Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Y 5 G 3 Abftyq
Uploaded by
Freddie KooOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Y 5 G 3 Abftyq
Uploaded by
Freddie KooCopyright:
Available Formats
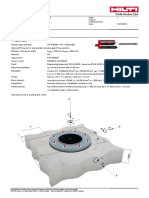
Hilti Solution for Fastenings (SOFA)
Yujie Li, Global Technical Marketing Manager, Business Anchors, Hilti AG
Dr. Jakob Kunz, Key expert, Cooperate Research and technology, Hilti AG
1. The basis of Hilti SOFA
The basis for anchor design in Europe is the design approach given in Annex C of ETAG 001 for
mechanical anchors, EOTA Technical Report TR 029 for adhesive anchors, and Annex E for
seismic condition. However, there are many cases where solutions cannot be found by using
design approach in those codes and regulations. Hilti SOFA is aiming to provide anchor design
solutions for such cases through internal stringent research program and assessment from Hilti
Fastening Design Board.
There are two premises of Hilti SOFA:
a. The gap between fixture and anchors shall be filled for many cases when applying
Hilti SOFA
The design methods in Annex C of ETAG 001 for mechanical anchors and EOTA Technical
Report TR 029 for adhesive anchors are based on the assumption of existence of annual gap.
Many of the limitations in those codes are relevant for this. Through Hilti internal research,
filling the annual gap between fixture and anchors can change the behavior of anchor
performance, such as load distribution can be assured always predictable, higher resistance
when anchor group close to edge or under combined tension and shear load compares to
normal case without filling the annual gap.
b. It can only apply to anchors which are embedded in Hilti Profis Anchor when
choosing SOFA design method
As all the internal research done by Hilti were using Hilti anchors, and the gap between fixture
anchor anchors is filled with Hilti mortar by using Hilti dynamic/seismic filling set.
It has also been verified that the gap cannot just be filled by directly injecting mortar towards
the gap, as shown in Fig.2.
Fig.1 Comparison of filling gap using Hilti Dynamic Set and Traditional Method
Hilti Corporation
9494 Schaan
Liechtenstein
Feldkircherstrasse 100 I P.O. Box 333
T +423-234 2111 I F +423-234 3332
www.hilti.com
Rechtsform: Aktiengesellschaft I Sitz: 9494 Schaan
HR-Nr.: FL-1.011.557-0 I MWST-Nr.: 50 555
There are also several level for going beyond current anchor design guidelines for Hilti SOFA. In
Hilti PROFIS anchor current version, they are reported as” Extended ETAG”, ”SOFA”, and
”SOFA+fib”, they are not conflicting to each other, just based on different supporting material for
different applications. Those design methods intend to provides solutions where current code
cannot as Fig.2 shows. More details are available upon requirement.
Fig.2 Comparison of filling gap using Hilti Dynamic Set and Traditional Method
2. Hilti SOFA explanation
2.1. Anchor configurations
2.1.1. Limitations of anchor configuration in current codes and regulations
Because all formulas provided in these guidelines are based on the assumption that the loads
can be distributed to the individual anchors in a predictable way, anchor configurations covered
by these guidelines are limited as shown in Fig.3. When anchor close to edge, the allowed
configuration is even limited up to 4 anchors in one anchor group, this is mainly due to the
existence of annular gap in the fixture, it can be assumed that in general not all anchors are
loaded equally when a shear load acts on the fixture.
Hilti Corporation
9494 Schaan
Liechtenstein
Feldkircherstrasse 100 I P.O. Box 333
T +423-234 2111 I F +423-234 3332
www.hilti.com
Rechtsform: Aktiengesellschaft I Sitz: 9494 Schaan
HR-Nr.: FL-1.011.557-0 I MWST-Nr.: 50 555
Fig.3 Anchor configuration covered by ETAG 001 Annex C and EOTA Technical Report TR 029
2.1.2. Verification method of anchor configuration covered in Hilti SOFA
To extend current design method to anchor configuration with more anchors or irregular
arrangement, the resistance of anchor group with such configuration was compared with the
theoretical design method provided in current codes and regulations.
