Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wala Lang Compress
Wala Lang Compress
Uploaded by
Vince RubiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wala Lang Compress
Wala Lang Compress
Uploaded by
Vince RubiCopyright:
Available Formats
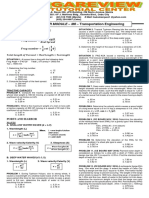
Competency Appraisal II – Hydraulics II
Problem Set Part 2 61. Oil flows from a tank through 150 m of 150 mm diameter
pipe and then discharges into air as shown in the figure. If the
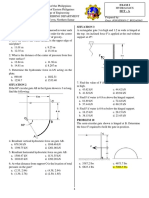
SIT. 13 Water flows through a 75 mm diameter pipe at a head loss from point 1 to point 2 is 600 mm, determine
velocity of 3 m/sec. Find: the pressure needed at point 1 to cause 17 lit/sec of oil to flow.
51. Volume flow rate in m3/sec and lit/sec.
52. Mass flow rate in kg/sec.
53. Weight flow rate in N/sec.
SIT 14. If the velocity of flow in a 75-mm diameter fire hose is
0.5 m/s,
54. Determine the velocity in a 25 mm diameter jet issuing from
a nozzle attached at the end of the pipe.
55. Compute the power available in the jet.
SIT. 16 The pump shown draws water from reservoir A at
elevation 10 m and lifts it to reservoir B at elevation 60 m. The
loss of head from A to 1 is two times the velocity head in the
200 mm diameter pipe and the loss of head from 2 to B is ten
times the velocity head in the 150 mm diameter pipe.
62. Water enters a motor through a 600-mm diameter pipe
under a pressure of 14 kPa. It leaves through a 900 mm
diameter exhaust pipe with a pressure of 4 kPa. A vertical
distance of 2.5 m separates the centers of the two pipes at the
sections where the pressures are measured. If 500 liters of
water pass the motor each second, compute the power
supplied to the motor.
Determine:
56. Rated horsepower of the pump when the discharge 0.03
m3/sec.
57. Pressure head at 1 in meters.
58. Pressure head at 2 in meters.
59. A pipeline with a pump leads to a nozzle as shown. Find the
flow rate when pump develops an 80 ft (24.4 m) head.
Assume head lost in the 6-inch (152 mm) pipe to be five times
its velocity head while the head lost in the 4-inch (102 mm)
pipe to be twelve times its velocity head. Compute the flow
rate. SIT. 17 A 50 mm diameter siphon discharges oil (sp. Gr.
=
0.82) from a reservoir (elev. 20 m) into open air (elev. 15 m). The
head loss from the reservoir (point 1) to the summit (point
2, elev. 22 m) is 1.5 m and from the summit to the discharge end
is 2.4 m. Determine:
63. Flow rate in the pipe in lit/sec
64. Absolute pressure at the summit assuming atmospheric
pressure to be 101.3 kPa.
65. Calculate the discharge in liters per second through a 100-
mm diameter orifice under a head of 5.5 m of water. Assume
Cc=0.61 and Cv=0.98
60. A pipe carrying oil of specific gravity 0.877 changes in size 66. An open cylindrical tank, 2.4 m in diameter and 6 m tall has
from 150 mm at section and 450 mm at section 2. Section 1 is 1 m of glycerin (Sg=1.5), 2.5 m of water, and 1.5 m of oil
3.6 m below section 2 and the pressures are 90 kPa and 60 (So=0.82). Determine the discharge through the 125 mm
kPa respectively. If the discharge is 150 lit/sec, determine the diameter located at the bottom of the tank. Assume C=0.65
head lost and the direction of flow. SIT. 18 A calibration test of a 12.5 mm diameter circular
sharp-edged orifice in a vertical side of a large tank showed a
discharge of 590 N of water in 81 seconds at a constant head of
4.70 m. Measurement of the jet showed that it traveled 2.35 m
horizontally while dropping 300 mm. Compute:
67. Coefficient of velocity
68. Coefficient of discharge.
69. Coefficient of contraction
SIT. 19 A 50 mm diameter circular sharp-edged orifice at the side
of tank discharges water under a head of 3 m. If the
coefficient of contraction Cc=0.63 and the head lost is 240 mm,
compute:
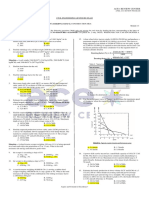
70. Coefficient of velocity 88. Compute the specific energy.
71. Coefficient of discharge 89. Compute the slope of the channel if n=0.014.
SIT. 20 A 1.5 m diameter vertical cylindrical tank 3 m high 90. Compute the average shearing stress at the boundary.
