Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Semi 2
Uploaded by
Garabig0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesThis document discusses two types of semiconductors: intrinsic and extrinsic. [1] Intrinsic semiconductors are chemically pure with equal numbers of electrons and holes, giving it poor conductivity. [2] Extrinsic semiconductors are improved by adding small amounts of impurities ("doping") which alters properties and improves conductivity, creating either n-type or p-type semiconductors. [3] N-type are made with pentavalent impurities like phosphorus that contribute extra electrons, while p-type are made with trivalent impurities like boron that create holes.
Original Description:
Original Title
SEMI-2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses two types of semiconductors: intrinsic and extrinsic. [1] Intrinsic semiconductors are chemically pure with equal numbers of electrons and holes, giving it poor conductivity. [2] Extrinsic semiconductors are improved by adding small amounts of impurities ("doping") which alters properties and improves conductivity, creating either n-type or p-type semiconductors. [3] N-type are made with pentavalent impurities like phosphorus that contribute extra electrons, while p-type are made with trivalent impurities like boron that create holes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesSemi 2
Uploaded by
GarabigThis document discusses two types of semiconductors: intrinsic and extrinsic. [1] Intrinsic semiconductors are chemically pure with equal numbers of electrons and holes, giving it poor conductivity. [2] Extrinsic semiconductors are improved by adding small amounts of impurities ("doping") which alters properties and improves conductivity, creating either n-type or p-type semiconductors. [3] N-type are made with pentavalent impurities like phosphorus that contribute extra electrons, while p-type are made with trivalent impurities like boron that create holes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
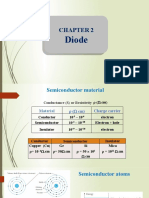
Asst. Lec. Ibrahim abdul-wahhab Semiconductors Materials Eng. Dep.
Types of Semiconductors:
Semiconductor may be classified as under:
1-Intrinsic Semiconductor
An intrinsic semiconductor material is chemically very pure and possesses poor
conductivity. It has equal numbers of negative carriers (electrons) and positive carriers
(holes). A silicon crystal is different from an insulator because at any temperature
above absolute zero temperature, there is a finite probability that an electron (which
have negative electricity and mass of 1.6*10-19 coulomb and 9.11*10-31Kg respectively)
in the lattice will be knocked loose from its position, leaving behind an electron
deficiency called a "hole".
If a voltage is applied, then both the electron and the hole can contribute to a small
current flow. The term intrinsic here distinguishes between the properties of pure
"intrinsic" silicon and the different properties of doped n-type or p-type
semiconductors.
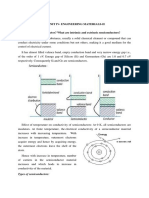
2-Extrinsic Semiconductor
Extrinsic semiconductor is an improved intrinsic semiconductor with a small
amount of impurities added by a process, known as doping, which alters the electrical
properties of the semiconductor and improves its conductivity.
Doping process produces two groups of semiconductors: the negative charge
conductor (n-type) and the positive charge conductor (p-type).
The Doping of Semiconductors
The addition of a small percentage of foreign atoms in the regular crystal lattice of
silicon or germanium produces dramatic changes in their electrical properties,
producing n-type and p-type semiconductors.
Page 4 First lecture
Asst. Lec. Ibrahim abdul-wahhab Semiconductors Materials Eng. Dep.
Pentavalent impurities (N-Type Semiconductor)
(5 valence electrons) produce n-type semiconductors by contributing extra electrons.
The addition of pentavalent impurities such as antimony, arsenic or phosphorous
contributes free electrons, greatly increasing the conductivity of the intrinsic
semiconductor. Phosphorous may be added by diffusion of phosphine gas (PH3).
ND = the concentration of donor atoms [atoms/cm3 or cm-3] ~1015-1020cm-3
Trivalent impurities (P-Type Semiconductor)
(3 valence electrons) produce p-type semiconductors by producing a "hole" or electron
deficiency. The addition of trivalent impurities such as boron, aluminum or gallium
Page 5 First lecture
Asst. Lec. Ibrahim abdul-wahhab Semiconductors Materials Eng. Dep.
to an intrinsic semiconductor creates deficiencies of valence electrons, called "holes".
It is typical to use B2H6 diborane gas to diffuse boron into the silicon material.
