Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and Liquids
Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and Liquids
Uploaded by
Ma Kiara Zen PitapitOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and Liquids
Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and Liquids
Uploaded by
Ma Kiara Zen PitapitCopyright:
Available Formats
GENERAL CHEMISTRY
CHAPTER 1: INTERMOLECULAR FORCES OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS
KINETIC MOLECULAR MODEL OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS
INTRODUCTION CHANGES OF STATE OF A MATTER
• Matter is anything that occupies space
and has mass
• Matter has the ability to undergo phase
changes
Vaporization
• Phase Changes is the transformation of
matter from one phase to another,
influenced by TEMPERATURE and
PRESSURE
KINETIC ENERGY
• SOLID TO LIQUID = Melting
It is the energy needed to keep the particles
• LIQUID TO GAS = Vaporization
moving, which is dependent upon
• GAS TO LIQUID = Condensation
TEMPERATURE
• LIQUID TO SOLID = Freezing
• SOLID TO GAS = Sublimation
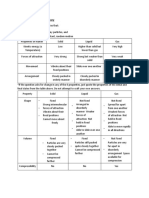
STATES OF MATTER
• GAS TO SOLID = Deposition
1. SOLID
• Closely packed together
• Compact Arrangement
• Definite shape and Volume
• Vibrate about fixed positions
• Moves Slow
• No freedom of Motion
2. LIQUID
• Slightly far from one another
• Has definite volume but
assumes the shape of a
container
• Slide past one another
• Moves fast
3. GAS
• Very far from one another
• Assumes the shape and
volume of its container
• Very free of motion
• Moves the fastest
You might also like
- Chap 5 MatterDocument32 pagesChap 5 MatterAimi Nadia Yusof71% (7)
- Matter and Phase Changes 2Document19 pagesMatter and Phase Changes 2vinujah100% (1)
- The Particle Nature of MatterDocument19 pagesThe Particle Nature of MatterChristian FernandezNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3-4 - KINETIC MOLECULAR AND PECHECKcdg Edited For PDFDocument72 pagesWEEK 3-4 - KINETIC MOLECULAR AND PECHECKcdg Edited For PDFMorissette GarciaNo ratings yet
- Phase ChangingDocument19 pagesPhase ChangingAnaa LegaspiNo ratings yet
- 4.3 The Particle ModelDocument10 pages4.3 The Particle ModelSarah ANo ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument9 pagesChem Reviewermatthew dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem Week 1 Properties of Matter and Its Various FormsDocument84 pagesGen Chem Week 1 Properties of Matter and Its Various FormsLeonard SalvacionNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument21 pagesStates of MatterRegina Mae Narciso NazarenoNo ratings yet
- KineticparticletheorypptDocument32 pagesKineticparticletheorypptAnand SarbabidyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document12 pagesChapter 1Phan BảoNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Unit 1Document22 pagesStates of Matter Unit 164274qjmzcNo ratings yet
- Boom Notes For Sec2Document7 pagesBoom Notes For Sec2Varsha Balasubramanian (Bowenss)No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2Document23 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2St. DymphaMaralit, Joyce Anne L.No ratings yet
- States of Matter PT 1Document10 pagesStates of Matter PT 1api-310503032No ratings yet
- Physics CH 4 MoleculesDocument42 pagesPhysics CH 4 MoleculesMuhammad Usman Khalid AminNo ratings yet
- The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument8 pagesThe Particulate Nature of MatterVibinraj K NileshwarNo ratings yet
- CT 1 Cheatsheet (IP)Document11 pagesCT 1 Cheatsheet (IP)22S47 ONG YU KAINo ratings yet
- Revision On Particles TheoryDocument35 pagesRevision On Particles TheoryHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Why Can The Smell of Durians Be Detected Even Very Far Away ?Document38 pagesWhy Can The Smell of Durians Be Detected Even Very Far Away ?Kavitha ThayagarajanNo ratings yet
- Apri State of Mater (What's The Matter)Document23 pagesApri State of Mater (What's The Matter)qcsrjj9d4dNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v4Document25 pagesCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v4Family TimeNo ratings yet
- The Particle TheoryDocument8 pagesThe Particle TheoryMuhammad Haikal ZainalNo ratings yet
- Physics II MidtermsDocument4 pagesPhysics II MidtermsHANNAH JEAN FRUELDANo ratings yet
- Genchem II Kinetic Theory I.F. of AttractionDocument2 pagesGenchem II Kinetic Theory I.F. of AttractionRosario Del PuertoNo ratings yet
- F1 Chapter 5 MatterDocument13 pagesF1 Chapter 5 Matteralya sophiaNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument31 pagesStates of Matterceeernest531No ratings yet
- Chemistry Matters Chapter 1Document7 pagesChemistry Matters Chapter 1Ayan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Understanding Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument50 pagesUnderstanding Kinetic Particle TheoryozmanNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsDocument63 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Solids and LiquidsEnna SertNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of MatterDocument4 pagesParticulate Nature of MatterSandy ItabNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument1 pageStates of Mattermaryam mughalNo ratings yet
- States of Matter and Thermal EnergyDocument2 pagesStates of Matter and Thermal EnergyphydotsiNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument27 pagesStates of MatterEstelito Tamonan AmarNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of The 3 StatesDocument23 pagesParticulate Nature of The 3 StatesJohn Dale MateoNo ratings yet
- G9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2Document35 pagesG9 UK W15 - Kinetic Model of Matter 2hk6sd6cf7vNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Matter and Atomic Structure: 2.1 Basic Concepts of Matter 2.2 The Development of The Atomic ModelDocument32 pagesChapter 2: Matter and Atomic Structure: 2.1 Basic Concepts of Matter 2.2 The Development of The Atomic Modelmenaga ilangkovanNo ratings yet
- State of Matter-HighlightDocument21 pagesState of Matter-HighlightZhimingNo ratings yet
- Nature of MatterDocument7 pagesNature of MatterRea Frias OclarinoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Module 1: Chapter 1: Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument5 pagesGeneral Chemistry Module 1: Chapter 1: Kinetic Particle TheoryKeano GelmoNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument29 pagesStates of MatterAndy GacuyaNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM II Kulang PaDocument12 pagesGEN CHEM II Kulang Pasara joyce pinedaNo ratings yet
- 2.1.) States of Matter (BIO40A)Document19 pages2.1.) States of Matter (BIO40A)Mary Ferl Jasmin LupagueNo ratings yet
- 01 States of MatterDocument3 pages01 States of MatterbadhriNo ratings yet
- States - of - Matter Year 8Document12 pagesStates - of - Matter Year 8b2.dakurahNo ratings yet
- Pdfcaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v11.PDF 7Document29 pagesPdfcaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v11.PDF 7aimaan1903No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - States of MatterDocument31 pagesChapter 10 - States of Matterjim tannerNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument38 pages1.1 Kinetic Molecular TheoryKéiNo ratings yet
- MatterDocument15 pagesMatterVictoria VirgoNo ratings yet
- TPNM Intro KCLVMDocument17 pagesTPNM Intro KCLVMEddiezr B de BorjNo ratings yet
- 2018 UPlink NMAT Review Chemistry 1 Lecture - MappataoDocument77 pages2018 UPlink NMAT Review Chemistry 1 Lecture - MappataoRovillene A. PanangweNo ratings yet
- SLIDE 1 - Sci 07 (Matter)Document81 pagesSLIDE 1 - Sci 07 (Matter)Allen Joy LazoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Principles of ChemistryDocument14 pagesUnit 1 Principles of ChemistryKhin Yadanar KyawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 MatterDocument44 pagesChapter 5 MatterNor Atikah Abdul RazakNo ratings yet
- Matter PPT 1Document48 pagesMatter PPT 1Vlad KaneNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Particulate Nature of MatterDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Particulate Nature of MatterShyam BudhwarNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 ScienceDocument14 pagesGrade 8 Scienceleighalbano7No ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument17 pagesStates of MatterVergilEstevesNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument19 pagesStates of MatterOmar ChaudhryNo ratings yet