Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Activity File
Uploaded by
Manjeet Singh RATHORE0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views14 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
59 views14 pagesPhysics Activity File
Uploaded by
Manjeet Singh RATHORECopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
PHYSICS ACTIVITY FILE (042)
Session (2022-23)
Submitted to: Submitted by:
MRs, KARANVEER SINGH STUDENTS NAME
Class-
1
ACTIVITY -1 Back Page
2
ACTIVITY – 1
AIM :– To assemble a household circuit comprising three bulbs, three (ON/OFF)
swtiches, a fuse and a power source.
APPARATUS :–
Tester, Three electric bulbs of 40W, 60 W and 100 W, Three bulb holders,
Three switches (ON/OFF), Red and black insulated flexible wires, Fuse wire
Tools, Main plug, Insulating tape.
THEORY / PRINCIPLE :- Household circuit fuctions on main supply of 220 V ac at 50 Hz
and current rating is 5A for domestic use for bulbs, fluorescent tubes, fans, etc. and 15 A for
heavy load appliances like refrigerator, air-conditioner, geyser, hot plates, etc.
Total power consumption P at any time, P = P1 + P2 + P3 + .......
where P1 , P2 and P3 are powers drawn by various appliances at a potential V, from
the mains, I = P/V
Here, P is in watt, V in volt and I in ampere. Electric fuse in a safety device which is
used to limit the current. It is a short piece of wire made up of a material of high resistivity and
of low melting point so that it may easily melt due to overheating, when excessive current
passes through the circuit. It is always connected in series with a supply source on phase
wire. Remember that in household circuits, all appliances are connected in
parallel while a switch is connected in series with each appliance on phase wire of
the supply line.
RESULT :– All the bulbs and switches work properly with controlled power supply.
PRECAUTIONS :–1. The connections should be tight.
2. The red lead should always act as the live wire and the fuse should be introduced
in this wire.
3. The switch should always be connected in the live wire.
4. All the joints should be properly insulated.
SOURCES OF ERROR :- 1. Personal error.
2. All the components must be checked before using.
3
ACTIVITY -2 Back Page
4
ACTIVITY – 2
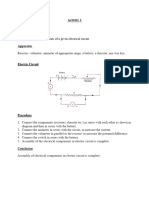
AIM :– To assemble the components of a given electrical circuit.
APPARATUS :–
Galvanometer, Two resistance boxes, Two one-way keys, Battery of two primary cells
Ammeter, Voltmeter, Rheostat, Connecting wires.
THEORY / PRINCIPLE :- In an electrical circuit, an ammeter is always connected in series
and a voltmeter is always connected in parallel to the two points of a circuit across which
potential difference is to be measured. Two resistors may be joined in parallel or in series
combination in the circuit.
RESULT :– If the assembled circuit is working properly, then the given components have
been assembled correctly.
PRECAUTIONS :–1. The ends of the connecting wires should be cleaned properly with
sandpaper.
2. While connecting different electrical components, make tight connections.
3. In the circuit, always connect the ammeter in series and the voltmeter in parallel to
the resistor.
4. Ammeter and voltmeter should be connected such that the current enters at their
positive terminal and leaves from the negative terminal.
SOURCES OF ERROR :-1. Volt / ammeter may not be connected with correct polarity in
the circuit.
2. Ammeter may be connected in parallel.
3. Voltmeter may be connected in series.
5
ACTIVITY -3 Back Page
6
ACTIVITY – 3
AIM :– To draw the diagram of a given open circuit comprising of at least a battery, a
resistor, a rheostat, a key, an ammeter and a voltmeter. Mark the component
that are not connected in proper order and correct the circuit and also the
circuit diagram.
APPARATUS :–
Battery, Rheostat, Voltmeter, Ammeter, One-way key, Resistor, Connecting wire.
THEORY / PRINCIPLE / FORMULA :-
Electric circuit is a conducting path consisting of electric components connected
between the two terminal of a cell.