This resistance has several dimensions, it covers the resistance under crack concrete, residual
capacity after crack cycling result from live load change, or a seismic event. It also includes
both tension and shear resistance. Therefore, the conducted test programs were the same as
how a single anchor being qualified for getting European Technical Assessment. Moreover, the
criteria not only require the resistance comply with the design method, but also all parameters
for qualifying single anchors. As shown in Fig.4, C2.5 test was conducted for a base plate with
8 anchors in a group.
Fig.4 Comparison of filling gap using Hilti Dynamic Set and Traditional Method
It was verified that the resistance calculated by current design method can always deliver more
conservative results than the testing results. Besides, for static condition, Hilti numerical study
shows more anchors in one anchor configuration delivers relatively more conservative results.
Hilti Corporation
9494 Schaan
Liechtenstein
Feldkircherstrasse 100 I P.O. Box 333
T +423-234 2111 I F +423-234 3332
www.hilti.com
Rechtsform: Aktiengesellschaft I Sitz: 9494 Schaan
HR-Nr.: FL-1.011.557-0 I MWST-Nr.: 50 555
2.1.3. Anchor configurations scope covered by Hilti SOFA
a. Static condition
There is no limitation on anchor arrangement up to 99 anchors, even for the irregular
configuration, as shown in Fig.5.
Fig.5 Anchor configuration scope covered by Hilti SOFA under static condition
b. Seismic condition
Due to the uncertainty of seismic, and capability to verify the design method for anchors more
than 8 anchors, Hilti SOFA covers the following configuration even when anchor placed close
to the edge for all load direction, as shown in Fig.6.
Fig.6 Anchor configuration scope covered by Hilti SOFA under static condition
2.2. Hilti SOFA for higher concrete edge resistance via taking consideration of the
second or third rows of anchors in an anchor group
2.2.1. The first row close to the edge governs the resistance of concrete edge failure for
an anchor group according to current code and regulations
In the case of anchor groups, due to the annular gap in the fixture it can be assumed that in
general not all anchors are loaded equally when a shear load acts on the fixture. For anchors
placed far away from the edge either pry-out failure of the whole anchor group can occur or
steel failure of the anchors. For pry-out failure tension loads are induced and therefore the
annular gap does not affect the failure load. Due to the ductility of the steel, deformation of
some anchors under shear loads can occur, until all anchors bear the load. In both cases, pry-
out failure and steel failure, the load applied on the fixture is transferred to all anchors in an
anchor group.
Hilti Corporation
9494 Schaan
Liechtenstein
Feldkircherstrasse 100 I P.O. Box 333
T +423-234 2111 I F +423-234 3332
www.hilti.com
Rechtsform: Aktiengesellschaft I Sitz: 9494 Schaan
HR-Nr.: FL-1.011.557-0 I MWST-Nr.: 50 555
The situation is different for anchor groups placed close to an edge. As an additional failure
mode concrete edge failure has to be considered when a shear load is applied. In the case of
e.g. a 2 x 2 anchor group it is possible that the anchor row close to the edge is loaded first or
the anchor row far from the edge. This depends on the position of the anchors in the fixture,
which cannot be determined exactly. The worst case is that the anchor row close to the edge is
loaded first. Since concrete is not as ductile as steel, the load will not be transferred to the back
anchor row. Therefore, in the design according Annex C and TR 029 for shear loads acting on
an anchor group close to the edge, only the anchor row closest to the edge is considered for
the resistance to concrete edge failure. The reinforcement in the concrete structure (if there is
any) would limit the crack width to 0,3 mm for cracked concrete design. However, this is only
valid far away from the edge. Close to the edge in general this cannot be guaranteed, even if
there is additional edge reinforcement.
2.2.2. Hilti SOFA concrete edge resistance design method
Hilti SOFA design method for concrete edge resistance refers to the design method described
in Fib bulletin 58: Design of anchorage in concrete for determining concrete edge resistance.
All anchors are loaded equally – for 2 rows of anchors, the anchor row closest to the edge is
loaded with 1/2 of the full load, for 3 rows 1/3. In addition, it is checked whether the resistance
of the whole anchor group to concrete edge failure (full load on last anchor row) is smaller than
the resistance of the first anchor row with 1/2 (1/3) of the load. If three rows of anchors are in
the fixture the calculation is also done for the second row with 2/3 of the full load. The smallest
value is decisive, as shown in Fig. 7.
