Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8d - Complex Reactions (Solution Through Matlab) PDF
Uploaded by
GRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADOR0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views7 pagesOriginal Title
8d - Complex Reactions (Solution through Matlab).pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views7 pages8d - Complex Reactions (Solution Through Matlab) PDF
Uploaded by
GRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
COMPLEX REACTIONS
ChE 2115: Chemical Reaction Engineering
Basil James S Santos
MATLAB PROBLEMS
ChE 2115: Chemical Reaction Engineering
Basil James S Santos
Matlab Problems
EXAMPLE
Consider the complex liquid-phase reactions shown below
𝐴 + 2𝐵 → 𝐶, −𝑟1𝐴 = 10𝐶𝐴 𝐶𝐵2
2𝐴 + 3𝐶 → 𝐷, −𝑟2𝐶 = 15𝐶𝐴2 𝐶𝐶3
Starting with CA0 = CB0 = 2M, calculate the concentrations of A, B, C, and D
after 1 min reaction time using batch reaction
ChE 2115: Chemical
Reaction Engineering
Matlab Problems
Consider the complex liquid-phase reactions shown below. Starting with CA0 = CB0 = 2M, calculate the concentrations of A, B, C, and D after 1
min reaction time using batch reaction
EXAMPLE 𝐴 + 2𝐵 → 𝐶, −𝑟1𝐴 = 10𝐶𝐴 𝐶𝐵2
2𝐴 + 3𝐶 → 𝐷, −𝑟2𝐶 = 15𝐶𝐴2 𝐶𝐶3
The differential equations to be used are
𝑑 2
𝑟𝐴 = 𝐶𝐴 = −10𝐶𝐴 𝐶𝐵 − 15 𝐶𝐴2 𝐶𝐶3
2
𝑑𝑡 3
𝑑
𝑟𝐵 = 𝐶𝐵 = −20𝐶𝐴 𝐶𝐵2
𝑑𝑡
𝑑
𝑟𝐶 = 𝐶𝐶 = 10𝐶𝐴 𝐶𝐵2 − 15𝐶𝐴2 𝐶𝐶3
𝑑𝑡
𝑑 1
𝑟𝐷 = 𝐶𝐷 = 15 𝐶𝐴2 𝐶𝐶3
𝑑𝑡 3
Stoichiometry can be used to check the correctness of the entered code
ChE 2115: Chemical
Reaction Engineering
Matlab Problems
Consider the complex liquid-phase reactions shown below. Starting with CA0 = CB0 = 2M, calculate the concentrations of A, B, C, and D after 1
min reaction time using batch reaction
EXAMPLE 𝐴 + 2𝐵 → 𝐶, −𝑟1𝐴 = 10𝐶𝐴 𝐶𝐵2
2𝐴 + 3𝐶 → 𝐷, −𝑟2𝐶 = 15𝐶𝐴2 𝐶𝐶3
𝐶𝐴 = 0.5786
𝐶𝐵 = 0.0660
𝐶𝐶 = 0.2854
𝐶𝐷 = 0.2272
Stoichiometry can be used to check the correctness of the entered code
𝐶𝐵 𝐶𝐵0
+ 𝐶𝐶 + 3𝐶𝐷 ≟ + 𝐶𝐶0 + 3𝐶𝐷0
2 2
0.0660 ✔2
+ 0.2854 + 0.2272 =
2 2
ChE 2115: Chemical
Reaction Engineering
Matlab Problems
EXAMPLE
Consider the series-reversible reaction shown below.
Starting at an initial concentration of 1 M A, calculate the maximum
possible concentration of R and the time it would occur.
ChE 2115: Chemical
Reaction Engineering
Matlab Problems
Consider the series-reversible reaction shown below. Starting at an initial concentration of 1 M A, calculate the maximum possible
concentration of R and the time it would occur.
