Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elsq2 L04
Uploaded by
Saber OnimaruOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elsq2 L04
Uploaded by
Saber OnimaruCopyright:
Available Formats
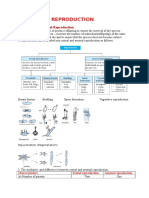
Lesson 4: Sexual Reproduction in Animals
Sexual reproduction - involves male and female parents to produce offspring through the fusion of gametes (sperm and
egg cells) generated by meiosis.
Since sexual reproduction needs two parents to produce an offspring, the combination of genes from both parents
increases the chances of species variation.
Gametogenesis - is the formation of male and female gametes.
Spermatogenesis - is the formation of sperm cells in males.
Oogenesis - pertains to the formation of the ova or egg cells through meiosis in the gonads known as ovaries.
Fertilization - is the union of male and female sex cells.
External fertilization - is the union of egg and sperm that occurs outside the female reproductive tract.
Internal fertilization - is the union of egg and sperm that occurs within the female reproductive tract.
Internal Fertilization
Animals that undergo internal fertilization produce offspring in any of the following ways:
In oviparity, the eggs are fertilized internally, but they would complete their development outside the mother’s
body.
In ovoviviparity, the eggs are fertilized internally, and they complete their development within the mother.
In viviparity, the eggs are fertilized internally. The embryos receive nourishment directly from the mother’s
blood through the placenta rather than from the yolk.
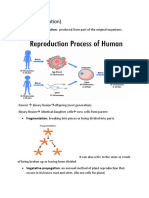
Post-fertilization
After fertilization, the fertilized egg undergoes a series of cell divisions termed as the cleavage.
Cleavage - is a series of extremely rapid mitotic divisions wherein a large volume of cellular materials are divided into
multiple smaller cells.
- A hollow ball called blastula is formed.
- The blastula further develops into gastrula that allows layering of cells in the developing embryo.
Cleavage formation in developing embryo
You might also like
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument69 pagesReproduction in AnimalsAliya CastroNo ratings yet
- Principles of Development: Developmental BiologyDocument86 pagesPrinciples of Development: Developmental BiologyPaolo OcampoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Animals - 2Document21 pagesReproduction in Animals - 2Raushan SinghNo ratings yet
- Animal - Development (Kel 1-5)Document83 pagesAnimal - Development (Kel 1-5)MelatiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument5 pagesReproduction in Animalsmokshithakapoor657No ratings yet
- Reproduction in Animals Class 8Document7 pagesReproduction in Animals Class 8jahnavi poddar100% (1)
- Lesson 10 - Reproduction in Plants and AnimalsDocument5 pagesLesson 10 - Reproduction in Plants and AnimalslemoniteNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction Grade 10Document23 pagesSexual Reproduction Grade 10Carol EscañoNo ratings yet
- Animal ReprodutionDocument10 pagesAnimal ReprodutionPANSARILI KONo ratings yet
- Perpetuation of Life: Week 13 Earth & Life ScienceDocument23 pagesPerpetuation of Life: Week 13 Earth & Life ScienceREYNANTE SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science SHS 3.4 Sexual Reproduction in AnimalsDocument20 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 3.4 Sexual Reproduction in AnimalsZaldy Emmanuel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Geneneral Biology PPT Ge-Ar Dumpa & Analie RioDocument25 pagesGeneneral Biology PPT Ge-Ar Dumpa & Analie RioApril Rose Caquilala GalauraNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument30 pagesReproduction in AnimalssobhshaikhshaikhNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument3 pagesReproduction in Animalsevelynlinda370No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - Reproduction 1.2Document15 pagesCHAPTER 4 - Reproduction 1.2Halizah RamthanNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology (Chapter 4: Reproduction)Document3 pagesForm 5 Biology (Chapter 4: Reproduction)Gerard Selvaraj100% (2)
- Reproduction in Animals PDFDocument7 pagesReproduction in Animals PDFBhupinder Arora33% (3)
- p5 Card Game, Reprod in HumansDocument4 pagesp5 Card Game, Reprod in HumansBernard ChanNo ratings yet
- Biology NoteDocument9 pagesBiology NotejuliaNo ratings yet
- Yr 8 WK 2 Bio NoteDocument3 pagesYr 8 WK 2 Bio Notesedrick ocheNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive System Yr 11 Biology 114629Document7 pagesHuman Reproductive System Yr 11 Biology 114629Zach ZaneNo ratings yet
- Reproduction PPT For IGCSE and O Level Biology (Easier)Document25 pagesReproduction PPT For IGCSE and O Level Biology (Easier)Tashwaar TamimNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Animals - TB QuestionsDocument7 pagesReproduction in Animals - TB Questionshafsatabarak.rNo ratings yet
