Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BL Chem Task 1
Uploaded by
Ha NaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BL Chem Task 1
Uploaded by
Ha NaCopyright:
Available Formats
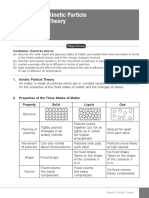
STATES OF MATTER
There are 3 main states of matter:
SOLID
Particles are closely packed in an
orderly arrangement, vibrating and
rotating about a fixed position
Very strong forces of attraction
between the particles
Fixed shape and volume
Incompressible
LIQUID
Particles are closely packed, but are
in a disorderly arrangement, and
can move freely
Strong forces of attraction between
the particles
Unfixed shape, but fixed volume
Incompressible
GAS
Particles are far apart in a
disorderly arrangement, and travel
at high speeds in random directions
Very weak forces of attraction
between the particles
Unfixed shape, unfixed volume
Compressible
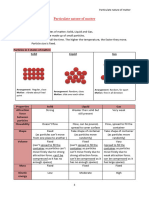
CHANGES IN STATE
sublimation
melting vaporisation
solid liquid gas
freezing condensation
deposition
During change of state, temperature of matter remains
constant. In heating, thermal energy is absorbed to
overcome forces of attraction between particles. In cooling,
thermal energy loss is compensated by thermal energy
released during formation of forces of attraction. A mixture
of the two states involved exist during a change in state.
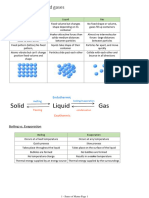
Vaporisation includes both evaporation and boiling:
Evaporation Boiling
Occurs only at the surface Occurs all throughout the
of a liquid liquid at once
Can happen at a range of Only occurs at the boiling
temperatures below the b.p* point of the liquid
Causes cooling in the rest of No change in temperature
the liquid Faster, effervescence is
Slower; no effervescence produced
*boiling point
Citations Particle Diagrams taken from:
Infographic made on canva.com https://www.teachoo.com/12513/3426/Difference- Done by Keagan, Ansley,
Temperature Icons taken from flaticon.com between-Solid--Liquid--Gas/category/Extra-Questions/ Kieran, Ngoc My - CHE510H
You might also like
- Z Notes Chemistry 2023-25Document31 pagesZ Notes Chemistry 2023-25ֆɦɛʀաɨռ ֆǟʀʄʀǟʐNo ratings yet
- Pdfcaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v11.PDF 7Document29 pagesPdfcaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v11.PDF 7aimaan1903No ratings yet
- Kami Export - Abbas Kamoona - Caie-Igcse-Chemistry-0620-Theory-V10Document29 pagesKami Export - Abbas Kamoona - Caie-Igcse-Chemistry-0620-Theory-V10Abbas KamoonaNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v13Document29 pagesCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v13Khoa DangNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v12Document29 pagesCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v12Roshni ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document12 pagesChapter 1Phan BảoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry KineticsDocument4 pagesChemistry KineticsmayaNo ratings yet
- Physics CH 4 MoleculesDocument42 pagesPhysics CH 4 MoleculesMuhammad Usman Khalid AminNo ratings yet
- 1 States of MatterDocument7 pages1 States of MatterAiman SanobarNo ratings yet
- State of Matter-HighlightDocument21 pagesState of Matter-HighlightZhimingNo ratings yet
- 1 Particle Theory&States of MatterDocument5 pages1 Particle Theory&States of Matter209garde10No ratings yet
- KPT SummaryDocument5 pagesKPT SummaryLymon SimNo ratings yet
- Particles in Solids Terminado FullDocument15 pagesParticles in Solids Terminado Fulljhunior carlos eduardo gamboa herreraNo ratings yet
- CT - 3Document45 pagesCT - 3Snehal BhasinNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Principles of ChemistryDocument14 pagesUnit 1 Principles of ChemistryKhin Yadanar KyawNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 2Document14 pagesLesson 5 2YwnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Matter and Atomic Structure: 2.1 Basic Concepts of Matter 2.2 The Development of The Atomic ModelDocument32 pagesChapter 2: Matter and Atomic Structure: 2.1 Basic Concepts of Matter 2.2 The Development of The Atomic Modelmenaga ilangkovanNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument23 pagesStates of MatterAngel MulyadiNo ratings yet
- Three States of MatterDocument2 pagesThree States of MatterWinner's AssociationNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 ReviewerDocument7 pagesGrade 12 ReviewerTin SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument9 pagesChem Reviewermatthew dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Revision On Particles TheoryDocument35 pagesRevision On Particles TheoryHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- KineticparticletheorypptDocument32 pagesKineticparticletheorypptAnand SarbabidyaNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Changing States & Water CycleDocument65 pages2.3 Changing States & Water CycleJohn Michael DitchonNo ratings yet