contains 2.5 m of water. A 100 mm diameter circular sharp-
edged orifice is located at its bottom. Assume C=0.60 91. The section of a storm drain tunnel is as shown. During the
72. How long will it take to lower the water level to 1 m deep after heavy storm, the water surface is 2.5 m above the semicircular
opening the orifice? section. If n=0.02 and the slope of the channel is 0.009,
73. How long will it take to empty the tank? calculate the discharge.
74. Water flows through a parabolic weir that is 2 m deep and 2
m wide at the top under a constant head of 1.50 m. Assuming
C=0.65, determine the discharge through the weir.
75. Water having kinematic viscosity v=1.3x10-6 m2/s flows in a
100 mm diameter pipe at a velocity of 4.5 m/s. Determine the
Reynold’s number.
76. Fluid flows through a 20 mm diameter pipe, 150 m long at a
Reynold’s number of 1750. Calculate the discharge if the head
lost is 175 m.
77. What is the hydraulic radius of a rectangular air duct 200
mm by 350 mm?
SIT. 21 Water is flowing at the rate of 300 lit/sec from A to E as
shown in the figure.
92. A 500 mm diameter concrete pipe is laid on a slope of 1 m
per 500 m and is required to carry water at the rate 0.04 m3/s.
Determine the normal depth of flow. Use roughness coefficient
n=0.013.
93. A flood occurs in a main channel having a trapezoidal
section (side slope on both side: 2H to 1V) and base width of
12 m. The depth of flow in this section is 3.60 m and the flood
spills out over an almost horizontal plane on one side of
the main channel. The width of the flood plain is 60 m with
an
overflow depth of 1 m. if n=0.025 for the main channel and two
Compute: times as large for the overflow section, estimate the discharge if
78. flow rate in pipe 1 the be slope for both is 0.00030.
79. flow rate in pipe 2
80. flow rate in pipe 3 SIT. 24 A rectangular canal, 6.5 m wide and 1.4 m deep lined
81. flow rate in pipe 4 with smooth stone (n=0.013) has a hydraulic slope of 0.001.
82. flow rate in pipe 5 94. What savings in earth excavation could have been affected
83. flow rate in pipe 6 by using the best proportion of rectangular section but adhering
to the same discharge and slope?
84. The turbine shown is in the 350 mm diameter line. If 95. What savings in lining per meter length of canal could have
the turbine efficiency is 90%, determine its output power been affected by using the best proportion of rectangular
in kilowatts. section but adhering to the same discharge and slope?
96. Determine the maximum flow through a 1.2 m diameter
concrete culvert which is laid on a slope of 0.009. Use n=0.013
97. A circular sewer pipe 1.6 m in diameter is laid on a slope of
2 m per kilometer. The pipe is made of concrete with n=0.013.
SIT. 22 Water flows uniformly in a rectangular concrete open Determine the discharge when the pipe is two-thirds full.
channel that is 10 m wide at a depth of 3 m. The channel slope 98. What is the hydraulic radius of the channel shown in the
is 0.0025. Using n=0.013, find: figure?
85. Velocity
86. Flow rate
87. Boundary shear stress
SIT. 23 A trapezoidal channel has a bottom width of 6 m and side
slopes of 2 horizontal to 1 vertical. If the depth is 1.2 m and
the flow is 20.40 m3/sec,
99. A trapezoidal canal section having side slope of 2H to 3V has
a total depth of 1.5 m. For a most efficient proportion, what is the
required bottom width in meters?
100. A turbine is rated at 600 hp when the flow of water
through it is 0.61 m3/s. Assuming an efficiency of 87%, what is
the head acting on the turbine?