Fig.7 Anchor configuration scope covered by Hilti SOFA under static condition
Design load can be up to twice or three times the design load according Annex C / TR 029
design, depending on the anchor row which is decisive for concrete edge resistance.
To be noticed, this only applies to static condition, whether this can be applied to seismic
condition is not verified for the time being.
2.3. Hilti SOFA for higher resistance for conditions with combined tension and shear
load
2.3.1. Interaction diagram for static and seismic for combined tension and shear
according to ETAG001 Annex C
Hilti Corporation
9494 Schaan
Liechtenstein
Feldkircherstrasse 100 I P.O. Box 333
T +423-234 2111 I F +423-234 3332
www.hilti.com
Rechtsform: Aktiengesellschaft I Sitz: 9494 Schaan
HR-Nr.: FL-1.011.557-0 I MWST-Nr.: 50 555
According to the Annex C of ETAG001, the ratio β between the load and resistance of tension
and shear respectively shall (βN)α + (βV) α < 1, where exponent =2.0, if both tension and shear
is governed by steel failure, otherwise, =1.5. The interaction diagram is shown as Fig.8.
The following equation must be satisfied for combined tension and shear loads:
(Eq. 1) (N)1,5 + (V)1,5 ≤ 1
Where N (V) is the ratio between the design value of action and resistance for tension (shear)
According to ETAG 001, Annex C, the following simplified equation may be applied:
(Eq. 2) N + V ≤ 1,2 and N ≤ 1, V ≤ 1
N
1,2
(Eq. 1)
1
(Eq. 2)
0,8
0,6
0,4
0,2
0 V
0 0,2 0,4 0,6 0,8 1 1,2
Fig.8 Anchor configuration scope covered by ETAG 001
2.4. Hilti SOFA interaction diagram for static and seismic for combined tension and
shear
Hilti SOFA design method for combined tension and shear resistance also refers to Fib bulletin
58: Design of anchorage in concrete. The difference of this approach is between tension and
shear comes when one is governed by steel failure mode while the other is governed by
concrete failure mode. In this case, Eq.1 with α = 1.5 shall be used according to the ETAG 001
Annex C. However, this is very conservative according to Fib bulletin 58, as the interaction
effect can only be taken into account for the same failure mode, therefore a separate analyze
for steel relevant failure mode and concrete relevant failure mode is used in Hilti SOFA, as
shown in Fig.9.
Hilti Corporation
9494 Schaan
Liechtenstein
Feldkircherstrasse 100 I P.O. Box 333
T +423-234 2111 I F +423-234 3332
www.hilti.com
Rechtsform: Aktiengesellschaft I Sitz: 9494 Schaan
HR-Nr.: FL-1.011.557-0 I MWST-Nr.: 50 555
NRd Eq.1(only use the steel failure
mode resistance) with α= 2.0
NRd,s
NRd,c Eq.1(only use the concrete failure
mode resistance) with α= 1.5
Eq.1with α= 1.5
VRd,s VRd,c VRd
Fig.9 Anchor configuration scope covered by ETAG 001
To be noticed, this approach only applies to static condition, whether similar approach can be
applied to seismic condition is not verified for the time being.
3. Implementation of Hilti SOFA and relationship with Hilti PROFIS Anchor software
As anchor applications can be quite diverse, the explanation or each single method in this
paper may not apply simultaneously for all cases. However, in Hilti PRFOSI anchor, it has been
automatically considered which detail method within SOFA can be implemented based on the
input.
4. Conclusion
Hilti SOFA is a design method which goes beyond current codes and regulations to give
solutions or provide more economical options to various tough engineering applications. It is
based on state-of-art public research results, Hilti internal research results and engineering
know-how. It does not tend to serve as a code and regulation, neither bond with legal
responsibilities for any consequence of it.