- Science: Unit 6 States of MatterDocument3 pagesScience: Unit 6 States of MatterahmedNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument32 pagesStates of MatterKeith BansrajNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Unit 1Document22 pagesStates of Matter Unit 164274qjmzcNo ratings yet
- The Particulate Nature of Matter: IGCSE ChemistryDocument8 pagesThe Particulate Nature of Matter: IGCSE ChemistryVibinraj K NileshwarNo ratings yet
- States of Matter NotesDocument8 pagesStates of Matter NotesRaya Ibarra LumogdangNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Document15 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Keeertththana SaravananNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument10 pagesStates of Matterm.umerfaizan1895No ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document5 pagesAssignment 5Ramim KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesChapter 1: The Particulate Nature of Matter: SolidsAshrafNo ratings yet
- O-Level Chemistry (0620)Document56 pagesO-Level Chemistry (0620)abdulwahabibnfayazNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument3 pagesChemistry NotesEain Chan MyaeNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 States of Matter - 22-23 - IGDocument12 pagesCh. 1 States of Matter - 22-23 - IGvfdfdNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Atom 2Document11 pagesThe Structure of Atom 2Dania NatashaNo ratings yet
- Change of State: Useful VocabularyDocument14 pagesChange of State: Useful VocabularyZhu JiankunNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1.1Document21 pagesGen Chem 1.1gjhesraelNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v1Document24 pagesCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v1mohammed darwazehNo ratings yet
- CH1 - States of Matter (IGCSE Study Notes)Document13 pagesCH1 - States of Matter (IGCSE Study Notes)Amal HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 MatterDocument44 pagesChapter 5 MatterNor Atikah Abdul RazakNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry ELSWB AnswersDocument30 pagesIGCSE Chemistry ELSWB AnswersMarin PesicNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v3Document21 pagesCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v3Adenekan Therhophic Orlanshilay100% (2)
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 1-Module 3Document31 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 1-Module 3Niño Edrianne NimoNo ratings yet
- Basics of DistillationDocument10 pagesBasics of DistillationAgus AkNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument4 pagesStates of MatterYssah Moira HamacNo ratings yet
- Chemisty Notes O-LevelDocument97 pagesChemisty Notes O-LevelMunashe BinhaNo ratings yet
- HKDSE F.3 Chemistry Introductory Summer Course To ChemistryDocument3 pagesHKDSE F.3 Chemistry Introductory Summer Course To ChemistryFalin WongNo ratings yet
- Metallic Crystals: Molecular OrderDocument3 pagesMetallic Crystals: Molecular OrderBrylle Jack PerezNo ratings yet
- Foundation Chemistry 1Document60 pagesFoundation Chemistry 1Ivan OgwangNo ratings yet
- KSSM f1c5Document52 pagesKSSM f1c5Tanisa SaminNo ratings yet
- The Kinetic Molecular Theory of Liquids & SolidsDocument11 pagesThe Kinetic Molecular Theory of Liquids & SolidszaneNo ratings yet
- Edgcse TTPP Cc1-2 SB AnswersDocument5 pagesEdgcse TTPP Cc1-2 SB Answersegcarty1009No ratings yet
- States of Matter SummaryDocument1 pageStates of Matter SummarySAMI DHAOUINo ratings yet
- Matter q3pptxDocument28 pagesMatter q3pptxmarzarishbvinculadoNo ratings yet
- 04 Copy of Compiled GenieDiary - The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument4 pages04 Copy of Compiled GenieDiary - The Particulate Nature of MatterEdric Teo Kai Feng (Msh)No ratings yet
- 2.1.) States of Matter (BIO40A)Document19 pages2.1.) States of Matter (BIO40A)Mary Ferl Jasmin LupagueNo ratings yet
- MODULE Class VIII C06Document26 pagesMODULE Class VIII C06animeshtechnosNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 - Degree of Hydration of Copper II SulfateDocument3 pagesExperiment 4 - Degree of Hydration of Copper II SulfateHa NaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Measurement and ErrorsDocument2 pagesExperiment 3 - Measurement and ErrorsHa NaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Accuracy and PrecisionDocument4 pagesExperiment 2 - Accuracy and PrecisionHa NaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Elements Compounds and MixturesDocument4 pagesExperiment 1 - Elements Compounds and MixturesHa NaNo ratings yet
