Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Luna G9 Health Q3 W2 For Final 1
Uploaded by
Jazzy Anne AquinoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Luna G9 Health Q3 W2 For Final 1
Uploaded by
Jazzy Anne AquinoCopyright:
Available Formats
Learning Area HEALTH Grade Level 9
W2 Quarter 3rd Date
I. LESSON TITLE UNINTENTIONAL INJURIES
II. MOST ESSENTIAL LEARNING Demonstrates proper techniques in carrying and transporting the victim of
COMPETENCIES (MELCs) unintentional injuries
Demonstrates proper first aid procedures for common unintentional injuries.
III. CONTENT/CORE CONTENT Carrying and Transporting An Injured Person
Suggested
IV. LEARNING PHASES Timeframe
Learning Activities
A. Introduction Day 1 Transporting an injured person to a safer place requires great care. A first aider must undergo
proper training. When doing this, a first aider must consider the following factors:
A. Weight and height of the victim
B. Status of the victim (conscious and unconscious)
C. Environment (safe, floor is smooth, narrow or wide)
D. Special need considerations (injuries of the victims)
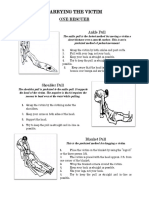
ONE MAN TRANSPORT
Fireman’s Carry Piggy Back Pack Strap Carry
Shoulder Drag Fireman’s Drag Blanket Drag
Fireman’s Carry -the easiest way to transport a light and smaller victim.
Piggy Back- when the victim is conscious
Pack Strap Carry- when the victim is smaller than the first aider.
Shoulder Drag -used when the floor is smooth, short distance transport
Fireman’s Drag or tied-hands Crawl -used when first aider and victim must crawl underneath a
low structure
Blanket Drag-used when the victim is seriously injured and should not be lifted
TWO MAN CARRY
Chair or Seat Carry -when there are two first aiders and chair
THREE OR MORE MAN TRANSPORT
Hammock Carry Bearer Alongside
Hammock Carry- when there are three first aider
Bearer Alongside- carries will stay on the injured side of the victim
Six Man Lift and Carry- when there are six first aider
PROCESSING QUESTIONS:
Suggested
IV. LEARNING PHASES Timeframe
Learning Activities
1. What should you remember before transporting the victim?
2. How do you transport an injured person?
3. What are the things to consider in transporting the victim?
FIRST AID FOR COMMON UNINTENTIONAL INJURIES
Chemical Burns- may occur when electricity passes through the body.
Burns - are often due to domestic incidents such as touching an hot iron, friction(rope burn)or
spilling or boiling water on the skin.
Heat Exhaustion -is caused by lost of salt and water due to excessively high temperature. This
may lead to heat stroke and even death.
Heart Attack-caused by a sudden obstruction of blood supply to the part of the heart muscles.
Choking-results when a foreign object block the throat
Drowning-happens when air cannot get into the lungs because of water. It can cause immediate
death when taken for granted.
Stroke-is a condition which the blood supply to a part of the brain is suddenly and seriously
impaired by a blood clot or ruptured blood vessels
Dislocation-is a partial or complete displacement of the bones
Sprain-is an injury to the ligaments of a bone due to accidental tearing or overstretching.
Suggested
IV. LEARNING PHASES Timeframe
Learning Activities
Fracture-is a break or crack in a bone. An open fracture pierces in the skin surface while in a
closed fracture, the skin above is intact.
Heat Stroke -is caused by a failure of the “thermostat”in the brain to regulate body temperature.
When this happens the body becomes seriously heated
Food Poisoning -is caused by consuming food or drink that is contaminated with bacteria o
viruses
B. Development Day 2 ACTIVITY 1“How Will You Bring Me to A Safe Place?”
Directions: An injured person needs your help. You are bringing her to safe place. How are you
going to do that? Study the situations and determine the kind of
transport that should be used.
SITUATIONS
No. Of Available Status of Injured Person Must Do Kind of
First Materials Transport
Aider
1 None Unconscious
Has no injury on
arm,leg,rib,neck and
back
1 None Unconscious Pass
underneath a
low structure
1 None Unconscious Transport the
victim up the
stairs
1 Malong Experiencing a very
serious injury and should
not be lifted
1 None Unconscious
Very Small
1 None Unconscious
Fat
2 Classroom chairs Unconscious Carry the
and tables No injury on neck, back victim
or pelvis downstairs
3 None unconscious Injured person
will be carried
on his back or
face
Suggested
IV. LEARNING PHASES Timeframe
Learning Activities
3 None Unconscious First aider will
have to stay
on one side of
the injured
person
C. Engagement Day 3 Activity 2 – Thinking of Others
Directions: Assume that you were the SK Chairman of your barangay, create an Action Plan that
will you offer First Aid skills training to the youth of your community. Use the format below as
your guide.
a. Goals/Target
b. Participants
c. Resource Person/Guest Speakers
d. Venue
e. Estimated Budget
f. Desired Outcome
D. Assimilation Day 4 Activity 3 – Campaign for Safety
Directions: Create a slogan that will encourage people in the community to join in the First Aid
Movement.