EXAMPLE
The differential equations to be used are
𝑑
𝑟𝐴 = 𝐶𝐴 = −10𝐶𝐴 + 𝐶𝑅
𝑑𝑡
𝑑
𝑟𝑅 = 𝐶𝑅 = 10𝐶𝐴 − 𝐶𝑅 − 𝐶𝑅 + 𝐶𝑆
𝑑𝑡
𝑑
𝑟𝑆 = 𝐶𝑆 = 𝐶𝑅 − 𝐶𝑆
𝑑𝑡
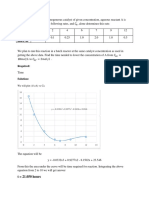
𝑡 = 0.27 𝑚𝑖𝑛, 𝐶𝑅 = 0.7337 𝑀
ChE 2115: Chemical
Reaction Engineering
You might also like
- 10 - Unsteady-State Reactor PDFDocument12 pages10 - Unsteady-State Reactor PDFGRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- 9 - Multiple Reactions in Continuous ReactorsDocument11 pages9 - Multiple Reactions in Continuous ReactorsGRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 8b - Series ReactionsDocument16 pages8b - Series ReactionsGRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Rate LawDocument23 pages3.2 Rate LawShane MillenaNo ratings yet
- Electronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesFrom EverandElectronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Rate Law: Chemical Reaction Engineering 1Document23 pagesRate Law: Chemical Reaction Engineering 1Patricia DavidNo ratings yet
- 7c - Continuous Reactors Graphical SolutionDocument20 pages7c - Continuous Reactors Graphical SolutionGRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- Exp 11 21110006 CL352Document7 pagesExp 11 21110006 CL352Abhinav AnandNo ratings yet
- Integral Method of Analysis of DataDocument13 pagesIntegral Method of Analysis of DataImran UnarNo ratings yet
- 8c - Reversible ReactionsDocument13 pages8c - Reversible ReactionsGRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- Che 125: Chemical Reaction Engineering IDocument2 pagesChe 125: Chemical Reaction Engineering IJelor GallegoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 2024Document21 pagesLecture 1 2024nonkululekomoya26No ratings yet
- CHEM 1211K Lab Fall 2020: Submission GuideDocument3 pagesCHEM 1211K Lab Fall 2020: Submission GuideParker Santo DomingoNo ratings yet
- Synthron Case Study Write UpDocument10 pagesSynthron Case Study Write UpTallo CruzNo ratings yet
- Batch LabDocument6 pagesBatch LabJocelyn Grisel García GonzálezNo ratings yet
- CHEN20051 Modelling and Optimization FinalDocument7 pagesCHEN20051 Modelling and Optimization FinalSKITTLE BEASTNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - EquilibriumDocument11 pagesUnit 7 - EquilibriumgigiNo ratings yet
- GROUP 4 - Final Design ProjectDocument48 pagesGROUP 4 - Final Design ProjectVince Nixau PadelNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Week 12 - Batch ReactorDocument17 pagesTutorial Week 12 - Batch Reactorsiti azilaNo ratings yet
- Answer: SolutionDocument3 pagesAnswer: SolutionCj CosteloNo ratings yet
- Kinetics (Gjjkkkgty)Document5 pagesKinetics (Gjjkkkgty)Chrysler Kane DepnagNo ratings yet
- Batch Reactor ExpDocument12 pagesBatch Reactor ExpJack AndreasNo ratings yet
- Module 7 GAS STOICHIOMETRYDocument4 pagesModule 7 GAS STOICHIOMETRYAnn DayritNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems in Chemical Reaction Engineering For GATEDocument16 pagesPractice Problems in Chemical Reaction Engineering For GATERasNo ratings yet
- Material Balance With Chemical ReactionsDocument53 pagesMaterial Balance With Chemical ReactionsAcademicBMNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - CHE 37 - Theoretical BackgroundDocument11 pagesGroup 4 - CHE 37 - Theoretical BackgroundVince Nixau PadelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Level N Chapter 12 BQ-AK 2223Document19 pagesChemistry Level N Chapter 12 BQ-AK 2223Dema IhabNo ratings yet