NA = the concentration of acceptor atoms [atoms/cm3 or cm-3]
Page 6 First lecture
You might also like
- Semi 1Document3 pagesSemi 1GarabigNo ratings yet
- Academy Phy NoteDocument29 pagesAcademy Phy NoteHambisa ShiferawNo ratings yet
- Electronics-I: AnswerDocument84 pagesElectronics-I: AnswerSafaruzzaman ShovoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. SemiconductorsDocument4 pagesChapter 2. SemiconductorsMary Joyce BelenNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors - NotesDocument12 pagesSemiconductors - NotesEshaan KuttikadNo ratings yet
- Diode and BJTDocument185 pagesDiode and BJTsujay nayakNo ratings yet
- BSC 5th - 01 - 09 - 2021Document8 pagesBSC 5th - 01 - 09 - 2021Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- EE201 Semiconductor Devices PDFDocument284 pagesEE201 Semiconductor Devices PDFHanamie JohanNo ratings yet
- Appl Phy Chap# 1Document55 pagesAppl Phy Chap# 1Jameel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv-Engineering Materials-Ii: Types of SemiconductorsDocument28 pagesUnit Iv-Engineering Materials-Ii: Types of SemiconductorsFeykish ClandestineNo ratings yet
- Nabin Term Paper Six SemDocument17 pagesNabin Term Paper Six Semsubamgiri9No ratings yet
- Video Series - ElectronicsDocument64 pagesVideo Series - ElectronicsDosOshRum JoshiNo ratings yet
- ECE 301 Electrical Engineering Materials 2Document28 pagesECE 301 Electrical Engineering Materials 2David ToonsNo ratings yet
- Nabin Term Paper Six SemDocument17 pagesNabin Term Paper Six Semsubamgiri9No ratings yet
- College of CS & IS Jazan University KSADocument19 pagesCollege of CS & IS Jazan University KSAazoozdhamriNo ratings yet
- الكترونيكDocument12 pagesالكترونيكDevil HyperNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 - Diode 2Document32 pagesChapter - 2 - Diode 2Hà ThiênNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3bDocument96 pagesLecture 3blaylaylinNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics IntroductionDocument4 pagesAnalog Electronics Introductionashfaque.eee.20200205055No ratings yet
- ECE 2262 - Fundamentals of Electronic Circuits - Module 2Document10 pagesECE 2262 - Fundamentals of Electronic Circuits - Module 2Rafael Jayson AñoraNo ratings yet
- DiodeDocument16 pagesDiodeSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices - Lecture 1Document61 pagesSemiconductor Devices - Lecture 1hassam saeedNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Lectures 10 To 13Document71 pagesUnit 2 - Lectures 10 To 13ankushchoudhary4631No ratings yet
- Introduction To Semiconductor DevicesDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Semiconductor DevicesMuhammad Sufyan100% (2)
- Krishnasamy College of Engineering and Technology: EC8252 Electronic DevicesDocument21 pagesKrishnasamy College of Engineering and Technology: EC8252 Electronic DevicessoundharyaNo ratings yet
- SemiconductorDocument15 pagesSemiconductorEkwama EwugaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - SemiconductorDocument49 pagesChapter 3 - SemiconductorBalqis yasin100% (1)
- Semiconductor Theory and DiodeDocument7 pagesSemiconductor Theory and DiodeStefon BishopNo ratings yet
- Iare - Ece - Edc - PPT - 0Document197 pagesIare - Ece - Edc - PPT - 0KARTHIKNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes-2Document17 pagesLecture Notes-2snagaraj.cool7813No ratings yet
- Module 2Document171 pagesModule 2ddfjfjfds dlijkfdifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Semiconductor MaterialsDocument62 pagesChapter 1-Semiconductor MaterialsMd Masudur Rahman Abir100% (1)
- Basic Electronics Engineering: Paschimanchal Campus (IOE), PokharaDocument14 pagesBasic Electronics Engineering: Paschimanchal Campus (IOE), PokharaTara Nath PoudelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document28 pagesLecture 1abram samNo ratings yet