Criteria:
Relevance 5 points
Persuasiveness 5 points
Total 10 points
V. ASSESSMENT Completion Type
(Learning Activity Sheets for Directions: Write the missing word/s to complete the following statement.
Enrichment, Remediation or 1. ________ carry the easiest way to transport a light and smaller victim.
Assessment to be given on 2. Pack Strap Carry is done when the victim is than the first aider.
Weeks 3 and 6) 3. Shoulder Drag -used when the floor is , short distance transport.
4. Lift and Carry is done when there are six first aider.
5. Carry can be done when there are three first aider.
VI. REFLECTION The learner communicates the explanation of their personal assessment as indicated in
the Learner’s Assessment Card.
The learner, in their notebook, will write their personal insights about the lesson using
the prompts below.
I understand that ___________________.
I realize that ________________________.
I need to learn more about __________.
Prepared by: GRADE 9-MAPEH TEACHERS/GFLMNHS Checked by: NIMFA P. MANALO
You might also like
- Grade 9 HEALTH Q3 - M2Document16 pagesGrade 9 HEALTH Q3 - M2Marjun Oliveros Macadangdang100% (6)
- Carrying and Transporting An Injured PersonDocument29 pagesCarrying and Transporting An Injured PersonAiza Rhea SantosNo ratings yet
- P.E. 2 First Aid Hand OutDocument11 pagesP.E. 2 First Aid Hand OutLaleth Mendoza Ojales100% (3)
- Emergency Rescue and Short Distance Transfer-N5Document3 pagesEmergency Rescue and Short Distance Transfer-N5Gerald Penner100% (5)
- Bisleri Marketing & Competitor Analysis New ProjectDocument82 pagesBisleri Marketing & Competitor Analysis New Projecthvsandeep86% (7)
- Health Week 4 - 3rd QuarterDocument5 pagesHealth Week 4 - 3rd QuarterNoemelyn VecinaNo ratings yet
- Modules in G9 Health Week 3 4Document2 pagesModules in G9 Health Week 3 4VINZ MAXIMUS DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 HEALTH Q3 - M2Document16 pagesGrade 9 HEALTH Q3 - M2Krizzane AcierdaNo ratings yet
- HEALTH-9-Q3-M8-wk8 OKDocument17 pagesHEALTH-9-Q3-M8-wk8 OKreymart pacutNo ratings yet
- First Aid and Water Safety - FinalDocument5 pagesFirst Aid and Water Safety - Finalnellrose emlanoNo ratings yet
- 3rd Grading Health Notes First Aid and Unintentional InjuryDocument1 page3rd Grading Health Notes First Aid and Unintentional Injuryblairemeri09No ratings yet
- Final Demo DLPDocument10 pagesFinal Demo DLPJohn DavidNo ratings yet
- Las Ro3 Final H9Q3W4 8Document17 pagesLas Ro3 Final H9Q3W4 8gloria tolentinoNo ratings yet
- Carrying and Transporting A Victim 2Document28 pagesCarrying and Transporting A Victim 2Rubielyn SerboNo ratings yet
- Passed-2790-13-21MELCS-Tabuk City - UnintentionalinjuriesDocument17 pagesPassed-2790-13-21MELCS-Tabuk City - Unintentionalinjuriesrangelynrish aguirreNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed LP For Carrying and Transporting An Injured PersonDocument4 pagesSemi Detailed LP For Carrying and Transporting An Injured Persontwengkolarquillo.29No ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan in Health 9Document6 pagesDaily Lesson Plan in Health 9Dea BiguerasNo ratings yet
- Las Ro3 Final h9q3w4 8Document17 pagesLas Ro3 Final h9q3w4 8Ian Santos B. SalinasNo ratings yet
- Division of Cebu Province: "Carrying and Transpoting An Injured Person"Document7 pagesDivision of Cebu Province: "Carrying and Transpoting An Injured Person"ALEX PANERIONo ratings yet
- Carrying Anf Transporting A VictimDocument34 pagesCarrying Anf Transporting A VictimAiza Rhea Perito SantosNo ratings yet
- Transport of Victim Using Improvised MaterialsDocument9 pagesTransport of Victim Using Improvised MaterialsTeacher JhenNo ratings yet
- Chapter-I: Search and RescueDocument16 pagesChapter-I: Search and Rescuedrager1969No ratings yet
