Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AP Lab 07
Uploaded by
muhammad arslan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesOriginal Title
AP_Lab_07
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesAP Lab 07
Uploaded by
muhammad arslanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
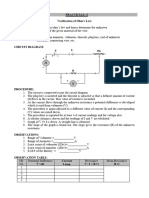
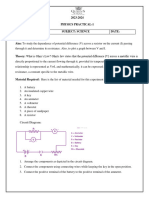
EXPERIMENT NO- 07
Verification of Ohm’s Law
Objective:
To find the value of voltage and current using DMM.
To verify the statement of ohm’s law
To plot the VI graph for the given resistor.
Apparatus:
Resistor 1k ohm and 100 ohm, 200ohm, bread board, DMM, connecting wires
THEORY:
Ohm's Law deals with the relationship between voltage and current in an ideal conductor. This
relationship states that: The potential difference (voltage) across an ideal conductor is
proportional to the current through it. The constant of proportionality is called the "resistance",
R. Ohm's Law is given by: V = I R
Where V is the potential difference between two points which include a resistance R. I is the
current flowing through the resistance. Or Ohm’s law states that the current through a conductor
between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points, and inversely
proportional to the resistance between them. V, I, and R, the parameters of Ohm's law. I = V / R
Ohm's law is among the most fundamental relationships in electrical engineering. It relates the
current, voltage, and resistance for a circuit element so that if we know two of the three
quantities we can determine the third. Thus, if we measure the current flowing in a resistor of
known value, we can deduce the voltage across the resistance according to V = IR. Similarly, if
we measure the voltage across a resistor and the current through it, we calculate the resistance of
the element to be R = V/I. Not only does this reduce the number of measurements that must be
made, it also provides a way to check the results of several different measurement methods.
PROCEDURE
1) Patch the circuit as shown in figure
2) For the supply of 2v find the current through the resistor 220 ohm by connecting ammeter
in series.
3) Repeat step (2) for 4V, 6V, 8V and 10 V power supply voltage.
4) Repeat step (3) for 100 ohm and 1kohm.
OBSERVATION AND CALCULATION:
R=220ohm R=100Ohm R=1KOhm
V (volts) I (mA) V (volts) I (mA) V (volts) I (mA)
2 2 2
4 4 4
6 6 6
7 7 7
8 8 8
Plot VI graph:
Voltage
Current
You might also like
- Experiment 1 Ohms LawDocument18 pagesExperiment 1 Ohms LawAbhishek Mishra GautamNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law Experiment ExplainedDocument12 pagesOhm's Law Experiment ExplainedAbhishek Mishra GautamNo ratings yet
- Assessment Rubric Lab2Document8 pagesAssessment Rubric Lab2Felix Erwin RajakNo ratings yet
- Abhishek GautamDocument14 pagesAbhishek GautamAbhishek Mishra GautamNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law To Find The Third Missing Value. Ohms Law Is Used Extensively in ElectronicsDocument3 pagesOhms Law To Find The Third Missing Value. Ohms Law Is Used Extensively in ElectronicsDarius Dave CruzNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law Relationship Between Series Parallel CircuitsDocument4 pagesOhm's Law Relationship Between Series Parallel CircuitsNur FarahidaNo ratings yet
- 6.verification of Ohms LawDocument2 pages6.verification of Ohms Laweee departmentNo ratings yet
- BS Labortary PH-193 by UsmanDocument19 pagesBS Labortary PH-193 by UsmanMuhammad Usman MalikNo ratings yet