- CRE ExperimentsDocument25 pagesCRE ExperimentsÀbhaý SìñģhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document12 pagesChapter 12api-2014792360% (1)
- Chapter 2 Rate Data AnalysisDocument57 pagesChapter 2 Rate Data AnalysisSINH NGUYỄN HỮUNo ratings yet
- CHE 492 HW 9 Fawaz AlsaiedeDocument8 pagesCHE 492 HW 9 Fawaz AlsaiedeTimelessNo ratings yet
- GenChem2 Chemical EquilibriumDocument2 pagesGenChem2 Chemical Equilibriumjohn carlo roblesNo ratings yet
- Kinetics 1Document3 pagesKinetics 1JuarezNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 Week 4 Stoichiometry CompilerDocument7 pagesChem 1 Week 4 Stoichiometry CompilerMelcorr MontesclarosNo ratings yet
- Chee4367 HW051231Document2 pagesChee4367 HW051231kimhoang_16927574No ratings yet
- Chapter 16.Ppt Sec.2Document43 pagesChapter 16.Ppt Sec.2فارس بوعبيدهNo ratings yet
- Notes in Limiting Reactant Day4Document3 pagesNotes in Limiting Reactant Day4Olga AsiaNo ratings yet
- E2 Reactor DesignDocument1 pageE2 Reactor DesigncamimedNo ratings yet
- امثلة ومسائل تحليلات المصدر exportDocument1 pageامثلة ومسائل تحليلات المصدر exportA. M. ANo ratings yet
- Cre Mse 2020 21Document2 pagesCre Mse 2020 21Chaudhary MundhaliaNo ratings yet
- 7.0 Reaction Kinetics 2019Document62 pages7.0 Reaction Kinetics 2019salman khanNo ratings yet
- U12 Rev Ws - 10 - No Ice or KSPDocument3 pagesU12 Rev Ws - 10 - No Ice or KSPetud3clNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 PDFDocument62 pagesChapter 9 PDF김민성No ratings yet
- CLP302 CLP303 ReportsDocument7 pagesCLP302 CLP303 ReportsamitNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Reaction Kinetics - 1Document10 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Reaction Kinetics - 1Parthapratim GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Abd17Document97 pagesChemistry Notes Abd17parth PatelNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Chemical Kinetics SolutionsDocument17 pagesUnit 3 Chemical Kinetics Solutionssuryansh.yt9641No ratings yet
- SCH4U Equilibrium Questions With SolutionsDocument28 pagesSCH4U Equilibrium Questions With SolutionsS P100% (1)
- Evaluation N°3 M1Document2 pagesEvaluation N°3 M1EL BOUJI SOUFIANENo ratings yet
- Exercise TRK 1Document14 pagesExercise TRK 1Ananda CahyaNo ratings yet
- Exam I Sem I 2011 12 Cheng 323Document7 pagesExam I Sem I 2011 12 Cheng 323Faisal MumtazNo ratings yet
- Balances On Reactive ProcessesDocument26 pagesBalances On Reactive ProcessesDanny LeeNo ratings yet
- Chep 424 2ND Semester 2013 Quiz 1Document1 pageChep 424 2ND Semester 2013 Quiz 1Clarissa AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Rates of ReactionsDocument71 pagesRates of ReactionsMel ManningNo ratings yet
- SDFGBNDocument16 pagesSDFGBN0721673895No ratings yet
- CKB 20104 - Reaction EngineeringDocument9 pagesCKB 20104 - Reaction EngineeringNoor FatihahNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction-Rev02Document33 pages01 Introduction-Rev02GRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- 02 Energy and Mass Transfers in Ecosystems - Rev02Document21 pages02 Energy and Mass Transfers in Ecosystems - Rev02GRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- 7c - Continuous Reactors Graphical SolutionDocument20 pages7c - Continuous Reactors Graphical SolutionGRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- 8a - Parallel ReactionsDocument26 pages8a - Parallel ReactionsGRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- 8c - Reversible ReactionsDocument13 pages8c - Reversible ReactionsGRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- 03 - Size Reduction Equipment (Reading Assignment)Document10 pages03 - Size Reduction Equipment (Reading Assignment)GRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- 1 Nature and Importance of WaterDocument22 pages1 Nature and Importance of WaterGRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- G3600 A4 Brochures PDFDocument4 pagesG3600 A4 Brochures PDFVictor NunezNo ratings yet