You might also like
- Design of Piping LoadsDocument13 pagesDesign of Piping LoadserodrguezNo ratings yet
- Stress Corrosion Cracking Recommended Practices 2007Document205 pagesStress Corrosion Cracking Recommended Practices 2007Vicknesh Thanabal80% (5)
- Diffraction and Wave Theory (77,88Document13 pagesDiffraction and Wave Theory (77,88cevevo4672No ratings yet
- November 2021 Ce Board Exam Tuzon 6: Eview NnovationsDocument3 pagesNovember 2021 Ce Board Exam Tuzon 6: Eview NnovationsamberNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Exam Geo Nov 2021Document10 pagesEvaluation Exam Geo Nov 2021Yedda M IlaganNo ratings yet
- Two Open TanksDocument10 pagesTwo Open TanksMaverick TimbolNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoMichael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Camarines Norte State College: College of Engineering SummDocument3 pagesCamarines Norte State College: College of Engineering SummjefreyNo ratings yet
- 601Document8 pages601Allan Añavisa Ostique Jr.No ratings yet
- No Answer Eval Hydraulics Nov 2018 Set ADocument4 pagesNo Answer Eval Hydraulics Nov 2018 Set AAlthara BaldagoNo ratings yet
- 2023 Nov Preboard 1 MathDocument5 pages2023 Nov Preboard 1 MathJanella Gail FerrerNo ratings yet
- CE Board Problems in Steel DesignDocument10 pagesCE Board Problems in Steel DesignVaughn Carlisle BacayonNo ratings yet
- Hge Mid PreboardDocument7 pagesHge Mid PreboardChrisneil Delosreyes0% (1)
- Orca Share Media1547387158279Document3 pagesOrca Share Media1547387158279menma chanNo ratings yet
- Feu Hydraulics PreboardDocument2 pagesFeu Hydraulics PreboardEla Macabante100% (1)
- HGE Refresher QuestionsDocument8 pagesHGE Refresher QuestionsCj SuarezNo ratings yet
- Tos 2Document4 pagesTos 2Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Geotechnical Answer KeyDocument2 pagesHydraulics and Geotechnical Answer KeyAngelica RomeroNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Chapter 6 Air PressureDocument6 pagesForm 2 Chapter 6 Air Pressurelccjane8504No ratings yet
- 2019 Hyd MayDocument13 pages2019 Hyd MayChantal Faye GacusanNo ratings yet
- Review - Hydraulics and Geotechnical Engineering Soil MechanicsDocument4 pagesReview - Hydraulics and Geotechnical Engineering Soil MechanicsPaulyne TuganoNo ratings yet
- Math Refresher Module 1Document4 pagesMath Refresher Module 1Nicole RodilNo ratings yet
- Policarpio 6 - Refresher SECDocument2 pagesPolicarpio 6 - Refresher SECJohn RoaNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET HydraulicsDocument1 pagePROBLEM SET HydraulicsErika Rose LaronNo ratings yet
- May 2022 Ce Board Exam Alvarez 3: Eview NnovationsDocument3 pagesMay 2022 Ce Board Exam Alvarez 3: Eview NnovationsKian InductivoNo ratings yet
- 2010 November CE Board ExamDocument15 pages2010 November CE Board ExamKai de LeonNo ratings yet
- Apr 2024 Preboard 1 HgeDocument3 pagesApr 2024 Preboard 1 HgeChrisjohn Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Ii Geotech HydraulicsDocument2 pagesAssignment-Ii Geotech Hydraulicspat cruzNo ratings yet
- Esplana SteelDesign3Document1 pageEsplana SteelDesign3Naigell SolomonNo ratings yet
- (Nov2023) PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION (PSAD) - CEBU (A-M) - QuestionsDocument63 pages(Nov2023) PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION (PSAD) - CEBU (A-M) - Questionsgt201901573100% (1)
- Set BDocument12 pagesSet BDan Casurao100% (1)
- (XPERTZ) Preboard Exam 1ST HGE Nov 2022Document9 pages(XPERTZ) Preboard Exam 1ST HGE Nov 2022Fely Joy RelatoresNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Geotech2Document101 pagesHydraulics Geotech2Sigue Ramel HinayasNo ratings yet
- Set ADocument12 pagesSet ADan Casurao0% (1)