Hilti Corporation
9494 Schaan
Liechtenstein
Feldkircherstrasse 100 I P.O. Box 333
T +423-234 2111 I F +423-234 3332
www.hilti.com
Rechtsform: Aktiengesellschaft I Sitz: 9494 Schaan
HR-Nr.: FL-1.011.557-0 I MWST-Nr.: 50 555
You might also like
- Hilti AnchorSystems2008Document36 pagesHilti AnchorSystems2008Loh Chung TatNo ratings yet
- Compliance Management CertificateDocument4 pagesCompliance Management CertificatetamanimoNo ratings yet
- Marudi-Wms003 - Piling Work - RC Square PileDocument31 pagesMarudi-Wms003 - Piling Work - RC Square PileKelvin LauNo ratings yet
- Hilti Solution For Fastenings (SOFA) - 10.28Document7 pagesHilti Solution For Fastenings (SOFA) - 10.28Sim Khoon AunNo ratings yet
- HIT-RE500 V3 Replacement Letter 18052016Document2 pagesHIT-RE500 V3 Replacement Letter 18052016Abhishek ShatagopachariNo ratings yet
- 1 Input Data: WWW - Hilti.aeDocument16 pages1 Input Data: WWW - Hilti.aeEren BoyaciNo ratings yet
- Hilti announces replacement of discontinued HUS-V screw anchorDocument1 pageHilti announces replacement of discontinued HUS-V screw anchorAnonymous zvQGXzNo ratings yet
- Hilti Malaysia - HIT Injection SystemDocument62 pagesHilti Malaysia - HIT Injection Systemgks6043No ratings yet
- HILTI - HIT INJECTION For REBARDocument30 pagesHILTI - HIT INJECTION For REBARPatrick Kelly FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Cast in PIM 3Document14 pagesCast in PIM 3Oecoep IteemNo ratings yet
- CSA Spec HILTI HIT 100 Technical SupplementDocument32 pagesCSA Spec HILTI HIT 100 Technical SupplementIsidro P. BuquironNo ratings yet
- Channel at End of SlabDocument10 pagesChannel at End of SlabOecoep IteemNo ratings yet
- Borradores - Concreto - 3 de Sep. de 2021Document4 pagesBorradores - Concreto - 3 de Sep. de 2021andres torregrozaNo ratings yet
- 1 Input Data: Profis Anchor 2.6.6Document6 pages1 Input Data: Profis Anchor 2.6.6Collin NguNo ratings yet
- 18 Refer PDFDocument11 pages18 Refer PDFgabox707No ratings yet
- ETV Block 9 (Pressure)Document16 pagesETV Block 9 (Pressure)Sibi SamNo ratings yet
- Group 3Document10 pagesGroup 3wagipe3094No ratings yet
- 1 Input Data: Hilti PROFIS Engineering 3.1.1Document8 pages1 Input Data: Hilti PROFIS Engineering 3.1.1Layth HashimNo ratings yet
- Drafts - Masonry - 7 Jul 2023Document7 pagesDrafts - Masonry - 7 Jul 2023anwar alamNo ratings yet
- Hilti Monitor - Pa2Document2 pagesHilti Monitor - Pa2Asaru DeenNo ratings yet
- Hilti Re 100Document35 pagesHilti Re 100nahuel curleNo ratings yet
- Branch Connections Bonney Forge PDFDocument44 pagesBranch Connections Bonney Forge PDFangels silvaNo ratings yet
- Anchor Fastening: Technology Manual February 2020Document684 pagesAnchor Fastening: Technology Manual February 2020JorisDaemsNo ratings yet
- H 200mm Thick Slab - Pa2Document6 pagesH 200mm Thick Slab - Pa2ihpeterNo ratings yet
- xl1 - Expansion JointDocument2 pagesxl1 - Expansion Jointwahyu.120723No ratings yet
- TOVP - Rebar - May 12, 2023Document20 pagesTOVP - Rebar - May 12, 2023prabhash kumarNo ratings yet
- HiltiDocument36 pagesHilticonsultachNo ratings yet
- Hilti Monitor - Pa2Document2 pagesHilti Monitor - Pa2Asaru DeenNo ratings yet
- Fey Kolca KatalogDocument46 pagesFey Kolca KatalogВиталий БобуличNo ratings yet
- 290mm Thick Slab and 540mm EcenDocument6 pages290mm Thick Slab and 540mm EcenihpeterNo ratings yet
- 1 Anchor Design: Hilti PROFIS Engineering 3.0.72Document18 pages1 Anchor Design: Hilti PROFIS Engineering 3.0.72Alan TanNo ratings yet
- Tech FTM 2019 02 Complete enDocument590 pagesTech FTM 2019 02 Complete enm_shahbaghiNo ratings yet
