Professional Documents
Culture Documents
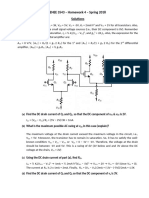
Class Discussion Section B Shockley
Uploaded by
MUSHFIQ UR RAHMAN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views2 pagesThis document summarizes MOSFET transistor operation. It defines key terms like Cox, W, L, Vgs, Vds, Vt. It derives equations for channel charge (Qchannel), drain current (Ids) in the linear and saturation regions. The linear region equation is Ids = β(VGT - Vds/2)Vds and the saturation region equation is Ids = (β/2)VGT^2, where β = μCox(W/L). It relates transistor parameters like mobility (μ), threshold voltage (Vt) to operating voltages and geometry.
Original Description:
Shockley math discussion.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes MOSFET transistor operation. It defines key terms like Cox, W, L, Vgs, Vds, Vt. It derives equations for channel charge (Qchannel), drain current (Ids) in the linear and saturation regions. The linear region equation is Ids = β(VGT - Vds/2)Vds and the saturation region equation is Ids = (β/2)VGT^2, where β = μCox(W/L). It relates transistor parameters like mobility (μ), threshold voltage (Vt) to operating voltages and geometry.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views2 pagesClass Discussion Section B Shockley
Uploaded by
MUSHFIQ UR RAHMANThis document summarizes MOSFET transistor operation. It defines key terms like Cox, W, L, Vgs, Vds, Vt. It derives equations for channel charge (Qchannel), drain current (Ids) in the linear and saturation regions. The linear region equation is Ids = β(VGT - Vds/2)Vds and the saturation region equation is Ids = (β/2)VGT^2, where β = μCox(W/L). It relates transistor parameters like mobility (μ), threshold voltage (Vt) to operating voltages and geometry.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Cg = Cox WL Cox is a constant
W = width
L = length of channel
Qchannel = Cg (Vgs – Vds/2 - Vt)
Time, t = L^2 / µVds
Current, I = charge, Q / time, t
Q C ox WL (V gs – V ds /2−V t ) C ox W µV d s(V gs – V ds /2−V t)
Ids = = =
t 2
L /µV d s L
W
Ids = µ Cox (Vgs - Vt – Vds/2 ) Vds
L
W
Beta, β = µ Cox
L
Vgs - Vt = VGT
Linear equation:
Ids = β (VGT – Vds/2 ) Vds…………………………….equation 1
Saturation Equation:
VGT = Vds replace Vds by VGT in equation 1 gives
Ids = β (VGT – VGT /2 ) VGT
Ids = β (VGT /2 ) VGT
Ids = (β/2)VGT^2 ……………equation 2
Qchannel = Cg V Vgs = voltage difference between gate and source
V = Vgc - Vt Vds = voltage difference between Drain and source
Vgc = Vgs – Vds/2 Vgd = voltage difference between gate and drain
Ids = current from drain to source
Vt = Threshold voltage
Time = distance/speed L = length of channel
V = velocity
Time = 300km/100km/h = 3 hrs
Time, t = L/v
Velocity, v = µVds/L
Time, t = L^2 / µVds
You might also like
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument1 pageFormula SheetdomingouclarayNo ratings yet
- HCTM Ece StudentsDocument22 pagesHCTM Ece StudentsMunish VermaNo ratings yet
- 16 Mosfet I-V and C-VDocument22 pages16 Mosfet I-V and C-VAntonio LeonNo ratings yet
- Mosfet Matlab Code PDFDocument19 pagesMosfet Matlab Code PDFbilluzakNo ratings yet
- VLSIDocument86 pagesVLSILorelei VasiloaiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter (5) Part (2) (Long Channel MOSFET)Document22 pagesChapter (5) Part (2) (Long Channel MOSFET)Ahmed SalehNo ratings yet
- Q4 Solution PDFDocument4 pagesQ4 Solution PDFDGMCNo ratings yet
- MOS PPTDocument13 pagesMOS PPTRenju TjNo ratings yet