- Rishav Dugar 19IM3FP30: Name: Roll NumberDocument5 pagesRishav Dugar 19IM3FP30: Name: Roll NumberS VrNo ratings yet
- Physics 221 Experiment 3: Simple DC Circuits and Resistors: October 1, 2008Document6 pagesPhysics 221 Experiment 3: Simple DC Circuits and Resistors: October 1, 2008lady GNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Lab FileDocument44 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Lab File032AkritiNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit FundamentalsDocument19 pagesElectric Circuit FundamentalsSana NgaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2. Achieve Ohm's Law The Used DevicesDocument1 pageExperiment 2. Achieve Ohm's Law The Used Devicesبلسم محمود شاكرNo ratings yet
- Verify Ohm's Law with Resistive CircuitsDocument4 pagesVerify Ohm's Law with Resistive Circuitshack AWKNo ratings yet
- Fow Seng Joe (B1757) - Lab 2 IEEDocument12 pagesFow Seng Joe (B1757) - Lab 2 IEERobert Fow JOENo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law 1Document5 pagesOhm's Law 1rajesh_patel_007No ratings yet
- JC6TD4N7 Lab2Document8 pagesJC6TD4N7 Lab2Emre SelviliNo ratings yet
- تقرير مختبر الكهرباء 1Document6 pagesتقرير مختبر الكهرباء 1ali dhiaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document9 pagesLab Report 1Moad AbusninaNo ratings yet
- To Verify Ohm's Law: ObjectiveDocument4 pagesTo Verify Ohm's Law: ObjectiveNasirAbbasNo ratings yet
- I V I 1/R I V/R V Ir: Department of Mechanical Engineering Djj20053: Electrical TechnologyDocument5 pagesI V I 1/R I V/R V Ir: Department of Mechanical Engineering Djj20053: Electrical TechnologyMohd ZahiruddinNo ratings yet
- Verify Ohm's Law ExperimentDocument2 pagesVerify Ohm's Law ExperimentKishlay KishoreNo ratings yet
- LAB Manual (EEE)Document27 pagesLAB Manual (EEE)imtiaz hossainNo ratings yet
- مختبر ابلايد2Document6 pagesمختبر ابلايد2عبد الرحمن أبوخاطر, أبو رزقNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No 2Document3 pagesLaboratory Exercise No 2John Clement HusainNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document9 pagesLab Report 1Hajer JejeNo ratings yet
- Experiment No-1 Objective: - Equipment RequiredDocument3 pagesExperiment No-1 Objective: - Equipment RequiredwondieNo ratings yet
- Testing Kirchhoff's Laws ExperimentallyDocument13 pagesTesting Kirchhoff's Laws ExperimentallyVenus IlaganNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic EngineeringDocument8 pagesElectrical and Electronic Engineeringخہٰہٰالہٰد ۦ' ۦ'No ratings yet
- OhmslawDocument17 pagesOhmslawBright OvieNo ratings yet
- Experiment No Experiment Name ObjectiveDocument12 pagesExperiment No Experiment Name ObjectiveZareen Rashid ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- شيت مختبر الاسس PDFDocument23 pagesشيت مختبر الاسس PDFMohamad AlhadithyNo ratings yet
- Newloydlab 28Document10 pagesNewloydlab 28marthabervellyNo ratings yet
- Verification of Ohm's Law: Experiment No# 02Document3 pagesVerification of Ohm's Law: Experiment No# 02Saad AliKhan50% (2)
- Physics Practical FinalDocument27 pagesPhysics Practical Finalsanjuktabhoi461No ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Lab1Document44 pagesElectrical Circuit Lab1rahmahamjad90No ratings yet
- Experiment NO.3Document7 pagesExperiment NO.3Yasmeen Yaseen tahaNo ratings yet
- Labs For Verification of Ohms Law Series and Parallel CircuitsDocument9 pagesLabs For Verification of Ohms Law Series and Parallel Circuitshuzaifaalisiddiqui270No ratings yet
