Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ACTIVITY 1 Microscope
Uploaded by
Castolo Bayucot Jvjc100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
190 views2 pagesOriginal Title
ACTIVITY 1 microscope
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
190 views2 pagesACTIVITY 1 Microscope
Uploaded by
Castolo Bayucot JvjcCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
NAME: ___________________________ _______DATE:___________ PARENT’S SIGNATURE:_________
SUBJECT: Science7 Section: ________________ TEACHER: ____________________________SCORE: _____
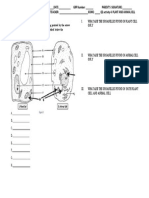
QUIZ 1. PARTS OF A MICROSCOPE Arrange the scrambled letters in order to identify the parts of the
Microscope. Write your answers beside the number.
It allows you to see things that cannot be seen by the unaided eyes.
______________ and _______________ produced the first compound microscope In 1608.
_____________________________ (1632-1723) was able to make a Compound microscope
A __________________ is a tool that provides an enlarged image of an object. that had a higher magnification than early compound microscopes.
NAME: ___________________________ _______DATE:___________ PARENT’S SIGNATURE:_________
SUBJECT: Science7 Section: ________________ TEACHER: ____________________________SCORE: _____
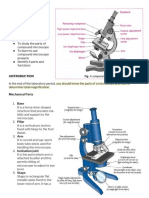
QUIZ 2: PARTS AND FUNCTION OF A MICROSCOPE
1. It is a tool which can help us see tiny objects and living organisms making them look
bigger.
A. Kaleidoscope B. Microscope C. Periscope D. Telescope II. Write the correct answer in the blank.
2. Which of the following instruments would you use to see a plant cell? ________________1. It allows the viewer to look at the enlarged
A. Kaleidoscope B. Microscope C. PeriscopeD. Telescope image of the specimen
3. It holds the objective lenses. _______________2. It supports the eyepiece
A. Adjustment knob B. Aperture C. Diaphragm D. Nosepiece _______________3. It allows the shifting of the objectives;
4. Which two parts of the light microscope magnify the image of an object? It holds the objectives
A. Eyepiece and mirror B. Eyepiece and objective _______________4. What kind of objectives that has (3x, 4x, 5x) – The shortest Objective
C. Objectives and mirror D. Objectives and diaphragm
_______________5. It has (40x, 43x or 60x) which allows you to see the detailed parts of the
5. Which statement below describes the function of the diaphragm?
A. It regulates the amount of light reflected in the object being viewed. specimen
B. It reflects light from the mirror, objects to be observed, and lenses. _________________6. It has (97x or 100x) – requires the use of oil used to view bacteria,
C. It changes the amount of light reflected. fungi and protists.
D. It focuses on the specimens in the glass slide. _______________7. It focuses the specimen under the scanner and objectives. It also
6. Which of the following is NOT a mechanical part of the microscope? facilitates the movement of the body tube up and down
A. Arm B. Base C. Body tube D. Diaphragm _______________8. It focuses the specimen under the high power objective and the oil-
7. What is the function of the mirror in a microscope? immersion objective.
A. It reflects light up the microscope. B. It captures light from the wall. _______________9. It reflects the light onto the specimen for viewing
C. It refracts light. D. It bends light. _______________10. It holds the glass slide in place.
8. The following are the mechanical parts of the microscope, EXCEPT: _______________11. This is where the glass slide is mounted
A. Arm B. Eyepiece C. Draw tube D. Nosepiece
_______________12. It allows you to tilt the microscope into different angles
9. How many objectives does the compound microscope have?
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 _______________13. It regulates the amount of light that will pass through the stage.
10. It allows movement of the body tube upward or downward. _______________14. It allows you to tilt the microscope into different angles.
