Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment 2. Achieve Ohm's Law The Used Devices
Uploaded by
بلسم محمود شاكر0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageOriginal Title
6_2022_04_11!11_34_47_PM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageExperiment 2. Achieve Ohm's Law The Used Devices
Uploaded by
بلسم محمود شاكرCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Experiment 2.
Achieve Ohm's Law
The used devices:-
1- A battery. 2- Variable resistance (rheostat). 3- A voltmeter. 4- Ammeter. 5- Resistance.
6-key.
The theory of experiment:
Ohm's Law states that the ratio of the voltage difference (V) between the two ends of a
conductor to the current (I) passing through it is a constant amount with constant
temperature of the conductor.
This constant quantity represents the value of the electrical resistance ®.
The mathematical expression for Ohm's law is:
R = V/I ………… (1)
It is clear from equation (1) that the current is a linear function of the voltage difference, as
the curve that connects the voltage difference between the two ends of the conductor and
the current passing through it is a straight line.
The experiment will be carried out in two cases:-
The method of experiment:-
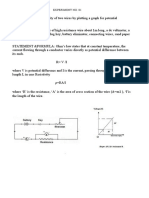
1- Connect the electrical circuit as shown in the figure.
R V
A
K
2- Close the electrical circuit, record the reading of the ammeter (I) by controlling the value
of the variable resistance as well as the reading of the voltmeter (V).
3- Change the value of the current passing through the circuit using the variable resistance
(Rheostat) at a rate of (0.1) mA and each time record the reading of the voltmeter (V).
4- Record the values of voltage and current in a table.
5- Draw a graph between the values of (I) and the corresponding (V) values and calculate the
value of the slope.
You might also like
- Verification of Ohms LawDocument3 pagesVerification of Ohms LawManju MathurNo ratings yet
- Experiment No-1 Objective: - Equipment RequiredDocument3 pagesExperiment No-1 Objective: - Equipment RequiredwondieNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Term 2 PracticalDocument10 pagesClass 10 Term 2 Practicalgaa849711No ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercices For Analog and Digital Circuits Using NI ELVIS II NI Multisim 2Document150 pagesLaboratory Exercices For Analog and Digital Circuits Using NI ELVIS II NI Multisim 2zohas13No ratings yet
- Sulaimani Polytechnic University Engineering Technical College Communication DepartmentDocument12 pagesSulaimani Polytechnic University Engineering Technical College Communication Departmentsarkar salamNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1: 1. What Is Meant by Charge?Document3 pagesUNIT-1: 1. What Is Meant by Charge?Manoj DNo ratings yet
- Report On "Basic Ohm's Law & Series and Parallel Circuits"Document18 pagesReport On "Basic Ohm's Law & Series and Parallel Circuits"JEJUNG67% (3)
- NotesDocument2 pagesNotesAshok Kumar DondatiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document9 pagesLab Report 1Moad AbusninaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 (Autosaved)Document76 pagesCHAPTER 2 (Autosaved)dray09100% (1)
- Lab Report 1Document9 pagesLab Report 1Hajer JejeNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic EngineeringDocument8 pagesElectrical and Electronic Engineeringخہٰہٰالہٰد ۦ' ۦ'No ratings yet
- Abhishek Gautam Exp1Document12 pagesAbhishek Gautam Exp1Abhishek Mishra GautamNo ratings yet
- AP Lab 07Document3 pagesAP Lab 07muhammad arslanNo ratings yet
- Aim of ProjectDocument5 pagesAim of Projectaayush sinhaNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument10 pagesOhm's LawChrisel Joy Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Thevinin and NortonDocument4 pagesThevinin and Nortonkudupudinagesh100% (1)
- EEE 124 Exp5Document4 pagesEEE 124 Exp5Rakibul Hassan SajonNo ratings yet
- Assessment Rubric Lab2Document8 pagesAssessment Rubric Lab2Felix Erwin RajakNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Lab1Document44 pagesElectrical Circuit Lab1rahmahamjad90No ratings yet
- To Verify Ohm's Law: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesTo Verify Ohm's Law: ObjectiveNasirAbbasNo ratings yet
- Elementary Electrical Engineering - Series Parallel ConditionsDocument14 pagesElementary Electrical Engineering - Series Parallel ConditionsRubdubRNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument9 pagesLab ReportMuhammad Faizan Tariq100% (1)