- Independent University, Bangladesh (IUB) : Experiment No: 02 Experiment Name: Verification of Ohm's Law ObjectiveDocument9 pagesIndependent University, Bangladesh (IUB) : Experiment No: 02 Experiment Name: Verification of Ohm's Law ObjectiveHridoy SarkarNo ratings yet
- Procedure: ExperimentDocument2 pagesProcedure: ExperimentRatnadeep PaulNo ratings yet
- Aim of ProjectDocument5 pagesAim of Projectaayush sinhaNo ratings yet
- Objective: The Resistor's Current I Is Equal To The Resistor's Voltage (V) Divided by The Resistance RDocument4 pagesObjective: The Resistor's Current I Is Equal To The Resistor's Voltage (V) Divided by The Resistance RHilal ErgünNo ratings yet
- Ohms Law PDFDocument44 pagesOhms Law PDFKeenjhar AyoobNo ratings yet
- Circuits LoveDocument10 pagesCircuits LoveMabethNo ratings yet
- Circuits Unit 2Document39 pagesCircuits Unit 2Mohamed A. HusseinNo ratings yet
- Learn Ohm's Law and Calculate Circuit ValuesDocument2 pagesLearn Ohm's Law and Calculate Circuit ValuesMat DaimNo ratings yet
- Electricity Lab Alan ArifDocument7 pagesElectricity Lab Alan ArifAlan ZaxoNo ratings yet
- Current Is Charge/unit Time, We See That Voltage Current Is Work/timeDocument6 pagesCurrent Is Charge/unit Time, We See That Voltage Current Is Work/timekranti29No ratings yet
- Ohm's Law Experiment Verifies Direct Proportionality Between Voltage and CurrentDocument4 pagesOhm's Law Experiment Verifies Direct Proportionality Between Voltage and CurrentJjjjNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law - Online - PHET PieroDocument9 pagesOhm's Law - Online - PHET PieroCarlos A. Villanueva Hilaro0% (1)
- Informe Laboratorio Ley de Ohm SDocument8 pagesInforme Laboratorio Ley de Ohm S0232120029 DANIELA ACEVEDO GONZALEZ ESTUDIANTE ACTIVONo ratings yet
- Electronics and Communication Circuits Lab. Experiment #2 Ohm'S LawDocument4 pagesElectronics and Communication Circuits Lab. Experiment #2 Ohm'S LawEng. Ahmad ELsamakNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument3 pagesOhm's LawqwerNo ratings yet
- Practical For Ohm's LawDocument3 pagesPractical For Ohm's LawIshanNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law AnimationDocument3 pagesOhm's Law Animationholisticwarehou94No ratings yet
- Ohms Law and Kirchhoffs Law Lab ReportDocument8 pagesOhms Law and Kirchhoffs Law Lab Reportlove to readNo ratings yet
- Eee 1102Document26 pagesEee 1102Rayhanul Islam LamunNo ratings yet
- What Is Ohm's Law Definition, Formula, Graph & LimitationsDocument10 pagesWhat Is Ohm's Law Definition, Formula, Graph & LimitationsjackNo ratings yet
- Verification of Ohm's LawDocument4 pagesVerification of Ohm's LawApu SarkarNo ratings yet
- AP Lab 12Document7 pagesAP Lab 12muhammad arslanNo ratings yet
- AP Lab 04Document4 pagesAP Lab 04muhammad arslanNo ratings yet
- AP Lab 01Document4 pagesAP Lab 01muhammad arslanNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 DSADocument7 pagesLab 6 DSAmuhammad arslanNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 DsaDocument10 pagesLab 3 Dsamuhammad arslanNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 DsaDocument7 pagesLab 2 Dsamuhammad arslanNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Grade 8 Science Worksheets Excluding STE 2Document26 pagesConsolidated Grade 8 Science Worksheets Excluding STE 2Sofia Abella100% (1)
- Ppt. On Transformer WindingsDocument23 pagesPpt. On Transformer WindingsSandhya Rathore100% (2)
- As 3007.1 - Electrical InstallationsDocument12 pagesAs 3007.1 - Electrical Installationsduckman2009No ratings yet
