Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pictures Tae
Uploaded by
Fredy AvellanoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pictures Tae
Uploaded by
Fredy AvellanoCopyright:
Available Formats
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
(Mechanical Digestion)
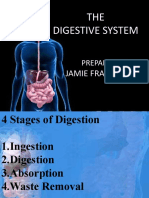
4 MAJOR PARTS/PROCESS:
Ingestion - taking in of food, eating
Digestion - Is when biomolecules polymers, remembering the 4 major biomolecules are broken down
physically/chemically into their building up blocks
Absorption – Is important as nutrients will eventually be delivered with the help of other body systems to
cells as cells need them in order to function or survive.
Elimination (defecation) – waste which includes anything that wasn’t digested will be removed.
INGESTION – Actually starts in the mouth, because your saliva contains enzymes that can break some
biomolecules which is the salivary amylase.
• Chemical Digestion – saliva contains enzymes that can breakdown some biomolecules-salivary amylase as
an example of breaking down some carbohydrates.
• Mechanical Digestion – when you have something physically breaksdown. Your teeth will help grind food
up
ESOPAHAGUS: The large hallow organs of your gastrointestinal tract contain a layer of muscle that enables
the walls to move.
MOVEMENT: it pushes the food angelique quid to your gastrointestinal tract and mixes the contents within
each organ. The muscle behind the food contracts and squeezes the food forward, require while the
muscle is in front of the food relaxes to allow the food to move.
DIGESTION – blocks trachea during act of swallowing food or liquid.
• EPIGLOTTIS – Small flap tissue called epiglottis that folds your windpipe to prevent choking in the food
passes through our esophagus when swallowing food.
• Peristalsis – Is the automatic wave-like movement of the muscles that line your gastrointestinal tract.
Peristalsis moves food through your digestive system, beginning in your throat when you swallow and
continuing through your esophagus, stomach and intestines while you digest.
SMALL INTESTINE PARTS:
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
Here, there will be significant chemical digestion of all four biomolecules:
Carbs — monosaccharides
Lipids — glycerol or fatty acids
Proteins – amino acids
Nucleic acid – nucleotides
There are enzymes involved here and also digestive juices that are released here from other organs as the
gallbladder, the liver and pancreas. There will also be mechanical digestion too, because peristalsis move
the chyme through this segmented space.
ABSORPTION – Most nutrients absorption happens in the small intestine
It absorbs:
• glucose, fructose = sugars
• amino acids = building blocks of protein
• electrolytes and vitamins and lipids
Absorption occurs through the lining of the small intestine which has projections called villi; and the villi
themselves have ‘microvilli’.
As we move along, we eventually enter the Large Intestine – known as colon
Large intestine has a major role that contains H2O is to reabsorb water, so that the body will not lose all
thus precious water involving in digestion.
ELIMINATION (Defecation)
Feces are composed of undigested contents and can contain other substances, and it can include the
bacteria that we’ve mentioned (good bacterias). The very END of the large intestine is the “RECTUM” and
feces will remain here until they are expelled from anus.
For better digestive health, follow these simple tips:
Eat a high-fiber diet.
Be sure you're getting both soluble and insoluble fiber.
Minimize your intake of foods high in fat.
Select lean meats.
Add probiotics to your diet.
Follow a regular eating schedule.
Drink plenty of water.
Reabsorb H2O
You might also like
- Shakila Hamed Report PDFDocument9 pagesShakila Hamed Report PDFShakila HamidNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesOverview of The Digestive SystemMehmet SaylıkNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Exams and AnswersDocument27 pagesNervous System Exams and AnswersMaria Simionescu100% (7)
- SCI-G8-Q4-Week-1-DIGESTIVE-SYSTEMDocument114 pagesSCI-G8-Q4-Week-1-DIGESTIVE-SYSTEM• S h ı m m y •No ratings yet
- Module 10-Digestive SystemDocument27 pagesModule 10-Digestive SystemDarlene FrueldaNo ratings yet
- Digestion: The Digestive SystemDocument66 pagesDigestion: The Digestive SystemTonique Gordon100% (1)
- Our Digestive System: A Concise GuideDocument35 pagesOur Digestive System: A Concise GuidecelineNo ratings yet
- MODULE-1Document24 pagesMODULE-1nutssdeez944No ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument17 pagesDigestive SystemRamjay M. AgloroNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer - Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesScience Reviewer - Digestive SystemCarlieseNo ratings yet
- Digestive system - An overview of digestion and nutrient absorptionDocument45 pagesDigestive system - An overview of digestion and nutrient absorptionKirubel FekaduNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PPT 1Document38 pagesDigestive System PPT 1robloxaltacc356No ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesStructure and Function of The Digestive Systemangelignacio2209No ratings yet