A. Adjustment knob B. Coarse Adjustment C. Eyepiece D. Stage _______________15. It supports the entire body of the microscope
You might also like
- Lesson Plan in Science 7Document4 pagesLesson Plan in Science 7angeline vacalaresNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter Summative Test-MDL Science VII S.Y. 2021-2022Document4 pagesSecond Quarter Summative Test-MDL Science VII S.Y. 2021-2022ShengNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 7 Test BankDocument3 pagesScience Grade 7 Test BankAlisha EnguanchoNo ratings yet
- 03 Biological OrganizationDocument2 pages03 Biological OrganizationIrish May TroyoNo ratings yet
- Procedure: Activity 2: Where in The World Is The Philippines? Part IiDocument28 pagesProcedure: Activity 2: Where in The World Is The Philippines? Part Iisamn cadNo ratings yet
- Quiz LRMDS Nature and Properties of LightDocument3 pagesQuiz LRMDS Nature and Properties of Lightambermikaela.siNo ratings yet
- Microscope Review GuideDocument34 pagesMicroscope Review GuideWwwanand111100% (1)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7 A Lesson Plan For Grade 7 October 09, 2018 I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7 A Lesson Plan For Grade 7 October 09, 2018 I. ObjectivesRiza Gabaya AliaNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Quarter 2 Plant and AnimalDocument6 pagesScience 7 Quarter 2 Plant and AnimalMelerose Dela SernaNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work in Science: Quarter: 3rd Grade Level: Grade 7 School: M.B. Asistio Sr. High School - MainDocument2 pagesBudget of Work in Science: Quarter: 3rd Grade Level: Grade 7 School: M.B. Asistio Sr. High School - MainRowena Sta MariaNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7 I. Learning ObjectivesDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 7 I. Learning ObjectivesRene Rulete MapaladNo ratings yet
- Elements vs CompoundsDocument4 pagesElements vs CompoundsRommel Dayson100% (1)
- Test Question 3rd ScienceDocument4 pagesTest Question 3rd ScienceClarissa Cudal ReboredoNo ratings yet
- Module 4 G7 Science Q1 Wk6Document16 pagesModule 4 G7 Science Q1 Wk6Ryza GloryNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion Test Grade 7 Science: A B C DDocument3 pagesForces and Motion Test Grade 7 Science: A B C DHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 1 - Science 7 - Second Quarter - Topic 1 - MicrosDocument3 pagesWORKSHEET 1 - Science 7 - Second Quarter - Topic 1 - MicrosMary Shaynah Jungwirth100% (1)
- Science 7 - Quarter 2 - Week 4 Learning Activity SheetDocument4 pagesScience 7 - Quarter 2 - Week 4 Learning Activity SheetTricia BrunoNo ratings yet
- Science 7-Module 1: Virgen Delas Flores High SchoolDocument2 pagesScience 7-Module 1: Virgen Delas Flores High SchoolMon Eric LomedaNo ratings yet
- DLL G7 Lesson 4 Levels of OrganizationDocument3 pagesDLL G7 Lesson 4 Levels of OrganizationJeffrey Selpo BondadNo ratings yet
- Science Quiz Q1Document1 pageScience Quiz Q1Mira Comendador BantilanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer Lesson PlanMaria Allen Ann CasilihanNo ratings yet
- " Seasons": Grade 7 Learner's Material, Internet, Compiled Notes Grade 7 Science Links Pp. 355-356Document11 pages" Seasons": Grade 7 Learner's Material, Internet, Compiled Notes Grade 7 Science Links Pp. 355-356Romeo Gabitanan JrNo ratings yet
- Table of Specifications for Science 8 2nd Quarter ExamDocument18 pagesTable of Specifications for Science 8 2nd Quarter ExamAraceli Manzano-edeleonNo ratings yet
- LANDMASSES AND BODIES OF WATER Simple Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesLANDMASSES AND BODIES OF WATER Simple Detailed Lesson PlanMonica Grace ManaloNo ratings yet
- Sta. Rosa, Lapu-Lapu City, Cebu PhilippinesDocument8 pagesSta. Rosa, Lapu-Lapu City, Cebu PhilippinesMet XiiNo ratings yet
- 04 Pyramid Biological Organization ProjectDocument2 pages04 Pyramid Biological Organization ProjectIrish May TroyoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 7Document4 pagesLesson Plan in Science 7Nelly Ballejos100% (1)
