Professional Documents
Culture Documents
03 - One-Point Perspective
Uploaded by
Rechaina Gwen0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views13 pagesOne-point perspective is a type of parallel perspective where two axes are parallel to the picture plane and lines parallel to these axes remain parallel in the image. The third axis is perpendicular to the picture plane and lines parallel to this axis converge at the vanishing point on the horizon line. One-point perspective is effective for depicting interiors where all receding lines seem to meet at a single vanishing point, such as streets, gardens, courtyards, and interior rooms. The document provides instructions on constructing a one-point perspective drawing.
Original Description:
Original Title
03 - ONE-POINT PERSPECTIVE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOne-point perspective is a type of parallel perspective where two axes are parallel to the picture plane and lines parallel to these axes remain parallel in the image. The third axis is perpendicular to the picture plane and lines parallel to this axis converge at the vanishing point on the horizon line. One-point perspective is effective for depicting interiors where all receding lines seem to meet at a single vanishing point, such as streets, gardens, courtyards, and interior rooms. The document provides instructions on constructing a one-point perspective drawing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views13 pages03 - One-Point Perspective
Uploaded by
Rechaina GwenOne-point perspective is a type of parallel perspective where two axes are parallel to the picture plane and lines parallel to these axes remain parallel in the image. The third axis is perpendicular to the picture plane and lines parallel to this axis converge at the vanishing point on the horizon line. One-point perspective is effective for depicting interiors where all receding lines seem to meet at a single vanishing point, such as streets, gardens, courtyards, and interior rooms. The document provides instructions on constructing a one-point perspective drawing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
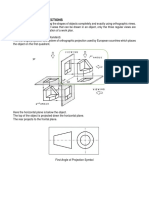
ONE-POINT PERSPECTIVE
Prepared by Genevieve C. Miala
Also known as parallel perspective.
Two (2) of the three (3) principal axes
(one vertical, and the other
horizontal) are parallel to the picture
plane (PP).
Lines parallel to these axes are also
parallel to the picture plane. These
lines:
➢ Retain their true orientation
➢ Do not appear to converge
The third principal axis is horizontal,
perpendicular to PP, and parallel
with the central axis of vision (CAV).
All lines parallel to CAV converge on
the horizon line (HL) at the center of
vision (C).
Effective in depicting the interior of a spatial volume.
Often used to present
experiential view of:
★ Street scenes
★ Formal gardens
★ Courtyards
★ Colonnades /
arcades
★ Interior rooms
Perspective-plan views
One-point perspectives of interior
spaces viewed from above–can be
effective in illustrating small, highly
detailed rooms.
Section perspective
Combines the scaled attributes of a
section drawing, and the pictorial depth of
a perspective drawing. It, therefore, is able
to illustrate both the constructional aspects
of a design as well as the quality of the
spaces formed by the structure.
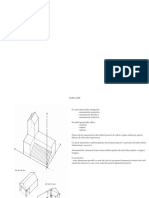
CONSTRUCTING A
ONE-POINT PERSPECTIVE
See the demonstration video on this.
See the demonstration video on this.
Homework time!
Go to the exercise folder on the
Google Classroom for the instructions.
