Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug NCP
Drug NCP
Uploaded by
Westley Rubino0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesNCP
Original Title
Drug NCp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNCP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesDrug NCP
Drug NCP
Uploaded by
Westley RubinoNCP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
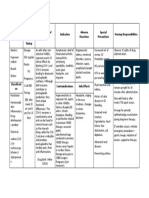
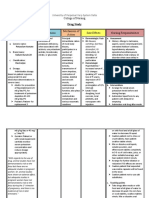
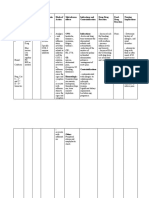
Name of Mechanism Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing
Drug of Action Responsibilities
Generic Magnesium To Parenteral CNS: Before:
Name: Sulfate is prevent administrati drowsiness Take an
Magnesium essential / on , depress appropriate
Sulfate element for control contraindica reflexes, seizure precaution.
muscle and seizure ted inpatient placid
Brand nerve in pre- with heart paralysis, During:
Name: transmission. eclamp block hypotherm Check
Magnesium Extracellular sia myocardial ia Magnesium
Sulfate fluid damage. CV: level repeat
levels:1.5 To hypotensio doses.
Dosage: – manage Use n, flushing Disappeara
>Preeclampsi 2.5 mg/L. Mg preter cautiously bradycardi nce of knee,
a depresses m inpatients a, Jerl and
woman: 4g the CNS and labor. with circulatory patellar
IV in 250mL controls impaired collapse, reflexes is a
D5W with convulsion by renal depress sign of
normal blocking function. cardiac impeding
saline and 4- release of function magnesium
5 g. deep IM acetylcholine Use Skin: toxicity.
into buttock at the cautiously in diaphoresis
alternate in myoneural pregnant Monitor
every 4hrs., junction. woman urine intake
P.R.N 4g I.V. Also, mg during labor. and output.
Lodding dose decrease
then 1-2 q sensitivity of After:
hr. as I.V motor end
Observe
infusion. plate to
neonates
Dose should acetylcholine
for signs of
not exceed and
magnesium
30-40 g. daily decreases the
toxicity.
excitability of
the mother
membrane.
Classification
as a laxative
:
it acts in the
Anticonvulsa
small and
nt
large
intestine to
attract and
retain water
in the
intestinal
lumen,
increasing
intraluminal
pressure, also
releases
cholecystokin
in
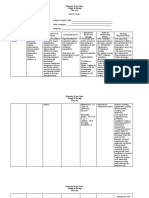
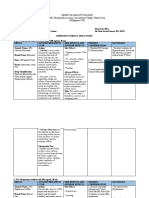
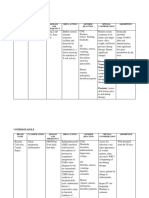
Drug Name Dosages Therapeutic Indications Adverse Contraindicati Nursing
Actions effects ons Responsibilities
Generic Drug: PO Betamethaso Systemic Sodium and Hypersensitivi Assessment
Betamethasone Allergic and ne is a administration fluid ty; systemic
inflammatory corticosteroi retention, fungal or History
Brand Name: disorders; d with mainly Hypercal potassium acute (Systemic
Celestone, congenital glucocorticoi cemia and calcium infections administration):
Celestone adrenal d activity. It associate depletion. Infections, fungal
Soluspan, hyperplasia prevents and d with Muscle infections,
Betaject, 0.5-5mg/day. by controlling cancer wasting, amebiasis, vaccinia
Betamethasone IM the rate of Short- weakness, and varicella, and
IM/PO Allergic and protein term osteoporosi antibiotic-resistant
inflammatory synthesis, manage s.GI infections; kidney
Classification: disorders as depressing ment of disturbance or liver disease;
Corticosteroids betamethasone the migration inflamm s and hypothyroidism;
Na phosphate of atory bleeding. ulcerative colitis
and polymorphon and Increased with impending
betamethasone uclear allergic appetite perforation;
acetate: leukocytes disorders and delayed diverticulitis; active
Initial:0.25-9 and , such as wound or latent peptic
mg/day in1-2 fibroblasts, rheumat healing; ulcer;
divided doses. and reversing oid hirsutism, inflammatory
Ophth Allergic capillary arthritis, bruising, bowel disease;
and permeability collagen striae, acne; CHF; hypertension;
inflammatory and diseases raised thromboembolic
conditions of lysosomal (eg, SLE), intracranial disorders;
the eye as 0.1% stabilization. dermatol pressure, osteoporosis;
soln: As Na ogic headache, seizure disorders;
phosphate: diseases depression, diabetes mellitus;
Instill 1-2 hrly (eg, psychosis, lactation
until symptoms pemphig menstrual
are controlled. us), irregularitie Physical:
As0.1% oint: status s. Baseline weight, T,
As Na asthmati Hyperglyce reflexes and grip
phosphate: cus, and mia, strength, affect
Apply2-4 autoimm DM. and orientation, P,
times/day or at une Suppression BP, peripheral
night w/ the disorders of pituitary- perfusion,
eyedrops. adrenocorti prominence of
Topical Skin Hematol cal axis. superficial veins,
disorders As ogic Growth Rand adventitious
dipropionate disorders retardation sounds, serum
(0.05%) or : in children electrolytes, blood
valerate (0.025 Thrombo (prolonged glucose
or 0.1%): Apply cytopeni therapy).