Circuit diagram is a diagram indicating the arrangement of various components in
an electric circuit with the help of their symbols.
Open circuit is a conducting path consisting of electric components connected
between the two terminal of a cell with a switch in OFF position. No current flows in open
circuit.
Closed circuit A circuit is said to be closed circuit if all the primary components in an
electric circuit are connected in proper order and current is drawn from the cell.
OBSERVATIONS:-1. Ammeter and voltmeter are not connected properly as clearly seen in
the circuit diagram.
2. When ammeter and voltmeter are connected in proper order they show reading
when circuit is closed.
RESULT :–1. Circuit diagram shown in Figure is not proper in which voltmeter and
ammeter are wrongly connected.
2. Circuit diagram shown in next Figure is proper and correct.
PRECAUTIONS :–1. All connections should be neat, clean and tight.
2. The insulated wires should be used for connections.
3. A given circuit should not be checked by inserting plug into the key. This may
damage any components of the circuit.
7
ACTIVITY -4 Back Page
8
ACTIVITY– 4
AIM :– To identify a diode, an LED, a transistor, an IC, a resistor and a capacitor from
a mixed collection of these items.
APPARATUS :– Collection of
A diode, LED, Transistor, IC, Resistor, Capacitor, Multimeter.
THEORY / PRINCIPLE :- For identification of items from a collection, we have to consider
both, their appearance and working.
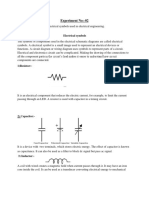
1. A diode :—A diode is a semiconducting device which has two terminals. It con-
ducts only when it is forward biased and it does not conduct when reverse biased.
2. A light emitting diode (LED) :—It is a two terminals device, which gives out
light when electric current passes through it. A diode and a LED both allow the flow of current
in one direction only.
3. A Resistor :—It is also a two terminal device. It conducts direct current and alter-
nating current both. A resistor can conduct equally even when the terminals of battery con-
nected across it are reversed.
4. A Capacitor :—It is also a two terminal device but it does not allow direct current
(dc) to flow through its self. It stores some charge when dc voltage is applied. It conducts
alternating current.
5. A Transistor :—It is a three terminal device (emitter, base and collector). It has
three terminals and it may be identified by appearance only.
6. An IC (intergrated circuit) :—In integrated circuit many circuits are intergrated in
one chip. ICs are obtained by a complex procedure involving diffusion, oxidation, photolitho-
graphy, metallisation, etc. It is a multiterminal component. Most of IC packages have flat
back. The tips of its legs are thinner than the tops.
IC is the component which has a flat back, a large number of legs / terminals, made of
flat metal strips.
OBSERVATIONS / RESULTS :– All the items in the mixed collection have been identified
and the result may be summed up as in the table given below.
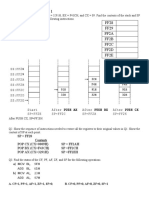
A. Identification of Components with the Help of Terminals
S.N. No. of terminals/legs Devices
1. More than three IC
2. Three Transistor
3. Two Diode, LED, resistor and capacitor
9
B. Identification of Components with the Help of Current Flow
S.N. No. of terminals/legs (02) Devices
1. Unidirectional with no light emission Diode
2. Unidirectional with light emission LED
3. Current in both direction (steady) Resistor
4. No flow of direct current in any direction Capacitor
PRECAUTIONS :–1. Connections should be neat and tight.
2. Strong current should not be passed through the components.
3. Polarity should be reversed for identifying the items, e.g., diode, LED, etc.
4. Students must handle the multimeter carefully since it is very sensitive.
SOURCES OF ERROR :-1. Multimeter shows zero resistance on touching its metal leads.
If it does not show zero resistance, bring the pointer to zero using zero adjustment knob on
the multimeter. If zero adjustment is not done, the resistance measurement will not be true.
