Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
Navdeep KaurOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled Document
Uploaded by
Navdeep KaurCopyright:
Available Formats
Asset - control
What is an asset?
- It is something that has value and is in possession of an economic entity such as a
business.
2 Types of Asset
- Current
- These are the short-term assets of the company that are ready for use such as cash,
inventory, or accounts receivable.
- Non-current
- These are long-term assets that have a useful life of more than a year. Some
examples are investments, real estate, or equipment.
How the Statement of Financial Position arranged
- Assets are written first, followed by liabilities then equity. In balancing the Statement of
the Financial Position, the total of the assets should be equal to the total of both the
liabilities and equity. This is in reference to the basic accounting equation wherein
liabilities plus equity equals assets.
How do you know if you own an asset?
- If what you own adds financial value then you owe assets. Technically, this means that
your balance for your assets should be in debit to consider it as yours.
What is PAS 1
- PAS 1 focuses on the presentation of financial statements. It provides guidelines, basis,
and requirements in preparing the financial statement.
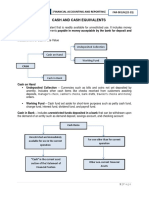
What is cash
- Cash in accounting includes money and other financial instruments that are accepted in
the bank or other financial institutions
Standards for cash
- An important criteria for an asset is that it should be unrestricted and readily available.
Why cash is a current asset
- Cash is liquid and readily available on hand which is why it is a current asset. It can
easily be used when needed even for purchases of other assets.
What are cash equivalents
- These are short term highly liquid investments that are readily convertible to cash. It is
also nearing its maturity that it presents insignificant risk of changes in value.
Possible that cash has interest
How we measure cash
- Cash is measured at face value. Meaning the value is as stated in the item.
Cash in foreign currency
- When cash is used as foreign currency it should be translated to PHP using the exchange
rate of the reporting period.
Bank overdraft
- This occurs when the bank accounts a credit balance which results from the issuance of
cheeks in excess of the deposit.
Is bank overdraft always a current liability?
- Yes it is classified a current liability as it results from acquiring credit balance in a bank
account because of a check
Classification of bank overdraft
- Current Assets and current liability
Materiality concept
- Materiality concept in accounting refers to the concept that all the material items should
be reported properly in the financial statements
Compensating balance
- It is the balance that should be maintained in a checking or demand deposit account
balance because of a borrowing arrangement with a bank.
Classification of compensating balance
-
Undelivered check
- These are checks that are unreleased to the payee before the end of the reporting date.
Adjusting entries for undelivered check
- Cash debit then accounts payable credit
Post Dated check
- Postdated checks are checks that are given to the payee before the reporting dates.
Adjusting entries for post dated check
- Cash for debit and accounts payable for credit
Stale check
- It is a check not encashed by the payee for a long time. According to bank practices, a
check is considered stale if it is not encashed within 6 months of issuance.
Adjusting entries for stale check
- If it’s immaterial then the debit should be cash while the credit should be miscellaneous
income
- If it’s material and liability is expected then it should be debited as cash and credited as
accounts payable.
