Professional Documents
Culture Documents
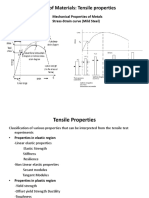
Quiz 7 Mechanical Properties of Metals
Uploaded by
Vince Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesThis document discusses various mechanical properties of metals including:
- Elastic deformation is a reversible change in shape due to applied stress, while plastic deformation causes a permanent change in shape.
- Toughness refers to a material's ability to absorb energy and deform plastically before fracturing. Yield strength is the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically.
- Fatigue is the tendency of materials to fail after repeated cyclic loading, even at stress levels below the yield strength.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various mechanical properties of metals including:
- Elastic deformation is a reversible change in shape due to applied stress, while plastic deformation causes a permanent change in shape.
- Toughness refers to a material's ability to absorb energy and deform plastically before fracturing. Yield strength is the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically.
- Fatigue is the tendency of materials to fail after repeated cyclic loading, even at stress levels below the yield strength.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesQuiz 7 Mechanical Properties of Metals
Uploaded by
Vince CruzThis document discusses various mechanical properties of metals including:
- Elastic deformation is a reversible change in shape due to applied stress, while plastic deformation causes a permanent change in shape.
- Toughness refers to a material's ability to absorb energy and deform plastically before fracturing. Yield strength is the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically.
- Fatigue is the tendency of materials to fail after repeated cyclic loading, even at stress levels below the yield strength.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Quiz 7 Mechanical Properties of Metals
This is a change of the shape of the body as a reaction to applied stress.
-elastic deformation
Time dependent recoverable deformation under load is called ____________ deformation.
-anelastic
It is the ability of a material to absorb energy and plastically deform before fracturing.
-toughness
A good malleable material possesses
- high degree of plasticity
It is known as the relationship between engineering stress and engineering strain for elastic deformation (tension
and compression).
-Hooke’s Law
The permanent mode of deformation of a material known as
- plasticity
It is the resistance of a material to breaking under tension.
-Tensile strength
The capacity of a material to absorb energy when it is deformed elastically and then, upon unloading, to have this
energy recovered.
-resilience
The net movement of anything generally from a region of a higher concentration to a region lower concentration.
-diffusion
Charpy’s V notch test is done on a building material to determine
-brittleness
Strain energy stored in a material when it is strained within its elastic limit is termed as
-resilience
It is used to determine how materials will behave under tension load,
-tension test
Elastic deformation is
-nonpermanent
It refers to the degree of deformation that a material withstands in the direction of applied forces
-shear stress
The ability of materials to develop a characteristic behavior under repeated loading known as
-fatigue
The tendency of a material to fracture without appreciable deformation is called
-brittleness
This is the stress at the maximum on the engineering stress-strain curve
-tensile strength
This is a variation of pure shear in which a structural member is twisted in the manner.
-torsion
The ability of a material to resist plastic deformation known as
-yield strength
It is particularly desirable in the materials which are subjected to shock loading.
-toughness
Deformation that occurs due to stress over a period of time is known as
-creep
Resistance of a material against any external force is termed as
-strength
Elastic deformation is
-nonpermanent
It is defined as load per unit area.
-stress
They produce a rotational motion about the longitudinal axis of one end of the member
relative to the other end.
-torsional forces
Time-dependent permanent deformation is called
-creep
This is the ratio of the stress in a body to the corresponding strain.
-modulus of elasticity
Ductility may be expressed quantitatively as either percent elongation or percent
reduction in
-area
The ability of a material to be formed by hammering or rolling is known as
-malleability
The failure of the material due to cyclic loads is known as
-fatigue
Elastic-plastic transition, the point of yielding may be determined as the initial departure from linearity of the stress-
strain curve; this is sometimes called the
-proportional limit
It is the degree of plastic deformation at fracture.
-ductility
This test is conducted in a manner similar to the tensile test, except that the force is compressive and the specimen
contracts along the direction of the stress.
-compression test
The stress corresponding to the intersection of this line and the stress–strain curve as it bends over in the plastic
region is defined as the
-yield strength
The deformation in which stress and strain are proportional is called
-elastic
Their role is to determine stresses and stress distributions within members that are subjected to well-defined loads.
