Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Translation Criticism by Berman
Uploaded by
AnnaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Translation Criticism by Berman
Uploaded by
AnnaCopyright:
Available Formats
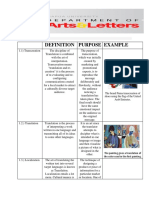
1) “ conception” and “perception”;
the basis of evaluation 1) ethics and poetics. 2) translator’s position verbalized, manifested and
transformed into representations;
3) translator’s depth - capricious freedom, temptation of self-
1) this is a crucial phase of methodology because we have effacement.
take into account the translating subject;
2) knowledge whether the translators also produced books,
from which languages, genres and all another “facts”
in search of transtion
1) poetic nature manifests itself in the textual work of a translator;
2) ethics and poetics guarantee that there is some
1) that is project which is not theoretical; correspondence or connection to the original and its language;
2) every coherent translation is sustained by a project, a 3) It ensure that the processes of creating works take place in the
conscious intention; translating language, enlarging, amplifying and enriching it at
3) existence in no way contradicts the immediate, intuitive every possible level.
aspects of translation that are so often invoked. the translator’s position
the translation project
) reading and rereading of translation
Analyzing translation 1) reread the translation while completely setting aside the
1) comparison of original and translation original;
Translation criticism 2) while rereading become visible “problem spots” and “miracle
by Berman spots”
3) read-reread- have impression.
1) the translator’s position bounded by a horizon;
2) it may be defined of all the linguistic, literary, cultural and
historical parameters;
3) notion is twofold ( action of translator is meaningful and the The translator’s horizon the reception of translation
translator in a circle of limited possibilities “first translation” - the most productive form, it demands a
retranslation;
the analysis may centre on one particular translation, it “calls
Comparing the texts up” other translations
The forms of analysis
4 levels:
1) selected elements and passages from original are
compared with translation;
2) problems spots should be compared with the
The analysis of translation becomes criticism in the highest
corresponding parts of the original;
possible sense, it achieves fulfillment as a productive, enriching,
3)the comparison with other critical act.
4) the work of translation is considered in terms of its project. Productive criticism
3 procedures:
1) clarity of expression;
2) reflexivity( face to face confrontation between the original
and translation);
The style of comparison 3) digressive analysis( opening up a serious of questions,
perspectives).
Reading and rereading the original
1) critic does the same work of reading that the translator
does;
2) that stage must be based on many other related texts,
other works by the same author;
3) critic does pre-analysis and select stylistic examples
independent into other levels of analysis
The reception of translation
You might also like
- Internship Report FormatDocument19 pagesInternship Report FormatraselNo ratings yet
- Alcoholism: A Very Real and Serious DiseaseDocument4 pagesAlcoholism: A Very Real and Serious DiseaseUksub AvtNo ratings yet
- Translation and Editing of TextDocument5 pagesTranslation and Editing of TextJuan Tamad0% (1)
- Essentials of TranslationDocument101 pagesEssentials of TranslationMihaela StcNo ratings yet
