Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atoms and Molecules Handout 2
Uploaded by
Zoya AdnanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atoms and Molecules Handout 2
Uploaded by
Zoya AdnanCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Atoms and Molecules
Class VI A and B
Name: _________________________ Handout No. 2
Date: ___________________
Difference between an atom and a molecule:
Atom is the smallest particle (basic unit) of an element. Example, Copper is an element and it is
used to make electrical wire. Every individual atom of this element has identical atoms.
Molecule is the smallest particle (basic unit) of a compound. Molecule is the group of atoms,
which is formed when identical (same) atoms e.g. H 2 (Hydrogen) or different kind (type) of atoms
combine chemically in a fixed ratio. Such as H2O (water), CO2 (Carbon Dioxide)
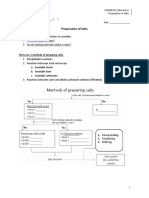
Difference between Mixture and Compound:
Mixture: It is formed when two or more substance combine physically in a variable (different)
ratio by mass. Examples, air, ketchup, tooth-paste, milk, jelly, blood, sea-water, etc.
Compound: It is formed when two or more substance combine chemically in a fixed ratio by mass.
Examples, water forms with two Hydrogen atoms and one Oxygen atom i.e chemically in a fixed
ratio.
Types of Molecules:
i. Molecule of an element.
ii. Molecule in a compound
Note: Definitions from book 2
Exercise No. 1 State the type of molecule
Chemical
S. No. Name of molecule Type of molecule
Formula
1. Water H2O Molecule of a compound
2. Oxygen gas O2 Molecule of an element
3. Carbon Dioxide CO2
4. Ammonia gas NH3
5. Sulfur S8
6. Methane gas CH4
7. Ozone O3
8. Ethanol C2H5OH
Prepared by Ms. F. Haider
2
Exercise No. 2 State the number of each kind of atoms in molecules
Chemical
S. No. Name of molecule Number of each kind of atoms in a molecule
Formula
1. Water H2O 2 Hydrogen atoms, 1 Oxygen atom
2. Hydrogen gas H2
3. Carbon Monoxide CO
4. Carbon Tetrachloride CCl4
5. Phosphorus P4
6. Sulfur Dioxide gas SO2
7. Ozone O3
8. Methanol CH3OH
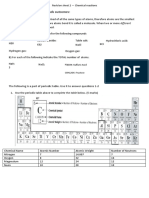
Exercise No. 3 Name the elements present in the following molecules.
Chemical
S. No. Name of molecule Name of each kind of atoms in a molecule
Formula
1. Carbon Dioxide CO2 Carbon, Oxygen
2. Chlorine gas Cl2
3. Methane gas CH4
4. Carbon Tetrachloride CCl4
5. Hydrogen Chloride HCl
6. Nitrogen Oxide gas NO
7. Ammonia gas NH3
8. Methanol CH3OH
Exercise No. 4 Total number of atoms in each molecule
Chemical
S. No. Name of molecule Total number of atoms in each molecule
Formula
1. Carbon Dioxide CO2 3 atoms
2. Magnesium Oxide MgO
3. Ethane gas C2H6
4. Carbon Tetrachloride CCl4
5. Hydrogen Fluoride HF
6. Sodium Chloride NaCl
7. Ammonia gas NH3
8. Glucose C6H12O6
Exercise No. 5 Describe the following molecules.
Prepared by Ms. F. Haider
3
i. Ethanol: It is a molecule of a compound. It consists of two atoms of carbon, one atom of
Oxygen and six atoms of Hydrogen combined chemically.
ii. Ammonia: ____________________________________________________________________________________
iii. Ozone: ____________________________________________________________________________________
iv. Glucose: ____________________________________________________________________________________
v. Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S): _____________________________________________________________________
vi. Phosphorus molecule: _____________________________________________________________________
vii. Methane: ____________________________________________________________________________________
viii. Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3): _______________________________________________________________
Exercise No. 6 Write chemical formula of the following molecules.
Magnesium Oxide Methane
Ammonia Nitrogen gas
Ethanol Sodium Fluoride
Exercise No. 7 Draw model diagram of the following molecules.
i. ii. Sulfur molecule
iii. Ammonia iv. Carbon Dioxide v. Methane vi. Phosphorus vii. Carbon Tetrachloride
viii. Sodium Chloride ix. Ozone x. Hydrogen molecule
Exercise No. 8
Fig. below shows some of the molecules in the air above an active volcano. For example, a water molecule
has the formula H2O and is shown in the diagram. Write the formulae for the other molecules in the air
above the volcano.