-structural engineers
This is the equivalent of the applied uniaxial tensile or compressive force at time.
-engineering stress
It is a measure of a material’s resistance to localized plastic deformation
-hardness
This is the law of elasticity.
- Hooke’s law
The ability of a material to absorb energy in the elastic region is called
-resilience
You might also like
- Stainless SteelDocument162 pagesStainless SteelNavya AnilNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1E - Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument24 pagesCHEM 1E - Mechanical Properties of MaterialsYani BongatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 and 2Document22 pagesLesson 1 and 2Mark MarkNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document59 pagesModule 2STEPHEN VILLARUZNo ratings yet
- "Mechanical Properties": September 2016Document18 pages"Mechanical Properties": September 2016Eric LamNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of PolymersDocument45 pagesMechanical Properties of PolymersJulian de Lara100% (3)
- Testing of Materials: Tensile Properties: Mechanical Properties of Metals Stress-Strain Curve (Mild Steel)Document17 pagesTesting of Materials: Tensile Properties: Mechanical Properties of Metals Stress-Strain Curve (Mild Steel)Srushti MNo ratings yet
- EMATPPTWEEK7Document25 pagesEMATPPTWEEK7Raniel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Construction Materials and TestingDocument16 pagesConstruction Materials and TestingAvis pittNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument17 pagesDocumentRizwan ArshadNo ratings yet
- Ems NotesDocument8 pagesEms NotesCynosure SkyNo ratings yet
- CE 3133 Chapter 2 Mechanical Behavior and Testing ProceduresDocument5 pagesCE 3133 Chapter 2 Mechanical Behavior and Testing ProceduresCharles DemaalaNo ratings yet
- University of Technology Chemical Engineering Oil and Refining BranchDocument13 pagesUniversity of Technology Chemical Engineering Oil and Refining Branchجعفر ذيابNo ratings yet
- Destructive Testing: TypesDocument26 pagesDestructive Testing: TypesIan DinglasanNo ratings yet
- Rezistenta MetalelorDocument7 pagesRezistenta Metalelorion_senNo ratings yet
- A.Mechanical Properties of Engineering Materials: F/A F/ADocument11 pagesA.Mechanical Properties of Engineering Materials: F/A F/AsrknotesNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument7 pagesStrength of Materialsletter_ashish4444100% (1)
- Ducti IlityDocument5 pagesDucti IlitycharichangNo ratings yet
- Lecture-5: Technological Properties of Metals Steel and Its ClassificationDocument51 pagesLecture-5: Technological Properties of Metals Steel and Its ClassificationSarojKumarSinghNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Basics: Stress (Intensity of Force)Document5 pagesStrength of Materials Basics: Stress (Intensity of Force)mdraikarNo ratings yet
- AST 212 M2 2021 Strength of MaterialsDocument15 pagesAST 212 M2 2021 Strength of MaterialsJessa BadilloNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials ReviewerDocument91 pagesStrength of Materials ReviewerBriant Dominik PongolNo ratings yet
- Architectural Structures Terminologies ReviewersDocument5 pagesArchitectural Structures Terminologies Reviewersbalictar.jyllpatrickNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of SolidDocument22 pagesMechanical Properties of SolidTrillionare HackNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Mechanical PropertiesDocument22 pagesLecture 2 Mechanical PropertiesSunny LeungNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PropertiesDocument3 pagesMechanical PropertiesFederica SoutoNo ratings yet
- Machine Design TerminologiesDocument14 pagesMachine Design TerminologiesJennie Vicenta50% (2)
- ErsdgDocument8 pagesErsdgOlle rrNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument3 pagesMechanical Properties of MaterialsTiras Ngugi0% (1)
- 02 Strength of Materials IntroDocument19 pages02 Strength of Materials IntroEricka HuseñaNo ratings yet
- Structural NotesDocument12 pagesStructural NotesCzareena DominiqueNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MetalsDocument6 pagesMechanical Properties of MetalsvinothenergyNo ratings yet
