Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BBB Poster - Ali Brack
BBB Poster - Ali Brack
Uploaded by
lostree9Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BBB Poster - Ali Brack
BBB Poster - Ali Brack
Uploaded by
lostree9Copyright:
Available Formats
In
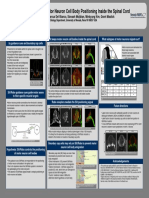
vitro model of the blood-‐brain barrier
Alison Brack, Anas Hamad, Kyle Alber9, Caleb Neufeld, Qiaobing Xu
What
is
the
Blood-‐Brain
Barrier?
Tes9ng
the
Model
Cell
Viability
on
Device
• Complex
organiza9on
of
endothelial
cells,
astrocytes,
and
• Seeded
Human
Umbilical
Vein
Endothelial
Cells
(HUVECs)
on
the
Cell
Viability
using
Alamar
Blue
assay
a5er
Incuba7on
on
Device
for
2
Days
pericytes
that
regulates
transport
between
the
brain
and
the
device
105
MDA-‐MD-‐231
cells
were
capillaries.
Carries
nutrients
from
the
blood
into
the
brain
• Added
a
solu9on
of
glucose
(supposed
to
pass
through),
β-‐ 100
incubated
on
the
device
for
• Transports
products
of
metabolic
ac9vity
from
the
brain
back
galactosidase
(not
supposed
to
pass
through),
and
a
lipidoid
95
2
days
and
then
an
Alamar
Percent
Viable
out
into
the
blood
nanopar9cle
(hydrophobic
and
large,
so
may
pass
but
not
as
easily)
90
Blue
assay
was
conducted,
• Composed
of
endothelial
cells,
which
coat
the
inside
of
the
containing
fluorescein
isothiocyanate
(FITC)
to
the
upper
chamber
85
with
the
result
of
92%
capillaries
and
regulate
transcellular
transport
into
the
brain,
of
the
device
80
viability
compared
with
pericytes
and
astrocytes,
which
both
regulate
endothelial
cell
• Device
was
incubated
overnight,
and
then
the
media
in
the
lower
75
Flask
Cells
Device
Cells
MDA
cells
from
a
flask.
ac9vity. chamber
was
tested
for
the
presence
of
the
three
substances
the
It’s
a
major
area
of
research
due
next
day.
to
its
barrier
func9on
and
how
it
tends
to
block
drugs
from
Discussion
entering
the
brain.
Developing
Results
Because
the
glucose
passed
through
the
model
of
the
blood-‐
an
effec9ng
model
of
the
blood-‐ brain
barrier
while
the
β-‐galactosidase
did
not,
as
expected,
the
Glucose
model
has
held
up
to
tes9ng
so
far.
However,
this
is
by
no
brain
barrier
could
help
to
gain
We
used
Benedict’s
Reagent
to
test
for
means
an
extensive
test,
so
more
tes9ng
with
a
wider
variety
of
insight
into
gefng
drugs
past
the
presence
of
glucose
in
the
media
substances
is
necessary
to
con9nue
assessing
the
model’s
the
blood-‐brain
barrier
to
treat
from
both
the
upper
and
lower
validity
is
necessary.
The
lipidoid
nanopar9cle
only
par9ally
the
disordered
and
diseased
chambers,
and
the
color
change
from
passed
through
the
device,
which
theore9cally
makes
sense,
as
brain.
Wilheim,
Fazakas,
Krizbai
(2011).
In
vitro
models
of
the
blood-‐brain
barrier.
blue
to
green
indicates
that
glucose
was
the
hydrophobicity
of
the
par9cle
would
allow
it
to
pass,
but
the
present
for
both
chambers.
(From
lec
large
size
would
decrease
the
permeability.
to
right:
Benedict’s
reagent,
reac9on
Addi9onally,
the
loss
of
8%
viability
is
most
likely
due
to
the
fact
result
from
the
lower
chamber,
and
Objec9ve
reac9on
result
from
the
upper
that
the
membrane
isn’t
coated
with
any
proteins
(like
collagen,
fibronec9n,
etc.)
so
it’s
not
as
healthy
of
an
environment
for
the
• Create
a
device
that
houses
an
in
vitro
model
of
the
blood-‐brain
chamber.)
cells
as
the
flask,
but
the
device
definitely
isn’t
killing
them.
barrier.
• The
device
also
allows
a
substance
to
be
flowed
across
to
β-‐galactosidase
determine
whether
it
passes
through
the
blood-‐brain
barrier
We
tested
for
β-‐galactosidase
by
adding
X-‐ Future
Work
model.
gal
to
the
media
from
the
two
chambers.