- Example 2.1: 2.2 Long-Channel I-V CharacteristicsDocument1 pageExample 2.1: 2.2 Long-Channel I-V CharacteristicsCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-3 With SolutionsDocument3 pagesTutorial-3 With SolutionsSandesh RSNo ratings yet
- I. Mosfet Circuit Models A. Large Signal Model - Nmos: Vgs VTN Id Vgs VTN Vds Vgs VTNDocument10 pagesI. Mosfet Circuit Models A. Large Signal Model - Nmos: Vgs VTN Id Vgs VTN Vds Vgs VTNmanohar487No ratings yet
- Pcirf 3 3 Mos 2Document25 pagesPcirf 3 3 Mos 2Marius FerdyNo ratings yet
- Lec17 MOSFET IVDocument49 pagesLec17 MOSFET IVBlanca MeLendezNo ratings yet
- 1 Eamta12 - 1Document14 pages1 Eamta12 - 1Kerubiel AnikkuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MOS Transistor Theory: Ox 2 Ox OxDocument1 pageChapter 2 MOS Transistor Theory: Ox 2 Ox OxCarlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- n-MOSFET (D) :: (I-V) Equations: Cut Off ModeDocument6 pagesn-MOSFET (D) :: (I-V) Equations: Cut Off ModeJo KontNo ratings yet
- Differential AmplifierDocument24 pagesDifferential AmplifierT H ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Output ResistanceDocument2 pagesMOSFET Output ResistanceMerlin SkariahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Feb 20Document4 pagesTutorial Feb 20sourish.ambatiNo ratings yet
- MOS Transistor Theory: OutlineDocument24 pagesMOS Transistor Theory: OutlineCarlos AzevedoNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document28 pagesWeek 2Muhammad FaizanNo ratings yet
- CMOS VLSI Design 92Document1 pageCMOS VLSI Design 92Carlos SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Inv 120923Document29 pagesInv 120923Aman KumarNo ratings yet
- ENG571 - Final Exam - 2021Document4 pagesENG571 - Final Exam - 2021SABINA MISHRANo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1: ObjectiveDocument9 pagesExperiment No. 1: ObjectiveNitin RajputNo ratings yet
- ENEE 3543 - Homework 4 - SolutionsDocument4 pagesENEE 3543 - Homework 4 - SolutionsTSwayNo ratings yet
- Kuo 2010Document22 pagesKuo 2010Quy HoangNo ratings yet
- EE42 100 Wb-Lecture18 080513-FDocument44 pagesEE42 100 Wb-Lecture18 080513-FozanistzNo ratings yet
- Lecturer On Mos InverterDocument24 pagesLecturer On Mos InvertersoumikbhNo ratings yet
- Lect 9,10 - MOSFET DC AnalysisDocument17 pagesLect 9,10 - MOSFET DC Analysisshashikala kotiNo ratings yet
- Rectifier Circuits: Half-Wave Rectifier (HWR)Document18 pagesRectifier Circuits: Half-Wave Rectifier (HWR)Md ArifNo ratings yet
- L3Document48 pagesL3sandeepNo ratings yet
- In Linear Region, I Depends On: How Much Charge Is in The Channel? How Fast Is The Charge Moving?Document11 pagesIn Linear Region, I Depends On: How Much Charge Is in The Channel? How Fast Is The Charge Moving?Puneet ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Problems: DD TH0 D N OX - 4Document2 pagesLecture 3 Problems: DD TH0 D N OX - 4Amir SharfuddinNo ratings yet
- Design Unit-II: Choose The Correct Option From Following A. Space RequirementDocument3 pagesDesign Unit-II: Choose The Correct Option From Following A. Space RequirementUrstruly SriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MOS Transistor TheoryDocument25 pagesChapter 2 MOS Transistor TheoryrasheeenNo ratings yet
- Slide03 DeviceI2022Document36 pagesSlide03 DeviceI2022yackinNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 Digital Integrated Circuit Design: N-Channel MOSFET EQUATIONDocument3 pagesHomework 2 Digital Integrated Circuit Design: N-Channel MOSFET EQUATIONKhánh TrầnNo ratings yet