2. While checking resistance, if metal ends of multimeter leads are touched by
hands, body resistance in parallel with the component resistance affects the value of the
resistance.
10
ACTIVITY -5 Back Page
11
ACTIVITY– 5
AIM :– Use of multimeter to (i) identify base of transistor, (ii) distinguish between
n-p-n and p-n-p type transistors, (iii) see the unidirectional flow of current in
case of a diode and an LED, (iv) check whether a given electronic component
(e.g., diode, transistor or IC) is in working order.
APPARATUS :–
Multimeter, n-p-n and p-n-p transistors, IC, Junction diode, LED.
THEORY / PRINCIPLE :-
Transistor :—It is a three terminal device which consists of two p-n junctions fused
back to back. a transistor is formed by sandwiching a thin layer of extrinesic semiconductor
(n-type or p-type) between the two comparatively thicker layers of the opposite type (p-type
or n-type) as shown in Figs. a and b.
Transistors are of two types :
(i) p-n-p- transistor
(ii) n-p-n transistor.
Middle thin layer is known as base (B) and the left and right layers are called emitter
(E) and collector (C) respectively.
For Identifications, we have the following :
1. Identification of the base of a transistor :—There are three terminals of a tran-
sistor say, a, b and c. If conduction of current takes place when multimeter is connected
between a and b as well as between b and c. Then common terminal b is the base of the
given transistor.
It may also be noticed that collector lead (or terminal) lies on the other side of the base
terminal and is far from the other two leads (emitter and base) which are situated close to
each other.
2. Identification of type of a transistor :—As in the above case, if the common
(base) terminal of transistor is connected to +ve terminal of the battery and conduction
takes place then transistor is of n-p-n type. On the other hand if conduction takes place
when the common (base) terminal of transistor is connected to –ve terminal then transistor is
of p-n-p type.
3. Conduction of a diode and an LED :—An LED and a diode, both conduct only
when they are connected in forward biased mode. There will be no flow of electric current if
they are connected in reverse biased mode.
IC is a multiterminal device with a flat back. Normally, it consists of minimum 8 legs.
4. Working order of given component :—In case of a diode and an LED, they will
allow current to pass through them in forward biased mode only.
A transistor conducts only when the base-emitter is forward biased and does not
conduct in reverse biased mode. If it allows the flow of current in both biasing or does not
allow the flow of current in both biasing then, it is damaged.
12
ACTIVITY -5 Back Page
13
PRECAUTIONS :–1. The multimeter should be set for appropriate range.
2. Students must handle the multimeter carefully since it is a very sensitive device.
3. First check the base of the transistor.
4. A suitable current should be allowed to pass through an electronic component
otherwise the component may be damaged.
You might also like
- Physics Activity FileDocument14 pagesPhysics Activity Filemeeralodhi5544No ratings yet
- Physics Activity FileDocument16 pagesPhysics Activity FileAyush Raj100% (1)
- Identify Electronic ComponentsDocument4 pagesIdentify Electronic ComponentsABHISHEK TIWARI82% (11)
- Physics Activity 3Document4 pagesPhysics Activity 3Ankit PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- List of ActivitiesDocument15 pagesList of Activitieskaustubhkushagra9No ratings yet