- Trenn Sealbeam Type A: C:/Working Folder/HFE Engineering/Exploded View/sub assemblies/Sealbeam-T/Assembly SB-A TS - DWGDocument1 pageTrenn Sealbeam Type A: C:/Working Folder/HFE Engineering/Exploded View/sub assemblies/Sealbeam-T/Assembly SB-A TS - DWGVentas COPEZANo ratings yet
- Mounting a Roof Hydrant in Two StepsDocument3 pagesMounting a Roof Hydrant in Two StepsChase GietterNo ratings yet
- Adhesivos Epoxicos y OtrosDocument33 pagesAdhesivos Epoxicos y OtrossergiosilvahNo ratings yet
- 1 Input Data: Hilti PROFIS Engineering 3.0.75Document3 pages1 Input Data: Hilti PROFIS Engineering 3.0.75Rosallind daBombNo ratings yet
- 7250 Dallas Parkway, Suite 1000 Plano, T X 75024 1-800-879-8000Document6 pages7250 Dallas Parkway, Suite 1000 Plano, T X 75024 1-800-879-8000rmsa17No ratings yet
- Anchor Presentation Hilti 2011 PDFDocument8 pagesAnchor Presentation Hilti 2011 PDFNelsonDay100% (1)
- Beam Spb01 - Length 5430mm - Pa2Document6 pagesBeam Spb01 - Length 5430mm - Pa2phuckha2012No ratings yet
- Ownership and permission details for HFE vacuum systems parts listDocument1 pageOwnership and permission details for HFE vacuum systems parts listVentas COPEZANo ratings yet
- Loctite To Hernon Conversion Revised PDFDocument4 pagesLoctite To Hernon Conversion Revised PDFLalit KumarNo ratings yet
- B3L01 - Detail 1Document7 pagesB3L01 - Detail 1vikramjain66No ratings yet
- Angle Valve Technical Specs and Parts ListDocument2 pagesAngle Valve Technical Specs and Parts ListARMANDONo ratings yet
- Liebherr Telescopic Grease 9613 PlusDocument1 pageLiebherr Telescopic Grease 9613 PlusUmar TauniNo ratings yet
- Drafts - SP3 - Copy - Deatil S1Document9 pagesDrafts - SP3 - Copy - Deatil S1GuthrieJohn CNo ratings yet
- High performance anchor systems for easy installation and versatilityDocument38 pagesHigh performance anchor systems for easy installation and versatilitytoru101No ratings yet
- Hatch Covers SeohaeDocument3 pagesHatch Covers SeohaecarlocftNo ratings yet
- Hilti Webinar - Anchor Design Influencing Factors PDFDocument57 pagesHilti Webinar - Anchor Design Influencing Factors PDFDoug WeirNo ratings yet
- Hilti HIT System - Rebar ApplicationDocument34 pagesHilti HIT System - Rebar ApplicationTerence CheeNo ratings yet
- Profis Anchor Design for KWIK HUS-EZ AnchorDocument6 pagesProfis Anchor Design for KWIK HUS-EZ AnchorJester AbucayNo ratings yet
- Long-term Performance of HIT-RE 500 MortarDocument16 pagesLong-term Performance of HIT-RE 500 MortarMarco Antonio TeranNo ratings yet
- Anchor Top Section - Pa2Document2 pagesAnchor Top Section - Pa2albertNo ratings yet
- FM Approval HST3Document1 pageFM Approval HST3WZNo ratings yet
- HS Cal01 000000000ecDocument4 pagesHS Cal01 000000000ecMarcoNo ratings yet
- Drafts - Concrete - Jan 28, 2023Document8 pagesDrafts - Concrete - Jan 28, 2023Dinesh GanapathyNo ratings yet
- SurDrive Washpipe 2019 - 4.00 Inch - 850 TONDocument4 pagesSurDrive Washpipe 2019 - 4.00 Inch - 850 TONAndros SustersickNo ratings yet
- Hilti AnchorDocument5 pagesHilti AnchorGopi KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Fibonacci and Gann Applications in Financial Markets: Practical Applications of Natural and Synthetic Ratios in Technical AnalysisFrom EverandFibonacci and Gann Applications in Financial Markets: Practical Applications of Natural and Synthetic Ratios in Technical AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Anglo–American Microelectronics Data 1968–69: Manufacturers A–PFrom EverandAnglo–American Microelectronics Data 1968–69: Manufacturers A–PNo ratings yet
- Polymer Science: A Materials Science HandbookFrom EverandPolymer Science: A Materials Science HandbookA. D. JenkinsNo ratings yet