- Topic 11 Manual 2023Document24 pagesTopic 11 Manual 2023Ha NaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Manual 4th Edition Ver1 2023Document44 pagesTopic 1 Manual 4th Edition Ver1 2023Ha NaNo ratings yet
- Blended Learning Activity 2 2023Document1 pageBlended Learning Activity 2 2023Ha NaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Class 21 2 1Document46 pagesChemistry Class 21 2 1Ha NaNo ratings yet
- BL1 - Element Compound MixtureDocument1 pageBL1 - Element Compound MixtureHa NaNo ratings yet
- EU Battery Demand and Supply (2019-2030) in A Global ContextDocument15 pagesEU Battery Demand and Supply (2019-2030) in A Global ContextSandeep GargNo ratings yet
- Science 4 Activity Sheet Quarter 4 - Melc 3 Week 3: Water CycleDocument9 pagesScience 4 Activity Sheet Quarter 4 - Melc 3 Week 3: Water CycleShareinne TeamkNo ratings yet
- Sustainability and Passive Energy DesignDocument6 pagesSustainability and Passive Energy DesignHaktasticDemonNo ratings yet
- Session Guide For Critical Content Periodic TableDocument11 pagesSession Guide For Critical Content Periodic TableDaphnie Serate NunezNo ratings yet
- Hiku7 Mono Perc: Cs7L-580 - 585 - 590 - 595 - 600 - 605MsDocument1 pageHiku7 Mono Perc: Cs7L-580 - 585 - 590 - 595 - 600 - 605MsShironNo ratings yet
- DM Fillerboard - HuntonDocument65 pagesDM Fillerboard - HuntonFahis V MNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Section: - Score: - GENERAL DIRECTION: MULTIPLE CHOICES: Read The Test Questions CarefullyDocument2 pagesName: - Date: - Section: - Score: - GENERAL DIRECTION: MULTIPLE CHOICES: Read The Test Questions CarefullyRovz GC BinNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science Mock Test 2016Document2 pagesGrade 9 Science Mock Test 2016REY AQUINO100% (1)
- Land Subsidence ReportDocument49 pagesLand Subsidence ReportsushmithakalkaniNo ratings yet
- Eutrophic at I OnDocument7 pagesEutrophic at I OnKrizelle Mae BaronganNo ratings yet
- Broiler MGMT Guide 2008Document72 pagesBroiler MGMT Guide 2008vinstar13100% (2)
- The Nuclear Atom 2 QPDocument15 pagesThe Nuclear Atom 2 QPGlimpseNo ratings yet
- Part1.4 Stratigraphic Interpretation PDFDocument26 pagesPart1.4 Stratigraphic Interpretation PDFNurulNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic System Protection Application Guide: Bussmann Circuit Protection SolutionsDocument34 pagesPhotovoltaic System Protection Application Guide: Bussmann Circuit Protection SolutionsEmir JusićNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument10 pagesLiterature Reviewapi-559056392No ratings yet
- Cy8151 Notes PDFDocument93 pagesCy8151 Notes PDFVignesh KNo ratings yet
- Triptico La Contaminación Ambiental en Ingles 2Document2 pagesTriptico La Contaminación Ambiental en Ingles 2Silvia TerronesNo ratings yet
- Channel Partners Off Grid Solar PVProgrammeDocument81 pagesChannel Partners Off Grid Solar PVProgrammeAajaysinh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Absorption in SemiconductorsDocument13 pagesUnit 2 Absorption in SemiconductorsKapilkoundinya NidumoluNo ratings yet
- Hamza Solar Energy AssignmentDocument9 pagesHamza Solar Energy AssignmentHamza Ali MinhasNo ratings yet
- HRSG Water Chemistry Control OverviewDocument5 pagesHRSG Water Chemistry Control OverviewRahul ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- X Chemistry WorksheetDocument2 pagesX Chemistry WorksheetMOHIT KUMAR WISDOMNo ratings yet
- Viteze CosmiceDocument6 pagesViteze CosmiceSolarisNo ratings yet
- Quiz For Nutrient Management Module No. 2: Plant Nutrition and Soil Fertility 1 CEU in Nutrient Management and 0.5 CEU in Soil Water ManagementDocument3 pagesQuiz For Nutrient Management Module No. 2: Plant Nutrition and Soil Fertility 1 CEU in Nutrient Management and 0.5 CEU in Soil Water ManagementEdward LeeNo ratings yet
- Organismal BiologyDocument49 pagesOrganismal BiologycelinaNo ratings yet
- Carac Biogas FlamelessDocument7 pagesCarac Biogas FlamelessTaine EstevesNo ratings yet
- Treasure of Knowledge Volume-2Document7 pagesTreasure of Knowledge Volume-2fayaz hussainNo ratings yet
- 5 Properties of Two-Phase and Vapor SystemsDocument36 pages5 Properties of Two-Phase and Vapor SystemsBERN CERTEZANo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesFluid MechanicsMariela MarceloNo ratings yet
- Berkley General Chemistry 1Document356 pagesBerkley General Chemistry 1Brent Arnold100% (19)