- 400,450 7 PDFDocument766 pages400,450 7 PDFNguyễn Huy100% (1)
- Translation Terminology PDFDocument25 pagesTranslation Terminology PDFdefdefaNo ratings yet
- Attunity Acx ReferenceDocument830 pagesAttunity Acx Referencewlodar2No ratings yet
- Endodontic-Periodontal Lesion: A Two-Way Traffic: Dr. Anindya Priya Saha, Dr. Anindya Chakraborty and Dr. Sananda SahaDocument6 pagesEndodontic-Periodontal Lesion: A Two-Way Traffic: Dr. Anindya Priya Saha, Dr. Anindya Chakraborty and Dr. Sananda Sahanovia chantikaNo ratings yet
- French English Translation Theory and PracticeDocument42 pagesFrench English Translation Theory and PracticezakNo ratings yet
- RA 8371 Key PointsDocument6 pagesRA 8371 Key PointsKristine DiamanteNo ratings yet
- Reiss1981 Type Kind and IndividualityDocument12 pagesReiss1981 Type Kind and IndividualityVictoria Solovei100% (1)
- Снимок экрана 2023-05-08 в 09.44.28Document34 pagesСнимок экрана 2023-05-08 в 09.44.28AnastasiaNo ratings yet
- Issues On InterpretingDocument8 pagesIssues On InterpretingjNo ratings yet
- Week2 - Act3 Traslating or TraslationDocument21 pagesWeek2 - Act3 Traslating or TraslationSuz MtzgNo ratings yet
- Discourse Analysis HanDocument36 pagesDiscourse Analysis HanMuhammedNo ratings yet
- Yeti ImutDocument8 pagesYeti ImutAryaNo ratings yet
- Discourse Analysis HANDOUTSDocument4 pagesDiscourse Analysis HANDOUTSAlain Delon Lim SerinoNo ratings yet
- General Topics in TranslationDocument12 pagesGeneral Topics in TranslationAlifia Gian DifayanaNo ratings yet
- Bản Full Powerpoint Thuyết Trình Lớp Thầy VânDocument103 pagesBản Full Powerpoint Thuyết Trình Lớp Thầy VânNgọc Linh ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Translation BaganDocument1 pageTranslation BaganLidwynna GuloNo ratings yet
- Type, Kind and Individuality of Text - Decision Making in Translation by Katharina ReissDocument12 pagesType, Kind and Individuality of Text - Decision Making in Translation by Katharina ReissMarcela Paz MuñozNo ratings yet
- What Is Discourse Analysis - SummDocument7 pagesWhat Is Discourse Analysis - SummAmine BennezzarNo ratings yet
- Translation As A Profession: by Group 1: Rizky Najerin Laila Rahmi RamunaDocument5 pagesTranslation As A Profession: by Group 1: Rizky Najerin Laila Rahmi RamunaAulia SafitriNo ratings yet
- Literary Criticism HandoutDocument6 pagesLiterary Criticism HandoutJulius BalingbingNo ratings yet
- Translation Kelompok 6Document14 pagesTranslation Kelompok 6Alvonzo VlImoteNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document2 pagesUnit 2rimaNo ratings yet
- Dewi 2016Document14 pagesDewi 2016mkielkuckaNo ratings yet
- Avt HM 2Document3 pagesAvt HM 2Оксана ТрапезунNo ratings yet
- Semantic Pragmatic-Speech ActDocument26 pagesSemantic Pragmatic-Speech ActDiah Retno WidowatiNo ratings yet
- Unit 9. Translating and Interpreting 2016Document13 pagesUnit 9. Translating and Interpreting 2016arifsahidNo ratings yet
- Frawley Berman VenutiDocument9 pagesFrawley Berman Venutieleonora rizzaNo ratings yet
- Literary Criticism HandoutDocument4 pagesLiterary Criticism HandoutMon ColinaNo ratings yet
- Peter Newmark 1977Document18 pagesPeter Newmark 1977马宁No ratings yet
- Creative SAC RubricDocument1 pageCreative SAC RubricKenny TranNo ratings yet
- BÀI TẬPDocument2 pagesBÀI TẬPBIBINo ratings yet
- Figurative Language and Semantic Connectivity in Translating Qur'ānic Discourse: A Cognitive PerspectiveDocument18 pagesFigurative Language and Semantic Connectivity in Translating Qur'ānic Discourse: A Cognitive PerspectiveasdNo ratings yet