- Hydrau 1Document3 pagesHydrau 1Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document56 pagesCH 02Giuseppe TestarossaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoDocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoMichael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Exam in Fluids1Document4 pagesExam in Fluids1Prince Winderic Gaza AclanNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics 3 Part 2Document1 pageHydraulics 3 Part 2YeddaMIlaganNo ratings yet
- BatteryExam MathDocument6 pagesBatteryExam MathjadeNo ratings yet
- Steel PDFDocument3 pagesSteel PDFCj Delos Reyes Macanas100% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines: Exam 2Document4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Exam 2Jan Jan AnoNo ratings yet
- HGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Document3 pagesHGE#003-Hydraulics Engineering 3Kim Ryan PomarNo ratings yet
- Preboard 2 GeoDocument4 pagesPreboard 2 GeoLienardNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 04 - M6 - Intermodal Transportation SystemDocument1 pageRefresher Module 04 - M6 - Intermodal Transportation SystemKiki Do youNo ratings yet
- Review Module: - Hydraulics 4Document2 pagesReview Module: - Hydraulics 4YeddaMIlaganNo ratings yet
- Ce Board Strength ReviewerDocument1 pageCe Board Strength ReviewerZherrinore RasayNo ratings yet
- CE Practice ProblemsDocument5 pagesCE Practice ProblemsLyra GurimbaoNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Activity No. 1Document6 pagesIrrigation Activity No. 1Jeiel ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (4th Year)Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics (4th Year)Jaypee Calamba100% (1)
- CE Module 13 - Materials For Construction (Answer Key)Document2 pagesCE Module 13 - Materials For Construction (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Document9 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Michael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Keyanalytic ExamDocument5 pagesKeyanalytic ExamIvy Vanessa OlapNo ratings yet
- EERC Fluid Mechanics Refresher May 2021Document2 pagesEERC Fluid Mechanics Refresher May 2021Chum ElbaNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Set - ADocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Set - AAnthony Jay PoraqueNo ratings yet
- Problem 1 Problem 8:: Dy DX y 3e - 5 2 e + 8 LN 5xDocument6 pagesProblem 1 Problem 8:: Dy DX y 3e - 5 2 e + 8 LN 5xPrince Winderic G. Aclan100% (1)
- Structural Engineering & ConstructionDocument13 pagesStructural Engineering & ConstructionREX AMPONGANNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument19 pagesUntitledRojane FloraNo ratings yet
- May 2018 HgeDocument11 pagesMay 2018 HgeHarly Demegillo GabineteNo ratings yet
- Refresher HYD Part2Document2 pagesRefresher HYD Part2Lionel LapuzNo ratings yet
- F.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Center: Refresher Course Hydraulics and Geotechnical EngineeringDocument3 pagesF.A.L. Conducive Engineering Review Center: Refresher Course Hydraulics and Geotechnical EngineeringKim Ryan PomarNo ratings yet
- Tos 1Document5 pagesTos 1Allyanna Elise Diam100% (1)
- Problem Set Part 2 Ready To Print CE PaperDocument15 pagesProblem Set Part 2 Ready To Print CE PaperJeffward Jaguio0% (1)
- CENG 197 Problem Set 2Document5 pagesCENG 197 Problem Set 2edmar limNo ratings yet
- Assessment Exam 03Document12 pagesAssessment Exam 03TachooNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Ethyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- ICEDocument2 pagesICEEthyl Jean Monday Gallarte100% (1)