- Las Ro3 Final h9q3w4 8Document17 pagesLas Ro3 Final h9q3w4 8Randolf CruzNo ratings yet
- Rescue and Carry Methods Power PointDocument75 pagesRescue and Carry Methods Power PointJean Minette Prado88% (8)
- F A - HandoutsDocument7 pagesF A - HandoutsIan Christian BalatayoNo ratings yet
- 3 and 4 of Fundamentals of First Aid ModuleDocument27 pages3 and 4 of Fundamentals of First Aid ModuleMark Joseph P. GaniaNo ratings yet
- Management of Injured PatientDocument22 pagesManagement of Injured PatientMohammad Ali Al-garniNo ratings yet
- Emergency Rescue TransferDocument91 pagesEmergency Rescue TransferJohn DavidNo ratings yet
- Health Education: Quarter 3-Module 6Document11 pagesHealth Education: Quarter 3-Module 6Christine SilawanNo ratings yet
- Prioritization and CarryingDocument8 pagesPrioritization and CarryingJordan ChavezNo ratings yet
- ULAS HEALTH 9 3rd Week 4 5Document9 pagesULAS HEALTH 9 3rd Week 4 5Mayrel Piedad ElandagNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanMargaret BroñolaNo ratings yet
- 4 Carrying and Transporting An Injured PersonDocument21 pages4 Carrying and Transporting An Injured PersonClarissa Joyce BagosNo ratings yet
- Lifegaurd Study GuideDocument4 pagesLifegaurd Study GuideEthanNo ratings yet
- Health9-Module2 Q3Document10 pagesHealth9-Module2 Q3ExequielNo ratings yet
- Carrying and Transporting An Injured Person (Autosaved)Document17 pagesCarrying and Transporting An Injured Person (Autosaved)Judaea Neve Garciano100% (1)
- Intro To First AidDocument3 pagesIntro To First AidKyla SaludoNo ratings yet
- Unintentional Injury Prevention, First Aid and SafetyDocument25 pagesUnintentional Injury Prevention, First Aid and SafetyCasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12&13 Plus Asst 1st AidDocument20 pagesChapter 12&13 Plus Asst 1st AidabyNo ratings yet
- Health. Carrying and Transporting An Injured PersonDocument21 pagesHealth. Carrying and Transporting An Injured PersonAndrew ZafraNo ratings yet
- Carrying and Transporting An Injured PersonDocument25 pagesCarrying and Transporting An Injured PersonGillier Abejuro75% (8)
- Rescue Plan For Confined SpaceDocument26 pagesRescue Plan For Confined SpaceSARFARAZ KHANNo ratings yet
- First AidDocument11 pagesFirst AidRhave MorenoNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document3 pagesModule 7LA MarieNo ratings yet
- Health: Quarter 3 - Module 5: Techniques in Carrying and Transporting The VictimDocument19 pagesHealth: Quarter 3 - Module 5: Techniques in Carrying and Transporting The VictimNnayz0% (1)
- 1st Aid AdultDocument71 pages1st Aid Adultzygomatic medicalresourcesNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - The Basics of First AidDocument6 pagesModule 2 - The Basics of First AidRonald Michael QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Carrying The VictimDocument5 pagesCarrying The VictimTchaikovsky AyopNo ratings yet
- Before During and After - 20231017 - 063818 - 0000Document14 pagesBefore During and After - 20231017 - 063818 - 0000celinebatislaongNo ratings yet
- NCM 121 Skills MidtermDocument5 pagesNCM 121 Skills MidtermShiehan Mae ForroNo ratings yet
- Emergency Rescue - DocsDocument3 pagesEmergency Rescue - DocsZhavia ShyNo ratings yet
- First Responders Functions, Responsibilities and ProceduresDocument36 pagesFirst Responders Functions, Responsibilities and ProceduresDennis Esik MaligayaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Giving Emergency CareDocument5 pagesGuidelines For Giving Emergency CareKath Lea Sanchez AbrilNo ratings yet
- Injury Prevention, Safety, and First AidDocument20 pagesInjury Prevention, Safety, and First AidAprille Maye CayogNo ratings yet
- Unit-10.pdf SHSHDocument11 pagesUnit-10.pdf SHSHvamsiNo ratings yet
- What Is First Aid?Document2 pagesWhat Is First Aid?Eleina Bea BernardoNo ratings yet
