Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Continuidad - Parte 1
Uploaded by
Rosa PYOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Continuidad - Parte 1
Uploaded by
Rosa PYCopyright:
Available Formats
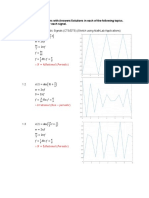
Estudia la continuidad de:
𝑥 2𝑦
(𝑥, 𝑦) ≠ 0
1. 𝑓(𝑥, 𝑦) = {𝑥 2+𝑦 2
(𝑥, 𝑦) = 0
0
I. 𝑓(0,0) = 0
II. 𝑓(𝑥, 𝑦) ≠ 0
𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥
𝑥 2𝑦 𝑥 2 𝑚𝑥 𝑥3𝑚
lim = lim = lim
(𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) 𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 (𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) 𝑥 2 + (𝑚𝑥)2 (𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) 𝑥 2 + 𝑚2 𝑥 2
3
𝑥 𝑚 𝑥𝑚
lim 2 2 = lim
(𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) 𝑥 (1 + 𝑚 ) (𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) (1 + 𝑚2 )
La funcion no es continua, entonces el limite no existe
𝑥+𝑦
𝑥≠𝑦
2. 𝑓(𝑥, 𝑦) = {𝑥−𝑦 𝑥 = 𝑦 , 𝑒𝑛 𝑒𝑙 𝑝𝑢𝑛𝑡𝑜 (0,0)
0
I. 𝑓(0,0) = 0
II. 𝑓(𝑥, 𝑦) ≠ 0
𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥
𝑥+𝑦 𝑥 + 𝑚𝑥 𝑥(1 + 𝑚)
lim = lim = lim
(𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) 𝑥 − 𝑦 (𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) 𝑥 − 𝑚𝑥 (𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) 𝑥(1 − 𝑚)
La funcion no es continua, entonces el limite no existe
1
𝑦 𝑠𝑒𝑛( ) (𝑥, 𝑦) ≠ 0
3. 𝑓(𝑥, 𝑦) = { 𝑥 2 +𝑦 2
0 (𝑥, 𝑦) = 0
I. 𝑓(0,0) = 0
II. 𝑓(𝑥, 𝑦) ≠ 0
𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥
1 1
lim 𝑦 𝑠𝑒𝑛 ( )= lim 𝑚𝑥 𝑠𝑒𝑛 ( 2 )
(𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) +𝑦 2 𝑥2(𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) 𝑥 + 𝑚𝑥 2
1
lim 𝑚𝑥. 𝑠𝑒𝑛 ( 2 )
(𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) 𝑥 (1 + 𝑚2 )
La funcion no es continua, entonces el limite no existe
𝑥𝑦
(𝑥, 𝑦) ≠ 0
4. 𝑓(𝑥, 𝑦) = {𝑥 2+𝑦 2
0 (𝑥, 𝑦) = 0
III. 𝑓(0,0) = 0
IV. 𝑓(𝑥, 𝑦) ≠ 0
𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥
𝑥𝑦 𝑥𝑚𝑥 𝑥2𝑚
lim = lim = lim
(𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) 𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 (𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) 𝑥 2 + (𝑚𝑥)2 (𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) 𝑥 2 + 𝑚2 𝑥 2
𝑥2𝑚 𝑚
lim 2 2 = lim
(𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) 𝑥 (1 + 𝑚 ) (𝑥,𝑦)→(0,𝑚𝑥) (1 + 𝑚2 )
La funcion no es continua, entonces el limite no existe
You might also like
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics 2 BEKG 2443: D ZiniDocument21 pagesEngineering Mathematics 2 BEKG 2443: D ZiniRashiqah RazlanNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Multivariate Calculus: MTH-174: LimitDocument17 pagesMultivariate Calculus: MTH-174: LimitNelli HariNo ratings yet
- Probar Que Los Limites No Existen A. Lim: Tarea N°6Document14 pagesProbar Que Los Limites No Existen A. Lim: Tarea N°6MIGUELNo ratings yet
- Taylor Series - Multiple Var Summer 22-23Document1 pageTaylor Series - Multiple Var Summer 22-23MRM MuhidNo ratings yet
- Taylor Series Multiple Variable FunctionDocument1 pageTaylor Series Multiple Variable Functionmakrosha11816No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - 1.2 PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 1 - 1.2 PDFThevhan MurallyNo ratings yet
- gr10t2 Functions Parabola Function MemoDocument8 pagesgr10t2 Functions Parabola Function MemoaaronmaburutseNo ratings yet