- OJT Evaluation FormDocument1 pageOJT Evaluation FormEthyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- Transpo - EthylDocument1 pageTranspo - EthylEthyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- BUILDINGDocument3 pagesBUILDINGEthyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- CMH Test Catalogue PDFDocument277 pagesCMH Test Catalogue PDFEthyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- Gallarte HW1Document1 pageGallarte HW1Ethyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- The Effct of Soil Variability On The Ultimate Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationDocument1 pageThe Effct of Soil Variability On The Ultimate Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationEthyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- LandscapeDocument20 pagesLandscapeEthyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- 1.-WPS OfficeDocument4 pages1.-WPS OfficeEthyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- LandscapeDocument2 pagesLandscapeEthyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- Problem 2: Westergaard Method For A Crack Under Concentrated ForcesDocument5 pagesProblem 2: Westergaard Method For A Crack Under Concentrated ForcesDishant BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant - Diagram, Layout, Working & ConstructionDocument25 pagesThermal Power Plant - Diagram, Layout, Working & ConstructionACME NKSTPPNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument2 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodiesmemowic458No ratings yet
- Barotropic WaveDocument55 pagesBarotropic WaveHsu Tien-YiaoNo ratings yet
- Under Suitable Conditions, Butane, C: © OCR 2022. You May Photocopy ThisDocument13 pagesUnder Suitable Conditions, Butane, C: © OCR 2022. You May Photocopy ThisMahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 (Part 1.1) - WEEK 1Document20 pagesCHAPTER 1 (Part 1.1) - WEEK 1Aliaa AkbarNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi S-Line (Barkey) - 2Document1 pageSpesifikasi S-Line (Barkey) - 2khataraNo ratings yet
- Weather Proof Louvre MDocument6 pagesWeather Proof Louvre Mntt_121987No ratings yet
- ARRI Lighting Handbook - English Version PDFDocument28 pagesARRI Lighting Handbook - English Version PDFKateElsahartyNo ratings yet
- DS PM0702 GB 3884Document2 pagesDS PM0702 GB 3884Filipe ismaolNo ratings yet
- Moving Charges & Magnetism Lecture 7 @physicswallahlakshyavideos PhysicswallahlakshyavideosDocument23 pagesMoving Charges & Magnetism Lecture 7 @physicswallahlakshyavideos PhysicswallahlakshyavideostanishsarmahNo ratings yet
- A Review of Water Treatment Membrane Nano Technologies 2011 Eric HoekDocument26 pagesA Review of Water Treatment Membrane Nano Technologies 2011 Eric Hoekrancak100% (1)
- Welding International: Click For UpdatesDocument9 pagesWelding International: Click For UpdatesHenry León HenaoNo ratings yet
- 10 Minutes Cycle Mix 2 Minutes: Clean in Place - Full Process Flow (Line 3, 4 & 5)Document4 pages10 Minutes Cycle Mix 2 Minutes: Clean in Place - Full Process Flow (Line 3, 4 & 5)siti amirahNo ratings yet
- Dual Shield II 110Document1 pageDual Shield II 110Nicolas MaximilianoNo ratings yet
- TH11 Experimental Manual PDFDocument46 pagesTH11 Experimental Manual PDFAYALEYDENNo ratings yet
- ID Perhitungan Nilai Dosis Dan Kontras CitrDocument9 pagesID Perhitungan Nilai Dosis Dan Kontras CitrNur cholisNo ratings yet
- Buffered and Isotonic Solutions: Lecturer Ghaidaa S Hameed Physical PharmacyDocument63 pagesBuffered and Isotonic Solutions: Lecturer Ghaidaa S Hameed Physical PharmacyloloNo ratings yet
- General Organic Chemistry Vishal Tiwari Carrer Poit Kota NotesDocument35 pagesGeneral Organic Chemistry Vishal Tiwari Carrer Poit Kota NotesBhaskar HarshitNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Vs Reciprocating Compressor - Turbomachinery Magazine PDFDocument2 pagesCentrifugal Vs Reciprocating Compressor - Turbomachinery Magazine PDFReyes SanchezNo ratings yet
- Process and Process VariablesDocument31 pagesProcess and Process VariablesAndrei Jose GilNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document46 pagesLecture 5ζοβαγεπ ἯοΣΣαῖηNo ratings yet
- Assignment - IDocument4 pagesAssignment - Ituhina27No ratings yet
- 01 1 hd1kv eDocument3 pages01 1 hd1kv eabboali9924No ratings yet
- 9th Physics Chapter#1 TestDocument1 page9th Physics Chapter#1 TestAsif Ayaz85% (13)