- PE FinalsDocument4 pagesPE FinalsehnzdhmNo ratings yet
- How to Fence: Containing Full Instruction for Fencing and the Use of the Broadsword; Also Instruction in ArcheryFrom EverandHow to Fence: Containing Full Instruction for Fencing and the Use of the Broadsword; Also Instruction in ArcheryNo ratings yet
- The Macrobiotic Genius of Walter RussellDocument20 pagesThe Macrobiotic Genius of Walter Russellklatifdg100% (2)
- Planning 1 Module Aug. 31, 2014Document38 pagesPlanning 1 Module Aug. 31, 2014Eli BerameNo ratings yet
- LET ReviewerDocument124 pagesLET ReviewerSo LenNo ratings yet
- How To Size A ThickenerDocument7 pagesHow To Size A ThickenerJesus Sing RoblesNo ratings yet
- Kettle ENDocument4 pagesKettle ENViktor XNo ratings yet
- Science 7 ExamDocument5 pagesScience 7 Examangge21No ratings yet
- Topic: Reverse Osmosis Subject: Chemical Process Industries - 1 Guided By: Dr. Subrahmanyam SIRDocument16 pagesTopic: Reverse Osmosis Subject: Chemical Process Industries - 1 Guided By: Dr. Subrahmanyam SIRAnanya DaveNo ratings yet
- Textile Dyeing Effluents and Environment Concerns - A Review M. R. Islam and M. G. MostafaDocument14 pagesTextile Dyeing Effluents and Environment Concerns - A Review M. R. Islam and M. G. MostafaZhulietaNo ratings yet
- Rain Water Harvesting For Residential Project Daulat Heights in SaswadDocument4 pagesRain Water Harvesting For Residential Project Daulat Heights in SaswadJournalNX - a Multidisciplinary Peer Reviewed JournalNo ratings yet
- STERILIZATION OF WATER USING BLEACHING POWDER Chemistry ProjectDocument23 pagesSTERILIZATION OF WATER USING BLEACHING POWDER Chemistry ProjectChandaNo ratings yet
- Heat of Combustion Ethanol CompleteDocument5 pagesHeat of Combustion Ethanol CompleteericaNo ratings yet
- Full Test 7 (Key) PDFDocument5 pagesFull Test 7 (Key) PDFhoang lichNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument234 pagesPDFOki NurpatriaNo ratings yet
- Gravity Dam - Y910026Document17 pagesGravity Dam - Y910026Ashish Sanghavi100% (1)
- Intro To Thermochem WorksheetDocument2 pagesIntro To Thermochem WorksheetAllyza Alimeos SobosoboNo ratings yet
- Ecolab CorporateDocument28 pagesEcolab CorporateNicolas Figueroa SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Performance Characteristics of An Air-Cooled Condenser Under Ambient ConditionsDocument6 pagesPerformance Characteristics of An Air-Cooled Condenser Under Ambient Conditionstarun_aseriNo ratings yet
- ISOBAR TWIN ManualDocument18 pagesISOBAR TWIN ManualSanto ENo ratings yet
- Calla 1452 Material Safety Data Sheet: Zip-Chem ProductsDocument7 pagesCalla 1452 Material Safety Data Sheet: Zip-Chem ProductsFidel ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Diesel-Water-Air Premixing Injector System in Burner System: A Literature ReviewDocument14 pagesDiesel-Water-Air Premixing Injector System in Burner System: A Literature ReviewPrathmesh KuraneNo ratings yet
- Designing of A Fire Tube Boiler: Author Name/sDocument7 pagesDesigning of A Fire Tube Boiler: Author Name/sMohit JagtapNo ratings yet
- MSDS-TMPTO SeriesDocument5 pagesMSDS-TMPTO Serieswu jasonNo ratings yet
- Risk Action Plan:: Risks Access Risk Score Controls Action Priority Timelines ResponsibleDocument2 pagesRisk Action Plan:: Risks Access Risk Score Controls Action Priority Timelines ResponsibleSadaf MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Ebook Building With Pallets PreviewDocument16 pagesEbook Building With Pallets PreviewGigi FrancoNo ratings yet
- Astm d5887Document7 pagesAstm d5887rajeshji_000No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 5E ScienceDocument17 pagesLesson Plan 5E ScienceSie MeeNo ratings yet
- AR W CenturyDocument74 pagesAR W CenturyJoão André100% (1)
- Junker's Gas CalorimeterDocument4 pagesJunker's Gas CalorimeterShanti Kiran ZNo ratings yet