- S98 Lecture10 PDFDocument10 pagesS98 Lecture10 PDFRama ThumuluriNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes: IC Fabrication ProcessDocument81 pagesDetailed Notes: IC Fabrication ProcessimmadiuttejNo ratings yet
- EeeDocument15 pagesEeeSoma SinhaNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Threshold Voltage: V MOSFET Operation (NMOS) : Case 1Document109 pagesMosfet: Threshold Voltage: V MOSFET Operation (NMOS) : Case 1LiferNo ratings yet
- EC410 Fall 2012 FinalDocument8 pagesEC410 Fall 2012 FinalRabee Adil JamshedNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Structure: Source Gate Drain Field Oxide Gate OxideDocument12 pagesMOSFET Structure: Source Gate Drain Field Oxide Gate OxideRaj HakaniNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 SMALL SIGNAL ANALYSIS OF MOSFETsDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 8 SMALL SIGNAL ANALYSIS OF MOSFETsshubhankar palNo ratings yet
- 3.6. Metal-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (Mesfets)Document5 pages3.6. Metal-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (Mesfets)Chirag JainNo ratings yet
- 9.small Signal Analysis of MosfetsDocument27 pages9.small Signal Analysis of MosfetsNitin Mehta - 18-BEC-030No ratings yet
- Kang Chap4Document14 pagesKang Chap4Mukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- EE 3313: Device Modelling Tutorial 7: N Ox - 4 2 BDocument1 pageEE 3313: Device Modelling Tutorial 7: N Ox - 4 2 BRahul VasanthNo ratings yet
- MOSFETSDocument102 pagesMOSFETSVedant WaliaNo ratings yet
- Analytic Models of CMOS Logic in Various Regimes: Branko Dokić, Tatjana Pešić-Brđanin, Radoš DabićDocument22 pagesAnalytic Models of CMOS Logic in Various Regimes: Branko Dokić, Tatjana Pešić-Brđanin, Radoš DabićsimoNo ratings yet
- 3.1. Resistive Load Mos Inverter: An ExampleDocument41 pages3.1. Resistive Load Mos Inverter: An Exampleerdem10139No ratings yet
- EC-189191 MicroDocument88 pagesEC-189191 MicrohsuyabNo ratings yet
- Field Effect TransistorsDocument40 pagesField Effect TransistorsRatanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2023 - AnsDocument3 pagesTutorial 2023 - Anschetannp121No ratings yet
- Inverter NmosDocument124 pagesInverter Nmosapoorva10393No ratings yet
- מעגלים ספרתיים- פתרון (חלקי ומבולגן) לתרגיל בית 2 - 2012Document5 pagesמעגלים ספרתיים- פתרון (חלקי ומבולגן) לתרגיל בית 2 - 2012RonNo ratings yet
- W L Vgs VTH) Vds - V DS: 2) Derive Equation For GMDocument3 pagesW L Vgs VTH) Vds - V DS: 2) Derive Equation For GMdigital libraryNo ratings yet
- CSE Syllabus Full-1Document102 pagesCSE Syllabus Full-1MUSHFIQ UR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- SololasivarogomajiwofDocument2 pagesSololasivarogomajiwofMUSHFIQ UR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Comst 2020 2975911Document6 pagesComst 2020 2975911MUSHFIQ UR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Access 2019 2961372Document15 pagesAccess 2019 2961372MUSHFIQ UR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- CCI Deliverables GuidelinesDocument6 pagesCCI Deliverables GuidelinesMUSHFIQ UR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- CCI Program AY 2023-2024 Application FormDocument8 pagesCCI Program AY 2023-2024 Application FormMUSHFIQ UR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Full Text 01Document66 pagesFull Text 01MUSHFIQ UR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- CCI Program Sampe Answer ChatgptDocument2 pagesCCI Program Sampe Answer ChatgptMUSHFIQ UR RAHMANNo ratings yet