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan IN Grade 7 SCIENCE: Prepared byDocument20 pagesA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan IN Grade 7 SCIENCE: Prepared byM-j DimaporoNo ratings yet
- 4th-Quarter-G7 Weekly LPDocument5 pages4th-Quarter-G7 Weekly LPArze IdleNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science7 2nd QuarterDocument28 pagesDLL - Science7 2nd QuarterJOCELYN HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science Activity on Saturated and Supersaturated SolutionsDocument8 pagesGrade 7 Science Activity on Saturated and Supersaturated SolutionsAnna Marie Ledesma UrrutiaNo ratings yet
- Science 7-2ND QUATER EXAMDocument4 pagesScience 7-2ND QUATER EXAMVincent S. RedolosaNo ratings yet
- DAILY LESSON LOG Week 3 Science 7Document3 pagesDAILY LESSON LOG Week 3 Science 7Matet GenerosaNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Quarterly ExamDocument6 pagesScience 7 Quarterly Examjoan marie PeliasNo ratings yet
- How To Use A MicroscopeDocument102 pagesHow To Use A MicroscopeDarlene Joyce ApolinarioNo ratings yet
- GRADE 7 DLL - Week 1Document7 pagesGRADE 7 DLL - Week 1Shaynie Mhe Amar AntonioNo ratings yet
- L PDocument3 pagesL Panon_987644252No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesLesson PlanJoanna Marie Guillano LabordoNo ratings yet
- Locating Places q4 Module 1Document21 pagesLocating Places q4 Module 1Sweetie Wilgee Rose ViñaNo ratings yet
- DLL G7 Lesson 5 MicroscopeDocument3 pagesDLL G7 Lesson 5 MicroscopeJeffrey Selpo Bondad100% (1)
- Scientific Process: The Heart of ScienceDocument9 pagesScientific Process: The Heart of ScienceFitz BaniquedNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 7: Name of Teacher: Joy Marie M. Abarquez School: Antonio R. Lapiz National High SchoolDocument2 pagesLesson Plan in Science 7: Name of Teacher: Joy Marie M. Abarquez School: Antonio R. Lapiz National High SchoolJeraldine RepolloNo ratings yet
- Grade 7Document36 pagesGrade 7Yanika BarasNo ratings yet
- Transparent Opaque and TranslucentDocument2 pagesTransparent Opaque and Translucentapi-349353506No ratings yet
- Week1 DLL ScienceDocument7 pagesWeek1 DLL ScienceLeo NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- LeaP-Science-G7-Week 8-Q3Document4 pagesLeaP-Science-G7-Week 8-Q3CriselAlamagNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Log in Science: Tigwi National High SchoolDocument4 pagesDaily Lesson Log in Science: Tigwi National High SchoolEdlhen Moreno JalacNo ratings yet
- GRADE 7 FINALS 3rd Grading (With Answers)Document4 pagesGRADE 7 FINALS 3rd Grading (With Answers)Dabe Genesis Ligalig100% (1)
- SAMPLE - 3rd Quarter 2nd Summative Test SOUND WAVESDocument2 pagesSAMPLE - 3rd Quarter 2nd Summative Test SOUND WAVESLudi Jane TorrefrancaNo ratings yet
- July 5Document2 pagesJuly 5Immanuel GranadaNo ratings yet
- Science 8 2nd Quiz 2 Understanding TyphoonDocument3 pagesScience 8 2nd Quiz 2 Understanding TyphoonRyan BersaminNo ratings yet
- Earth and Space 7Document6 pagesEarth and Space 7Martinez JoemNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science Lesson on MonsoonsDocument5 pagesGrade 7 Science Lesson on Monsoonsjen mcbrideNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 9 - Philippine ClimateDocument1 pageWorksheet 9 - Philippine ClimateVanessa Rose Rota100% (1)
- Activity 1+2 - Seperation Technique.Document1 pageActivity 1+2 - Seperation Technique.Usman Mukhtar Abbasi0% (1)
- Fertilization in Flowering PlantsDocument6 pagesFertilization in Flowering PlantsJeffrey Selpo BondadNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document5 pagesModule 6Sandy CarbonillaNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Paete Paete, Laguna: ScoreDocument1 pageLiceo de Paete Paete, Laguna: ScoreMaricar Leonida BalbuenoNo ratings yet
- You Need To Know All of This Plus How To Write A Hypothesis and How To Make Scientific Data Tables and GraphsDocument2 pagesYou Need To Know All of This Plus How To Write A Hypothesis and How To Make Scientific Data Tables and GraphsKaiNo ratings yet