- Nutrition (Digestive System)Document57 pagesNutrition (Digestive System)anglie feNo ratings yet
- NUTRITIONDocument11 pagesNUTRITIONRushana SadaqatNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Digestive SystemDocument3 pages2.6 Digestive SystemOke AdasenNo ratings yet
- Uman Digestive System Structure and Function: DR Neelam SharmaDocument37 pagesUman Digestive System Structure and Function: DR Neelam SharmaBishal Khaidem0% (1)
- Digestive System and Process of DigestionDocument4 pagesDigestive System and Process of DigestionSid QNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive System GuideDocument31 pagesHuman Digestive System GuideAbdullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology - Lauras NotesDocument20 pagesHuman Physiology - Lauras NotesLaya ShrbagiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Digestive SystemJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- B 10 VRV 8303Document41 pagesB 10 VRV 8303Reaper-sanNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument46 pagesDigestive SystemsheenanogpoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Breakdown and AbsorptionDocument35 pagesDigestive System Breakdown and AbsorptionNYL BRIAN BUISERNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: Reporeted By: Jabel, Honeylyn Lou Wong, Leah Castro, Shiela MaeDocument42 pagesThe Digestive System: Reporeted By: Jabel, Honeylyn Lou Wong, Leah Castro, Shiela MaeRaisa GravadorNo ratings yet
- Digestive System DraftDocument39 pagesDigestive System DraftDiosa BakingNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Alimentary Tract of The Digestive System MouthDocument5 pagesDigestive System Alimentary Tract of The Digestive System MouthJoNo ratings yet
- NUTRITION IN HUMAN BEINGS.pptxDocument25 pagesNUTRITION IN HUMAN BEINGS.pptxraghavrungtambwaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument19 pagesThe Digestive Systemianpoblete13No ratings yet
- DisgestionDocument1 pageDisgestionandressookdeo29No ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Nutrition in MammalsDocument25 pagesChapter-6 Nutrition in MammalsRaeed FarshidNo ratings yet
- Human Digestion PresentationDocument35 pagesHuman Digestion PresentationYamyang Galay-BañoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Week 1 OverviewDocument26 pagesDigestive System Week 1 Overviewlau dashNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument32 pagesNutrition in AnimalsIonela HoteaNo ratings yet
- Human NutritionDocument23 pagesHuman NutritionShechem KumarNo ratings yet
- THE Digestive System: BY: Jamie Francis C. RayDocument22 pagesTHE Digestive System: BY: Jamie Francis C. RayJamoi Ray VedastoNo ratings yet
- Report in Biology: by Rey Aldrien G. Dela CruzDocument25 pagesReport in Biology: by Rey Aldrien G. Dela CruzRey Aldrien Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument25 pagesThe Gastrointestinal SystemAssyifaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: A&P QQI Level 5 Leah DunneDocument39 pagesThe Digestive System: A&P QQI Level 5 Leah DunneBlanca Marco de la IglesiaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System ExplainedDocument39 pagesDigestive System Explainedteacher.sarahNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesDigestive SystemFrancisco D. AndaquigNo ratings yet
- Getting Foods To Cell 1Document4 pagesGetting Foods To Cell 1ScatchJhel PascuaNo ratings yet
- CO5-1 Animal NutritionDocument39 pagesCO5-1 Animal NutritionHURHURNo ratings yet
- Calamba Doctors' College Lecture on Digestion, Absorption, and MetabolismDocument13 pagesCalamba Doctors' College Lecture on Digestion, Absorption, and MetabolismMelody DoriaNo ratings yet
- Competitive Exams: Feeding: ExamraceDocument3 pagesCompetitive Exams: Feeding: ExamraceManohar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Uman Digestive System Structure and Function: Anam FarzandDocument25 pagesUman Digestive System Structure and Function: Anam FarzandTahir AzizNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Diet & NUTRITIONDocument30 pagesModule 1 Diet & NUTRITIONarzooNo ratings yet
- m6 Digestive SystemDocument23 pagesm6 Digestive Systemapi-464344582No ratings yet
- AbsorbtionDocument2 pagesAbsorbtionÁšhlëy Ålïãh GhåñįęNo ratings yet
- The Human Digestive System ExplainedDocument21 pagesThe Human Digestive System ExplainedAshley MohammedNo ratings yet
- Handout - Chapter 3 - Digestion - Google Docs - 1665372467933 3Document8 pagesHandout - Chapter 3 - Digestion - Google Docs - 1665372467933 3NC ExistentialNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesThe Digestive SystemKashif KhokharNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Presentations BIOLOGYDocument33 pagesPowerpoint Presentations BIOLOGYRea AnsusNo ratings yet
- 13 Digestion 1Document25 pages13 Digestion 1Ana RamosNo ratings yet
- The Human Digestive Process in 40 CharactersDocument19 pagesThe Human Digestive Process in 40 CharactersRirin A SaputriNo ratings yet
- The Human Digestive SystemDocument37 pagesThe Human Digestive SystemEvangeline Basilan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument48 pagesDigestive SystemAlyanna Marie CarilloNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument72 pagesDigestive System NotesQueen SarrahNo ratings yet
