Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table 54-8
Uploaded by
Dragutin Petrić0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageOriginal Title
Table 54–8_
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageTable 54-8
Uploaded by
Dragutin PetrićCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Critical Care >Postcardiothoracic Surgery Care
John M. Oropello, Stephen M. Pastores, Vladimir Kvetan+
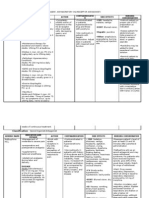
Table 54–8Agents for rate and rhythm control.
Agents Mechanism Dose Considerations
Bolus: 0.25 mg/kg IV over 2 min
•Afib with RVR
Diltiazem Calcium channel blocker •Negative inotropic effect may be detrimental in
Continuous: 5-15 mg/h IV
the postcardiac surgical patient and patient with
low EF
PO: 120-360 mg/d in divided doses
Bolus: 2.5-5 mg IV × 3
Metoprolol β1-selective blocker
Standing: 5 mg IV q4h •Afib with RVR
PO: 12.5-100 mg q12h
Bolus: 150 mg IV over 10 min × 2
•Useful in patients on vasopressors, inotropes, or
Continuous: 1 mg/min × 6 h then 0.5 mg/min ×
Amiodarone Na+, K+, Ca2+ and β-blockade with low EF
18 h
•Avoid in patients with liver, pulmonary, or thyroid
dysfunction
PO: 400 mg q12h × 1 wk, then 600 mg daily × 1
wk, then 400 mg daily × 4-6 wk
Load: 0.25 mg IV then 0.125 × 2 q8h
•Dose cautiously in patients with renal
insufficiency
Digoxin Inhibits Na-K ATPase Maintenance: 0.125-0.25 daily or every other day
•Avoid hypokalemia
•Digoxin-specific antibody fragments available for
PO: 0.5 mg daily × 2 d, then 0.125-0.375 PO
digoxin toxicity
daily or every other day
Load: 1 mg/kg
Lidocaine Na channel blocker
Maintenance: 1 mg/h
500 μg/kg IV over 1 min
Esmolol β1-selective blockade
•Short half-life
60-200 μg/kg/min
Afib, atrial fibrillation; EF, ejection fraction; IV, intravenous; PO, oral; RVR, rapid ventricular response.
Date of download: 01/01/23 from AccessMedicine: accessmedicine.mhmedical.com, Copyright © McGraw Hill. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Feline Drug Formulary June 2020 FINAL Updated-1Document5 pagesFeline Drug Formulary June 2020 FINAL Updated-1Ernesto GuadarramaNo ratings yet
- CEG Formulary: Cardiac Medications For Dogs: ... Bringing Cardiology Into PracticeDocument6 pagesCEG Formulary: Cardiac Medications For Dogs: ... Bringing Cardiology Into PracticeAngeles MerinoNo ratings yet
- RENAL DosingDocument8 pagesRENAL Dosingsumayyah995No ratings yet
- Venous Thromboembolism With Blanks ResidentsDocument9 pagesVenous Thromboembolism With Blanks Residentsapi-648714317No ratings yet
- Table 16-3 - Nonopioid AnalgesicsDocument1 pageTable 16-3 - Nonopioid AnalgesicsDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- BMC COVID Anticoagulation Algorithm Update 5 1 20Document1 pageBMC COVID Anticoagulation Algorithm Update 5 1 20Avinash KumbharNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation TDDocument6 pagesAtrial Fibrillation TDapi-594366475No ratings yet
- Drug Study ClozapineDocument2 pagesDrug Study ClozapineRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Tools: Doses, Routes, and Uses of Common DrugDocument1 pagePharmacological Tools: Doses, Routes, and Uses of Common DrugApuntesdemedicinaa blogNo ratings yet
- Pre-Operative Orders Post-Op Orders (Ga)Document3 pagesPre-Operative Orders Post-Op Orders (Ga)Alissandra OcampoNo ratings yet
- Medication Administration PolicyDocument76 pagesMedication Administration PolicyJully GaciasNo ratings yet
- PRADAXA: Dosing Guide: Starting Patients On PRADAXADocument2 pagesPRADAXA: Dosing Guide: Starting Patients On PRADAXAPapp Szodorai BeátaNo ratings yet
- Lisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationDocument6 pagesLisinopril, TAB: Generic Name of Medication: Brand/trade Name of MedicationCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord CompressionDocument4 pagesSpinal Cord Compressionian3yeung-2No ratings yet