- Semicounductors & Pn-Junction (Complete)Document47 pagesSemicounductors & Pn-Junction (Complete)Khalid AliNo ratings yet
- Lec - Introduction To SemiconductorsDocument89 pagesLec - Introduction To Semiconductorszaheerduaa27No ratings yet
- PN Junction TheoryDocument4 pagesPN Junction TheorysumitNo ratings yet
- MODULE1Document2 pagesMODULE1Jericho MejiaNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Course Code:: Electronic Circuit ETE 215Document54 pagesCourse Title: Course Code:: Electronic Circuit ETE 215Rayhan TalukderNo ratings yet
- 305 Ch2Document11 pages305 Ch2makram.22en498No ratings yet
- PN Junction Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesPN Junction Lecture Notessuperbangadak100% (1)
- Applied Electronics I Exit Exam NotesDocument242 pagesApplied Electronics I Exit Exam Notesassefa295No ratings yet
- Material Science AssignmentsDocument5 pagesMaterial Science AssignmentspaeinjamaludinNo ratings yet
- PN Junction Lecture 3Document44 pagesPN Junction Lecture 3Vimal KunwarNo ratings yet
- EDC-Unit1 PN Junction DiodeDocument3 pagesEDC-Unit1 PN Junction DiodeShiva Goud NimmalaNo ratings yet
- EE201 Semiconductor DevicesDocument284 pagesEE201 Semiconductor Devicesatha89No ratings yet
- ECE220a - Topic 1Document10 pagesECE220a - Topic 1John RivasNo ratings yet
- There Are Two Main Types of Semiconductor MaterialsDocument4 pagesThere Are Two Main Types of Semiconductor MaterialsGaurav TheHeartbreakerNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Unit-2.1Document69 pagesMechatronics Unit-2.1nagsanthosh3No ratings yet
- Mechatronics U2 PDFDocument253 pagesMechatronics U2 PDFnagsanthosh3No ratings yet
- Part 1-Semiconductor Devices SemiconductorDocument10 pagesPart 1-Semiconductor Devices SemiconductorBASIL KUMAR N.KNo ratings yet
- Band Theory and SemiconductorDocument17 pagesBand Theory and SemiconductorAkshat GuptaNo ratings yet
- ECE101 Modules 1& 2 Semiconductor Theory DiodeDocument47 pagesECE101 Modules 1& 2 Semiconductor Theory DiodeChariza MaicoNo ratings yet
- PN Junction DiodeDocument44 pagesPN Junction DiodePrasanth. SNo ratings yet
- Diode As A Temperature SensorDocument34 pagesDiode As A Temperature SensorBefzzNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Diodes Notes FermarfajardoDocument6 pagesSemiconductor Diodes Notes Fermarfajardokuro AishiroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DIODEDocument64 pagesChapter 2 DIODEMathSolo Nam XBNo ratings yet
- ' Semiconductor Materials and Diodes: Rizal Technological UniversityDocument8 pages' Semiconductor Materials and Diodes: Rizal Technological UniversityVam ArmodiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - SemiconductorDocument49 pagesChapter 3 - SemiconductorIkhmal Firdaus100% (1)
- HI 800 069 AEA: Circulating Fan K 9203Document1 pageHI 800 069 AEA: Circulating Fan K 9203GarabigNo ratings yet
- Four Steps To HMI Screen Design: 1. Create, Define StandardsDocument2 pagesFour Steps To HMI Screen Design: 1. Create, Define StandardsGarabigNo ratings yet
- 08 - 03R300 - 1 - Intro. To HMIWeb Display Builder DynamicsDocument18 pages08 - 03R300 - 1 - Intro. To HMIWeb Display Builder DynamicsGarabigNo ratings yet
- 19 - 03R300 - 1 - Final Projects - HMIWeb Display BuilderDocument10 pages19 - 03R300 - 1 - Final Projects - HMIWeb Display BuilderGarabigNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Model Identification: Bottom Side Temperature Reboiler Valve Position Upper Sidetemperature Reflux Valve PositionDocument4 pages7.1 Model Identification: Bottom Side Temperature Reboiler Valve Position Upper Sidetemperature Reflux Valve PositionGarabigNo ratings yet