- Absolute Returns: The Risk and Opportunities of Hedge Fund InvestingFrom EverandAbsolute Returns: The Risk and Opportunities of Hedge Fund InvestingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Ferrocement Water TanksDocument35 pagesFerrocement Water TanksFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- Vol. 4 (4) - Dec. 2013: Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Menoufia University, Shebin El-Kom, EgyptDocument12 pagesVol. 4 (4) - Dec. 2013: Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Menoufia University, Shebin El-Kom, EgyptFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- Hilti PROFIS Engineering 3.0.81 Anchor DesignDocument15 pagesHilti PROFIS Engineering 3.0.81 Anchor DesignFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- Defu Barrier ConceptDocument1 pageDefu Barrier ConceptFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- Design of Micropile FoundationDocument7 pagesDesign of Micropile FoundationEncik BadrulNo ratings yet
- 80410-19 - TPJC - Drainage Markup - KZXDocument1 page80410-19 - TPJC - Drainage Markup - KZXFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- 1082 Rawlplug en R Hptii ZF Zinc Flake ThroughboltDocument8 pages1082 Rawlplug en R Hptii ZF Zinc Flake ThroughboltFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- Drafts 80637 Typical Connection R1Document16 pagesDrafts 80637 Typical Connection R1Freddie KooNo ratings yet
- Comparison SPTDocument8 pagesComparison SPTسجى EngNo ratings yet
- Design - Part 1 - TWIDocument9 pagesDesign - Part 1 - TWIFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- Drafts 80637 Typical Connection R1Document16 pagesDrafts 80637 Typical Connection R1Freddie KooNo ratings yet
- Fire Shutter: SHD +42.000 7th StoreyDocument3 pagesFire Shutter: SHD +42.000 7th StoreyFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- Why Choose Magnesium?: Materials Science Forum April 2009Document6 pagesWhy Choose Magnesium?: Materials Science Forum April 2009Freddie KooNo ratings yet
- Rawlplug-HPTIIZF-20160 23122022Document7 pagesRawlplug-HPTIIZF-20160 23122022Freddie KooNo ratings yet
- Design - Part 3 - TWIDocument9 pagesDesign - Part 3 - TWIFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- Design Part 2 - TWIDocument9 pagesDesign Part 2 - TWIFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- V4 Eurocode2Part4 Booklet 160x160 enDocument15 pagesV4 Eurocode2Part4 Booklet 160x160 ensubham sahuNo ratings yet
- Design Considerations and Guidelines in The Use of Grade 600 Steel Reinforcements For Reinforced Concrete ConstructionDocument11 pagesDesign Considerations and Guidelines in The Use of Grade 600 Steel Reinforcements For Reinforced Concrete ConstructionFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- 01-Slides-D & C of Driven RC Piles-7 Aug 18-BriefDocument144 pages01-Slides-D & C of Driven RC Piles-7 Aug 18-BriefFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- OrmanN - Challenges of Sewer Rehab WS Dec2016Document2 pagesOrmanN - Challenges of Sewer Rehab WS Dec2016Sen HuNo ratings yet
- Design - TWIDocument7 pagesDesign - TWIFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- 0677Document8 pages0677Jack DoverNo ratings yet
- Design of Piles - Danish Practice: April 2016Document31 pagesDesign of Piles - Danish Practice: April 2016Freddie KooNo ratings yet
- Characteristic Values of Geo Parameters in EC7Document12 pagesCharacteristic Values of Geo Parameters in EC7Freddie KooNo ratings yet
- Protection of Public Sewerage System PDFDocument13 pagesProtection of Public Sewerage System PDFFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- Transport Impact Assessment Guidelines - 28 Sep 2017Document78 pagesTransport Impact Assessment Guidelines - 28 Sep 2017Ed SalangaNo ratings yet