You might also like
- Three Dimensional Projection: Unlocking the Depth of Computer VisionFrom EverandThree Dimensional Projection: Unlocking the Depth of Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Tech Drawing and DraftingDocument14 pagesTech Drawing and Draftinganjali narNo ratings yet
- Perspective DrawingsDocument41 pagesPerspective DrawingsCykiNo ratings yet
- Lecture03-Architectural Drawing SystemsDocument15 pagesLecture03-Architectural Drawing SystemsQuarda Dohny100% (2)
- Architectural Drawing SystemsDocument9 pagesArchitectural Drawing Systemsbhavesh shettyNo ratings yet
- Paraline DrawingsDocument9 pagesParaline Drawingsbhavesh shettyNo ratings yet
- IntroToArchiDesign1 QSADocument19 pagesIntroToArchiDesign1 QSAkennedy obazeNo ratings yet
- 01 - Paraline vs. PerspectiveDocument20 pages01 - Paraline vs. PerspectiveRechaina GwenNo ratings yet
- Multiviews and Auxiliary Views (Bertoline)Document66 pagesMultiviews and Auxiliary Views (Bertoline)Adarsh C KurupNo ratings yet
- ProjectionsDocument16 pagesProjectionsHùng Khánh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- CurssDocument40 pagesCurssDoroteea BalabanNo ratings yet
- Architectural Graphics, 4th Edition Francis DK. Ching 32Document1 pageArchitectural Graphics, 4th Edition Francis DK. Ching 32Ina Alexandra0% (3)
- Drawings: Tugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa InggrisDocument10 pagesDrawings: Tugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa InggrisRoihans Muhammad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Views PDFDocument4 pagesAuxiliary Views PDFChandima K PriyamalNo ratings yet
- Projection DwgsDocument13 pagesProjection DwgsRobert C ChenowethNo ratings yet
- Projective GeometryDocument61 pagesProjective GeometryAileen Grace Delima100% (4)
- Introduction: 1. Plan DrawingDocument6 pagesIntroduction: 1. Plan DrawingSadeeq YusufNo ratings yet
- ProjectionsDocument21 pagesProjectionsPalashAhujaNo ratings yet
- Handprint Perspective Part 2Document73 pagesHandprint Perspective Part 2savrtuthdNo ratings yet
- SPD - Unit 3Document89 pagesSPD - Unit 3Shif renNo ratings yet
- GEC 117 Module 9-10 Lecture Note (Repaired)Document19 pagesGEC 117 Module 9-10 Lecture Note (Repaired)Alexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Adv Perspective Techniques PDFDocument48 pagesAdv Perspective Techniques PDFChristopher ErnstNo ratings yet
- Technique: Advanced Perspective TechniquesDocument36 pagesTechnique: Advanced Perspective TechniquesNishant Kounder100% (1)
- 03D - Methods of Drawing Representation (Pictorial)Document24 pages03D - Methods of Drawing Representation (Pictorial)1B44RizalMNo ratings yet
- Orthographic ProjectionsDocument14 pagesOrthographic Projectionspshantanu123No ratings yet
- Perpective Presentation2Document26 pagesPerpective Presentation2gociy20905No ratings yet
- Orthographic ProjectionDocument51 pagesOrthographic ProjectionAjit ParwaniNo ratings yet
- Orthographic Projection: Review: Projections Orthographic ProjectionsDocument47 pagesOrthographic Projection: Review: Projections Orthographic ProjectionsLeo Dev WinsNo ratings yet
- Orthographic Projection For LrmsDocument35 pagesOrthographic Projection For LrmsnoniNo ratings yet
- Engineering DrawingDocument41 pagesEngineering DrawingAdepu Sanju BhargavNo ratings yet
- Three Point PerspectiveDocument49 pagesThree Point PerspectiveCaleb M. FairchildNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 Projection of PointDocument41 pagesLecture5 Projection of PointGaurav MeenaNo ratings yet
- Edd 10205Document3 pagesEdd 10205Haffiz AtingNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Parallel & Perspective Projection CGMDocument5 pagesUnit - 3 Parallel & Perspective Projection CGMmanyasharma1298No ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Viva QuestionsDocument9 pagesEngineering Drawing Viva QuestionsPranavi100% (1)