- Using Microscopes to Examine SpecimensDocument1 pageUsing Microscopes to Examine SpecimensMarian Alexis Fernandez100% (1)
- Science7 Q2 M1A v4 No Key AnswerDocument11 pagesScience7 Q2 M1A v4 No Key AnswerCastolo Bayucot Jvjc100% (1)
- Activity 4 Plant and Animal CellDocument1 pageActivity 4 Plant and Animal CellCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Levels of biological organization quizDocument3 pagesLevels of biological organization quizCastolo Bayucot Jvjc100% (1)
- Q2 Long Test 2 Levels of Biological OrganizationDocument4 pagesQ2 Long Test 2 Levels of Biological OrganizationCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Spotlight LetterDocument1 pageSpotlight LetterCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Science7 Q2 M3 V4no Key AnswerDocument26 pagesScience7 Q2 M3 V4no Key AnswerCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Welcome GCPSDocument1 pageWelcome GCPSCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Mancom FinalDocument5 pagesMancom FinalCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Q2 LONG TEST 1 MicroscopeDocument5 pagesQ2 LONG TEST 1 MicroscopeCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- On LRMD PortalDocument22 pagesOn LRMD PortalCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Q2 4TH PerformanceDocument1 pageQ2 4TH PerformanceCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Summary of Scores BlankDocument2 pagesSummary of Scores BlankCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Q3 Assessment ReviewDocument4 pagesScience 7 Q3 Assessment ReviewCastolo Bayucot Jvjc0% (1)
- Tupsan National High School Quarter 2 Grading SheetDocument21 pagesTupsan National High School Quarter 2 Grading SheetCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Unpacking of MELCS Science 7Document1 pageUnpacking of MELCS Science 7Castolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Bondpaper RequestDocument5 pagesBondpaper RequestCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science CG-unpacked-objectivesDocument28 pagesGrade 7 Science CG-unpacked-objectivesSherCabs100% (5)
- At The Back For Performance No. 4Document1 pageAt The Back For Performance No. 4Castolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Enrolment Grade 8 2020 2021Document14 pagesConsolidated Enrolment Grade 8 2020 2021Castolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- DepEd LAS Template - Sample Learning Activity Sheet for TeachersDocument1 pageDepEd LAS Template - Sample Learning Activity Sheet for TeachersMelba Alferez100% (1)
- Tupsan National High School Teacher's Weekly ActivitiesDocument2 pagesTupsan National High School Teacher's Weekly ActivitiesCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Journey Into The CellDocument27 pagesJourney Into The CellCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Income Generating Project ProposalDocument2 pagesIncome Generating Project ProposalJovenil Bacatan90% (104)
- Lesson Plan TemplateDocument2 pagesLesson Plan TemplateCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Individual Workweek Target and Accomplishment ReportDocument7 pagesDepartment of Education: Individual Workweek Target and Accomplishment ReportCastolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The Philippines Region X Division of Camiguin Mambajao, CamiguinDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The Philippines Region X Division of Camiguin Mambajao, CamiguinCastolo Bayucot Jvjc75% (4)
- DepEd LAS Template - Sample Learning Activity Sheet for TeachersDocument1 pageDepEd LAS Template - Sample Learning Activity Sheet for TeachersMelba Alferez100% (1)
- Individual Workweek Accomplishment Report 2020Document3 pagesIndividual Workweek Accomplishment Report 2020Castolo Bayucot JvjcNo ratings yet
- DepEd LAS Template - Sample Learning Activity Sheet for TeachersDocument1 pageDepEd LAS Template - Sample Learning Activity Sheet for TeachersMelba Alferez100% (1)