- 8 Model Verification: Model Overview in DeltavDocument3 pages8 Model Verification: Model Overview in DeltavGarabigNo ratings yet
- 10 Conclusion: 94.45% 69.95KPP H 71.13 BPD 76.90 Bbl/day 92.48% 65.11KPP H 70.25 BPD 74.75 Bbl/dayDocument1 page10 Conclusion: 94.45% 69.95KPP H 71.13 BPD 76.90 Bbl/day 92.48% 65.11KPP H 70.25 BPD 74.75 Bbl/dayGarabigNo ratings yet
- S ∆ X ∆u (k) ∆ X S ∆ u (k) ∆ u ∆ u ∆ u Г Г Г Г Г Г: Dynamic matrix vector by the vectorDocument2 pagesS ∆ X ∆u (k) ∆ X S ∆ u (k) ∆ u ∆ u ∆ u Г Г Г Г Г Г: Dynamic matrix vector by the vectorGarabigNo ratings yet
- Kpe τ ps +1 Kpe τ S+1 θ τ: 6 Process Modeling EquationsDocument6 pagesKpe τ ps +1 Kpe τ S+1 θ τ: 6 Process Modeling EquationsGarabigNo ratings yet
- F F 218.91 F F 217.62 F: 10 ConclusionDocument1 pageF F 218.91 F F 217.62 F: 10 ConclusionGarabigNo ratings yet
- Meera-MPCforDistillationControl - 3Document4 pagesMeera-MPCforDistillationControl - 3GarabigNo ratings yet
- F F 218.91 F F 217.62 F: 10 ConclusionDocument1 pageF F 218.91 F F 217.62 F: 10 ConclusionGarabigNo ratings yet
- S ∆ X ∆u (k) ∆ X S ∆ u (k) b b b b b b b b b b b b b b ∆u ∆ u ∆ u Г Г Г Г Г ГDocument3 pagesS ∆ X ∆u (k) ∆ X S ∆ u (k) b b b b b b b b b b b b b b ∆u ∆ u ∆ u Г Г Г Г Г ГGarabigNo ratings yet
- 5 Process Model: Kpe τ ps +1 Kpe τ S+1 θ τDocument6 pages5 Process Model: Kpe τ ps +1 Kpe τ S+1 θ τGarabigNo ratings yet
- 3 Challenges For DesignDocument1 page3 Challenges For DesignGarabigNo ratings yet
- 10 Conclusion: How Better Interactive Process Is Handled by MPC Over PIDDocument1 page10 Conclusion: How Better Interactive Process Is Handled by MPC Over PIDGarabigNo ratings yet
- 3 Challenges For DesignDocument1 page3 Challenges For DesignGarabigNo ratings yet
- 6 7 MPC Implementation On The Part of Distillation Column: 7.1 Model IdentificationDocument4 pages6 7 MPC Implementation On The Part of Distillation Column: 7.1 Model IdentificationGarabigNo ratings yet
- 3 Challenges For DesignDocument1 page3 Challenges For DesignGarabigNo ratings yet
- ABSTRACT:-In This Paper, Application of Advanced Process Control Has Been Studied For Distillation Control andDocument1 pageABSTRACT:-In This Paper, Application of Advanced Process Control Has Been Studied For Distillation Control andGarabigNo ratings yet
- X Y, Y, Y,, Y: 4 MPC TheoryDocument5 pagesX Y, Y, Y,, Y: 4 MPC TheoryGarabigNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Model Identification: Bottom Side Temperature Reboiler Valve Position Upper Sidetemperature Reflux Valve PositionDocument4 pages7.1 Model Identification: Bottom Side Temperature Reboiler Valve Position Upper Sidetemperature Reflux Valve PositionGarabigNo ratings yet
- 2 Process of Distillation ColumnDocument1 page2 Process of Distillation ColumnGarabigNo ratings yet
- 2 Process of Distillation ColumnDocument1 page2 Process of Distillation ColumnGarabigNo ratings yet
- 7 Mpc Implementation On The Part Of Distillation Column: Kpe τ ps +1 Kpe τ S+1 θ τDocument4 pages7 Mpc Implementation On The Part Of Distillation Column: Kpe τ ps +1 Kpe τ S+1 θ τGarabigNo ratings yet
- 6 Process Modeling Equations: Kpe τ ps +1 Kpe τ S+1 θ τDocument5 pages6 Process Modeling Equations: Kpe τ ps +1 Kpe τ S+1 θ τGarabigNo ratings yet
- X AX B U FW y CX X Y, Y, Y,, Y: 6 Process Modeling EquationsDocument4 pagesX AX B U FW y CX X Y, Y, Y,, Y: 6 Process Modeling EquationsGarabigNo ratings yet
- 75Th Anniversary of The Transistor Arokia Nathan Full ChapterDocument67 pages75Th Anniversary of The Transistor Arokia Nathan Full Chapterryan.riley589100% (7)
- Band TheoryDocument15 pagesBand TheorysamhayerNo ratings yet
- Density Functional TheoryDocument34 pagesDensity Functional TheoryChang Jae LeeNo ratings yet