- Decking For Micropile PDFDocument2 pagesDecking For Micropile PDFFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- Please Do Not Remove This Page: Thank You For Do Wnloading This Docum Ment From The Rmit R Research R RepositoryDocument9 pagesPlease Do Not Remove This Page: Thank You For Do Wnloading This Docum Ment From The Rmit R Research R RepositoryFreddie KooNo ratings yet
- Thrust Block For Pipelines - Case Study of Water Sup-Ply Scheme For A Town BerinagDocument6 pagesThrust Block For Pipelines - Case Study of Water Sup-Ply Scheme For A Town BerinagsatyamNo ratings yet
- Justice - BA243 1A - Assignment 2Document5 pagesJustice - BA243 1A - Assignment 2Nur FatehaNo ratings yet
- Stamps Sticky BusinessDocument2 pagesStamps Sticky BusinessJugnu KaulNo ratings yet
- Doc Ssm.nurulhedayahDocument2 pagesDoc Ssm.nurulhedayahrezza590No ratings yet
- Central Bank - Annual Report - 2018Document76 pagesCentral Bank - Annual Report - 2018olhNo ratings yet
- Five Forces Analysis Sido MunculDocument5 pagesFive Forces Analysis Sido MunculAndreas Audi KemalNo ratings yet
- 1.3 SCP201 Assignment Worksheet - Jan 2023 PDFDocument4 pages1.3 SCP201 Assignment Worksheet - Jan 2023 PDFfang weiNo ratings yet
- Online Trading ProposalDocument14 pagesOnline Trading ProposalAlex CurtoisNo ratings yet
- 4th Annual Aerotropolis Brochure 7 PDFDocument6 pages4th Annual Aerotropolis Brochure 7 PDFPablo Gil-CornaroNo ratings yet
- Trade Secret LicensingDocument12 pagesTrade Secret Licensingpriya jainNo ratings yet
- Timetable of OfferDocument1 pageTimetable of OfferAbdo ElbannaNo ratings yet
- Dispute Freight ContractDocument15 pagesDispute Freight ContractVy Trần Thị ThảoNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Teachers' Knowledge Sharing Behaviors and Motivation: System Functions That WorkDocument8 pagesFactors Affecting Teachers' Knowledge Sharing Behaviors and Motivation: System Functions That Worksaeed h.gholizadehNo ratings yet
- Floor SupervisorDocument3 pagesFloor SupervisorJohn Carlo BautistaNo ratings yet
- The Emergency Stop - 2012 Ver 2.0Document27 pagesThe Emergency Stop - 2012 Ver 2.0Arturs StangainisNo ratings yet
- Purchasing Purchase Requisition in SAP MM 1677253319Document8 pagesPurchasing Purchase Requisition in SAP MM 1677253319Rodrigo Toledo SoaresNo ratings yet
- UML Diagrams ExplainedDocument39 pagesUML Diagrams ExplaineddarwinabadNo ratings yet
- Brazil SWOT Analysis: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, ThreatsDocument1 pageBrazil SWOT Analysis: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, ThreatsShivendra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document7 pagesChapter 8Jimmy LojaNo ratings yet
- People ManagementDocument12 pagesPeople Managementyater32875100% (1)
- Certificate of Incorporation-20190704Document1 pageCertificate of Incorporation-20190704Pinky KumariNo ratings yet
- STANDARD COSTING Materials LaborDocument2 pagesSTANDARD COSTING Materials LaborCesNo ratings yet
- FH Method Statement For Procurement ServicesDocument5 pagesFH Method Statement For Procurement Servicesjovana samNo ratings yet
- The Demand For Audit and Other Assurance Services: Concept Checks P. 34Document15 pagesThe Demand For Audit and Other Assurance Services: Concept Checks P. 34hsingting yu100% (2)
- Sistem Informasi Manajemen Presensi Siswa Berbasis MobileDocument6 pagesSistem Informasi Manajemen Presensi Siswa Berbasis Mobilefahmi nur baihaqiNo ratings yet
- Ess TcodeDocument1 pageEss TcodeViral PatelNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument26 pagesBusiness Planroshan kcNo ratings yet
- Forex Business Plan.01Document8 pagesForex Business Plan.01Kelvin Tafara SamboNo ratings yet
- MBA Orientation Manual March 2021Document9 pagesMBA Orientation Manual March 2021SaranyaNo ratings yet