as directed a Increased Interventions
purpura, susceptibilit
erythrobl y for Systematic use
astopeni infections.
a Topical use: Give daily
Dermal dose 9am
Ulcerativ atrophy, to mimic
e colitis, local normal
acute irritation, peak
exacerba folliculitis, corticoste
tions of hypertricho roid blood
MS, and sis. levels.
palliation Inhalation: Increase
in some Hoarseness, dosage
leukemia candidiasis when
s and of mouth patient is
lympho and subject to
mas throat. stress
Topical Taper
Trichinos application doses
is with to the eye: when
neurolog Corneal discontinu
ic or ulcers, ing high
myocardi raised IOP dose or
al and reduced long-term
involvem visual therapy
ent acuity.
Do not
Intradermal
give live
injection:
virus
Local
vaccines
hypopigmen
with
tation of
immunos
deeply
uppressiv
pigmented
e doses of
skin. Intra-
corticoste
articular
roids.
injection:
Joint
Topical
damage,
dermatologic
fibrosis, esp.
preparations
in load
bearing
joints Examine area for
infections and
skin integrity
before application
Administ
er
cautiousl
y to
pregnant
patients’
topical
corticost
eroids
have
caused
teratoge
nic
effects
and can
be
absorbed
from
systemic
site.
You might also like
- Baffert Motion To Stay and or For Temporary InjunctionDocument37 pagesBaffert Motion To Stay and or For Temporary InjunctionMatthew StahlNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyDharylle CariñoNo ratings yet
- GM Steroid LadderDocument2 pagesGM Steroid LadderRenee McGuinnessNo ratings yet
- Naproxen Sodium Drug StudyDocument1 pageNaproxen Sodium Drug StudyKarl Lourenz Deysolong100% (1)
- MetoclopramideDocument1 pageMetoclopramideIvanne Hisoler89% (27)
- Drug Study ClozapineDocument2 pagesDrug Study ClozapineRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-ClindamycinDocument3 pagesDrug Study-ClindamycinDUMANGENG ELLAINE D.100% (1)
- DexamethasoneDocument3 pagesDexamethasoneGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Aurochem GlobalDocument16 pagesAurochem GlobalEyeberdi AllaberdiyevNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For HepatitisDocument4 pagesDrug Study For Hepatitisunyokies100% (1)
- Drug Study Potassium ChlorideDocument5 pagesDrug Study Potassium ChlorideKenneth Mark B. TevesNo ratings yet
- Final ColistinDocument3 pagesFinal ColistinGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Phenytoin Drug StudyDocument1 pagePhenytoin Drug StudyRoland Yuste100% (3)
- StudyDocument5 pagesStudyWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy 2Document5 pagesDrugstudy 2Westley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Antihypertension DrugsDocument2 pagesAntihypertension DrugsMarieCrisNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Sulfate 250 500 MG Metoclopramide Drug StudyDocument4 pagesMagnesium Sulfate 250 500 MG Metoclopramide Drug Studyprog.ecleo.swuNo ratings yet
- 1magsu 2methergineDocument5 pages1magsu 2metherginelaiza_lumbaNo ratings yet
- NALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsDocument6 pagesNALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsBeth100% (1)
- Medici Di Makati College 1061 Metropolitan Avenue, San Antonio Village, Makati City, Philippines 1200Document18 pagesMedici Di Makati College 1061 Metropolitan Avenue, San Antonio Village, Makati City, Philippines 1200Andee SalegonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Irene 9 11Document10 pagesDrug Study Irene 9 11Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Magnesium SulfateDocument3 pagesDrug Study Magnesium SulfateSchyna Marielle VitaleNo ratings yet
- BethametasoneDocument3 pagesBethametasoneWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Salazar Colleges of Science and Institute of TechnologyDocument2 pagesSalazar Colleges of Science and Institute of Technologyroby soriano100% (1)
- Drug Study-MsGO4 (A)Document3 pagesDrug Study-MsGO4 (A)Ronel ResurricionNo ratings yet
- Drug StuyDocument4 pagesDrug Stuykyle100% (1)