• More
extensive
tes9ng
of
the
accuracy
of
the
model
with
a
X-‐gal
turns
blue
when
it’s
cleaved
by
β-‐ greater
variety
of
substances.
galactosidase,
so
a
blue
solu9on
is
a
• Without
altering
the
design
of
the
device,
using
cerebral
posi9ve
test
for
the
enzyme.
The
well
on
Device
Design
the
lec
is
from
the
upper
chamber,
and
the
endothelial
cells
instead
of
HUVECs
would
increase
the
accuracy
of
the
device
by
preven9ng
paracellular
transport
Main
Idea
right
is
the
lower,
so
the
enzyme
did
not
between
the
chambers.
pass
through
the
model.
• Incorpora9ng
astrocytes
into
the
design
would
also
increase
Lipidoid
Nanopar9cle
accuracy
drama9cally,
but
would
require
a
redesign
of
the
device.
We
tested
for
the
presence
of
the
nanopar9cles
by
measuring
the
fluorescence
of
the
FITC
inside
of
them
(excita9on
at
475nm
and
emission
at
519nm).
The
result
was
16%
of
the
fluorescence
of
the
References
Current
Design
Fluorescence
of
FITC
in
Media
Samples
from
Different
upper
chamber
was
Wilheim,
I.,
Fazakas,
C.,
&
Krizbai,
I.
(2011).
In
vitro
models
of
the
Chambers
of
BBB
Device
detected
in
the
lower
blood-‐brain
barrier.
Acta
Neurobiologiae
Experimentalis,
71,
• Made
of
polycarbonate.
140
chamber.
• Uses
a
transwell
120
113-‐128.
membrane
as
the
upper
100
chamber.
Special
thanks
to
Kyle
Alber9,
Caleb
Fluorescnce
(RFU)
80
Neufeld, and Qiaobing Xu for all of their
60
40
20
0
help
with
this
project!
Upper
Chamber
Lower
Chamber
You might also like
- HSB June 2020Document18 pagesHSB June 2020Osmany MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Cay, COAIFDocument3 pagesCay, COAIFSapphire RedNo ratings yet
- 2 Analytical Applications of Galvanic CellsDocument8 pages2 Analytical Applications of Galvanic Cellssaeed.pdNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document3 pagesModule 2Grayka QuiapoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Title:: Understand Understand Understand Understand UnderstandDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Title:: Understand Understand Understand Understand Understandsteven rogerNo ratings yet
- LetsBuildAPlantCell PDFDocument7 pagesLetsBuildAPlantCell PDFmasturinaNo ratings yet
- SAFC Biosciences - Technical Bulletin - EX-CELL™ Serum-Free Media For Virus ProductionDocument2 pagesSAFC Biosciences - Technical Bulletin - EX-CELL™ Serum-Free Media For Virus ProductionSAFC-GlobalNo ratings yet
- Von Willebrand Factor Antigen - 0020002300: Limitations/interfering SubstancesDocument3 pagesVon Willebrand Factor Antigen - 0020002300: Limitations/interfering Substances28850No ratings yet
- Guide Test Strip Insert - 85125 - 09074937004 - WEBDocument2 pagesGuide Test Strip Insert - 85125 - 09074937004 - WEBErsa BayungNo ratings yet
- SAFC Biosciences Scientific Posters - Proteomic Analysis of CHO Cells During Recombinant Protein Production in High-Density CultureDocument1 pageSAFC Biosciences Scientific Posters - Proteomic Analysis of CHO Cells During Recombinant Protein Production in High-Density CultureSAFC-Global100% (1)
- 3.1 Levels - of - Organisation 1b Igcse - 9 1 - Edexcel BiologyDocument11 pages3.1 Levels - of - Organisation 1b Igcse - 9 1 - Edexcel BiologyIsini sehansa amarathungaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Ana Lec 2Document53 pagesNervous System Ana Lec 2hey lolNo ratings yet
- Big Picture On The Cell PosterDocument1 pageBig Picture On The Cell PosterWellcome Trust100% (1)
- Endocrine System EditedDocument80 pagesEndocrine System EditedKyle Gwyneth BobierNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-The CellDocument29 pagesLecture 2-The Celldmutethia68No ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument54 pagesCentral Nervous SystemShabir KhanNo ratings yet
- Golgi Outposts and Satellites in Neurons - Secretory Trafficking in Neuronal DendritesDocument7 pagesGolgi Outposts and Satellites in Neurons - Secretory Trafficking in Neuronal DendritesEshaNo ratings yet
- Jove Protocol 62178 Immunostaining of Wholemount Retinas With The Clarity Tissue Clearing MethodDocument16 pagesJove Protocol 62178 Immunostaining of Wholemount Retinas With The Clarity Tissue Clearing Methodmdjgyv1933No ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument1 pagePlant Cellallan.uyNo ratings yet