- Physics ActivitiesDocument8 pagesPhysics Activitiestanyaverma2729No ratings yet
- Physics Activity-2022-2023 OkDocument15 pagesPhysics Activity-2022-2023 OkAdarsh Gyan Mandir Se Sec SchoolNo ratings yet
- Activity Notes BookDocument12 pagesActivity Notes Bookkaran singh class 11 aNo ratings yet
- Physics 1Document17 pagesPhysics 1ashishktomar33No ratings yet
- ActivitiesDocument10 pagesActivitieskalashNo ratings yet
- Identifying Electrical ComponentsDocument9 pagesIdentifying Electrical ComponentsVARSHNo ratings yet
- Grade 12physics Practical - Activities - 2022-23Document13 pagesGrade 12physics Practical - Activities - 2022-23kartik ajitNo ratings yet
- Information Sheets 6.1.4Document12 pagesInformation Sheets 6.1.4api-196541959No ratings yet
- Six Activities Class 12Document16 pagesSix Activities Class 12Priyanshu jhaNo ratings yet
- EE Lab ME - IntroDocument13 pagesEE Lab ME - IntroNandhu NandhuNo ratings yet
- UIET Lab Manual Basic ElectronicsDocument48 pagesUIET Lab Manual Basic ElectronicsHarry HarryNo ratings yet
- Deek ShaDocument13 pagesDeek ShaShivani SharmaNo ratings yet
- ActivitiesDocument4 pagesActivitiespoliovacjieNo ratings yet
- Physics ActivitiesDocument16 pagesPhysics ActivitiesSoumik MahapatroNo ratings yet
- Workshop Training Manual COURSE: WS1020: Central Workshop Indian Institute of Technology Madras CHENNAI - 600036, INDIADocument44 pagesWorkshop Training Manual COURSE: WS1020: Central Workshop Indian Institute of Technology Madras CHENNAI - 600036, INDIAhariharanhemanthNo ratings yet
- Detect AC Voltage Safely with Non-Contact AC Line DetectorDocument5 pagesDetect AC Voltage Safely with Non-Contact AC Line DetectorShubham DandgeNo ratings yet
- Phy ActivitiesDocument20 pagesPhy ActivitiesGaurav SinhaNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Electrical Workshop LabDocument15 pagesGovernment Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Electrical Workshop LabTapobroto Chatterjee100% (1)
- WS 1020Document44 pagesWS 1020Sunil Sree NathNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Identification0001Document6 pagesActivity 1 - Identification0001Lalchandsahani SahaniNo ratings yet
- Acee5 - Bsee2b - Manaois - Ethan Zachary - Albelar - Assign1Document15 pagesAcee5 - Bsee2b - Manaois - Ethan Zachary - Albelar - Assign1Kazuha MinatoNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit IndicatorDocument4 pagesShort Circuit IndicatorDasari Navya sriNo ratings yet
- Bee 18esee02l Lab ManualDocument43 pagesBee 18esee02l Lab ManualGemechu TayeNo ratings yet
- Construction & Operation of Some Simple Electrical Circuits: Name of The ExperimentDocument7 pagesConstruction & Operation of Some Simple Electrical Circuits: Name of The ExperimentSayeed MohammedNo ratings yet
- GRADE 12 PHYSICS ACTIVITIES LISTDocument15 pagesGRADE 12 PHYSICS ACTIVITIES LISTHARSHA VARDAN KARTHIK SELVAN 6466100% (1)
- Activity Sec-ADocument3 pagesActivity Sec-A༈mran Rashid៚No ratings yet
- To Assemble A Household Circuit Comprising Three Bulbs, Three (On/off) Switches A Fuse and A Power Source.Document4 pagesTo Assemble A Household Circuit Comprising Three Bulbs, Three (On/off) Switches A Fuse and A Power Source.Study Material100% (1)
- Lab ManualDocument33 pagesLab ManualsimeeraataaddeseeNo ratings yet
- 2Q Laboratory Activity No.1 - Let There Be Light!-FDocument5 pages2Q Laboratory Activity No.1 - Let There Be Light!-FAiza CabatinganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Electronic Components & SignalsDocument12 pagesChapter 1. Electronic Components & SignalsPavankumar Gosavi100% (2)