- Pharmacology Part 2Document5 pagesPharmacology Part 2cherrymaemidoriNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - DiazepamDocument2 pagesDrug Study - DiazepamCerie Anne Olay40% (5)
- VTE - Prophylaxis - PROTOCOL - V1.1 - With Forms - 07 - Dec - 2023Document20 pagesVTE - Prophylaxis - PROTOCOL - V1.1 - With Forms - 07 - Dec - 2023hatem newishyNo ratings yet
- VTE Prophylaxis PROTOCOL V1.2 Withforms 31 Dec 2023Document19 pagesVTE Prophylaxis PROTOCOL V1.2 Withforms 31 Dec 2023hatem newishyNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Hypertension MIMSDocument13 pagesDrugs For Hypertension MIMSriczen mae vilaNo ratings yet
- ABC (Peripherally Acting)Document1 pageABC (Peripherally Acting)Sibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Atrial Flutter Medication: Drugs DoseDocument8 pagesAtrial Flutter Medication: Drugs DoseVictoria Castillo TamayoNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs in Obsgyn 2Document42 pagesCommon Drugs in Obsgyn 2Meekel SusikuNo ratings yet
- TABLE 8-4 Frequently Used Chemotherapeutic AgentsDocument7 pagesTABLE 8-4 Frequently Used Chemotherapeutic AgentsBethel MontemayorNo ratings yet
- TABLE 8-4 Frequently Used Chemotherapeutic AgentsDocument7 pagesTABLE 8-4 Frequently Used Chemotherapeutic AgentsBethel MontemayorNo ratings yet
- TABLE 8-4 Frequently Used Chemotherapeutic AgentsDocument7 pagesTABLE 8-4 Frequently Used Chemotherapeutic AgentsBethel MontemayorNo ratings yet
- TABLE 8-4 Frequently Used Chemotherapeutic AgentsDocument7 pagesTABLE 8-4 Frequently Used Chemotherapeutic AgentsBethel MontemayorNo ratings yet
- TABLE 8-4 Frequently Used Chemotherapeutic AgentsDocument7 pagesTABLE 8-4 Frequently Used Chemotherapeutic AgentsBethel MontemayorNo ratings yet
- TABLE 8-4 Frequently Used Chemotherapeutic AgentsDocument7 pagesTABLE 8-4 Frequently Used Chemotherapeutic AgentsBethel MontemayorNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Drugs & Treatment: BWH Quick-Reference GuideDocument1 pageCOVID-19 Drugs & Treatment: BWH Quick-Reference GuideBoules AtefNo ratings yet
- Anti EpilepticsDocument4 pagesAnti EpilepticsWajih FarhanNo ratings yet
- Rawabi Saleh Bakrman Fatima Mohammed Dawood Supervision: Dr. Hassan BayashootDocument21 pagesRawabi Saleh Bakrman Fatima Mohammed Dawood Supervision: Dr. Hassan BayashootRawabi SalehNo ratings yet
- TablesDocument21 pagesTablesMélissa BlancNo ratings yet
- 2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmDocument1 page2010 Integrated Updated Circulation ACLS Tachycardia AlgorithmRyggie ComelonNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - LavlyDocument10 pagesDRUG STUDY - Lavlylabsky_evol100% (1)
- ANTI-ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS Veterinary PharmacologyDocument5 pagesANTI-ARRHYTHMIC DRUGS Veterinary PharmacologyljramosNo ratings yet
- Newer Oral Anticoagulant: DR Shivaom Chaurasia Resident Internal MedicineDocument57 pagesNewer Oral Anticoagulant: DR Shivaom Chaurasia Resident Internal MedicineMuhammad Reza FirdausNo ratings yet
- Agent For Treating Heart FailureDocument26 pagesAgent For Treating Heart FailureClarisse SuanNo ratings yet
- Bumetanide Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument2 pagesBumetanide Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- Antidepressant Use in Adults With Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument1 pageAntidepressant Use in Adults With Chronic Kidney DiseaseAzhar Ali100% (1)
- AmlodipineDocument2 pagesAmlodipineAnonymous QqyLDoW1No ratings yet
- Drug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFDocument4 pagesDrug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFDocument4 pagesDrug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasNo ratings yet