- Ed For Pet: Clinical DescriptionDocument2 pagesEd For Pet: Clinical DescriptionShah NawazNo ratings yet
- Outline: Introduction To The CellDocument3 pagesOutline: Introduction To The Cellvinnie0905No ratings yet
- Final NervousDocument48 pagesFinal NervousJanny Ver DacayNo ratings yet
- 2007 AAPS - Poster - High Throughput Solubility AnalysisDocument1 page2007 AAPS - Poster - High Throughput Solubility Analysismr_jpwalsh8941No ratings yet
- Lonza CelldiscoveryDocument380 pagesLonza CelldiscoveryMai Khoi NguyenNo ratings yet
- The Bionic Eye: by Henri LorachDocument3 pagesThe Bionic Eye: by Henri LorachLuis Eduardo Gomez EspinosaNo ratings yet
- 2 Organelle Function Checklist PDFDocument1 page2 Organelle Function Checklist PDFLovelinnel PacañaNo ratings yet
- 3.fundamentals of Neurobiology - UpdatedDocument32 pages3.fundamentals of Neurobiology - UpdateddavidNo ratings yet
- Article in Press: Seminars in Cell & Developmental BiologyDocument7 pagesArticle in Press: Seminars in Cell & Developmental BiologyrefestufuNo ratings yet
- Organelle WorkDocument7 pagesOrganelle Workblackman694202No ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemLabDocument7 pagesLymphatic SystemLabMax DelvalleNo ratings yet
- Activity #11 Urogenital SystemDocument4 pagesActivity #11 Urogenital SystemNathaniel FelicianoNo ratings yet
- PIPAc Technical Note2Document1 pagePIPAc Technical Note2Jonayed Hossain SarkerNo ratings yet
- Meelis Kull, Miquel Perello Nieto, Markus Kängsepp, Telmo Silva Filho, Hao Song, Peter FlachDocument1 pageMeelis Kull, Miquel Perello Nieto, Markus Kängsepp, Telmo Silva Filho, Hao Song, Peter FlachNeelabh MadanNo ratings yet
- Chief Taxonomic Subdivisions and Organ Systems of The Animal PhylaDocument2 pagesChief Taxonomic Subdivisions and Organ Systems of The Animal PhylaL P100% (1)
- Pentra 120 DXDocument2 pagesPentra 120 DXnbiolab6659No ratings yet
- Ch. 3 CellsDocument53 pagesCh. 3 CellsAiza CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Bulletin 6000ADocument1 pageBulletin 6000AKala KingNo ratings yet
- Ivermectin Promotes Peripheral Nerve RegenerationDocument11 pagesIvermectin Promotes Peripheral Nerve RegenerationbiaravankNo ratings yet
- Hidden Brain Glia 11Document8 pagesHidden Brain Glia 11Riya MathurNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Total Corneal Power MeasurementsDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Total Corneal Power MeasurementsMariana Luzardo bravoNo ratings yet
- 8 Cells - Simile - AssignmentDocument4 pages8 Cells - Simile - AssignmentRileytucks8No ratings yet
- Ed For Pet: Clinical DescriptionDocument2 pagesEd For Pet: Clinical DescriptionShah NawazNo ratings yet
- 0.-Rules of Thumb (Walas)Document7 pages0.-Rules of Thumb (Walas)Bryan PiguaveNo ratings yet
- Epidural Spinal Cord Stimulation Facilitates Immediate Restoration of Dormant Motor and Autonomic Supraspinal Pathways After Chronic Neurologically Complete Spinal Cord InjuryDocument41 pagesEpidural Spinal Cord Stimulation Facilitates Immediate Restoration of Dormant Motor and Autonomic Supraspinal Pathways After Chronic Neurologically Complete Spinal Cord InjurynorazmiNo ratings yet
- Colin Wilhelm, Marcus Del Bianco, Siavash Mojibian, Minkyung Kim, Grant MastickDocument1 pageColin Wilhelm, Marcus Del Bianco, Siavash Mojibian, Minkyung Kim, Grant MastickColin WilhelmNo ratings yet
- Brain DevDocument11 pagesBrain DevAndreea MacoveiNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 08 Mar 2023Document11 pagesAdobe Scan 08 Mar 2023itsmesupu25No ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cells 2023 (1) - TaggedDocument37 pagesEukaryotic Cells 2023 (1) - Taggedvalkrye.100servesNo ratings yet
- Lab Values 1Document30 pagesLab Values 1Ezekiel John GarciaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Week 2Document6 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Week 2Florene Bhon GumapacNo ratings yet
- ATAC-Seq Poster 11072019111Document1 pageATAC-Seq Poster 11072019111Julio SantanaNo ratings yet