- Atwinisoneoftwo: OffspringDocument18 pagesAtwinisoneoftwo: OffspringanjanareadNo ratings yet
- Animal ReproductionDocument46 pagesAnimal Reproductionrufino delacruzNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer Second SemDocument26 pagesBiology Reviewer Second Semblooming flowerrNo ratings yet
- Phases of Embryonic DevelopmentDocument9 pagesPhases of Embryonic DevelopmentIshu ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Animal Form and Function 2: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityDocument79 pagesAnimal Form and Function 2: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityThu AnhNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in AnimalsDocument2 pagesSexual Reproduction in Animalsmallorca albertNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument5 pagesReproduction in AnimalsOnlymexxNo ratings yet
- Ready Reckoner BiologyDocument19 pagesReady Reckoner BiologyMrigank MitraNo ratings yet
- Biology Summary Modules 5+6+7 CompleteDocument70 pagesBiology Summary Modules 5+6+7 Complete1811ameliaNo ratings yet
- Biology Folio: Name: Amir Afiq Bin AzlanDocument26 pagesBiology Folio: Name: Amir Afiq Bin AzlanAmir AfiqNo ratings yet
- Gametogenesis and FertilizationDocument10 pagesGametogenesis and FertilizationJustus MutuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 9 NotesChahat SanataniNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy - Human ReproductionDocument36 pagesPregnancy - Human ReproductionDICKSONNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 DescriptiveEmbryology PDFDocument18 pagesLecture1 DescriptiveEmbryology PDFideapadNo ratings yet
- CAHPTER 6 NOTES Class 8Document8 pagesCAHPTER 6 NOTES Class 8dasakshyat098No ratings yet
- Reproduction AND Development: (In Plants and Animals)Document29 pagesReproduction AND Development: (In Plants and Animals)Samarra LouisseNo ratings yet
- Genbio 4th Quarter ReviewerDocument6 pagesGenbio 4th Quarter ReviewerKatherine Mars ArandaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis: Four Haploid CellsDocument10 pagesSexual Reproduction and Meiosis: Four Haploid CellsJohnieer Bassem MoferdNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalDocument5 pagesReproduction in AnimalRANJIT KUMAR SHAHNo ratings yet
- Animal Form and FunctionDocument12 pagesAnimal Form and FunctionHanna GalatiNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Gamete FormationDocument17 pages4.1 Gamete FormationKasmahwati MattailNo ratings yet
- Early Development of A Human ZygoteDocument32 pagesEarly Development of A Human ZygoteBenay ÇakaloğluNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Science: Reproduction in AnimalsDocument21 pagesClass 8 Science: Reproduction in AnimalsJ CNo ratings yet
- FERTILIZATIONDocument9 pagesFERTILIZATIONchrlsemil02zNo ratings yet
- Reproduction & Growth: Form 5Document203 pagesReproduction & Growth: Form 5Foh Lian HuaiNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Gamete FormationDocument48 pages4.1 Gamete FormationIMELDANo ratings yet
- Chapter 46 Animal ReproductionDocument11 pagesChapter 46 Animal ReproductionEmilja ZeneliNo ratings yet
- Note1 - Reproduction in HumansDocument2 pagesNote1 - Reproduction in HumansSandalu Romeshika PereraNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 9Document8 pagesReproduction in Animals Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 9zodika khiangteNo ratings yet
- Module 4 ReproductionDocument15 pagesModule 4 Reproductionapi-18956468950% (2)
- Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument18 pagesReproduction and DevelopmentJvc CawiliNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Sciences SLHTQ2 3Document9 pagesEarth and Life Sciences SLHTQ2 3Melissa GerzonNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument108 pagesReproduction and DevelopmentCarl Johnave Manigbas MonzonNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction FullDocument46 pagesSexual Reproduction FullSharara YMNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument28 pagesHuman ReproductionPriyaprasad PandaNo ratings yet
- 6454f634e4b0ad3aaf22e06f OriginalDocument7 pages6454f634e4b0ad3aaf22e06f OriginalSuprit JainNo ratings yet
- Selecting Male Or Female Child Here's How It Works - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: A Guide To Gender SelectionFrom EverandSelecting Male Or Female Child Here's How It Works - Based On The Teachings Of Dr. Andrew Huberman: A Guide To Gender SelectionNo ratings yet
- Elsq2 L06Document1 pageElsq2 L06Saber OnimaruNo ratings yet
- GMQ2 L03 IncDocument2 pagesGMQ2 L03 IncSaber OnimaruNo ratings yet
- GMQ2 L02Document2 pagesGMQ2 L02Saber OnimaruNo ratings yet
- Elsq2 L05Document1 pageElsq2 L05Saber OnimaruNo ratings yet
- Elsq2 L03Document3 pagesElsq2 L03Saber OnimaruNo ratings yet