- Abas Drug Study Nicu PDFDocument4 pagesAbas Drug Study Nicu PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasNo ratings yet
- Dapa HF TrialDocument36 pagesDapa HF Trialvarshith kumarNo ratings yet
- Hospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Document4 pagesHospital Treatment Protocol For Covid-19Adrian BoboceaNo ratings yet
- Reversing The New AnticoagulantsDocument24 pagesReversing The New AnticoagulantsFurman BorstNo ratings yet
- H Receptor AntagonistDocument3 pagesH Receptor AntagonistNicholas TagleNo ratings yet
- MC AtorvastatinDocument3 pagesMC AtorvastatinCliff by the seaNo ratings yet
- MedicationsDocument63 pagesMedicationssaraNo ratings yet
- Cardio Case Study 11Document5 pagesCardio Case Study 11api-646131765No ratings yet
- Drug Action Indication/Contraindicatio N Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesDrug Action Indication/Contraindicatio N Nursing ResponsibilitiesBryan BosqueNo ratings yet
- ALS Algorithms LS Tachycardia 2.0Document1 pageALS Algorithms LS Tachycardia 2.0Lucian Alin DinuNo ratings yet
- Hosp Ops II Week 2 Questions 1Document3 pagesHosp Ops II Week 2 Questions 1api-650133203No ratings yet
- Dose Modification GuidelinesDocument1 pageDose Modification GuidelinesAhmed Maged FadelNo ratings yet
- Treatment Protocol Acute GoutDocument2 pagesTreatment Protocol Acute Goutapi-456313554No ratings yet
- Emocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDocument153 pagesEmocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- ŠizofrenijaDocument216 pagesŠizofrenijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- PsihijatrijaDocument223 pagesPsihijatrijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology (Fourth Edition) (Jerry Meyer) (Z-Library)Document841 pagesPsychopharmacology (Fourth Edition) (Jerry Meyer) (Z-Library)Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Emocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDocument153 pagesEmocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Clinical Handbook of Psychotropic Drugs, 25e (May 8, 2023) - (0889376328) - (Hogrefe Publishing) (Etc.) (Z-Library)Document555 pagesClinical Handbook of Psychotropic Drugs, 25e (May 8, 2023) - (0889376328) - (Hogrefe Publishing) (Etc.) (Z-Library)Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- EtikaDocument218 pagesEtikaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Selected Root Causes of Moral DistressDocument1 pageSelected Root Causes of Moral DistressDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Gender PsychiatryDocument12 pagesGender PsychiatryDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Agitacija Verbalna DeeskalacijaDocument2 pagesAgitacija Verbalna DeeskalacijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Medications For Acute AgitationDocument1 pageMedications For Acute AgitationDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Etika (Benedikt de Spinoza) (Z-Library)Document238 pagesEtika (Benedikt de Spinoza) (Z-Library)Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy For Patients With Bipolar DisordersDocument1 pageDrug Therapy For Patients With Bipolar DisordersDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Upitnik o TWEAKDocument1 pageUpitnik o TWEAKDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Upitnik TDocument1 pageUpitnik TDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Okvir S-2Document1 pageOkvir S-2Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Upitnik o CAGE-uDocument1 pageUpitnik o CAGE-uDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- S ADHD LDocument4 pagesS ADHD LDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Salon Building Guidelines PDFDocument8 pagesSalon Building Guidelines PDFtsnie toNo ratings yet