- Checkliste Druck en FD A9Document1 pageCheckliste Druck en FD A9Anonymous ggRTHDKe6No ratings yet
- JBL PRX425.v2Document2 pagesJBL PRX425.v2Edwin Mamani QuispeNo ratings yet
- DK Medical System ELMO-T3 X-ray Generator SpecsDocument2 pagesDK Medical System ELMO-T3 X-ray Generator SpecsFachrurazy Ismail100% (1)
- 8THDocument11 pages8THPiyush KumarNo ratings yet
- Hoja de Datos - Pararrayos Ohio BrassDocument12 pagesHoja de Datos - Pararrayos Ohio BrassVicente ColvenNo ratings yet
- TK 40D - Ver2manual 1Document2 pagesTK 40D - Ver2manual 1GigiNo ratings yet
- Thaumaturgy in v5Document9 pagesThaumaturgy in v5Yency TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Egat Smart Grid Roadmap Rev2Document37 pagesEgat Smart Grid Roadmap Rev2Lance Vanderhaven100% (1)
- 03HYUNDAI Intelligent Preventative Diagnostic System (HiPDS)Document12 pages03HYUNDAI Intelligent Preventative Diagnostic System (HiPDS)juliancansenNo ratings yet
- Experimental Studies On The Plasma Bullet Propagation and Its InhDocument8 pagesExperimental Studies On The Plasma Bullet Propagation and Its InhvenuanandNo ratings yet
- SCR 50kW Fast ChargerDocument6 pagesSCR 50kW Fast ChargerDeepak GehlotNo ratings yet
- The Role of GOvernment To Develop Solar Energy Industry in Indonesia - Ministry of IndustryDocument18 pagesThe Role of GOvernment To Develop Solar Energy Industry in Indonesia - Ministry of IndustryBambangNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Generators, Protection Schemes, Relays and MaintenanceDocument44 pagesIntroduction to Generators, Protection Schemes, Relays and MaintenancerahulNrana100% (1)
- DC Machines: Faraday's Laws and ConstructionDocument34 pagesDC Machines: Faraday's Laws and ConstructionSaravanan T YNo ratings yet
- OPGW Our Experience in KESCDocument6 pagesOPGW Our Experience in KESCjorge plaNo ratings yet
- Product Specifications: DBXLH-6565S-T0MDocument4 pagesProduct Specifications: DBXLH-6565S-T0MRaluca Roxana SzaszNo ratings yet
- Black Decker VP 331 DustbusterDocument17 pagesBlack Decker VP 331 DustbusterKavita VliegheNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Circuit Breaker (VCB) Working and ApplicationsDocument11 pagesVacuum Circuit Breaker (VCB) Working and ApplicationsMoe Oo KoNo ratings yet
- DEFRA Electric Fencing ManualDocument41 pagesDEFRA Electric Fencing Manualgrahamcox_81No ratings yet
- Be Electrical 7 Sem PLC and Scada Application P (08) Dec 2016 PDFDocument3 pagesBe Electrical 7 Sem PLC and Scada Application P (08) Dec 2016 PDFParesh MahajanNo ratings yet
- Sistec Major Project Report Microcontroller Enabled Speaking System For Deaf and DumbDocument32 pagesSistec Major Project Report Microcontroller Enabled Speaking System For Deaf and Dumbukpandey2580% (5)
- Transformer Differential Protection ANSI Code 87 TDocument4 pagesTransformer Differential Protection ANSI Code 87 TFarooq KhanNo ratings yet
- MultiLoad II SMP Installation Guide v1-2Document56 pagesMultiLoad II SMP Installation Guide v1-2Javierfox98No ratings yet
- Si 7636 DPDocument12 pagesSi 7636 DPnhbrNo ratings yet
- Method of Procedure MOP FormDocument10 pagesMethod of Procedure MOP FormmarcipomoyfanNo ratings yet
- FCU - FAT CONTROLLERS (Fan Coil Unit - Fan Air Terminal) Model CU780Document1 pageFCU - FAT CONTROLLERS (Fan Coil Unit - Fan Air Terminal) Model CU780vineethNo ratings yet
- W79E2051 Chip Controls LED Meteor Shower SimulationDocument2 pagesW79E2051 Chip Controls LED Meteor Shower SimulationLaurentiu IacobNo ratings yet