Professional Documents
Culture Documents
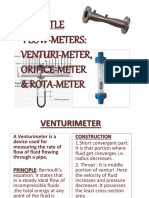
Working of A Venturi Meter
Uploaded by
vijay kumar honnaliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Working of A Venturi Meter
Uploaded by
vijay kumar honnaliCopyright:
Available Formats
Working of a Venturi Meter
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
The venturi meter works on the principle of Bernoulli’s equation which states that the
pressure decreases as the velocity increases.
The crosssection of the throat is less than that of the inlet pipe.
As the crosssection from the inlet pipe to the throat of venturimeter decreases,
the fluid velocity increases, and therefore the pressure decreases.
Due to a decrease in the pressure, a pressure difference is created between the
throat of the venturi meter and the inlet pipe.
This is further measured by applying a differential manometer between the throat
section and the inlet section. It can also be measured by using two gauges on
the inlet section and throat.
The pressure difference through the pipe is then calculated after obtaining the
rate of flow.
Mechanical Properties of Fluids – Related Topics
Elastic Limit Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Pressure Fluid Friction
Buoyant Force Mechanical Properties of Solid
Shearing Stress Barometer
Surface Energy Critical Velocity
Venturimeter Formula
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A Venturi Meter contains two tubes connected by a pipe at narrow ends. The venturi-
meter is positioned horizontally and the liquid enters end 1 and passes through end
2. Let,
P1 is the pressure in the inlet section
P2 is the pressure in the throat section
v1 is the velocity of the fluid passing through the inlet section
v2 is the velocity of the fluid passing through the throat section
ρ is the density of the liquid
A1 and A2 be the area of the cross-section at the inlet section and throat section
respectively.
Working of a Venturi Meter
You might also like
- Venturi Meter PresentationDocument9 pagesVenturi Meter PresentationVaishnavi Iyer100% (1)
- Instrumentation Basics - 02 - Flow MeasurementDocument62 pagesInstrumentation Basics - 02 - Flow MeasurementGhassan AL HaririNo ratings yet
- Flow ElementDocument66 pagesFlow ElementTej Bahadur KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Flow MeasurementDocument10 pagesFlow Measurementnirvan93No ratings yet
- Calibration of An Orifice Plate Flow Meter (Fluid Exp 8)Document7 pagesCalibration of An Orifice Plate Flow Meter (Fluid Exp 8)hayder alaliNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement BasicDocument87 pagesFlow Measurement BasicSri100% (2)
- Flow MetersDocument21 pagesFlow MetersEverlynn Joy JosephNo ratings yet
- Process Instrumentation Module 4Document68 pagesProcess Instrumentation Module 4ibuddhaNo ratings yet
- Energy Equation & Its ApplicationsDocument47 pagesEnergy Equation & Its ApplicationsRopah ChihuriNo ratings yet
- FlowDocument54 pagesFlowsourajpatelNo ratings yet
- Flowmeter Types and Their PrinciplesDocument14 pagesFlowmeter Types and Their PrincipleszaydFG100% (2)
- Flow MeasurementDocument37 pagesFlow MeasurementVarad DateNo ratings yet
- FLOWDocument31 pagesFLOWHassan HaiderNo ratings yet
- INSTRUMENTATIONfebDocument35 pagesINSTRUMENTATIONfebBalli SinghNo ratings yet
- Process Instrumentation (Flow) .Document40 pagesProcess Instrumentation (Flow) .PratoyoNo ratings yet
- Flow Measuring DevicesDocument39 pagesFlow Measuring DevicesAbdul Moeed Kalson100% (1)
- Flow Measurement PDFDocument32 pagesFlow Measurement PDFmn_sundaraam100% (1)
- Energy Line & Hydraulic Grade Line: Piezometric HeadDocument19 pagesEnergy Line & Hydraulic Grade Line: Piezometric HeadMaryam Arif100% (1)
- VenturimeterDocument2 pagesVenturimetervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Flow MeasurementDocument22 pagesFlow MeasurementinamNo ratings yet