- Schwinger's Approach To Einstein's Gravity and BeyondDocument6 pagesSchwinger's Approach To Einstein's Gravity and BeyondMuhammad Rehan QureshiNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Laser Diode Group MembersDocument16 pagesPresentation On Laser Diode Group MembersRiddhijit ChattopadhyayNo ratings yet
- CHEM F313: Instrumental Methods of Analysis: Energy & Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument7 pagesCHEM F313: Instrumental Methods of Analysis: Energy & Electromagnetic SpectrumradhikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter (2) Atomic Structure and BondingDocument56 pagesChapter (2) Atomic Structure and BondingJessica De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Quantum Theory of The Submicroscopic WorldDocument28 pagesChapter 1: The Quantum Theory of The Submicroscopic WorldHun Qiu LimNo ratings yet
- JEE-Main - Moles & Atomic StructureDocument4 pagesJEE-Main - Moles & Atomic StructureDivyanshu RawatNo ratings yet
- Hybridization: DR Karimah Kassim CHM 475Document34 pagesHybridization: DR Karimah Kassim CHM 475api-386303659No ratings yet
- Can Quantum-Mechanical Description of Physical Reality Be Considered Complete?Document4 pagesCan Quantum-Mechanical Description of Physical Reality Be Considered Complete?Irina AmarieiNo ratings yet
- Single-Event Effects in Silicon Carbide High Voltage Power DevicesDocument17 pagesSingle-Event Effects in Silicon Carbide High Voltage Power DevicesTeststeNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Review - Quantum PhysicsDocument12 pagesIB Physics Review - Quantum PhysicsChirag HablaniNo ratings yet
- Griffiths Chapter 2: Dan Wysocki February 19, 2015Document6 pagesGriffiths Chapter 2: Dan Wysocki February 19, 2015akjsdnfNo ratings yet
- Molecular Orbital TheoryDocument6 pagesMolecular Orbital TheoryleejhNo ratings yet
- The PN Junction: Power ElectronicsDocument8 pagesThe PN Junction: Power ElectronicsYewNo ratings yet
- Electron - Scattering - For - Nuclear - and - Nucleon - Structure Walecka J D PDFDocument379 pagesElectron - Scattering - For - Nuclear - and - Nucleon - Structure Walecka J D PDFanil ariNo ratings yet
- Physics of Semiconductor Devices: Third EditionDocument5 pagesPhysics of Semiconductor Devices: Third EditionZafar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Superlattices and MicrostructuresDocument8 pagesSuperlattices and MicrostructuresIsmael AnconaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Numbers NotesDocument8 pagesQuantum Numbers NotesMamidanna SashankNo ratings yet
- Schrodinger's Atomic ModelDocument4 pagesSchrodinger's Atomic ModeljaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41 - Conduction of Electricity in SolidsDocument11 pagesChapter 41 - Conduction of Electricity in SolidsVV Cephei100% (1)
- Imre CNT DevicesDocument25 pagesImre CNT DevicesAkshay PatharkarNo ratings yet
- Quantum Bouncing BallDocument2 pagesQuantum Bouncing BallAndré Manzoni de LimaNo ratings yet
- Special Purpose DiodesDocument4 pagesSpecial Purpose DiodesArvinALNo ratings yet
- Computational Physics - Exercise 5: 0 Python PrimerDocument2 pagesComputational Physics - Exercise 5: 0 Python PrimerToon PillaertNo ratings yet
- Thyristor MCQDocument6 pagesThyristor MCQnandhakumarme0% (3)
- Particle in RingDocument6 pagesParticle in RingAnjani GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1980 - Roos - Chem Phys - A Complete Active Space SCF Method (CASSCF) Using A Density Matrix Formulated Super-CI ApproachDocument17 pages1980 - Roos - Chem Phys - A Complete Active Space SCF Method (CASSCF) Using A Density Matrix Formulated Super-CI Approachvitoribeiro90No ratings yet
- Lee Smolin - A Real Ensemble Interpretation of Quantum MechanicsDocument14 pagesLee Smolin - A Real Ensemble Interpretation of Quantum MechanicsGeorge OvermeireNo ratings yet