- Beta Drug StudyDocument3 pagesBeta Drug StudyWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Mechanism of Action: Side Effects/ Adverse Effects: Nursing Responsibilities: Brand NameDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Mechanism of Action: Side Effects/ Adverse Effects: Nursing Responsibilities: Brand NameMacarayo AldemaeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1-Ward1Document4 pagesDrug Study 1-Ward1Annaoj Esor DarasNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Tramadol KCLDocument5 pagesParacetamol Tramadol KCLDani DaniNo ratings yet
- StreptomycinDocument1 pageStreptomycinDemilyn Fat100% (2)
- 6 Drug StudyDocument4 pages6 Drug StudyIvan VillapandoNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone Methylergometrine Maleate Bupivacaine HydrochlorideDocument3 pagesDexamethasone Methylergometrine Maleate Bupivacaine HydrochlorideOmyl-Khayr M. SulogNo ratings yet
- 1.inhibit Synergistic EffectDocument8 pages1.inhibit Synergistic EffectSITTIE JOBAISAH TOMINAMAN ALINo ratings yet
- Clozapine Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 pagesClozapine Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComVinz OñoNo ratings yet
- Pedia: Initial Therapy: 12.5 MGDocument3 pagesPedia: Initial Therapy: 12.5 MGVinz OñoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Atorvastatin Brand Name: Lipitor Dosage and RouteDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Atorvastatin Brand Name: Lipitor Dosage and RouteRamsam UayanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For HELLP SyndromeDocument19 pagesDrug Study For HELLP SyndromeRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis and NCP Ob Ward PoldoDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis and NCP Ob Ward PoldosatruetalagaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studyfaula rocamoraNo ratings yet
- IDEA - PharmaDocument18 pagesIDEA - PharmapamelaideaNo ratings yet
- Marfori - Activity 3 Antineoplastic Agents Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMarfori - Activity 3 Antineoplastic Agents Drug Studyckkyle0% (1)
- Medical ManagementDocument3 pagesMedical ManagementMark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Para, Plasil, CiprofloxacinDocument5 pagesDRUG STUDY - Para, Plasil, CiprofloxacinrhegellNo ratings yet
- Tdi de AsisDocument1 pageTdi de AsisEnaWahahaNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGYDocument3 pagesPHARMACOLOGYjonel lorenzoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DRDocument3 pagesDrug Study DRGershom Perez AcaboNo ratings yet
- Brand and Generic Name Action Uses/ Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument12 pagesBrand and Generic Name Action Uses/ Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationBiggs JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Format EheheDocument17 pagesDrug Study Format EhehejesonNo ratings yet
- Elbert A. Mutuc Drug Study BSN III - 1 Group 2Document4 pagesElbert A. Mutuc Drug Study BSN III - 1 Group 2Elbert Aquitania Mutuc RNNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3EDocument10 pagesDrug Study: Labini, Dienizs Bsn-3EDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - DrugsDocument4 pagesCase Study - DrugsYza DizaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Therape Utic Actions Indica Tion Adverse Reaction Contraindi Cation Nursing Consider Ation Generic Name: Acetylcholine ChlorideDocument8 pagesDrug Name Therape Utic Actions Indica Tion Adverse Reaction Contraindi Cation Nursing Consider Ation Generic Name: Acetylcholine ChlorideFredie O HadjimudinNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY Update (Table 3)Document5 pagesDRUGSTUDY Update (Table 3)SONY MANDAPNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJEWEL DEEN VILLARMENTE OQUIANANo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drugana IIIJDocument7 pagesDrugana IIIJNikki DarleneNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NOt COmpleteDocument6 pagesDrug Study NOt COmpletejiellianemaeNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesKarl Lourenz DeysolongNo ratings yet