Prepared by Ms. F. Haider
You might also like
- Flare SystemsDocument93 pagesFlare SystemsEduardo Paulini Villanueva100% (1)
- Water Treatment GEDocument283 pagesWater Treatment GEJorge Mauricio Justiniano Helbingen100% (1)
- Design Calculations For Slurry Agitators in Alumina RefineryDocument3 pagesDesign Calculations For Slurry Agitators in Alumina RefineryChristopher LloydNo ratings yet
- Specification For Sprinkler DesignDocument14 pagesSpecification For Sprinkler DesignFarhan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption of CarbohydratesDocument25 pagesDigestion and Absorption of CarbohydrateskhadijaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics For Chemists, GlasstoneDocument533 pagesThermodynamics For Chemists, GlasstoneRowie Carpio100% (2)
- Sma Multi Functional Resins (Europe)Document16 pagesSma Multi Functional Resins (Europe)kang88860210% (1)
- Tubing and Casing ConnectionsDocument2 pagesTubing and Casing ConnectionsYougchu LuanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manualrussellsmithnjcoydzkfm100% (9)
- Ce 5230 Water Treatment Plant DesignDocument25 pagesCe 5230 Water Treatment Plant Designapi-297914209No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- ???? ??? ?????????Document1 page???? ??? ?????????Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid 8th Edition by Seager Slabaugh ISBN 1285185978 9781285185972Document32 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid 8th Edition by Seager Slabaugh ISBN 1285185978 9781285185972lindseyallenizqtgdakmw100% (19)
- Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid 8th Edition by Seager Slabaugh ISBN 1285185978 9781285185972Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid 8th Edition by Seager Slabaugh ISBN 1285185978 9781285185972christopher.manteca185100% (11)
- Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesIntroductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualEdwardMasseyentky100% (14)
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid Edition 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument24 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid Edition 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualBrettStoutxcqdi100% (13)
- Expt. No. 4 Oxidation and Reduction Reaction - For On LineDocument8 pagesExpt. No. 4 Oxidation and Reduction Reaction - For On LineJames Val SalazarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions Manualalborakinfect.ufid12100% (26)
- Module 2 Formulas of Common Chemical SubstancesDocument11 pagesModule 2 Formulas of Common Chemical SubstancesIcarusNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manualalborakinfect.ufid12100% (21)
- General-Chemistry1 Quarter1 Week2Document24 pagesGeneral-Chemistry1 Quarter1 Week2Rose RepuestoNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manual PDFschmitzerallanafx100% (11)
- Full Download Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Introductory Chemistry For Today 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manualhaineytattiis100% (25)
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid Edition 8th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry Hybrid Edition 8th Edition Seager Solutions Manualalborakinfect.ufid12100% (23)
- Solution Manual For Introductory Chemistry For Today 8Th Edition Seager Slabaugh 1133605133 9781133605133 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Introductory Chemistry For Today 8Th Edition Seager Slabaugh 1133605133 9781133605133 Full Chapter PDFlois.payne328100% (14)
- Las Atoms Molecules IonsDocument7 pagesLas Atoms Molecules IonsPrince Dave NievesNo ratings yet
- Name/identify What Is Asked in Every Item Below. Choose Your Answer On The Box BelowDocument1 pageName/identify What Is Asked in Every Item Below. Choose Your Answer On The Box BelowDonna RemitarNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly Chapterwise Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesHalf Yearly Chapterwise Important Questionsfood loverNo ratings yet
- Last Name: ID# # On The Signature List: First Name: Chemistry 205/4 Mid Term ExaminationDocument7 pagesLast Name: ID# # On The Signature List: First Name: Chemistry 205/4 Mid Term Examinationb76xxn4rdjNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Activity 7 Lessons 3 7Document5 pagesChemistry Activity 7 Lessons 3 7Nikkaa XOXNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 1 Class 9thDocument9 pagesExercise Chapter 1 Class 9thShah SaqibNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th EditionDocument37 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Editionrepastgraffitie17pv100% (14)