- What Is Pragmatics: Syntax, Semantics and PragmaticsDocument3 pagesWhat Is Pragmatics: Syntax, Semantics and PragmaticsTrần Quỳnh TrangNo ratings yet
- Aja10318471 129Document54 pagesAja10318471 129Zulema EmirNo ratings yet
- The Translation of Metaphors in Harry PoDocument9 pagesThe Translation of Metaphors in Harry PokhanaNo ratings yet
- Descriptors For Translator Certifications Version 1 June 2017pdf PDFDocument3 pagesDescriptors For Translator Certifications Version 1 June 2017pdf PDFSojanya KatareNo ratings yet
- The Bible and Related StudiesDocument5 pagesThe Bible and Related StudiesFigoredo DidokNo ratings yet
- Madani: Universitas Pohuwato Jl. Trans Sulawesi No 147 Kab. Pohuwato, GorontaloDocument16 pagesMadani: Universitas Pohuwato Jl. Trans Sulawesi No 147 Kab. Pohuwato, Gorontaloakhmad_sholikinNo ratings yet
- NLP PDFDocument20 pagesNLP PDFThakur Sahil NarayanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Translation Jurnal Alya Hasna NadhilahDocument14 pagesTugas Translation Jurnal Alya Hasna NadhilahalyaNo ratings yet
- Applying Language Technology in Humanities Researc... - (2.4 Corpus and Natural Language Processing Tools)Document11 pagesApplying Language Technology in Humanities Researc... - (2.4 Corpus and Natural Language Processing Tools)Luyi ZhangNo ratings yet
- WELCOME TO 21st CENTURY PHILIPPINES AND WORLD LITERATUREDocument8 pagesWELCOME TO 21st CENTURY PHILIPPINES AND WORLD LITERATURELJ PaguiganNo ratings yet
- Week 1 English 8 and 10 Very FinalDocument8 pagesWeek 1 English 8 and 10 Very FinalCristy Gasco SumpayNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LinguisticDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Linguistictulia carabaliNo ratings yet
- Main Issues of Translation StudiesDocument30 pagesMain Issues of Translation StudiesMischelle C. TorregosaNo ratings yet
- The Translator Explained Exploring FossiDocument3 pagesThe Translator Explained Exploring FossiOgxoyNo ratings yet
- Audiovisual Translation: Conception, Types, Characters' Speech and Translation Strategies AppliedDocument7 pagesAudiovisual Translation: Conception, Types, Characters' Speech and Translation Strategies Applieddede jdjNo ratings yet
- The Unit of TranslationDocument7 pagesThe Unit of TranslationalmaNo ratings yet
- Ramos Pinto-Sociolinguistics and Translation-Handbook - of - Translation - Studies - Volume - 3Document24 pagesRamos Pinto-Sociolinguistics and Translation-Handbook - of - Translation - Studies - Volume - 3hesaviNo ratings yet
- Pragmatics 1-1 StudentsDocument8 pagesPragmatics 1-1 StudentsDîrmină Oana DianaNo ratings yet
- Peter Newmark: An English Professor of Translation at The University of SurreyDocument65 pagesPeter Newmark: An English Professor of Translation at The University of SurreyNhan ThanhNo ratings yet
- Eng 102Document4 pagesEng 102Leah RoseNo ratings yet
- Week 3 English 8 and 10 Very FinalDocument6 pagesWeek 3 English 8 and 10 Very FinalCristy Gasco SumpayNo ratings yet
- The Translation of Metaphors in Harry PoDocument9 pagesThe Translation of Metaphors in Harry PokhanaNo ratings yet
- Other Contemporary ApplicationsDocument4 pagesOther Contemporary ApplicationsMari TalanayNo ratings yet
- Discourse Analysis Poster - Alaa NajeebDocument1 pageDiscourse Analysis Poster - Alaa NajeebÃlaa NajeebNo ratings yet
- Lujan Semantic ChangeDocument15 pagesLujan Semantic ChangeMustafa AlanNo ratings yet
- Istituto Italiano Per L'Africa E L'Oriente (Isiao) Is Collaborating With Jstor To Digitize, Preserve and Extend Access To East and WestDocument3 pagesIstituto Italiano Per L'Africa E L'Oriente (Isiao) Is Collaborating With Jstor To Digitize, Preserve and Extend Access To East and Westdixson1965No ratings yet