- Perspective Drawing 11-04-17 ModifyDocument21 pagesPerspective Drawing 11-04-17 ModifyRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Calculo IntegralDocument5 pagesCalculo Integralriosedithh33No ratings yet
- Orthographic ProjectionDocument8 pagesOrthographic ProjectionDeven MallaNo ratings yet
- PERSPETIVE - Three Point PerspectiveDocument89 pagesPERSPETIVE - Three Point PerspectiveAdarsh PatilNo ratings yet
- Door Schedules Spell Out The Specific Details of Every Door and Are Keyed To The Floor PlanDocument1 pageDoor Schedules Spell Out The Specific Details of Every Door and Are Keyed To The Floor PlanĐức ToànNo ratings yet
- SLM Part 2Document7 pagesSLM Part 2CHARISSE MERCADONo ratings yet
- SLM Part 2-ChariseDocument7 pagesSLM Part 2-ChariseCHARISSE MERCADONo ratings yet
- Rochell Oliver Bse 3F EmtDocument2 pagesRochell Oliver Bse 3F EmtRochellNo ratings yet
- Unit 08Document21 pagesUnit 08elliottashley22No ratings yet
- Primary ElementsDocument13 pagesPrimary ElementsAbhishek KadianNo ratings yet
- Compositional Devises Including Linear and Aerial PerspectivesDocument28 pagesCompositional Devises Including Linear and Aerial Perspectivesjohan shane carsidoNo ratings yet
- 07 - Architectural Drawing Systems - Multiview and Isonometric DrawingsDocument32 pages07 - Architectural Drawing Systems - Multiview and Isonometric DrawingsAngela Gabrielle LorenoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document14 pagesLecture 2ЮлияNo ratings yet
- Orthographic SketchingDocument38 pagesOrthographic SketchingPhiw TabuzoNo ratings yet
- Parallel ProjectionDocument7 pagesParallel ProjectionAnsuman MahantyNo ratings yet
- Types of PerspectiveDocument4 pagesTypes of PerspectivePurvi AryaNo ratings yet
- Paraline DrawingsDocument3 pagesParaline DrawingsviditghaiNo ratings yet
- Final Topics Drawing Perspectives: Methods of ConstructionDocument9 pagesFinal Topics Drawing Perspectives: Methods of ConstructionNasrea Galmak Hadji Mohammad0% (1)
- Chapter 4 Orthographic ProjectionDocument24 pagesChapter 4 Orthographic ProjectionKhadijah ZainudinNo ratings yet
- ProjectionDocument6 pagesProjectionistiake zahanNo ratings yet
- Projection NewDocument27 pagesProjection NewAysha Akter UrmiNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Drawing Lect 4 PDFDocument23 pagesCivil Engineering Drawing Lect 4 PDFEngr Muhammad Asif JavaidNo ratings yet
- Pictorial DrawingDocument15 pagesPictorial DrawingDharam JagroopNo ratings yet
- 1st & 3rd Angle ProjectionsDocument23 pages1st & 3rd Angle ProjectionsSaadii RajaNo ratings yet
- 2ND Yr Subito Pavilion 2Document7 pages2ND Yr Subito Pavilion 2Rechaina GwenNo ratings yet
- V4 - 02 - Watercolor Techniques & ConsistenciesDocument16 pagesV4 - 02 - Watercolor Techniques & ConsistenciesRechaina GwenNo ratings yet
- Church of San VitaleDocument5 pagesChurch of San VitaleRechaina GwenNo ratings yet
- Archist1 - Greek Architecture - NotesDocument17 pagesArchist1 - Greek Architecture - NotesRechaina GwenNo ratings yet
- Activity AnthropometricsDocument1 pageActivity AnthropometricsRechaina GwenNo ratings yet
- Color Wheel + HarmoniesDocument1 pageColor Wheel + HarmoniesRechaina GwenNo ratings yet
- Entrep Business Plan TemplateDocument19 pagesEntrep Business Plan TemplateRechaina GwenNo ratings yet
- 01 - Paraline vs. PerspectiveDocument20 pages01 - Paraline vs. PerspectiveRechaina GwenNo ratings yet
- 00 - Scaling & Paraline DrawingsDocument21 pages00 - Scaling & Paraline DrawingsRechaina GwenNo ratings yet
- Painting Analysis - DumandanDocument2 pagesPainting Analysis - DumandanRechaina GwenNo ratings yet
- Functions of Art Reflection About The Subject - DumandanDocument2 pagesFunctions of Art Reflection About The Subject - DumandanRechaina GwenNo ratings yet