- Element and CompoundDocument21 pagesElement and CompoundJoey PotterNo ratings yet
- Jai Shree RamDocument10 pagesJai Shree RamRenu YadavNo ratings yet
- AP C S W: Hemistry Ummer ORKDocument28 pagesAP C S W: Hemistry Ummer ORKLeslie BenetezNo ratings yet
- 9TH Class Chemistry Guess PaperDocument11 pages9TH Class Chemistry Guess PaperMarkpiciNo ratings yet
- Elements and Compounds Outcomes:: WriteDocument4 pagesElements and Compounds Outcomes:: WriterayNo ratings yet
- Self Practice - Block Test IIDocument2 pagesSelf Practice - Block Test IIDwayneNo ratings yet
- Gateways Institute of Science & Technology: Configuration of The Following Nuclides. (2pts - Each)Document2 pagesGateways Institute of Science & Technology: Configuration of The Following Nuclides. (2pts - Each)Donna RemitarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesChemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions Manualwarlyyersthdvmv100% (35)
- Atoms and Molecules QuestionsDocument4 pagesAtoms and Molecules QuestionsweblogicdocsNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Pre-TestDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Pre-TestMae Pia Flor CawalingNo ratings yet
- Activity Binary Compounds Set 1Document2 pagesActivity Binary Compounds Set 1Zian Lei MienNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and Elements TES UploadDocument127 pagesPeriodic Table and Elements TES Upload18811301255No ratings yet
- Review Guide Moles and Molecular FormulasDocument4 pagesReview Guide Moles and Molecular FormulashejajsNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th EditionDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Editionunwill.eadishvj8p100% (47)
- KimDocument104 pagesKimBayby SiZzle'zNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Module Form 4Document32 pagesChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol100% (3)
- (Basic Concepts) : How N and CO Have Same Number of Electrons, Protons and NeutronsDocument1 page(Basic Concepts) : How N and CO Have Same Number of Electrons, Protons and NeutronsJarar VirkNo ratings yet
- 1st Puc Chemistry Fix QuestionsDocument4 pages1st Puc Chemistry Fix QuestionserannakalivalNo ratings yet
- Full Download Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition PDF Full Chaptermeow.switchel.2kjze7100% (22)
- JR. CHEMISTRY Important QuestionsDocument8 pagesJR. CHEMISTRY Important QuestionsRocky Water0% (1)
- 9th Atoms and Molecules Chemistry Test PaperDocument3 pages9th Atoms and Molecules Chemistry Test Paperanupamkhanna100% (1)
- ElementsAtoms and Compounds SC Answer Key YR7Document5 pagesElementsAtoms and Compounds SC Answer Key YR7ishanroy3julyNo ratings yet
- XI Chemistry Basic Basic QuestionsDocument8 pagesXI Chemistry Basic Basic QuestionsBichitra GautamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Properties of MatterDocument5 pagesLesson 1: Properties of MatterKen Christian As a StudentNo ratings yet
- Molecular CompoundsDocument10 pagesMolecular Compoundsapi-449002661No ratings yet
- Full Download Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 9th Edition Seager Solutions Manual PDF Full Chapterforcingcureless.z93zi7100% (16)
- Chemistry-1st PU: 2&3 Marks Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesChemistry-1st PU: 2&3 Marks Important QuestionsDaksha SubrhamanyaNo ratings yet
- Draw A Line Between The Molecule and Its NameDocument58 pagesDraw A Line Between The Molecule and Its NameJulia Geonzon LabajoNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument6 pagesChemsohailuwu3168No ratings yet
- Grade 7: First Term Examination-2018Document3 pagesGrade 7: First Term Examination-2018ApoorvaNo ratings yet
- File-Example PDF 1MBDocument19 pagesFile-Example PDF 1MBAsif AliNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions - Unit Test 2Document6 pagesChemical Reactions - Unit Test 2소피아No ratings yet
- Chemistry IGCSE Revision QuestionsDocument6 pagesChemistry IGCSE Revision QuestionsJannahNo ratings yet