- Strenght of Material ExplanationDocument7 pagesStrenght of Material ExplanationMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties Lecture Notes - Part 1Document34 pagesMechanical Properties Lecture Notes - Part 1Lester BialogNo ratings yet
- What Is The Upper Limit of Stress That Can Be Reached in The Material of The Beam?Document2 pagesWhat Is The Upper Limit of Stress That Can Be Reached in The Material of The Beam?raja369nareNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument3 pagesMechanical Properties of MaterialsSuyash KhannaNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and CreepDocument14 pagesStrength of Materials and Creepfabyan mayharNo ratings yet
- Mat SciDocument2 pagesMat SciMark RamosNo ratings yet
- BFBM Unit - 3Document38 pagesBFBM Unit - 3Kripa NNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument8 pagesStrength of Materials - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaLeo Kyaw MinNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesStrength of Materials: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAerocfdfreakNo ratings yet
- Chem 131......... 2Document13 pagesChem 131......... 2Nicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- Material Testing 1. Tension TestingDocument5 pagesMaterial Testing 1. Tension TestingcarolineNo ratings yet
- Structural: Question and Answer Samples and TechniquesDocument100 pagesStructural: Question and Answer Samples and TechniquesCasas SweetNo ratings yet
- Stress-Strain CurveDocument8 pagesStress-Strain Curvedani chNo ratings yet
- 03 Properties of Composite MaterilasDocument17 pages03 Properties of Composite MaterilasMD Sunjin AhsunNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document30 pagesLecture 6Mlkhr lgndbNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Engineering MaterialsDocument26 pagesMechanical Properties of Engineering MaterialsJoeNo ratings yet
- Useful Solutions For Standard ProblemsDocument2 pagesUseful Solutions For Standard ProblemsAmjad Khan BanuzaiNo ratings yet
- Diploma Strength of Materials 1st UnitDocument70 pagesDiploma Strength of Materials 1st UnitSuresh BalamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 and 2-1 PDFDocument22 pagesLesson 1 and 2-1 PDFDenver NieverasNo ratings yet
- The Following General Properties Are Important in The Study of Dental MaterialsDocument5 pagesThe Following General Properties Are Important in The Study of Dental MaterialsruchikaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Mechanical PropertiesDocument25 pagesUnit 1 - Mechanical PropertiesPavithra SivanathanNo ratings yet
- MM 212 Materials Evaluation Techniques Fall Semester 2020, FMCE, GIKIDocument39 pagesMM 212 Materials Evaluation Techniques Fall Semester 2020, FMCE, GIKIElbert VonVerimNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials, Also Called Mechanics of Materials, Deals With The Behavior of Solid ObjectsDocument3 pagesStrength of Materials, Also Called Mechanics of Materials, Deals With The Behavior of Solid ObjectsZoe FallurinNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv - Mechanical Testing and CharacterisationDocument259 pagesUnit Iv - Mechanical Testing and CharacterisationDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Biomaterial Stress Strain Curve Lecture 5Document12 pagesBiomaterial Stress Strain Curve Lecture 5mohamedemad.me189No ratings yet
- Strength of Materials ModulesDocument30 pagesStrength of Materials ModulesJaninne SalesNo ratings yet
- The Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingFrom EverandThe Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingNo ratings yet
- 1.) Seiri (Sort or Suriin)Document1 page1.) Seiri (Sort or Suriin)Vince CruzNo ratings yet
- System Safety ProcessDocument1 pageSystem Safety ProcessVince CruzNo ratings yet
- Fire Electrical Machine SafetyDocument1 pageFire Electrical Machine SafetyVince CruzNo ratings yet
