 pagesRapid Extreme Tropical Precipitation and Flood Inundation Mapping Framework (RETRACE) : Initial Testing For The 2021-2022 Malaysia FloodTang Wei KuangNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Module 7Document11 pagesEarth and Life Science Module 7Perry FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Mayur EstDocument12 pagesMayur EstRavindra SalunkheNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Coastal Engineering and Management - (2Nd Edition) © World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. LTDDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Coastal Engineering and Management - (2Nd Edition) © World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. LTDSon TranNo ratings yet
- ELS - Q1 - Module 20 - Mitigation To Coastal Processes and HazardsDocument25 pagesELS - Q1 - Module 20 - Mitigation To Coastal Processes and HazardsZack WilliamNo ratings yet
- Latest, Updated and Complete Thesis 1.0 PDFDocument123 pagesLatest, Updated and Complete Thesis 1.0 PDFCristian PurayNo ratings yet
- Drainage & Flood Risk Assessment On Flooded Urban Barangays in Laoag CityDocument10 pagesDrainage & Flood Risk Assessment On Flooded Urban Barangays in Laoag CityZen DolorosoNo ratings yet
- Coastal Processes Lesson Exemplar Explains Erosion, Submersion & IntrusionDocument4 pagesCoastal Processes Lesson Exemplar Explains Erosion, Submersion & IntrusionRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- News Letter Vol 2Document16 pagesNews Letter Vol 2Nala FertuNo ratings yet
- 19 Core Subject Science 11 Earth - Life Science Q1 Module 19Document27 pages19 Core Subject Science 11 Earth - Life Science Q1 Module 19Winsear VardeNo ratings yet
- Balica2012 PDFDocument33 pagesBalica2012 PDFJoecoNo ratings yet
- AmehehrjekekdDocument7 pagesAmehehrjekekdcf867837No ratings yet
- Full ThesisDocument94 pagesFull ThesisRonan Erickson CuaNo ratings yet
- Marine Engineering Thesis ExamplesDocument7 pagesMarine Engineering Thesis Examplespatriciaviljoenjackson100% (1)
- Deenbandhu Chhoturam University of Science and Technology Murthal, SonipatDocument30 pagesDeenbandhu Chhoturam University of Science and Technology Murthal, SonipatKomal RawatNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment Methodology at Isla Del Carmen, MexicoDocument13 pagesRisk Assessment Methodology at Isla Del Carmen, MexicoKaritza KenyNo ratings yet
- Kurniawan 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 982 012036Document12 pagesKurniawan 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 982 012036munawirbpmNo ratings yet
- 0097 0145 000053Document14 pages0097 0145 000053Marcelo ProtzNo ratings yet
- Engineering HydrologyDocument75 pagesEngineering HydrologygladNo ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument11 pagesDisaster ManagementKunal AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Sciences Week 7 8Document11 pagesEarth Life Sciences Week 7 8ginayumo0No ratings yet
- 158.CC 09Document6 pages158.CC 09tugustraNo ratings yet
- Grade-12 DRRR Q2 Wk2 GLAKDocument16 pagesGrade-12 DRRR Q2 Wk2 GLAKClarisse De GuiaNo ratings yet
- 2013 Bookmatter CoastalHazardsDocument21 pages2013 Bookmatter CoastalHazardsAyesha AzizNo ratings yet
- Core (STEM) - SLM 13-Grade1112DRRR-1st Quarter - Analyze The Effects of The Different Earthquake HazardsDocument20 pagesCore (STEM) - SLM 13-Grade1112DRRR-1st Quarter - Analyze The Effects of The Different Earthquake HazardsRjay Cada100% (2)
- Reseach Science 2Document13 pagesReseach Science 2Monaida Umpar IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Danger ZoneDocument44 pagesChapter 4 Danger ZoneArgie LynNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar in Earth and Life Science G11 Cristina V. Maquinto, LPTDocument9 pagesLesson Exemplar in Earth and Life Science G11 Cristina V. Maquinto, LPTcristina maquinto100% (1)
- Earth and Life Science Week 7BDocument10 pagesEarth and Life Science Week 7BMa Cindy Foronda AntonioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11.1Document28 pagesLesson 11.1Fahad LumambasNo ratings yet
- DRRR q2 Mod6 Hydrometeorological-Hazards v2Document33 pagesDRRR q2 Mod6 Hydrometeorological-Hazards v2Precious100% (1)
- Lesson 16a Earth and Life ScienceDocument11 pagesLesson 16a Earth and Life ScienceJelai MedinaNo ratings yet
- 001 CraaDocument116 pages001 Craacamaroding.hsocorNo ratings yet
- ACCO WhitePaper PublicSectorSLR September2014Document6 pagesACCO WhitePaper PublicSectorSLR September2014Carlos PelaezNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE - Q1 - W8 - Mod19 - Earth and Life Science (Coastal Processes)Document10 pagesSCIENCE - Q1 - W8 - Mod19 - Earth and Life Science (Coastal Processes)LieselNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Unit 2 Hydrometeorological HazardDocument5 pagesModule 3 Unit 2 Hydrometeorological HazardLIAM GABRIEL DAWAWANo ratings yet
- Dam Safety Management, ICBESCF - Delhi 4-6 September 2008.Document8 pagesDam Safety Management, ICBESCF - Delhi 4-6 September 2008.Chris LawsonNo ratings yet
- Ocean & Coastal Management: J.R. Nelson, T.H. Grubesic, L. Sim, K. Rose, J. GrahamDocument11 pagesOcean & Coastal Management: J.R. Nelson, T.H. Grubesic, L. Sim, K. Rose, J. GrahamDony LatiefNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Water Management ThesisDocument4 pagesIrrigation Water Management Thesisijofwkiig100% (2)