- Full Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8Th Edition PDF Docx Full Chapter ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Solution Manual For Chemistry For Today General Organic and Biochemistry 8Th Edition PDF Docx Full Chapter Chapterseesaw.insearchd8k4100% (17)
- SNC2D - ReviewDocument4 pagesSNC2D - ReviewZeenat ShahidullahNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument37 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Atoms, Molecules and IonsSeth CapellanNo ratings yet
- ???? ??? ????????? ?????????Document1 page???? ??? ????????? ?????????Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Density NotesDocument1 pageDensity NotesZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Karachi Grammar School Middle Section First Term Examination, 2019 Syllabus Class IxDocument6 pagesKarachi Grammar School Middle Section First Term Examination, 2019 Syllabus Class IxZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument5 pagesPDF DocumentZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Atomic STRCDocument2 pagesAtomic STRCZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Light Test Paper2Document2 pagesLight Test Paper2Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Sec 1 Science SA2 Juying Sec 2018Document44 pagesSec 1 Science SA2 Juying Sec 2018Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Physical QuanitiesDocument8 pagesPhysical QuanitiesZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Sec 1 Science SA2 Hua Yi Sec 2018Document33 pagesSec 1 Science SA2 Hua Yi Sec 2018Zoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- SaltsDocument4 pagesSaltsZoya AdnanNo ratings yet
- Module Outline 2011: Architects Need To Know But Can Never Find. Rockport: MassDocument5 pagesModule Outline 2011: Architects Need To Know But Can Never Find. Rockport: Massapi-115534435No ratings yet
- Performance Report: Critical Deepwater Frac-Pack Recovery and Successful Workover Attributed To DIPRO SystemDocument2 pagesPerformance Report: Critical Deepwater Frac-Pack Recovery and Successful Workover Attributed To DIPRO SystemRuben Waldir Segarra MoralesNo ratings yet
- HZL Chanderiya Pyro Training ReportDocument48 pagesHZL Chanderiya Pyro Training Reportkunalmech100% (5)
- 2021exam 2013Document8 pages2021exam 2013Kamuel Ming WanNo ratings yet
- Union Wire Rope - Galfan CoatingDocument1 pageUnion Wire Rope - Galfan CoatingBosNo ratings yet
- STPM Chem Project 4.3 DiscussionDocument3 pagesSTPM Chem Project 4.3 DiscussionXiangjun WooNo ratings yet
- Photosyn-Thesis: Calvin Cycle: Reporters: Group 4Document11 pagesPhotosyn-Thesis: Calvin Cycle: Reporters: Group 4John Allen GuisdanNo ratings yet
- Seppic Hand HygieneDocument37 pagesSeppic Hand HygieneVinay Bahadur KulshreshthaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 6 Pit Furnace Melting Practice: Aim TheoryDocument3 pagesExperiment No. 6 Pit Furnace Melting Practice: Aim TheoryDhananjay ShimpiNo ratings yet
- The Application and Properties of ATI NuShield™ Borated Stainless SteelsDocument9 pagesThe Application and Properties of ATI NuShield™ Borated Stainless Steelsmp87_ingNo ratings yet
- NEW Atlanta Duracon 2020Document2 pagesNEW Atlanta Duracon 2020janpaul2481100% (1)
- Vietnam Pesticide Use QuestionnaireDocument13 pagesVietnam Pesticide Use QuestionnaireSharmadevan SundrasegaranNo ratings yet
- 2023CHE 3241 TEST 2 and ASSIGNMENT 2 - DISTANCEDocument3 pages2023CHE 3241 TEST 2 and ASSIGNMENT 2 - DISTANCEjmbalush74No ratings yet
- Sample Paper For Grade 6Document4 pagesSample Paper For Grade 6Navvye AnandNo ratings yet
- 303 - Gastrointestinal Physiology) Gastric Secretion - The Cephalic - Gastric PhaseDocument5 pages303 - Gastrointestinal Physiology) Gastric Secretion - The Cephalic - Gastric Phasekedas70No ratings yet
- HD 35-04 Provisions For The Use of Secondary and Recycled Materials (Nov 2004)Document16 pagesHD 35-04 Provisions For The Use of Secondary and Recycled Materials (Nov 2004)sandycastleNo ratings yet
- Kimia Organik: Prof. Setiyo Gunawan, ST., Ph.D. Chemical Engineering Department Fti-ItsDocument7 pagesKimia Organik: Prof. Setiyo Gunawan, ST., Ph.D. Chemical Engineering Department Fti-ItsMohammad Farhan SNo ratings yet
- A Procedure To Measure The Antiradical EfficiencyDocument7 pagesA Procedure To Measure The Antiradical EfficiencyLucila Sanchez BoadoNo ratings yet
- Ashima JMLDocument11 pagesAshima JMLPrachi PatnaikNo ratings yet
- Tech D (048-069)Document22 pagesTech D (048-069)Alejandro CouceiroNo ratings yet