- Title: Transportation of FluidsDocument72 pagesTitle: Transportation of FluidsRishi Gethu MassNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Fluid FlowDocument10 pagesMeasurement of Fluid FlowMd Ashikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.1 FMDocument39 pagesUnit 4.1 FMRishi Gethu MassNo ratings yet
- Flow MetersDocument12 pagesFlow MetersJohn AdewaleNo ratings yet
- Air CalibrationDocument7 pagesAir Calibrationendang dian lestariNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement Notes2015Document14 pagesFlow Measurement Notes2015Abhilash MohanNo ratings yet
- 1) Torsion Testing MachinesDocument7 pages1) Torsion Testing MachinesPagan jatarNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement BasicDocument87 pagesFlow Measurement BasicSrinivasarao YenigallaNo ratings yet
- Sensors and Transducers NotesDocument20 pagesSensors and Transducers Notessubisubish67No ratings yet
- Esra Dhyaa Fluid Report Second StageDocument7 pagesEsra Dhyaa Fluid Report Second StageMostafa HamawandyNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurements: Prepared By: Mirroyal Ismayilov (R6KX99) Pu Ruijie (D13L6M) Kashif Ali (DL0YNX) Tobi Eso (DBZIC5)Document39 pagesFlow Measurements: Prepared By: Mirroyal Ismayilov (R6KX99) Pu Ruijie (D13L6M) Kashif Ali (DL0YNX) Tobi Eso (DBZIC5)Mahmoud Abo ElnasrNo ratings yet
- Venturi MeterDocument5 pagesVenturi Meterashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Fluid LABDocument9 pagesFluid LABKayfe sayfadeenNo ratings yet
- Me Lab 1 Draft Group ReportDocument12 pagesMe Lab 1 Draft Group ReportAngelo PontivedraNo ratings yet
- Fluids: Laminar or TurbulentDocument8 pagesFluids: Laminar or TurbulentSelwah Hj AkipNo ratings yet
- Venturi MeterDocument2 pagesVenturi MeterVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Figure1.1: U-Tube ManometerDocument5 pagesFigure1.1: U-Tube Manometeraydn_89No ratings yet
- MEE-361-Flow Measurement - UpdatedDocument35 pagesMEE-361-Flow Measurement - UpdatedSalvation EnarunaNo ratings yet
- Venturi MeterDocument42 pagesVenturi MeterMUHAMMAD NABEEL ARIFNo ratings yet
- Working of Orifice Meter: Orifice Meter Structure and Working:-Orifice Meter Is An Instrument Which IsDocument2 pagesWorking of Orifice Meter: Orifice Meter Structure and Working:-Orifice Meter Is An Instrument Which Is9944805552No ratings yet
- Flowmeasurement 130921001436 Phpapp01Document18 pagesFlowmeasurement 130921001436 Phpapp01Nasser ShelilNo ratings yet
- Measurement Techniques - Lesson05Document46 pagesMeasurement Techniques - Lesson05Umut ŞENNo ratings yet
- Liquid Engineering: Reynolds NumbersDocument12 pagesLiquid Engineering: Reynolds NumbersajaymechengineerNo ratings yet
- Flow ElementsDocument23 pagesFlow ElementsG Vengat VinayagamNo ratings yet
- Types of Gas Mass Flow MetersDocument12 pagesTypes of Gas Mass Flow MetersFirmansyah Budhi SaputhraNo ratings yet
- Loss in Pipe and Fitting SystemDocument17 pagesLoss in Pipe and Fitting SystemGulshan Raza KhanNo ratings yet
- Oil and Gas Refining Engineering DepartmentDocument15 pagesOil and Gas Refining Engineering DepartmentHamzah A. LaftaNo ratings yet
- LOW EasurementDocument18 pagesLOW EasurementShahnaz DarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Flow MeasurementDocument10 pagesUnit 4 Flow Measurement08 Dadarkar Mujtaba MEANo ratings yet
- Venturi Meter - Final TranscriptDocument3 pagesVenturi Meter - Final TranscriptRavi KantNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Engineering Department Flow Loop ExperimentDocument8 pagesPetroleum Engineering Department Flow Loop ExperimentEbied Yousif AlyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Flow MeterDocument12 pagesFundamentals of Flow Meteralan_yaobin8409No ratings yet
- 2263 34 350 Module4Document78 pages2263 34 350 Module4RameshNo ratings yet
- 1 Flow MetersDocument16 pages1 Flow MetersVinaya NaralasettyNo ratings yet
- Introduction Flow MeterDocument4 pagesIntroduction Flow MeterohdausNo ratings yet
- A Brief Study of The Most Commonly Used Flow MetersDocument21 pagesA Brief Study of The Most Commonly Used Flow MeterssumeghNo ratings yet
- Pipe Flow Rate MetersDocument6 pagesPipe Flow Rate MetersMostafa HamawandyNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment 2 - VenturimeterDocument8 pagesLab Experiment 2 - VenturimeterLance HernandezNo ratings yet
- Flow Sensors: Prepared By: Jesamy Van Carlo D. ValenzuelaDocument24 pagesFlow Sensors: Prepared By: Jesamy Van Carlo D. ValenzuelaAaron Fredriel De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Fick's Laws of DiffusionDocument5 pagesFick's Laws of Diffusionvijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- D Alembert's SolutionDocument3 pagesD Alembert's Solutionvijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- AmmeterDocument5 pagesAmmetervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Decanter CentrifugeDocument2 pagesDecanter Centrifugevijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- GalvanometerDocument5 pagesGalvanometervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Compressible Flow in OrificemterDocument3 pagesCompressible Flow in Orificemtervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Pressure Tappings of OrificemeterDocument3 pagesPressure Tappings of Orificemetervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Rotameter - Working & ApplicationsDocument3 pagesRotameter - Working & Applicationsvijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- OrificemeterDocument3 pagesOrificemetervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Orifice PlateDocument2 pagesOrifice Platevijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Components of A RotameterDocument5 pagesComponents of A Rotametervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Rotameters - Design AspectsDocument13 pagesRotameters - Design Aspectsvijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Types of RotametersDocument9 pagesTypes of Rotametersvijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- RotameterDocument4 pagesRotametervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Equation of BarometerDocument2 pagesEquation of Barometervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Number TheoryDocument1 pageAlgebraic Number Theoryvijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- MEMS BarometersDocument1 pageMEMS Barometersvijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Ajugate Matrices - Proof Using Matrices of EndomorphismsDocument4 pagesAjugate Matrices - Proof Using Matrices of Endomorphismsvijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Applications of BarometerDocument2 pagesApplications of Barometervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Fortin BarometerDocument2 pagesFortin Barometervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Pump Oil BarometerDocument1 pageVacuum Pump Oil Barometervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Adjugate MatricesDocument2 pagesAdjugate Matricesvijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Well Type ManomaterDocument2 pagesWell Type Manomatervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Matrix FunctionsDocument2 pagesMatrix Functionsvijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Determinant and Inverse MatrixDocument3 pagesDeterminant and Inverse Matrixvijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
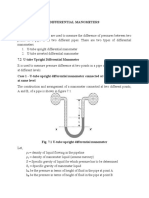
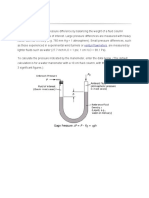
- Differential ManometersDocument3 pagesDifferential Manometersvijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Non Linear Differential EquationsDocument3 pagesNon Linear Differential Equationsvijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Manometer PressureDocument1 pageManometer Pressurevijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- Fluid PressureDocument3 pagesFluid Pressurevijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet
- What Is A BarometerDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Barometervijay kumar honnaliNo ratings yet