- Ohm's Law ReportDocument8 pagesOhm's Law ReportFelicia Paya FrancisNo ratings yet
- 1.ohms's LawDocument3 pages1.ohms's LawPartikNo ratings yet
- Elementary Electrical Engineering - MODULE 8 Part 2 - Series Parallel ConditionsDocument14 pagesElementary Electrical Engineering - MODULE 8 Part 2 - Series Parallel ConditionsRubdubRNo ratings yet
- Experimental Guidance 1.2. Voltage-Current Characteristic 2nd WeekDocument14 pagesExperimental Guidance 1.2. Voltage-Current Characteristic 2nd WeeksadmanNo ratings yet
- JC6TD4N7 Lab2Document8 pagesJC6TD4N7 Lab2Emre SelviliNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Ohms LawDocument18 pagesExperiment 1 Ohms LawAbhishek Mishra GautamNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity PDF (16-19)Document18 pagesCurrent Electricity PDF (16-19)Abhay MauryaNo ratings yet
- (4.2) e - ResistanceDocument8 pages(4.2) e - ResistanceShaikh Usman AiNo ratings yet
- Abhishek GautamDocument14 pagesAbhishek GautamAbhishek Mishra GautamNo ratings yet
- مختبر ابلايد2Document6 pagesمختبر ابلايد2عبد الرحمن أبوخاطر, أبو رزقNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law 1Document5 pagesOhm's Law 1rajesh_patel_007No ratings yet
- 3 X7 EBcf 78 Auzh Emn C5 ETDocument26 pages3 X7 EBcf 78 Auzh Emn C5 ETAnas AlamNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measuring InstrumentsDocument17 pagesElectrical Measuring InstrumentsLawrence Wahome ngariNo ratings yet
- UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS ANALYSIS Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesUNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS ANALYSIS Important QuestionsBharath PonNo ratings yet
- Notes Electric CircuitDocument5 pagesNotes Electric CircuitSTACEYLEEN CYENTHIA LADIUN BK22110177No ratings yet
- Lab Manual EE1251Document35 pagesLab Manual EE1251Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- 18ELE13 23 - Module 1Document18 pages18ELE13 23 - Module 1AkhilNo ratings yet
- NOTES (2023-2024) Subject: PHYSICS Class: XII Experiment No.1: Ohm'S LawDocument5 pagesNOTES (2023-2024) Subject: PHYSICS Class: XII Experiment No.1: Ohm'S LawMichael IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DC Circuit TheoryDocument37 pagesChapter 2 DC Circuit TheoryTynoh MusukuNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualsDocument24 pagesLab ManualsPranoy MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Basics of ElectricityDocument18 pagesBasics of Electricitygsantosh06No ratings yet
- Electrical Components and Circuits Not MineDocument21 pagesElectrical Components and Circuits Not MineMark Cliffton BadlonNo ratings yet
- Labs For Verification of Ohms Law Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument9 pagesLabs For Verification of Ohms Law Series and Parallel Circuitshuzaifaalisiddiqui270No ratings yet
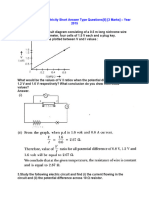
- Class 10 Science Electricity Short Answer Type QuestionsDocument39 pagesClass 10 Science Electricity Short Answer Type QuestionsLawrence GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Current Electricity Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesClass 10 Current Electricity Lesson PlanObul Reddy PolimeraNo ratings yet
- Verification of Ohm's Law: Experiment No# 02Document3 pagesVerification of Ohm's Law: Experiment No# 02Saad AliKhan50% (2)
- Electricity Lab Alan ArifDocument7 pagesElectricity Lab Alan ArifAlan ZaxoNo ratings yet
- Newloydlab 28Document10 pagesNewloydlab 28marthabervellyNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Join @cbse10bystudentshelper On TelegramDocument26 pagesOhm's Law: Join @cbse10bystudentshelper On TelegramValerie CoxNo ratings yet
- Phy12l E306 ISI-PaperDocument8 pagesPhy12l E306 ISI-PaperGrace ReyesNo ratings yet
- Exp4 2K20CO153Document6 pagesExp4 2K20CO153divye guptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: DC Circuit TheoryDocument37 pagesChapter 2: DC Circuit TheoryTaonga NhambiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 12: ElectricityDocument18 pagesChapter - 12: Electricitysachin121083No ratings yet
- General Physics-2 Lab - Phys ( 2 02 )Document15 pagesGeneral Physics-2 Lab - Phys ( 2 02 )حكاياحلمNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument49 pagesElectricityShubham Rout100% (1)
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2From EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2No ratings yet