- Function - Even & Odd Functions, Domain of Definition and ContinuityDocument1 pageFunction - Even & Odd Functions, Domain of Definition and ContinuityB MNo ratings yet
- Вариац. 1-3Document3 pagesВариац. 1-3Артём ЖевнеренкоNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document9 pagesLecture 2owronrawan74No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (Answers)Document2 pagesAssignment 1 (Answers)Rilland Carl AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- Lec2 MathDocument8 pagesLec2 Mathowronrawan74No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1Archana SinghNo ratings yet
- 5-Lecture-Special Functions MAT - M Sc-IVDocument6 pages5-Lecture-Special Functions MAT - M Sc-IVMadina GraphicsNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note-Calculus of Function of Several Variables-2024Document40 pagesLecture Note-Calculus of Function of Several Variables-2024Naol junierNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document18 pagesChapter 1krymatf741No ratings yet
- Medi1 U2 A3Document6 pagesMedi1 U2 A3Magally Conde ArandaNo ratings yet
- Clave de Primer Parcial de Matemática IV. 2022Document9 pagesClave de Primer Parcial de Matemática IV. 2022César Augusto GuidoNo ratings yet
- Cónicas CuadroDocument1 pageCónicas CuadroJuan Ignacio PirosoNo ratings yet
- Nucleo - Imagen - Nulidad y RangoDocument4 pagesNucleo - Imagen - Nulidad y RangoἉρῆδ ΠολέμουNo ratings yet
- Lecture 22 Continuity and Partial Derivatives MTH165Document18 pagesLecture 22 Continuity and Partial Derivatives MTH165James PrakashNo ratings yet
- Sturm-Liouville & FourierDocument36 pagesSturm-Liouville & FourierEhab WilsonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 6Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 6Avinash Kumar Jha 4-Year B.Tech. Mechanical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- TAREA 3 Rosas Perez ErikaDocument12 pagesTAREA 3 Rosas Perez ErikaRosas Pérez Erika ArlethNo ratings yet
- Jawab Uts Kalkulus 2020 - TipDocument2 pagesJawab Uts Kalkulus 2020 - TipNurul KhasanahNo ratings yet
- Class XII Differential Equations AssignmentDocument4 pagesClass XII Differential Equations AssignmentPriyankAhujaNo ratings yet
- Mat. IV - Clase 3 - Ecuaciones Difer. ExactasDocument18 pagesMat. IV - Clase 3 - Ecuaciones Difer. ExactasEDIN ORLANDO NU�EZ DULANTONo ratings yet
- Solutions - Assignment - No - 5 - EditedDocument8 pagesSolutions - Assignment - No - 5 - EditedJahid HasanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument19 pagesUntitledLucas WesnerNo ratings yet
- Calculo 3: Ecuaciones DiferencialesDocument6 pagesCalculo 3: Ecuaciones DiferencialesJOSUÉ G. USQUIZA COLÁNNo ratings yet
- Practica de Transformaciones LinealesDocument3 pagesPractica de Transformaciones LinealesLizbeth Patty PattyNo ratings yet
- 7-Lecture-Special Functions MAT - M Sc-IVDocument6 pages7-Lecture-Special Functions MAT - M Sc-IVMadina GraphicsNo ratings yet
- Upto Mid-TermDocument39 pagesUpto Mid-TermSourav DeNo ratings yet
- Lineal Bryan VenturaDocument5 pagesLineal Bryan VenturaBryan VenturaNo ratings yet
- Suprafata Cilindru Paralel Generatoare Rotire DRPT)Document1 pageSuprafata Cilindru Paralel Generatoare Rotire DRPT)chiricacosmin97No ratings yet
- Final P.E E.D (1bryan VenturaDocument88 pagesFinal P.E E.D (1bryan VenturaBryan VenturaNo ratings yet
- Resolução: 2. : Cálculos AuxiliaresDocument5 pagesResolução: 2. : Cálculos AuxiliaresmarianaNo ratings yet
- Kalkulus 2Document3 pagesKalkulus 2Nur AstryantyNo ratings yet
- Solution. The Limit Is 0. First Show ThatDocument2 pagesSolution. The Limit Is 0. First Show ThateouahiauNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument37 pagesUntitledMiguel GomezNo ratings yet
- 4-Lecture-Special Functions MAT - M Sc-IVDocument8 pages4-Lecture-Special Functions MAT - M Sc-IVMadina GraphicsNo ratings yet
- Gr.12 CH.3.3Document10 pagesGr.12 CH.3.3Sagvan AlixanNo ratings yet
- Eulers TheoremDocument6 pagesEulers Theorem01795494168nazmulhasanNo ratings yet
- Volumen de Sólidos de Revolución (Apunte)Document3 pagesVolumen de Sólidos de Revolución (Apunte)JordanVergaraNo ratings yet
- Partial Diffrentaion BBA 28th FinalDocument26 pagesPartial Diffrentaion BBA 28th FinalMd. Rifat HasanNo ratings yet
- FinalsDocument27 pagesFinalsRias GremoryNo ratings yet
- Function of Several Variables Assignment: Mathophilic Education Mob. No.-7239082744Document10 pagesFunction of Several Variables Assignment: Mathophilic Education Mob. No.-7239082744SunnyNo ratings yet
- Nama: Friska Veronika Lenak NIM: 19 504 007 Kelas: SENIN, 10:15 - 12:45, RM 04 Mata Kuliah: Kalkulus Variabel Banyak SoalDocument2 pagesNama: Friska Veronika Lenak NIM: 19 504 007 Kelas: SENIN, 10:15 - 12:45, RM 04 Mata Kuliah: Kalkulus Variabel Banyak SoalFriska Veronika LenakNo ratings yet
- Final Exam 2015 NewDocument7 pagesFinal Exam 2015 NewMohamed AbdelazizNo ratings yet
- QUISPE OCHOA Johan David 2018-119016Document3 pagesQUISPE OCHOA Johan David 2018-119016David 8ANo ratings yet
- Clase 3 - Mat. IV - Ecuaciones Difer. ExactasDocument18 pagesClase 3 - Mat. IV - Ecuaciones Difer. ExactasPæül AlarconNo ratings yet
- Diff Eqn Tut (3) Solution PartDocument4 pagesDiff Eqn Tut (3) Solution PartMohamed Ahmed FadelNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة السابعة MathsDocument7 pagesالمحاضرة السابعة MathsDheyaa Al-JubouriNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة السادسة MATHSDocument10 pagesالمحاضرة السادسة MATHSDheyaa Al-JubouriNo ratings yet
- Trayectorias OrtogonalesDocument6 pagesTrayectorias OrtogonalesShelly Stefhany Laban SeminarioNo ratings yet
- Problemario Unidad 2 CMDocument5 pagesProblemario Unidad 2 CMRobles Ramírez Angel EliasNo ratings yet
- Cálculus UnivDocument15 pagesCálculus UnivPEDRO ARTEAGANo ratings yet
- 03 Derivadas (TP2)Document3 pages03 Derivadas (TP2)JORGE SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)From EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No ratings yet
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Images of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryFrom EverandImages of Mathematics Viewed Through Number, Algebra, and GeometryNo ratings yet
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsFrom EverandHow Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (9)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- A Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathFrom EverandA Guide to Success with Math: An Interactive Approach to Understanding and Teaching Orton Gillingham MathRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)