Ante dated check
You might also like
- White PaperDocument5 pagesWhite PaperZara Jane DinhayanNo ratings yet
- W6 Module 9 Cash and Cash Equivalents Part 1Document11 pagesW6 Module 9 Cash and Cash Equivalents Part 1haven AvyyNo ratings yet
- INTACC1 Chap 1 9Document14 pagesINTACC1 Chap 1 9Rommel estrellado100% (1)
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument37 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsReiner Jan AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument6 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsPam LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Xfar ReviewerDocument6 pagesXfar ReviewerAliyah Ishi UcagNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1-Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument43 pagesCHAPTER 1-Cash and Cash EquivalentsMarriel Fate CullanoNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument34 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsJennalyn S. GanalonNo ratings yet
- Cash Cash Equivalents - Part 1Document35 pagesCash Cash Equivalents - Part 1Lily of the ValleyNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument7 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentAlex VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Legal Accounting - AssetsDocument5 pagesLegal Accounting - AssetsWEDDANEVER CORNELNo ratings yet
- A31 Cash and ReceivablesDocument3 pagesA31 Cash and Receivablesdre thegreatNo ratings yet
- Module 16 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument7 pagesModule 16 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsLuiNo ratings yet
- L10-Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument1 pageL10-Cash and Cash EquivalentsRosalle BesinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 CashDocument13 pagesChapter 5 CashAkkama100% (1)
- Fa - I Chapter 6Document13 pagesFa - I Chapter 6Hussen AbdulkadirNo ratings yet
- 05 Fa-I Chapter 5Document8 pages05 Fa-I Chapter 5History and EventNo ratings yet
- IA1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument20 pagesIA1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsJohn Rainier QuijadaNo ratings yet
- Lecture No.1 Cash Cash Equiv TheoriesDocument3 pagesLecture No.1 Cash Cash Equiv TheoriesbsasociondaisyremarieNo ratings yet
- Cash Cash EquivalentDocument92 pagesCash Cash EquivalentInzaghi CruiseNo ratings yet
- Assets - Syn 101Document35 pagesAssets - Syn 101Marianne SironNo ratings yet
- Acfm Unit 4Document47 pagesAcfm Unit 4begumayesha7366No ratings yet
- Module 1Document12 pagesModule 1bhettyna noayNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument16 pagesModule 1 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsJehPoy0% (1)
- Module 004 Accounting For Cash: Definition, Nature and Composition of Cash and Cash Equivalents CashDocument12 pagesModule 004 Accounting For Cash: Definition, Nature and Composition of Cash and Cash Equivalents CashLee-chard EboeboNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument31 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsMark LouieNo ratings yet
- FAR LectureDocument6 pagesFAR Lecturewingsenigma 00No ratings yet
- 02 Chapter 2 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument10 pages02 Chapter 2 Cash and Cash Equivalentssoyoung kimNo ratings yet
- Week 02 - 01 - Module 04 - Accounting For CashDocument12 pagesWeek 02 - 01 - Module 04 - Accounting For Cash지마리No ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents - ReviewerDocument6 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents - ReviewerKairo ZeviusNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument7 pagesCash and Cash Equivalentjustinenakpil09No ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents (Chapter 1)Document171 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents (Chapter 1)chingNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument27 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsPatOcampoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pagesLesson 1 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsPol Moises Gregory Clamor88% (16)
- W6 Module 9 Cash and Cash Equivalents Part 1Document7 pagesW6 Module 9 Cash and Cash Equivalents Part 1leare ruazaNo ratings yet
- Cashandcashequivalent 150620153356 Lva1 App6892 PDFDocument27 pagesCashandcashequivalent 150620153356 Lva1 App6892 PDFMary Ann BaguioNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFDocument4 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents PDFJade Gomez100% (1)
- Cash and Cash EquivalentDocument22 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentCamille MaterumNo ratings yet