- MV FeSO4 Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMV FeSO4 Drug StudyZiaNo ratings yet
- M&N MGMTDocument3 pagesM&N MGMTMark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument5 pagesNursing DiagnosisWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Unfinish Drug StudyDocument3 pagesUnfinish Drug StudyWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- BethametasoneDocument3 pagesBethametasoneWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Beta Drug StudyDocument3 pagesBeta Drug StudyWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- DR StudyDocument7 pagesDR StudyWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Tin NCP AntepartumDocument2 pagesTin NCP AntepartumWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- 104 CompileDocument20 pages104 CompileWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- NCP AntepartumDocument2 pagesNCP AntepartumWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- ملف اصناف رامافارماDocument31 pagesملف اصناف رامافارمادطه الصمديNo ratings yet
- Adults, Elderly and Children Over 1 YearDocument7 pagesAdults, Elderly and Children Over 1 YeardindaikaputriNo ratings yet
- Betnovate NDocument11 pagesBetnovate NAhmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Momate-S SSDocument28 pagesMomate-S SSkurutalaNo ratings yet
- Desoximetasone Cream and OintmentDocument9 pagesDesoximetasone Cream and OintmentskndinaviaNo ratings yet
- Fucicort ®: What Is in This LeafletDocument9 pagesFucicort ®: What Is in This LeafletRi KiNo ratings yet
- BetamethasoneDocument3 pagesBetamethasoneMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Wasfaty Catalogue UpdatedDocument21 pagesWasfaty Catalogue Updatedreham.researchNo ratings yet
- Provider Resources Obstetrics Late Preterm Steroids July2016Document10 pagesProvider Resources Obstetrics Late Preterm Steroids July2016Pediatrics SLCM-WHQMNo ratings yet
- Betnesol InformationDocument6 pagesBetnesol InformationsmazNo ratings yet
- Product ListDocument12 pagesProduct ListUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Usp 43 NF 38 IndexDocument72 pagesUsp 43 NF 38 IndexNumixx SasNo ratings yet
- Bahawalpur (Aslam Traders) Monthly Closing Sales 2020, 2021Document6 pagesBahawalpur (Aslam Traders) Monthly Closing Sales 2020, 2021Ali AsadNo ratings yet
- 13.2 Aplikasi TopikalDocument42 pages13.2 Aplikasi TopikalSaha DirllahNo ratings yet
- Table REQ - MedicamentsDocument996 pagesTable REQ - MedicamentsMicrotech DzNo ratings yet
- Fucicort CreamDocument4 pagesFucicort Creamcupcake xNo ratings yet
- Medic NesDocument29 pagesMedic Nespink_key711No ratings yet
- Dha-Fmc Preferred Product List-Apr23Document297 pagesDha-Fmc Preferred Product List-Apr23JOBIN K JNo ratings yet
- Pharma Health Price ListDocument1 pagePharma Health Price ListJaweed NaqshbandiNo ratings yet
- Human Medicines Register Blue Book 03.06.2021 (1) BotswanaDocument181 pagesHuman Medicines Register Blue Book 03.06.2021 (1) BotswanavdvedNo ratings yet
- Oscar House, Badi Majra, Yamuna Nagar 135001. Price List W.E.F. 01.04.2010Document4 pagesOscar House, Badi Majra, Yamuna Nagar 135001. Price List W.E.F. 01.04.2010Piyu JainNo ratings yet
- Registered Product List: Vega Pharmaceuticals (PVT.) LTDDocument12 pagesRegistered Product List: Vega Pharmaceuticals (PVT.) LTDWaheedullah AhmadiNo ratings yet
- Hospital Formulary ADocument13 pagesHospital Formulary Alesliemaebarlaan03No ratings yet
- Betnovate C For Acne Scars: 6 Betamethasone Valerate Foam PriceDocument7 pagesBetnovate C For Acne Scars: 6 Betamethasone Valerate Foam PriceAhmed ImranNo ratings yet
- Structural Formula and Chemistry Gentamicin SulfateDocument8 pagesStructural Formula and Chemistry Gentamicin SulfateRph AinNo ratings yet
- Nppa Updated Price List As On 01.04.2021Document385 pagesNppa Updated Price List As On 01.04.2021bvs prasadNo ratings yet
- Section 2.0 Active Ingredients: (S) - MethopreneDocument71 pagesSection 2.0 Active Ingredients: (S) - Methopreneakhilkhattar1No ratings yet