0% found this document useful (0 votes)
379 views5 pagesCondenser Design Calculations and Analysis
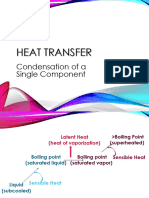
This document summarizes the design of a condenser with the following key details:
- It uses a horizontal exchanger with condensation in the shell and 2 tube passes.
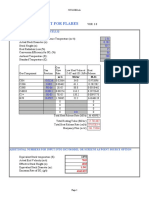
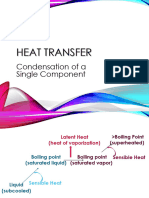
- Design parameters include a cooling water inlet temperature of 30°C, outlet of 40°C, and vapor/components inlet of 300°C reducing to 100°C.
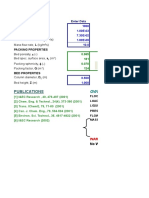
- Calculations determine a heat transfer of 2257.78 kW, cooling water flow of 54.0138 kg/h, and mean temperature difference of 144.7965°C.
- The designed exchanger has 100 tubes with 16mm diameter, 3.65m length, in a 269mm shell with 14 baffles. Pressure
Uploaded by
sandeshCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
379 views5 pagesCondenser Design Calculations and Analysis
This document summarizes the design of a condenser with the following key details:
- It uses a horizontal exchanger with condensation in the shell and 2 tube passes.
- Design parameters include a cooling water inlet temperature of 30°C, outlet of 40°C, and vapor/components inlet of 300°C reducing to 100°C.
- Calculations determine a heat transfer of 2257.78 kW, cooling water flow of 54.0138 kg/h, and mean temperature difference of 144.7965°C.
- The designed exchanger has 100 tubes with 16mm diameter, 3.65m length, in a 269mm shell with 14 baffles. Pressure
Uploaded by
sandeshCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Vapor and Cooling Calculations: This section covers heat transfer calculations from vapor and includes cooling water equations, showcasing practical applications of thermodynamics.
- Tube Specifications and Thermal Analysis: Focuses on the specifics of tube dimensions and materials, along with the thermal analysis of tube bundles under various conditions.
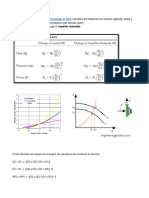
- Fluid Dynamics and Pressure Drop Analysis: Discusses the fluid dynamics in the system, analyzing velocity, pressure drop across tubes, and presenting calculation of various pressure coefficients.
- Continued Calculations: Continues from the previous page with further calculations, providing more detailed derivations from previous work.
- Final Analysis and Results: Concludes the analysis with final formulas and summary calculations necessary for design decisions or further study.



![conversions:
kg/h
2.777778 kg/s
be passes, the correction factor, F t :
1−S
1−RS )
−S( R+1−√( R2+1 ))
−S( R+1+√(R2+1)) ]
−(T2](https://screenshots.scribd.com/Scribd/252_100_85/326/617377845/4.jpeg)
![Db=d0(
Nt
K1)
1
n1
ρV )g
Γh
]
1
3
Nr
−1
6](https://screenshots.scribd.com/Scribd/252_100_85/326/617377845/5.jpeg)