- Garbage Truck of The BrainDocument3 pagesGarbage Truck of The BrainbenqtenNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 - Cell Parts & FunctionDocument23 pagesLESSON 2 - Cell Parts & FunctionThe DarkCrafter 423No ratings yet
- Endotelial LesionDocument5 pagesEndotelial LesionNST MtzNo ratings yet
- Zoology Lec Module 3Document6 pagesZoology Lec Module 3Camille AlzolaNo ratings yet
- Nallamothu URTCPOSTEROFFICIALDocument1 pageNallamothu URTCPOSTEROFFICIALSirihaasa NNo ratings yet
- RND Systems Autoimmunity PMDocument1 pageRND Systems Autoimmunity PMFikri GhNo ratings yet
- Notas CNSDocument3 pagesNotas CNSdaniela.garciagarciaNo ratings yet
- C Elegans Timbers2009Document8 pagesC Elegans Timbers2009ami501No ratings yet
- Tadano Mobile Crane TR 200m 2 P 02 Parts Catalog 520231Document22 pagesTadano Mobile Crane TR 200m 2 P 02 Parts Catalog 520231amandahammond230400ncp100% (119)
- PI e TRIG - 10 15Document2 pagesPI e TRIG - 10 15labor baiturrahimNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de SimulacionDocument80 pagesTrabajo de SimulacionFran RexmanNo ratings yet
- Energy Psychology BooksDocument4 pagesEnergy Psychology Booksanabastan100% (2)
- Jurnal Jambu Biji 4Document11 pagesJurnal Jambu Biji 4Wanhosi Nirvani NirvaniNo ratings yet
- Lungfish Adaptations AbstractDocument2 pagesLungfish Adaptations AbstractEmily MagkourilouNo ratings yet
- Spinal Instability Neoplastic ScoreDocument9 pagesSpinal Instability Neoplastic ScoreJacklyn YekNo ratings yet
- Company Name Key Information Questions Answers File Reference Reviews & ApprovalsDocument7 pagesCompany Name Key Information Questions Answers File Reference Reviews & ApprovalsMAT-LIONNo ratings yet
- H&N Mod. Wk1 ScalpDocument10 pagesH&N Mod. Wk1 ScalpUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 To 5 Joshua (Recovered)Document94 pagesChapter 1 To 5 Joshua (Recovered)Mark Joshua UyNo ratings yet
- Shaker Rotator Vortex BoecoDocument4 pagesShaker Rotator Vortex BoecoIndharKhaerati RamingNo ratings yet
- Muscular StrengthDocument13 pagesMuscular StrengthSam TabujaraNo ratings yet
- Tenp DPT Biochemistry: DR Pius KiptemburDocument13 pagesTenp DPT Biochemistry: DR Pius KiptemburGerald Limo Arap ChebiiNo ratings yet
- Agriculture 4Document16 pagesAgriculture 4NAVEED AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Tranexamic Acid For Lower GI HemorrhageDocument8 pagesTranexamic Acid For Lower GI HemorrhagekarinalavianiNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Herpetological SurveyDocument7 pagesThe Importance of Herpetological Surveyabeje kassieNo ratings yet
- Yogesh Bio BatteryDocument28 pagesYogesh Bio BatteryYogeshraj NsNo ratings yet
- 2019 Yokdil Ilkbahar Fen PDFDocument20 pages2019 Yokdil Ilkbahar Fen PDFgizemcetinNo ratings yet
- Ecology of The City: A Perspective From ScienceDocument5 pagesEcology of The City: A Perspective From SciencePrajitha Jinachandran T KNo ratings yet
- Basti Bikash Mapdanda 2072Document17 pagesBasti Bikash Mapdanda 2072Aayush Koirala100% (1)
- Blood SmearDocument7 pagesBlood SmearMarice Ferrufino SchmidtNo ratings yet
- Majestic TB Matt AntifungalDocument5 pagesMajestic TB Matt AntifungalYUSRINo ratings yet
- 002 ARA CCHI Mini - Glossary ENT EarDocument5 pages002 ARA CCHI Mini - Glossary ENT Eartarboosh20146No ratings yet
- Liver PathologyDocument9 pagesLiver PathologyAman BasidaNo ratings yet
- Micturition 2022Document20 pagesMicturition 2022Mohammad zreadNo ratings yet
- Ebook Human Development A Life Span View PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument77 pagesEbook Human Development A Life Span View PDF Full Chapter PDFronald.mcneil866100% (29)
- Final Exam Psychology G11Document4 pagesFinal Exam Psychology G11Meetali ArchitNo ratings yet
- DISCO RAJA (2020) Telugu TRUE WEB-DL - ESub - SRTDocument149 pagesDISCO RAJA (2020) Telugu TRUE WEB-DL - ESub - SRTvaquentNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Planning Template: Cambridge Lower Secondary Science Stage 7Document3 pagesLong-Term Planning Template: Cambridge Lower Secondary Science Stage 7marycperez100% (1)