- Writing Techniques for Developing IdeasDocument46 pagesWriting Techniques for Developing IdeasFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property RightsDocument40 pagesIntellectual Property RightsFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Good Day!: Reading and WritingDocument15 pagesGood Day!: Reading and WritingFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Coping Strategies for Managing StressDocument3 pagesCoping Strategies for Managing StressFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Stress and Coping Strategies of Working STEM StudentsDocument9 pagesStress and Coping Strategies of Working STEM StudentsFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Ganito MunaDocument1 pageGanito MunaFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Effective Strategies For The Teaching of ReadingDocument2 pagesEffective Strategies For The Teaching of ReadingFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Stress and Coping Strategies of Working STEM StudentsDocument9 pagesStress and Coping Strategies of Working STEM StudentsFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal: SystemDocument16 pagesSkeletal: SystemFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemnewDocument22 pagesEndocrine SystemnewFlor AidaNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy Physiology SAT REVEIWDocument35 pagesPlant Anatomy Physiology SAT REVEIWFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Final Script For Radio BroadcastingDocument7 pagesFinal Script For Radio BroadcastingFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument37 pagesUntitledFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Plant Organ SystemsDocument8 pages2.2 Plant Organ SystemsFredy AvellanoNo ratings yet
- Nonmedelian 2015Document33 pagesNonmedelian 2015Rehana MopacNo ratings yet
- Mendelian WorksheetsDocument17 pagesMendelian WorksheetsLesley AntojadoNo ratings yet
- DigestionpracticetestDocument41 pagesDigestionpracticetestRennik McCaigNo ratings yet
- Nigeria Paediatric 2007 PDFDocument185 pagesNigeria Paediatric 2007 PDFsusanaadolina sipathaNo ratings yet
- Analyst Cover LetterDocument2 pagesAnalyst Cover LetterRebecca AbbottNo ratings yet
- Tay Sachscasestudyplan2015Document6 pagesTay Sachscasestudyplan2015api-288678270No ratings yet
- Cer Chart For Who Killed Carleton CometDocument2 pagesCer Chart For Who Killed Carleton Cometapi-336683878No ratings yet
- Suggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseDocument26 pagesSuggested Answers To Exercise, Reading To Learn and Cross-Topic ExerciseBernardNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Kebangsaan Bukit Kuchai First Monthly TestDocument4 pagesSekolah Kebangsaan Bukit Kuchai First Monthly TestkamaloshoNo ratings yet
- Gene expression and cloning overviewDocument30 pagesGene expression and cloning overviewNthabeleng NkaotaNo ratings yet
- Dextrose Tryptone Broth cultivation microorganisms foodDocument2 pagesDextrose Tryptone Broth cultivation microorganisms foodgelorrantNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesCell Parts Lesson PlanHeesung LeeNo ratings yet
- Seed Size Variation in The Cleistogamous Species, Ruellia HumilisDocument3 pagesSeed Size Variation in The Cleistogamous Species, Ruellia HumilisManu MandaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-7 - Q2 - Mod6 - Ecological Relationship V3Document47 pagesSCIENCE-7 - Q2 - Mod6 - Ecological Relationship V3MrLonely Drake Deniel Sanchez100% (15)
- LTSC Handbook 2014 Low Res-April8 PDFDocument146 pagesLTSC Handbook 2014 Low Res-April8 PDFblinking02No ratings yet
- 9700 s15 Ms 41Document13 pages9700 s15 Ms 41Rahique ShuaibNo ratings yet
- Micro-Para-Lec Prelims ReviewerDocument22 pagesMicro-Para-Lec Prelims ReviewerEingel Mer Evangelista100% (1)
- Surat Pernyataan Kelas Bahasa Mandarin (Selasa)Document1 pageSurat Pernyataan Kelas Bahasa Mandarin (Selasa)Yanang Surya Putra HardyantoNo ratings yet
- BT Talong ReportDocument16 pagesBT Talong ReportEmrys PendragonNo ratings yet
- Role of Chemicals Used in DNA Extraction: 1. CtabDocument3 pagesRole of Chemicals Used in DNA Extraction: 1. CtabSonu LangayaNo ratings yet
- BMC Evol BiolDocument17 pagesBMC Evol BiolStacy JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Ampliscribe t7 Flash Transcription KitDocument8 pagesAmpliscribe t7 Flash Transcription KitNeha KarekarNo ratings yet
- Cell City Worksheet Answer KeyDocument7 pagesCell City Worksheet Answer KeyNorain TalanganNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Nursery Crop Propagation - Nursery ManagementDocument9 pagesBasic Principles of Nursery Crop Propagation - Nursery Managementlekh raj shivaNo ratings yet
- YersiniaDocument46 pagesYersiniajamal nasir50% (2)
- Incomplete DominanceDocument31 pagesIncomplete Dominanceregine13 ikiNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 8.11-8.16 Plant Hormones, Coordination and The Brain - Edexcel IAL Biology A-LevelDocument65 pagesFlashcards - Topic 8.11-8.16 Plant Hormones, Coordination and The Brain - Edexcel IAL Biology A-LevelBara' HammadehNo ratings yet
- BUITEMS Sensation and Perception DocumentDocument6 pagesBUITEMS Sensation and Perception DocumentAleksandarNo ratings yet
- NematodaDocument16 pagesNematodatapas kunduNo ratings yet
- Difteria 1Document18 pagesDifteria 1Kelly SVNo ratings yet