- Quiz 8 Electrical PropertiesDocument1 pageQuiz 8 Electrical PropertiesVince CruzNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For CHM 007A - Materials Science and EngineeringDocument9 pagesSyllabus For CHM 007A - Materials Science and EngineeringVince CruzNo ratings yet
- CHM Quiz 6Document2 pagesCHM Quiz 6Vince CruzNo ratings yet
- Fatima WorkDocument6 pagesFatima WorkMaharNadirAliNo ratings yet
- What Is An EarthquakeDocument2 pagesWhat Is An EarthquakeFahad RadiamodaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Statics (Center of Pressure Problem)Document6 pagesFluid Statics (Center of Pressure Problem)nadimduet1No ratings yet
- Cone Penetration TestinCone Penetration TestingDocument9 pagesCone Penetration TestinCone Penetration Testingr0n001No ratings yet
- CAESAR Stress Analysis of GRPDocument3 pagesCAESAR Stress Analysis of GRPA.Subin DasNo ratings yet
- Static Analysis of Functionally Graded Sandwich Plates Using An Efficient and Simple Refined TheoryDocument16 pagesStatic Analysis of Functionally Graded Sandwich Plates Using An Efficient and Simple Refined TheoryGogyNo ratings yet
- Commercial Unit Cooler:Cubic Type: F30HC 622 E 7 N. Units: 1Document2 pagesCommercial Unit Cooler:Cubic Type: F30HC 622 E 7 N. Units: 1วงศกร สิงห์เอี่ยมNo ratings yet
- Astm-F1759 - Hdpe Mahole DesignDocument12 pagesAstm-F1759 - Hdpe Mahole DesignSusanta PanigrahyNo ratings yet
- For Examiner's UseDocument1 pageFor Examiner's UseTanzim RahmanNo ratings yet
- 300+ TOP STRENGTH of Materials Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument36 pages300+ TOP STRENGTH of Materials Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersM/S Sew Infrastructure Ltd100% (1)
- INTER Paper 49-07-03Document13 pagesINTER Paper 49-07-03Ulrich HübnerNo ratings yet
- Type of Structural SteelDocument18 pagesType of Structural SteelaltavanoarNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 2389 1037Document7 pagesPaper 1 2389 1037Intan Anyelir NursanNo ratings yet
- 2001-10 Pages 28-32 PDFDocument5 pages2001-10 Pages 28-32 PDFDavidNo ratings yet
- ETD Assignment Presentation 21Document2 pagesETD Assignment Presentation 21shiva snekhaNo ratings yet
- Dimension Metric Metric/English: Conversion FactorsDocument2 pagesDimension Metric Metric/English: Conversion FactorsValentina Mejia GallonNo ratings yet
- Open Channel Hydraulics Exite Exam (1)Document16 pagesOpen Channel Hydraulics Exite Exam (1)Awad MohammudNo ratings yet
- Lecture Mod 3Document15 pagesLecture Mod 3amlan sahuNo ratings yet
- Toyota BT Traigo 9FBMK20T-35T Chapter 11 (Material Handling) 25-02-2022 Service TrainingDocument15 pagesToyota BT Traigo 9FBMK20T-35T Chapter 11 (Material Handling) 25-02-2022 Service TrainingDennis SteinbuschNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Hydronic System DesignDocument60 pagesFundamentals of Hydronic System DesignNajam24No ratings yet
- Fluid Composition Equilibrium A Proxy FoDocument15 pagesFluid Composition Equilibrium A Proxy FoAhmed GharbiNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study of Rigid Beam-To-Box Column Connections With Types of Internal/external StiffenersDocument16 pagesExperimental Study of Rigid Beam-To-Box Column Connections With Types of Internal/external StiffenersJairo MasaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Fluid MachinesDocument36 pagesHydraulics and Fluid MachinesPmohamedFazilNo ratings yet
- AJ Physics S.3 ENDDocument5 pagesAJ Physics S.3 ENDJohn MUTNo ratings yet
- HT Mobiltherm 600 Series EngDocument2 pagesHT Mobiltherm 600 Series EngJessicaNo ratings yet
- Structures - Problem Sheet Level 2Document5 pagesStructures - Problem Sheet Level 2YogendraKumar100% (1)
- 3 - InfiltrationDocument25 pages3 - InfiltrationBry RamosNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2 - Quiz #2 (Set A) : 1 1-k 1 K 2 1-k 2 KDocument2 pagesThermodynamics 2 - Quiz #2 (Set A) : 1 1-k 1 K 2 1-k 2 KCabagnot Piolo JuliusNo ratings yet
- NPSH Calculator For Process EngineerDocument14 pagesNPSH Calculator For Process Engineerlutfi awnNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Bearing Capacity Driven PileDocument22 pagesAnalysis of Bearing Capacity Driven PileGEOMAHESHNo ratings yet