- DeskView Client 6 45 enDocument166 pagesDeskView Client 6 45 enRazvan22081997No ratings yet
- CA-Clipper For DOS Version 5.3 Programming and Utilities GuideDocument718 pagesCA-Clipper For DOS Version 5.3 Programming and Utilities GuideChris Harker91% (11)
- Pspice Project-BJT AmplifierDocument4 pagesPspice Project-BJT AmplifierSerdar7tepe100% (1)
- PhysioEx Ex. 9 Act. 2Document4 pagesPhysioEx Ex. 9 Act. 2Juvy Anne LozanoNo ratings yet
- NPTEL CC Assignment4Document4 pagesNPTEL CC Assignment4Paul Stark100% (1)
- 1 Priority KeywordDocument8 pages1 Priority KeywordKavithaNo ratings yet
- LatheDocument74 pagesLatheChandrakantha K100% (1)
- Change ManDocument17 pagesChange Mansrikanth9gannuNo ratings yet
- BQ 76 PL 102Document23 pagesBQ 76 PL 102AlexNo ratings yet
- NASA Facts Explorer XVI The Micrometeoroid SatelliteDocument4 pagesNASA Facts Explorer XVI The Micrometeoroid SatelliteBob AndrepontNo ratings yet
- Excretion in Humans: Test Yourself 11.1 (Page 223)Document2 pagesExcretion in Humans: Test Yourself 11.1 (Page 223)leeNo ratings yet
- Bluebeam Revu Keyboard Shortcuts 2017-UKDocument8 pagesBluebeam Revu Keyboard Shortcuts 2017-UKStigNo ratings yet
- Database Management SystemsDocument19 pagesDatabase Management Systemsshreeya PatilNo ratings yet
- TractionDocument26 pagesTractionYogesh GurjarNo ratings yet
- PDF 4.6 MDocument2 pagesPDF 4.6 MmdisicNo ratings yet
- Identification - of - Vulkan Vulastik-L CouplingsDocument2 pagesIdentification - of - Vulkan Vulastik-L CouplingsBill NevisNo ratings yet
- Soda Ash PDFDocument45 pagesSoda Ash PDFM TNo ratings yet
- Artigo - Control Tests For ConcreteDocument24 pagesArtigo - Control Tests For ConcreteRonald Rolim de Moura100% (1)
- Quiz 3 Basic ProbabilityDocument38 pagesQuiz 3 Basic ProbabilityjacobtianNo ratings yet
- SuperDeck All ModelsDocument12 pagesSuperDeck All Modelsarthur chungNo ratings yet
- ABB MNS IAC Additional Test ReportDocument14 pagesABB MNS IAC Additional Test ReportSheik100% (1)
- Just in Time AlgebraDocument289 pagesJust in Time AlgebraamaiscNo ratings yet
- J R Rice - Path Independentt Integral - JAM68Document8 pagesJ R Rice - Path Independentt Integral - JAM68CJCONSTANTENo ratings yet
- Syllabus 3210 Fall 2012 PDFDocument4 pagesSyllabus 3210 Fall 2012 PDFRahul KarnaNo ratings yet
- How To Upload Excel File Into Internal Table With Required FormatDocument2 pagesHow To Upload Excel File Into Internal Table With Required FormatErick ViteNo ratings yet
- B I 1A Fundamentals of Reservoir Phase Behavior PDFDocument92 pagesB I 1A Fundamentals of Reservoir Phase Behavior PDFsereptNo ratings yet
- Completation Inteligent RevistaDocument9 pagesCompletation Inteligent RevistaGabriel Castellon HinojosaNo ratings yet
- All The Questions of Section - A Are in Google Form and The Link To Attempt Them Is " Https://Forms - Gle/Jfvq8Wszicewchrj7 " 12 M Section - BDocument4 pagesAll The Questions of Section - A Are in Google Form and The Link To Attempt Them Is " Https://Forms - Gle/Jfvq8Wszicewchrj7 " 12 M Section - BKamal AnandNo ratings yet
- PLCC-28: FeaturesDocument5 pagesPLCC-28: Features肖磊No ratings yet