- Project Load Protector Final 22Document42 pagesProject Load Protector Final 22virendkumarNo ratings yet
- Automatic Bottle Filling System Circuit Diagram and ComponentsDocument15 pagesAutomatic Bottle Filling System Circuit Diagram and ComponentsNurulSyafiqahNo ratings yet
- 15EI251L E&ilap ManualDocument56 pages15EI251L E&ilap ManualAnushka TantiaNo ratings yet
- PHY547 - LAb Manual-2019Document26 pagesPHY547 - LAb Manual-2019zulhaimirasheedNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 Section BDocument3 pagesActivity 4 Section BSahil BijarniaNo ratings yet
- Mannat Physics Activity FileDocument18 pagesMannat Physics Activity FileAryan RajputNo ratings yet
- Activity de PhysicsDocument11 pagesActivity de Physicsshivam100% (3)
- Introduction Electrical Instruments ComponentsDocument7 pagesIntroduction Electrical Instruments Componentsnational printersNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 1Document7 pagesExperiment No: 1naeemullah786057No ratings yet
- Experiment-1 - To Make A Center-Tap Full-Wave RectifierDocument5 pagesExperiment-1 - To Make A Center-Tap Full-Wave RectifierSKMNo ratings yet
- Experiment No:-02: Electrical SymbolsDocument6 pagesExperiment No:-02: Electrical SymbolsAdesh Bhortakke100% (2)
- FEEEDocument56 pagesFEEEnetra msajjan100% (1)
- Broken Wire Detector Circuit Using IC CD4069Document40 pagesBroken Wire Detector Circuit Using IC CD4069olawale gbadebo100% (1)
- EE-331 Lab ReportDocument5 pagesEE-331 Lab Reportlaksh rathiNo ratings yet
- Active & PassiveDocument3 pagesActive & Passivevirendra.aryaNo ratings yet
- How to assemble a basic household circuitDocument11 pagesHow to assemble a basic household circuitKrishnashis DasNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Lab ExperimentsDocument25 pagesBasic Electrical Lab ExperimentschaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Parts in Your Kit: BreadboardDocument5 pagesParts in Your Kit: BreadboardcesarNo ratings yet
- Electronics Code Lock Using One TransistorDocument18 pagesElectronics Code Lock Using One TransistorAnonymous TvXDUWDaol50% (2)
- Physics Activity 2Document4 pagesPhysics Activity 2Ankit PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Eec 115 Experiment I & IiDocument12 pagesEec 115 Experiment I & IiOreoluwa OmiyaleNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2From EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2No ratings yet
- RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS OVERVIEWDocument17 pagesRELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS OVERVIEWManjeet Singh RATHORENo ratings yet
- Physics Lab ManualDocument16 pagesPhysics Lab ManualManjeet Singh RATHORENo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab ManualDocument16 pagesChemistry Lab ManualManjeet Singh RATHORENo ratings yet
- Mathematics Lab ActivitiesDocument1 pageMathematics Lab ActivitiesManjeet Singh RATHORENo ratings yet
- Electrostatics and Ohms LawDocument48 pagesElectrostatics and Ohms LawLourdes Marie MirasolNo ratings yet
- SPARK Z2.0 Kit Contains Conducted Electrical Device and AccessoriesDocument5 pagesSPARK Z2.0 Kit Contains Conducted Electrical Device and AccessoriesGraciela LlanosNo ratings yet
- Project PresentationDocument21 pagesProject PresentationANEESA NAZ MEMONNo ratings yet
- C60NDocument5 pagesC60NJoxe Purizaga AraujoNo ratings yet
- HCA8C-4AD User's ManualDocument12 pagesHCA8C-4AD User's ManualHudson CostaNo ratings yet