- MIBO-111 PracticalDocument55 pagesMIBO-111 PracticalShinchan DoremonNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument10 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitologynelle adriatico100% (1)
- Ice Cream StructureDocument11 pagesIce Cream StructureHon Le VanNo ratings yet
- Pe 300 White Datasheet PDFDocument3 pagesPe 300 White Datasheet PDFtek5No ratings yet
- TEM Manual - JEOL-2100 PDFDocument179 pagesTEM Manual - JEOL-2100 PDFAnonymous gx9eFIe8No ratings yet
- Manual de Usuario Microscopio Carl-Zeiss Opmi-Pico OrlDocument278 pagesManual de Usuario Microscopio Carl-Zeiss Opmi-Pico OrlAlejandroNo ratings yet
- IRPrestige 21Document24 pagesIRPrestige 21FA MonsterNo ratings yet
- ESA SME Initiative Course D:MaterialsDocument64 pagesESA SME Initiative Course D:MaterialsJoseph JonathanNo ratings yet
- A Complete Microscope HistoryDocument3 pagesA Complete Microscope HistoryPechey FernandezNo ratings yet
- Catalogo General Microscopios OpticosDocument22 pagesCatalogo General Microscopios OpticosValentina HerreraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biology Lab & Class Activity WorksheetsDocument133 pagesIntroduction To Biology Lab & Class Activity WorksheetsNick PiresNo ratings yet
- BX51WI/BX61WI Fixed Stage Upright MicroscopeDocument8 pagesBX51WI/BX61WI Fixed Stage Upright MicroscopestreetcribdealerNo ratings yet
- Microbiology An Evolving Science 4th Edition Slonczewski Test BankDocument18 pagesMicrobiology An Evolving Science 4th Edition Slonczewski Test BankLaurenThompsonnfcqy100% (17)
- Tic-Tac-Toe Menu Choice BoardDocument1 pageTic-Tac-Toe Menu Choice Boardapi-621917909No ratings yet
- Medical Microbiology Specialist Portfolio V4.2reference Copy 2Document137 pagesMedical Microbiology Specialist Portfolio V4.2reference Copy 2cookiedaniel6No ratings yet
- Analysis of Surface Roughness of Enamel and Dentin After Laser TreatmentDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Surface Roughness of Enamel and Dentin After Laser TreatmentmustafaNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms and Infection: A History of MicrobiologyDocument28 pagesMicroorganisms and Infection: A History of MicrobiologySai KunchalaNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of a Compound Microscope - S7 Module 1Document69 pagesParts and Functions of a Compound Microscope - S7 Module 1AURORA () CARIAGANo ratings yet
- Electron MicroscopeDocument12 pagesElectron Microscopekhuki saikiaNo ratings yet
- Science7 Q2 M1A v4Document24 pagesScience7 Q2 M1A v4aiza arcilloNo ratings yet
- Lit11 ReportDocument6 pagesLit11 ReportAlexis RamirezNo ratings yet
- Journal in Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - PlantDocument14 pagesJournal in Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - PlantYuliyaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of vaccination vial confirms presence of graphene nanoparticlesDocument20 pagesAnalysis of vaccination vial confirms presence of graphene nanoparticlesnionmaNo ratings yet
- Wet Mount Technique PDFDocument2 pagesWet Mount Technique PDFCheLimOrton100% (1)
- M.Sc. Physics University Department MS 403 - Characterization of MaterialsDocument15 pagesM.Sc. Physics University Department MS 403 - Characterization of MaterialsFast FeneNo ratings yet
- Phased Array ASNTDocument92 pagesPhased Array ASNTMohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Glass TechnologyDocument5 pagesResearch Paper On Glass Technologygz7gh8h0100% (1)
- General Biology Laboratory ModuleDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology Laboratory ModuleEunice Moureen MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Imperfections in Solids: Issues To Address..Document53 pagesImperfections in Solids: Issues To Address..jose antonio villena medinaNo ratings yet
- Experienced Test, Measurement, and Automation System Developer Seeking New OpportunitiesDocument4 pagesExperienced Test, Measurement, and Automation System Developer Seeking New Opportunitiesrizwansurti1No ratings yet