- E Catalog YooilDocument10 pagesE Catalog Yooilom jangidNo ratings yet
- LPP - Problem Number 2Document9 pagesLPP - Problem Number 2CT SunilkumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hydraulic System in The Construction Machinery - Copy ALIDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Hydraulic System in The Construction Machinery - Copy ALImahadNo ratings yet
- EASA Part-66 Module 17 QBDocument53 pagesEASA Part-66 Module 17 QBFaisal Ahmed Newon80% (5)
- Learner Cala Guide: PART A: Identification of Knowledgeable Elderly Part BDocument5 pagesLearner Cala Guide: PART A: Identification of Knowledgeable Elderly Part BPrimrose MurapeNo ratings yet
- Mooka Panchsati Arya SatakamDocument18 pagesMooka Panchsati Arya SatakamPrasad Raviprolu100% (1)
- Electric Heater Datasheet: Duty Bundle (@nom Voltage) Duty Heater (@nom Voltage)Document3 pagesElectric Heater Datasheet: Duty Bundle (@nom Voltage) Duty Heater (@nom Voltage)SonNguyenNo ratings yet
- God Reborn - The Birth of God and The Creation of The UniverseDocument204 pagesGod Reborn - The Birth of God and The Creation of The UniverseTony Bermanseder100% (1)
- Designing The Workplace For CollaborationDocument17 pagesDesigning The Workplace For Collaborationmas zak danielNo ratings yet
- Azure Arc DoccumentDocument143 pagesAzure Arc Doccumentg.jithendarNo ratings yet
- Floating Solar Photovoltaic Systems - An Overview and Their Feasibility at Kota in Rajasthan - IEEE Conference Publication - IEEE XploreDocument3 pagesFloating Solar Photovoltaic Systems - An Overview and Their Feasibility at Kota in Rajasthan - IEEE Conference Publication - IEEE XploreJames KazoobaNo ratings yet
- P Training For ResilienceDocument35 pagesP Training For ResilienceLbrito01100% (1)
- Operating Instructions: Vacuum Drying Oven Pump ModuleDocument56 pagesOperating Instructions: Vacuum Drying Oven Pump ModuleSarah NeoSkyrerNo ratings yet
- Certification Programs: Service As An ExpertiseDocument5 pagesCertification Programs: Service As An ExpertiseMaria RobNo ratings yet
- Report Palazzetto Croci SpreadsDocument73 pagesReport Palazzetto Croci SpreadsUntaru EduardNo ratings yet
- (1908) Mack's Barbers' Guide: A Practical Hand-BookDocument124 pages(1908) Mack's Barbers' Guide: A Practical Hand-BookHerbert Hillary Booker 2nd100% (1)
- PostmanPat Activity PackDocument5 pagesPostmanPat Activity PackCorto Maltese100% (1)
- Minglana-Mitch-T-Answers in Long QuizDocument9 pagesMinglana-Mitch-T-Answers in Long QuizMitch MinglanaNo ratings yet
- HimediaDocument2 pagesHimediaWiwit MarianaNo ratings yet
- Kyoto Seika UniversityDocument27 pagesKyoto Seika UniversityMalvinNo ratings yet
- WB-Mech 120 Ch05 ModalDocument16 pagesWB-Mech 120 Ch05 ModalhebiyongNo ratings yet
- PQS Catalogue 4 2Document143 pagesPQS Catalogue 4 2sagarNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Controllers: Basic Ladder Logic ProgrammingDocument9 pagesProgrammable Logic Controllers: Basic Ladder Logic Programminganuradha19No ratings yet
- PMP Exam Questions and Answers PDFDocument12 pagesPMP Exam Questions and Answers PDFAshwin Raghav SankarNo ratings yet
- Networking With OrganizationsDocument23 pagesNetworking With OrganizationsClaudette Lui Cabanos- Mercado-ReyesNo ratings yet
- Empowerment TechnologyDocument2 pagesEmpowerment TechnologyRegina Mambaje Alferez100% (1)
- Pre-Qin Philosophers and ThinkersDocument22 pagesPre-Qin Philosophers and ThinkersHelder JorgeNo ratings yet
- 5G, 4G, Vonr Crash Course Complete Log AnaylsisDocument11 pages5G, 4G, Vonr Crash Course Complete Log AnaylsisJavier GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Defining The Market Research Problem & Developing An ApproachDocument77 pagesDefining The Market Research Problem & Developing An ApproachSakshi Bhati I H21O41No ratings yet