- 4module in Environmental ScienceDocument5 pages4module in Environmental ScienceVirgie OrtizNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Structures & Irrigation Design CourseDocument93 pagesHydraulic Structures & Irrigation Design CourseRavi Kumar85% (27)
- Download ebook The Water Cycle Pdf full chapter pdfDocument50 pagesDownload ebook The Water Cycle Pdf full chapter pdfronald.abreu950100% (22)
- Design Review Checklist Box Culverts Bridge - 201711081516193760Document20 pagesDesign Review Checklist Box Culverts Bridge - 201711081516193760Sumber UnduhNo ratings yet
- General Design and Construction RequirementsDocument30 pagesGeneral Design and Construction RequirementsLester BaculiNo ratings yet
- World Piping Solutions CatalogueDocument8 pagesWorld Piping Solutions Cataloguesales wpsNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation of Septic Tank WorksDocument4 pagesRehabilitation of Septic Tank WorksAbdi MusaNo ratings yet
- Overview of The ASTM Risk-Based Corrective Action (RBCA) ProgramDocument8 pagesOverview of The ASTM Risk-Based Corrective Action (RBCA) ProgramFábio MathiasNo ratings yet
- Concept of Soil Confinement and Applicable MeasuresDocument16 pagesConcept of Soil Confinement and Applicable MeasuresHimanshu RanaNo ratings yet
- GSPC Pipavav Power Plant Industrial Training ReportDocument100 pagesGSPC Pipavav Power Plant Industrial Training ReportRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- R2 Four Basic Components of A Refrigeration System: #1 EvaporatorsDocument43 pagesR2 Four Basic Components of A Refrigeration System: #1 EvaporatorsAhmad NasrudinNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle GizmosDocument8 pagesCarbon Cycle GizmosEduardo Correa67% (3)
- Question Excerpt From National Plumbing Code of The PhilippinesDocument17 pagesQuestion Excerpt From National Plumbing Code of The PhilippinesVholts Villa Vitug80% (5)
- Class 10th English Notes Final 2020Document52 pagesClass 10th English Notes Final 2020Husain Ali67% (3)
- Karthik PDFDocument24 pagesKarthik PDFinscNo ratings yet
- People Matter,: Planet MattersDocument4 pagesPeople Matter,: Planet MattersVideo DingNo ratings yet
- Meridian Park Design GuidelinesDocument68 pagesMeridian Park Design GuidelinesJerzy Mae GloriosoNo ratings yet
- Iv. The HydrosphereDocument43 pagesIv. The HydrosphereJohn Alfred FernandezNo ratings yet
- 9c Children - Articles PDFDocument10 pages9c Children - Articles PDFaramNo ratings yet
- Jet Oil Safety Data SheetDocument9 pagesJet Oil Safety Data SheetArun RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter V: Run Off: Phases of Hydrologic CycleDocument49 pagesChapter V: Run Off: Phases of Hydrologic Cyclejefferson v. sabadoNo ratings yet
- Large Scale PEM ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesLarge Scale PEM ElectrolysisTarek ShoukryNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1 Nepal National Chapter Report and Future PlansDocument8 pages3.2.1 Nepal National Chapter Report and Future PlansRifka RifkaNo ratings yet
- Resource Governance Agriculture and Sustainable Livelihoods in The Lower Mekong Basin CompressedDocument397 pagesResource Governance Agriculture and Sustainable Livelihoods in The Lower Mekong Basin CompressedNguyen Viet DungNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0964569122004124 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0964569122004124 MainRahma ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Water ResourcesDocument27 pagesWater Resourcessharon ranjitha paulNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document27 pagesModule 2Sajed AbdulrahmanZaiNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Man-Made Slopes and Retaining WallsDocument14 pagesMaintaining Man-Made Slopes and Retaining WallsmdelvallevNo ratings yet
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (63)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Why Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeFrom EverandWhy Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (699)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutFrom EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (142)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsFrom EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (222)
- The Big, Bad Book of Botany: The World's Most Fascinating FloraFrom EverandThe Big, Bad Book of Botany: The World's Most Fascinating FloraRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogFrom EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateFrom EverandThe Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1002)
- The Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanFrom EverandThe Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanNo ratings yet
- The Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (11)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeFrom EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (19)
- Last Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderFrom EverandLast Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (283)