- Transmotec: 770 Series Ø45 MM 21-114 WDocument1 pageTransmotec: 770 Series Ø45 MM 21-114 WzyozkdNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Inverter 715G2824-6-5 AocDocument2 pagesPower Supply Inverter 715G2824-6-5 AocViktor CymbalyukNo ratings yet
- Level Measurement Techniques in 40 CharactersDocument38 pagesLevel Measurement Techniques in 40 CharactersBHAVESH JAINNo ratings yet
- 2019 Sec 4 Science Physics SA2 Assumption EnglishDocument30 pages2019 Sec 4 Science Physics SA2 Assumption EnglishLi HongNo ratings yet
- EntelliGuard L Catalogue English Ed12-13 680837 PDFDocument84 pagesEntelliGuard L Catalogue English Ed12-13 680837 PDFferreiramarco56No ratings yet
- Carrier Current ProtectionDocument21 pagesCarrier Current ProtectionManendra Singh100% (2)
- EN VEGAWELL 52 4 20 MaDocument40 pagesEN VEGAWELL 52 4 20 MaHelder Pascoal Macuacua MacuacuaNo ratings yet
- 2.5 - FAT - C1574 - FAT Procedure PDFDocument7 pages2.5 - FAT - C1574 - FAT Procedure PDFGeorge Jhonson100% (2)
- DS Kymeta U8 Antenna PDFDocument2 pagesDS Kymeta U8 Antenna PDFEric FORTINNo ratings yet
- BasicstampmanDocument353 pagesBasicstampmanJuan BlancoNo ratings yet
- Data Pengiriman Unit AC LG Tahap Ke 3 29 April - 2 Mei 2017: Model QtyDocument12 pagesData Pengiriman Unit AC LG Tahap Ke 3 29 April - 2 Mei 2017: Model QtyChris DesmonNo ratings yet
- The Company: STAB SRL Via Seminiato, 79 44034 Ambrogio (FE) Italy Tel. 0532830739 Fax 0532830609Document10 pagesThe Company: STAB SRL Via Seminiato, 79 44034 Ambrogio (FE) Italy Tel. 0532830739 Fax 0532830609Dami HaNo ratings yet
- Elec 451 Hw1Document4 pagesElec 451 Hw1MishtuDeepNo ratings yet
- Lightning & Protection Against LightningDocument46 pagesLightning & Protection Against LightningMohammed Jalaluddin RayeenNo ratings yet
- Test Report: Shenzhen Huaxia Testing Technology Co., LTDDocument35 pagesTest Report: Shenzhen Huaxia Testing Technology Co., LTDGordinhorsNo ratings yet
- Denver Inst Analytical Balances M-Series Operation ManualDocument29 pagesDenver Inst Analytical Balances M-Series Operation ManualRichard BedellNo ratings yet
- Description Mechanical Dimensions: 2.0 Amp Schottky Barrier RectifiersDocument2 pagesDescription Mechanical Dimensions: 2.0 Amp Schottky Barrier RectifiersStuxnetNo ratings yet
- Streamlight ProTac HL Flashlight InstructionsDocument11 pagesStreamlight ProTac HL Flashlight InstructionsRichard JohnsonNo ratings yet
- CD4093BC Quad 2-Input NAND Schmitt Trigger: General Description FeaturesDocument8 pagesCD4093BC Quad 2-Input NAND Schmitt Trigger: General Description FeaturesClovis BentoNo ratings yet
- Programmable power supply sequencing and monitoring solutionsDocument2 pagesProgrammable power supply sequencing and monitoring solutionsLeth ComputerRepairNo ratings yet
- Soluciones 9Document4 pagesSoluciones 9manuNo ratings yet
- QinetiQ certifies Japan Radio Co.'s ECDIS and Raster Chart Display SystemDocument4 pagesQinetiQ certifies Japan Radio Co.'s ECDIS and Raster Chart Display Systemcem100% (1)
- Mechanical Torque Wrenches - SaltusDocument20 pagesMechanical Torque Wrenches - SaltusEnbotic AutomatykaNo ratings yet
- Product Data and Installation Sheet Elt10 E L T S: Mergency Ighting EST Witch D ODocument2 pagesProduct Data and Installation Sheet Elt10 E L T S: Mergency Ighting EST Witch D OGerardo ColmenaresNo ratings yet
- Amateur Radio Magazin 01 - January - 1975 PDFDocument164 pagesAmateur Radio Magazin 01 - January - 1975 PDFJoão Pedro AlmeidaNo ratings yet