- Nota Ringkas Hermeneutics Gordon FeeDocument2 pagesNota Ringkas Hermeneutics Gordon FeeKi C PungitNo ratings yet
- FILE - 20200308 - 043957 - Bài thuyết trình DA Week 1 (QH2019D2)Document43 pagesFILE - 20200308 - 043957 - Bài thuyết trình DA Week 1 (QH2019D2)Huỳnh Thu HằngNo ratings yet
- From Mimetic Translation to Artistic Transduction: A Semiotic Perspective on Virginia Woolf, Hector Berlioz, and Bertolt Brecht.From EverandFrom Mimetic Translation to Artistic Transduction: A Semiotic Perspective on Virginia Woolf, Hector Berlioz, and Bertolt Brecht.No ratings yet
- One Past But Many Histories Controversies and Conflicting Views in Philippine HistoryDocument28 pagesOne Past But Many Histories Controversies and Conflicting Views in Philippine HistoryShiela Marie Gadayos100% (1)
- Booth ProposalDocument3 pagesBooth ProposalChristian ResustaNo ratings yet
- USH 1.05 HonorsDocument7 pagesUSH 1.05 HonorsAubrey HovanNo ratings yet
- Thoth (Djhuty) Analysis and Etymology - by - Alexis BianchiniDocument9 pagesThoth (Djhuty) Analysis and Etymology - by - Alexis BianchiniAlexis BianchiniNo ratings yet
- Texto para Discussão: Departamento de EconomiaDocument43 pagesTexto para Discussão: Departamento de EconomiaAna ScaletNo ratings yet
- 0004.22-Erma Modes of OperationDocument4 pages0004.22-Erma Modes of OperationDrug Luka PopovicNo ratings yet
- The Entrepreneurial LifeDocument3 pagesThe Entrepreneurial Lifegeffa fadoNo ratings yet
- Distance Learning BrochureDocument8 pagesDistance Learning BrochurecaphilNo ratings yet
- Pan Am Rehab Symposium 2019 Lumbar SpineDocument2 pagesPan Am Rehab Symposium 2019 Lumbar SpineGusti TettaNo ratings yet
- 22 23 34Document20 pages22 23 34anilmathew244No ratings yet
- Planning Technical ActivitiesDocument29 pagesPlanning Technical ActivitiesMaria Cecille Sarmiento GarciaNo ratings yet
- BC548 - Datashet PDFDocument2 pagesBC548 - Datashet PDFBraian KonzgenNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 DLL English 4 q4 Week 5Document6 pagesGrade 4 DLL English 4 q4 Week 5Cristina SingsingNo ratings yet
- The OS/2 Debugging Handbook - Volume I Basic Skills and Diagnostic TechniquesDocument388 pagesThe OS/2 Debugging Handbook - Volume I Basic Skills and Diagnostic TechniquesMichael GreeneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5: I Felt The Ground Shaking When The Earthquake HitDocument2 pagesLesson 5: I Felt The Ground Shaking When The Earthquake HitZhangw VictorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 2-003 (Basis)Document6 pagesChapter 2 2-003 (Basis)Jamiel CatapangNo ratings yet
- Rademacher Dropout: An Adaptive Dropout For Deep Neural Network Via Optimizing Generalization GapDocument11 pagesRademacher Dropout: An Adaptive Dropout For Deep Neural Network Via Optimizing Generalization Gapbob aaNo ratings yet
- Basic Immunology PDFDocument6 pagesBasic Immunology PDFAnastasia ENo ratings yet
- Gatekeepers of Heaven Earth LightDocument43 pagesGatekeepers of Heaven Earth Lightdreampurpose97No ratings yet
- SHRII P.R. Sarkar's English GrammarDocument53 pagesSHRII P.R. Sarkar's English GrammarRipudaman SinghNo ratings yet
- Medina v. KoikeDocument5 pagesMedina v. KoikeHannah MedNo ratings yet
- Cpar Tos Diagnostic-TestDocument2 pagesCpar Tos Diagnostic-TestAvelyn Narral Plaza-ManlimosNo ratings yet
- Hanoi Open University PDFDocument18 pagesHanoi Open University PDFLinh ChuNo ratings yet
- Condom Nation by Emily LimbaughDocument1 pageCondom Nation by Emily LimbaughCrisostomo GregNo ratings yet