- CCE HeheDocument19 pagesCCE HeheJam SurdivillaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument9 pagesModule 1 - Cash and Cash Equivalentsjay classroomNo ratings yet
- Cash and Account ReceivableDocument27 pagesCash and Account Receivableletkristal shineNo ratings yet
- Intermediate AccountingDocument33 pagesIntermediate AccountingHannah Baniqued100% (1)
- It Is A Current Asset. It Is Part of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pagesIt Is A Current Asset. It Is Part of Cash and Cash EquivalentsBts Army ForeverNo ratings yet
- 06 ReceivableDocument104 pages06 Receivablefordan Zodorovic100% (4)
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument23 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsGennelyn Grace Penaredondo100% (1)
- Module 1 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument10 pagesModule 1 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsGRACE ANN BERGONIONo ratings yet
- FABM2 - Statement of Financial PositionDocument36 pagesFABM2 - Statement of Financial PositionVron Blatz100% (6)
- Ia 1 CH 4Document9 pagesIa 1 CH 4hamidNo ratings yet
- Afar NotesDocument24 pagesAfar NotesCoreen ElizaldeNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting ModuleDocument4 pagesBasic Accounting ModuleHazel Joy Batocail100% (1)
- Asset & Its ClassificationDocument5 pagesAsset & Its ClassificationSyed Shaker AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument33 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsMerry Julianne DaymielNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting - Study Guide Chapter 7: Internal Control and Cash Internal Control SystemDocument3 pagesFinancial Accounting - Study Guide Chapter 7: Internal Control and Cash Internal Control SystemMurtaza HussainNo ratings yet
- Cash Cash Equivalents: Practical Accounting 1 Theory of AccountsDocument4 pagesCash Cash Equivalents: Practical Accounting 1 Theory of AccountsMaria Fe ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting I - Notes (9.13.2022)Document18 pagesIntermediate Accounting I - Notes (9.13.2022)Mainit, Shiela Mae, S.No ratings yet
- Financial Control Blueprint: Building a Path to Growth and SuccessFrom EverandFinancial Control Blueprint: Building a Path to Growth and SuccessNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?From EverandFinancial Accounting - Want to Become Financial Accountant in 30 Days?Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mastering Bookkeeping: Unveiling the Key to Financial SuccessFrom EverandMastering Bookkeeping: Unveiling the Key to Financial SuccessNo ratings yet
- Title I - Obligations General Provisions 1156. An Obligation Is A Juridical Necessity To Give, To Do, or Not To DoDocument26 pagesTitle I - Obligations General Provisions 1156. An Obligation Is A Juridical Necessity To Give, To Do, or Not To DoNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- AsdfasdfDocument4 pagesAsdfasdfNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- AlbertDocument2 pagesAlbertNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- F 3 EwrefsdgveDocument1 pageF 3 EwrefsdgveNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Exam Answer KeyDocument40 pagesExam Answer KeyNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- FgrefsfdfDocument2 pagesFgrefsfdfNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Illegal Access & InterceptionDocument6 pagesIllegal Access & InterceptionNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- OBLICON ReviewerDocument54 pagesOBLICON ReviewerMaria Diory Rabajante93% (301)
- ChemDocument2 pagesChemNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ExercisesDocument3 pagesChapter 3 ExercisesLê Chấn PhongNo ratings yet
- ExplanationDocument1 pageExplanationNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of Youths Launching An Online Business During The Covid-19 PandemicDocument9 pagesPros and Cons of Youths Launching An Online Business During The Covid-19 PandemicNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- AdsfewefeDocument4 pagesAdsfewefeNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- CFAS and FAR Quiz BeeDocument6 pagesCFAS and FAR Quiz BeeNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Iliad Play EssayDocument23 pagesIliad Play EssayNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- PresidentDocument1 pagePresidentNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Cfas - Quiz QuestionsDocument3 pagesCfas - Quiz QuestionsNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument30 pagesBusiness PlanNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Graft and Corruption in The GovernmentDocument2 pagesGraft and Corruption in The GovernmentNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- A.4 ConductingDocument4 pagesA.4 ConductingNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- What Are The Pros and Cons of Employment-At-Will Doctrine?Document1 pageWhat Are The Pros and Cons of Employment-At-Will Doctrine?Navdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of Youths Launching An Online Business During The Covid-19 PandemicDocument9 pagesPros and Cons of Youths Launching An Online Business During The Covid-19 PandemicNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Application LetterDocument1 pageApplication LetterNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its BackgroundDocument13 pagesThe Problem and Its BackgroundNavdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Answer 3Document2 pagesAnswer 3Navdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Financial Accounting 6E by Libby Chapter 08Document45 pagesTest Bank Financial Accounting 6E by Libby Chapter 08Ronald James Siruno Monis0% (1)
- Reference-Weygandt, Kimmel, Kieso: Financial Accounting, IFRS Edition, 2e, Chapter 2Document10 pagesReference-Weygandt, Kimmel, Kieso: Financial Accounting, IFRS Edition, 2e, Chapter 2FerryNo ratings yet
- So NLtga PZ 48 Oo OTNDocument6 pagesSo NLtga PZ 48 Oo OTNporseenaNo ratings yet
- BLD 416 Budgeting and Financial Control 1 Lecture Note 2Document9 pagesBLD 416 Budgeting and Financial Control 1 Lecture Note 2Oluwayomi MalomoNo ratings yet
- No 1.accounting For Practices - p1-10Document12 pagesNo 1.accounting For Practices - p1-10minhhquyetNo ratings yet
- KuisDocument34 pagesKuismc2hin9No ratings yet
- Q1 G11-ABM - L06 Business Transactions & Their Analysis As Applied To Accounting Cycle of Service Business PDFDocument40 pagesQ1 G11-ABM - L06 Business Transactions & Their Analysis As Applied To Accounting Cycle of Service Business PDFAntonia JessaNo ratings yet
- Cfas - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument5 pagesCfas - Cash and Cash EquivalentsYna SarrondoNo ratings yet
- Correct?Document29 pagesCorrect?Hong Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Accounting Principles 10th Edition Weygandt Kimmel Chapter 3 PDFDocument139 pagesAccounting Principles 10th Edition Weygandt Kimmel Chapter 3 PDFbeenie manNo ratings yet
- Allied Banking Corporation v. Spouses Macam (Fausto)Document3 pagesAllied Banking Corporation v. Spouses Macam (Fausto)Bluei FaustoNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Accounting For Governmental and Not-For-Profit Organizations 12th Edition Copley Solutions Manual 1Document37 pagesEssentials of Accounting For Governmental and Not-For-Profit Organizations 12th Edition Copley Solutions Manual 1elizabeth100% (35)
- Ch5 Additional Q OnlyDocument13 pagesCh5 Additional Q OnlynigaroNo ratings yet
- LU2 Lecturer NotesDocument23 pagesLU2 Lecturer NotesShweta SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Product Costing SystemsDocument17 pagesChapter 4-Product Costing SystemsQuế Hoàng Hoài ThươngNo ratings yet
- AG Office AccountingDocument165 pagesAG Office AccountingabadeshNo ratings yet
- Job, Batch, ContractDocument25 pagesJob, Batch, ContractParminder Bajaj100% (1)
- PLA Refunds Post GSTDocument35 pagesPLA Refunds Post GSTManish Sachdeva67% (9)
- Accounting June 2009 MSDocument36 pagesAccounting June 2009 MSgopiNo ratings yet
- RMJ LKJT XP1 e SJAo IDocument5 pagesRMJ LKJT XP1 e SJAo IRahul NailwalNo ratings yet
- Home Office and BranchDocument4 pagesHome Office and BranchRed YuNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document91 pagesCH 03Sayed Farrukh AhmedNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesManagerial Accounting Multiple Choice Questionsmobinil1100% (1)
- Masb TR 1share Buybacks - Accounting and DisclosureDocument13 pagesMasb TR 1share Buybacks - Accounting and DisclosureNiki KhorNo ratings yet
- BIR Form 1702 (November 2011)Document18 pagesBIR Form 1702 (November 2011)Jecon BonsucanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 The Double-Entry System: Discussion QuestionsDocument16 pagesChapter 3 The Double-Entry System: Discussion QuestionskietNo ratings yet
- Worksheet PreparationDocument3 pagesWorksheet PreparationJon PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Asssignment Transaction, Jounal, Ledger, Trial Balance, Adjusting Entry, Final Account, ClosingDocument2 pagesAsssignment Transaction, Jounal, Ledger, Trial Balance, Adjusting Entry, Final Account, ClosingShakil HossainNo ratings yet
- Industrial Finance ProjectDocument62 pagesIndustrial Finance ProjectSantosh PawarNo ratings yet
- 12 Accountancy sp08Document15 pages12 Accountancy sp08sneha muralidharanNo ratings yet