- Sources of Radiation: Dr. Nada Farhan Kadhim/2019 Fourth Class/ Health PhysicsDocument3 pagesSources of Radiation: Dr. Nada Farhan Kadhim/2019 Fourth Class/ Health Physicsبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 & 4: Environmental ProblemDocument7 pagesLecture 3 & 4: Environmental Problemبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
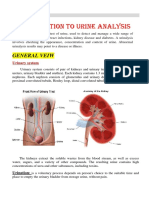
- Introduction To Urine Analysis: General VeiwDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Urine Analysis: General Veiwبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Units of Radiation 1. Unit of Radiation E×posure: Roentgen (R)Document5 pagesUnits of Radiation 1. Unit of Radiation E×posure: Roentgen (R)بلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Urine Analysis: General VeiwDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Urine Analysis: General Veiwبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Nanomaterials: Dr. Afraa Ali AlaskareeDocument9 pagesCharacterization of Nanomaterials: Dr. Afraa Ali Alaskareeبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- 6 2022 04 17!11 15 27 AmDocument2 pages6 2022 04 17!11 15 27 Amبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- معمارية 1Israa AlsaadiDocument91 pagesمعمارية 1Israa Alsaadiبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Lec.1 Food Microbiology Dr. Jehan Abdul SattarDocument6 pagesLec.1 Food Microbiology Dr. Jehan Abdul Sattarبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- 6 2022 04 17!11 15 53 AmDocument2 pages6 2022 04 17!11 15 53 Amبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Chemical KineticsDocument10 pagesPhysical Chemistry Chemical Kineticsبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- هياكل متقطعة المرحلة الاولى الكورس الاولDocument111 pagesهياكل متقطعة المرحلة الاولى الكورس الاولبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- 6 2022 04 17!11 15 41 AmDocument2 pages6 2022 04 17!11 15 41 Amبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- H 2.01410u of Proton 1.007825u And, of Neutron 1.008665uDocument6 pagesH 2.01410u of Proton 1.007825u And, of Neutron 1.008665uبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- رياضيات2 د اوراس خالدDocument21 pagesرياضيات2 د اوراس خالدبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Neutrons 2Document5 pagesNeutrons 2بلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- رياضيات1 د اوراس خالدDocument61 pagesرياضيات1 د اوراس خالدبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument1 pageExercisesبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Lecture #3: Al-Mustansiriyah University College of Sciences Physics DepartmentDocument12 pagesLecture #3: Al-Mustansiriyah University College of Sciences Physics Departmentبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- 6 2021 09 20!09 28 44 PMDocument15 pages6 2021 09 20!09 28 44 PMبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument1 pageExercisesبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- احصاء واحتمالية L.Ahmed jameelDocument37 pagesاحصاء واحتمالية L.Ahmed jameelبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four InductanceDocument11 pagesChapter Four Inductanceبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Ch2: Arrays and Matrices: ReferenceDocument4 pagesCh2: Arrays and Matrices: Referenceبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Department of Physics, College of Science Mustansiriyah UniversityDocument8 pagesDepartment of Physics, College of Science Mustansiriyah Universityبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- 6 2019 04 28!07 59 22 AmDocument1 page6 2019 04 28!07 59 22 Amبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Department of Physics, College of Science Mustansiriyah UniversityDocument13 pagesDepartment of Physics, College of Science Mustansiriyah Universityبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Induced Electromotive Force Induced Electromotive Force 3.1. Faraday's Law of InductionDocument7 pagesChapter Three Induced Electromotive Force Induced Electromotive Force 3.1. Faraday's Law of Inductionبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Aberrations: Geometriic Optiics LectureDocument5 pagesAberrations: Geometriic Optiics Lectureبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Sources of The Magnetic Field Sources of The Magnetic FieldDocument6 pagesChapter Two Sources of The Magnetic Field Sources of The Magnetic Fieldبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet