Professional Documents
Culture Documents
First Aid and Water Safety - Final
Uploaded by
nellrose emlanoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
First Aid and Water Safety - Final
Uploaded by
nellrose emlanoCopyright:
Available Formats
D BUTUAN CITY COLLEGES
BCC BLDG., MONTILLA BLVD., BUTUAN CITY
E-mail: butuancitycollegesbc@gmail.com
Contact No: | (085) 300-1337 | 09125315725
E FIRST AID AND WATER SURVIVAL
FINAL
F (1-4 weeks)
1ST1LDCKLDNJMCKV
T
A
C
3
Prepared By: Nellrose B. Emlano
Instructor
NOT FOR SALE
I. EMERGENCY RESCUE TRANSFER 6. Danger of collapsing walls
This part presents the emergency rescue techniques for FACTORS TO BE CONSIDERED IN THE SELCTION OF
different situations in consideration of the injuries suffered by TRANSFER METHOD.
the victim. The different methods of emergency rescue transfer
1. Nature and severity of the injury
are also discussed in this chapter. Some pictures are provided
2. Size and weight of the victim
for better understanding, but demonstrations and return-
3. Physical capabilities of the first aider
demonstrations are imperative to effectively learn the skills of
4. Number of personnel and equipment available
emergency rescue transfer.
5. Nature of the evacuation route
6. Distance to be covered
7. Sex of the victim
Definition of Terms
POINTERS TO BE OBSERVED DURING TRANSFER
1. Emergency Rescue is the rapid movement of victims from
an unsafe place to a safe place. 1. Victim’s airway must be kept often.
2. Transfer refers to the moving of victim from one place to 2. Prevent haemorrhage to avoid shock.
another after giving the first aid. 3. Victim should be safely maintained in the correct
3. Dragging refers to the act of rescuer of cautiously pulling position.
a victim by the shoulders or feet on a smooth ground. 4. Regularly check the victim’s condition.
This is usually done if the rescuers is alone and is not 5. Supporting bandages and dressing should be effectively
strong enough to carry the victim. applied.
6. The method of transfer is safe, comfortable and as speedy
INDICATIONS FOR EMERGENCY RESCUE as circumstances permit.
7. The patient’s body should be moved as one unit to avoid
1. Danger of Fire or Explosion injury at the joints and extremities.
2. Danger of toxic gases or asphyxia due to lack of oxygen 8. The taller first aiders should stay at the head of the
3. Serious traffic hazards victim.
4. Risk of drowning 9. First aiders must observe ergonomics in the lifting and
5. Danger of electrocution moving the patient.
NOT FOR SALE
METHODS OF EMERGENCY RESUCUE TRANSFER for victims to rescue. This is also used to avoid smoke
inhalation injuries while rescuing during a fire.
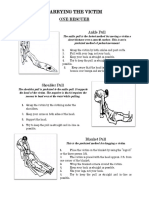
A. ONE MAN CARRY METHODS
7. Inclined Drag is used when transporting a victim,
1. Lovers carry or carry in arms is commonly used by any
especially on stairways. Always remember to elevate the
person in carrying or transporting another.
head of the victim while walking to prevent him or her
2. Fireman’s carry is used when there is no injury at or
from losing consciousness.
there is near the abdomen.
C. TWO MAN ASSIST/ CARRY METHODS
3. Pack Strap carry is usually used to carry victim for a
1. Four hand Seat is used when the victim is conscious.
short distance.
2. Hands as a Litter is applied when the victim is not
4. Piggy Back Carry is used to transport victims for longer
conscious.
distances.
3. Carry by Extremities is applied when injuries of victim
are at the body parts except the hands and feet.
B. ONE MAN ASSIST/ DRAG METHODS
4. Assist to Walk is applied when a person cannot walk
alone, especially for persons under the influence of liquor
1. Assist to Walk is usually done to assist a person who
or drugs.
cannot walk by himself or herself due to injury or illness.
5. Chair Carry is a method of carrying the victim by letting
2. Cloth Drag is used when cloth is available. The surface of
him or her sit on a strong chair and letting at least two
the ground should be smooth when performing this drag
individuals carry the chair with the victim on it.
to avoid further injury to the victim.
6. Fireman’s Carry with Assistance is used when there are
3. Feet Drag is used when the ground is smooth by fixing
a lot of victims who need immediate transfer from an
the hands and dragging the victim by the feet.
unsafe to a safe place.
4. Armpit/ Shoulder Drag is also used to drag a victim by
the armpits away from an unsafe place.
D. THREE- MAN CARRY METHODS
5. Blanket Drag is used when the victim is lying on a
1. Hammock Carry is used to carry a victim who cannot be
blanket. This is done by holding the ends of the blanket
carried by a single rescuer because of heavy weight,
and gently dragging the blanket carrying the victim.
nature of injury, and a nature of terrain. This method of
6. Fireman’s Drag is done in a building that is burning and
transporting a victim is ideal for wide alleys.
that the victims are confirmed to be still inside. The
rescuer crawls at estimated one foot on the floor and look
NOT FOR SALE
2. Bearers Alongside is usually used in narrow alleys. The INITIAL TRIAGE AND TAGGING
rescuers carry the victim along one side of the victim is
Triage and tagging are done to prioritize victims in a
clipped against the chests of the rescuers to avoid falling
mass disaster such as plane crash, vehicular accident, earth
and further injury.
quake, massive landslide, flood, fire and other natural or man-
E. IMPROVISED STRETCHER USING TWO POLES
made disasters. It also refers to the method of sorting patients
MATERIALS: into categories of priority for care and transport base on the
severity of injuries and medical emergencies.
1. Blanket
2. Empty sacks The S.T.A.R.T System refers to Simple Triage and Rapid
3. Shirts or coats Treatment. It is one method of triages that has been proven to
4. Triangular Bandages be effective.
F. FOUR/SIX/EIGHT- MAN CARRY can be done when the
weight of the victim/patient cannot be carried by 1-3
persons. This procedure is the same with three-man TAGGING OF VICTIMS/PATIENTS
carry.
G. BLANKET CARRY is different from the stretcher and it 1. RED TAG – 1ST PRIORITY. The victim has a life
uses a blanket with poles. This is done by proper threatening or serious injury that needs immediate first
insertion of blanket under the victim, testing the blanket aid and rescue.
and lifting. 2. YELLOW TAG- 2ND PRIORITY. The victim has a less
H. COMMERCIAL STRETCHER is a ready-made stretcher threatening injury and care can be delayed within one
designed for purpose of carrying a victim/patient. hour.
I. AMBULANCE/RESCUE VAN. Most ambulances are 3. GREEN TAG- 3RD PRIORITY. The victim can walk on
designed with stretchers inside that can be folded to serve his/her own; rescue/assistance of victim maybe delayed.
as a bed for patients/ victims. Others may also be used 4. BLACK TAG-4TH PRIORITY. No care is required. The victim
as rescue vehicles for the purpose of transferring victims. is dead or close to death. All victims tagged with Black
shall be the last priority during rescue operations.
NOT FOR SALE
REFERENCES
Hand book on First Aid, Rescue and Water Safety
NOT FOR SALE
You might also like
- Essentials of Fire Fighting and Fire Department Operations 6th Edition Ifsta Test BankDocument14 pagesEssentials of Fire Fighting and Fire Department Operations 6th Edition Ifsta Test Banksexton.garookuh6lsjr100% (25)
- P.E. 2 First Aid Hand OutDocument11 pagesP.E. 2 First Aid Hand OutLaleth Mendoza Ojales100% (3)
- Emergency Rescue and Short Distance Transfer-N5Document3 pagesEmergency Rescue and Short Distance Transfer-N5Gerald Penner100% (5)
- Grade 9 HEALTH Q3 - M2Document16 pagesGrade 9 HEALTH Q3 - M2Marjun Oliveros Macadangdang100% (6)
- 3 and 4 of Fundamentals of First Aid ModuleDocument27 pages3 and 4 of Fundamentals of First Aid ModuleMark Joseph P. GaniaNo ratings yet
- Carrying The VictimDocument5 pagesCarrying The VictimTchaikovsky AyopNo ratings yet
- Emergency Rescue TransferDocument91 pagesEmergency Rescue TransferJohn DavidNo ratings yet
- Moving A VictimDocument16 pagesMoving A VictimMarian Drew Parcon LopezNo ratings yet
- LAS MAPEH 9 Q3 W6 HealthDocument6 pagesLAS MAPEH 9 Q3 W6 HealthJemalyn Hibaya LasacaNo ratings yet
- Las Ro3 Final h9q3w4 8Document17 pagesLas Ro3 Final h9q3w4 8Ian Santos B. SalinasNo ratings yet
- Passed-2790-13-21MELCS-Tabuk City - UnintentionalinjuriesDocument17 pagesPassed-2790-13-21MELCS-Tabuk City - Unintentionalinjuriesrangelynrish aguirreNo ratings yet
- Health9-Module2 Q3Document10 pagesHealth9-Module2 Q3ExequielNo ratings yet
- A. Different Techniques and Types of LiftingDocument18 pagesA. Different Techniques and Types of LiftingLanzen DragneelNo ratings yet
- Las Ro3 Final H9Q3W4 8Document17 pagesLas Ro3 Final H9Q3W4 8gloria tolentinoNo ratings yet
- HEALTH-9-Q3-M8-wk8 OKDocument17 pagesHEALTH-9-Q3-M8-wk8 OKreymart pacutNo ratings yet
- Rescue and Carry Methods Power PointDocument75 pagesRescue and Carry Methods Power PointJean Minette Prado88% (8)
- Lift and CarriesDocument25 pagesLift and CarriesJohn Dan FerreriaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 HEALTH Q3 - M2Document16 pagesGrade 9 HEALTH Q3 - M2Krizzane AcierdaNo ratings yet
- Health Week 4 - 3rd QuarterDocument5 pagesHealth Week 4 - 3rd QuarterNoemelyn VecinaNo ratings yet
- Final Demo DLPDocument10 pagesFinal Demo DLPJohn DavidNo ratings yet
- Las Ro3 Final h9q3w4 8Document17 pagesLas Ro3 Final h9q3w4 8Randolf CruzNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanMargaret BroñolaNo ratings yet
- Transport of Victim Using Improvised MaterialsDocument9 pagesTransport of Victim Using Improvised MaterialsTeacher JhenNo ratings yet
- Emergency Methods of Evacuating Casualties Without EquipmentDocument16 pagesEmergency Methods of Evacuating Casualties Without EquipmentKartini MedikalNo ratings yet
- Chapter-I: Search and RescueDocument16 pagesChapter-I: Search and Rescuedrager1969No ratings yet
- Health: Quarter 3 - Module 5: Techniques in Carrying and Transporting The VictimDocument19 pagesHealth: Quarter 3 - Module 5: Techniques in Carrying and Transporting The VictimNnayz0% (1)
- Luna G9 Health Q3 W2 For Final 1Document4 pagesLuna G9 Health Q3 W2 For Final 1Jazzy Anne AquinoNo ratings yet
- Rescue Plan For Confined SpaceDocument26 pagesRescue Plan For Confined SpaceSARFARAZ KHANNo ratings yet
- 69 - Lesson 3 z33dTfDocument6 pages69 - Lesson 3 z33dTfJohn Ace MataNo ratings yet
- Emergency Rescue - DocsDocument3 pagesEmergency Rescue - DocsZhavia ShyNo ratings yet
- Online QuizDocument2 pagesOnline QuizMary Ann NeypesNo ratings yet
- Unintentional Injury Prevention, First Aid and SafetyDocument25 pagesUnintentional Injury Prevention, First Aid and SafetyCasNo ratings yet
- PPT Module 3 - Patient Casualty HandlingDocument3 pagesPPT Module 3 - Patient Casualty HandlingRodessa CacayuranNo ratings yet
- Emergency Carry TechniquesDocument37 pagesEmergency Carry Techniquesjojo ramirez0% (1)
- Emergency Rescue and Transfer HardDocument5 pagesEmergency Rescue and Transfer HardJorhally B Edzraphil100% (1)
- First Aid EducationDocument39 pagesFirst Aid Education2C- VILLACARLOS, LEONA ROSE M.100% (1)
- Emergency Rescue and TransferDocument35 pagesEmergency Rescue and Transferlura castroNo ratings yet
- Emergency Rescue and TransferDocument12 pagesEmergency Rescue and TransferColeen Ann Bagasol100% (1)
- 3rd Grading Health Notes First Aid and Unintentional InjuryDocument1 page3rd Grading Health Notes First Aid and Unintentional Injuryblairemeri09No ratings yet
- SodapdfDocument12 pagesSodapdfALEOSAN BFP12No ratings yet
- ALS FA Poster Resus Adult v3Document1 pageALS FA Poster Resus Adult v3Giovanni RossiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12&13 Plus Asst 1st AidDocument20 pagesChapter 12&13 Plus Asst 1st AidabyNo ratings yet
- CWTS 2 Module 2 Bandaging Rescue...Document9 pagesCWTS 2 Module 2 Bandaging Rescue...Jozel ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Health 2ND Grading With Long TestDocument3 pagesReviewer in Health 2ND Grading With Long TestNeil Love Gestiada HernandezNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed LP For Carrying and Transporting An Injured PersonDocument4 pagesSemi Detailed LP For Carrying and Transporting An Injured Persontwengkolarquillo.29No ratings yet
- First Aid NotesDocument13 pagesFirst Aid NotesVian ArccenioNo ratings yet
- Emergency Rescue and TransferDocument11 pagesEmergency Rescue and Transferkyuleen05No ratings yet
- The Golden Rule You Need To Know Before Moving A Casualty - ST John VicDocument1 pageThe Golden Rule You Need To Know Before Moving A Casualty - ST John VicLeniza SorianoNo ratings yet
- Final Chapter 5Document7 pagesFinal Chapter 5Joshua WisudawanNo ratings yet
- ALS FA Poster Aed CPR v3Document1 pageALS FA Poster Aed CPR v3seeNo ratings yet
- 1 Aids-321-346Document26 pages1 Aids-321-346Ehtesham AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Emergency Rescue and TransferDocument31 pagesEmergency Rescue and TransferJhoana Rose Joaquin Santos95% (20)
- Modules in G9 Health Week 3 4Document2 pagesModules in G9 Health Week 3 4VINZ MAXIMUS DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- The Golden Rules of First AidDocument2 pagesThe Golden Rules of First AidSheryl SabadoNo ratings yet
- Unit-10.pdf SHSHDocument11 pagesUnit-10.pdf SHSHvamsiNo ratings yet
- Transfer and AmbulationDocument15 pagesTransfer and AmbulationpleburNo ratings yet
- First Aid & Emergency Companions: First Aid & Emergencies at SeaFrom EverandFirst Aid & Emergency Companions: First Aid & Emergencies at SeaNo ratings yet
- Technolgy For Teaching and Learning Final ModulesDocument16 pagesTechnolgy For Teaching and Learning Final Modulesnellrose emlanoNo ratings yet
- Intro To Agri-Fisheries - Midterm (Week 1 To 4)Document81 pagesIntro To Agri-Fisheries - Midterm (Week 1 To 4)nellrose emlanoNo ratings yet
- First Aid and Water Safety-Semi FinalsDocument12 pagesFirst Aid and Water Safety-Semi Finalsnellrose emlanoNo ratings yet
- Technolgy For Teaching and Learning Week 1 To 4 MidermDocument31 pagesTechnolgy For Teaching and Learning Week 1 To 4 Midermnellrose emlanoNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Exam Grade 7Document2 pages1st Periodical Exam Grade 7nellrose emlanoNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Exam Grade 8Document2 pages1st Periodical Exam Grade 8nellrose emlanoNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Exam Grade 10Document2 pages1st Periodical Exam Grade 10nellrose emlanoNo ratings yet
- Region XiiiDocument2 pagesRegion Xiiinellrose emlanoNo ratings yet
- Techniques of Questioning:: B. KindsDocument8 pagesTechniques of Questioning:: B. Kindsnellrose emlanoNo ratings yet
- The Laguna Copp-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageThe Laguna Copp-WPS Officenellrose emlanoNo ratings yet
- The Laguna Copp-WPS OfficeDocument1 pageThe Laguna Copp-WPS Officenellrose emlanoNo ratings yet
- Peralta Assignment 1Document9 pagesPeralta Assignment 1kim loNo ratings yet
- Jacksonville Civil Unrest After-Action ReportDocument14 pagesJacksonville Civil Unrest After-Action ReportSam MathersNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Comparative Politics and DisastersDocument36 pagesChapter - Comparative Politics and Disastershe20003009No ratings yet
- National Simultaneous Earthquake Drill Accomplishment ReportDocument8 pagesNational Simultaneous Earthquake Drill Accomplishment ReportKuyaJv Plaza EscareNo ratings yet
- Contingency Plan ManualDocument30 pagesContingency Plan ManualEmmanuel AdenolaNo ratings yet
- Marine Accident Investigation Branch (MAIB) - Safety Digest 2/2000Document59 pagesMarine Accident Investigation Branch (MAIB) - Safety Digest 2/2000Çağlar KazmanoğluNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Organizing DCG and ICS 1Document47 pagesModule 3 - Organizing DCG and ICS 1Nadine VillaretNo ratings yet
- It Disaster Recovery Plan TemplateDocument9 pagesIt Disaster Recovery Plan TemplateARCO EXPORTNo ratings yet
- UNpomDocument20 pagesUNpomMatheen AhmedNo ratings yet
- DRR Lesson 6.1Document56 pagesDRR Lesson 6.1Leo EspinoNo ratings yet
- Tobor NHS Contingency PlanningDocument19 pagesTobor NHS Contingency PlanningJanus SalinasNo ratings yet
- Official Notice by Edano On April 11 On New Kinds of Evacuation Areas Pages From ML12123A059Document3 pagesOfficial Notice by Edano On April 11 On New Kinds of Evacuation Areas Pages From ML12123A059EnformableNo ratings yet
- DPR Synthesis-Report en ScreenDocument184 pagesDPR Synthesis-Report en ScreenWahyu HidayatiNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument1 pageNSTPWelroseAndradeNo ratings yet
- GAIL - RPNHQ - Ahmedabad - Base - Station - IMS - Rev02 - CorrectionDocument89 pagesGAIL - RPNHQ - Ahmedabad - Base - Station - IMS - Rev02 - Correctionjai chaudhariNo ratings yet
- El 32104173 Ic448 GBDocument15 pagesEl 32104173 Ic448 GBmohamed algharbiNo ratings yet
- Handling Non-Normal Situations - Ver3Document10 pagesHandling Non-Normal Situations - Ver3hristoskydiveNo ratings yet
- JRC Handbook 2015Document334 pagesJRC Handbook 2015AndreyNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Contingency PlanDocument4 pagesVolcanic Contingency Planbladeliger22No ratings yet
- Operation Instruction XC10 PDFDocument2 pagesOperation Instruction XC10 PDFEng M ElseaidyNo ratings yet
- Ics 211Document12 pagesIcs 211Josanne Wadwadan De Castro100% (2)
- Fung Et - Al.Document6 pagesFung Et - Al.Noi Mae NebreaNo ratings yet
- 4.D Process Safety Management Emergency Response TrainingDocument3 pages4.D Process Safety Management Emergency Response Trainingمحمد المريسيNo ratings yet
- Bhopal Disaster:: Immediate AftermathDocument2 pagesBhopal Disaster:: Immediate AftermathAhtishamNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report DRRMDocument9 pagesAccomplishment Report DRRMPalmes Joseph100% (1)
- Philippine DRRM SystemDocument20 pagesPhilippine DRRM SystemRyan Q. BlancoNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety Policy - AppendicesDocument7 pagesFire Safety Policy - AppendicesHasan ShakeelNo ratings yet
- 02 - LEC - Disaster TriageDocument4 pages02 - LEC - Disaster Triageericka abasNo ratings yet
- Appendix - Select Em-Related Terms and DefinitionsDocument97 pagesAppendix - Select Em-Related Terms and DefinitionsHarold IdjaoNo ratings yet