Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Uploaded by
Abdallah Alasal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesThe document defines key terms related to cell anatomy including anatomy, physiology, cell, tissue, organ, and organism. It describes the major components of animal cells including the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, organelles, cytoskeleton, and nucleus. It provides details on the structure and functions of important organelles - the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vacuoles. The summary highlights that the document defines cell anatomy terms and describes the major components of animal cells and their organelles.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines key terms related to cell anatomy including anatomy, physiology, cell, tissue, organ, and organism. It describes the major components of animal cells including the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, organelles, cytoskeleton, and nucleus. It provides details on the structure and functions of important organelles - the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vacuoles. The summary highlights that the document defines cell anatomy terms and describes the major components of animal cells and their organelles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesUntitled
Uploaded by
Abdallah AlasalThe document defines key terms related to cell anatomy including anatomy, physiology, cell, tissue, organ, and organism. It describes the major components of animal cells including the plasma membrane, cytoplasm, organelles, cytoskeleton, and nucleus. It provides details on the structure and functions of important organelles - the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vacuoles. The summary highlights that the document defines cell anatomy terms and describes the major components of animal cells and their organelles.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
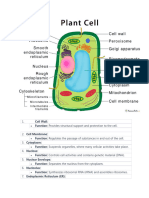
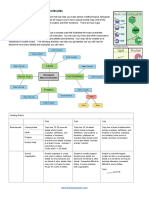
Anatomy (Animal Cell)
What is the meaning of:
1. Anatomy: is the study of the structure and relationships among body parts.
2. Physiology: branch of biology deals with normal functions of organisms and their parts.
3. Cell: Is the basic unit of structure and function of living organisms.
4. Tissue: group cells and extracellular substances that carry out specialized tasks.
5. Organ: two or more tissues organized in a specific way to carry out specific tasks.
6. System: Two or more organs and other components interacting in a common task.
7. Organism: Entire living thing that can carry out all basic life processes.
8. Cytosol: All the stuff in between the organelles.
9. Cytoplasm: Everything inside a cell except the nucleus.
10.Protoplasm: nucleus + cytoplasm
What are the major types of cells?
1. Prokaryotes: Found in micro-organisms
2. Eukaryotes: Found in all other forms of life
What are the characteristics of eukaryotes?
1. Plasma membrane.
2. Cytoplasm (cytosol + organelles)
3. Nucleus.
What are the types of Organelles?
1. Membrane-bounded organelles: RER, SER, Golgi complex, Mitochondria, Lysosomes,
Peroxisomes
2. Non Membrane-bounded organelles: Ribosomes, Filaments, Microtubules, Centrioles
What are the components of Plasma Membrane?
1. A double layer of phospholipids: formed of hydrophilic head, and two hydrophobic tails.
2. Variable protein molecules.
What are the functions of Plasma Membrane?
1. Protection of the cell components.
2. Gives the shape to the cell.
3. Surface for ion and molecule transport.
4. Receives signals and facilitates communication.
What are the components of Nucleus?
Nucleolus, nucleoplasm and chromatin (chromosomes)
What are the component of Cytoplasm?
1. Interconnected filaments and fibers.
2. Semi-fluid = cytosol.
3. Organelles (not nucleus).
4. Storage substances.
What are the types of Endoplasmic Reticulum?
1. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER): ribosomes attached, function is protein synthesis.
2. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER): lacks ribosomes, function in lipid synthesis.
What is the functions of Endoplasmic Reticulum?
1. Protein synthesis.
2. Lipid synthesis.
3. Storage and release of calcium ions.
4. Storage and release of glycogen.
5. Facilitates ions and molecules transport
What are the components of Mitochondria?
1. Outer membrane and a highly-folded inner membrane (cristae).
2. The inner membrane encloses the matrix that contains: DNA, ribosomes, and enzymes.
What is the function of Mitochondria?
1. Energy production (ATP).
2. Storage tanks of calcium ions.
3. Programmed cell death.
What is the Golgi apparatus?
Network of flattened smooth membranous sacs (cisternae and vesicles).
It works in combination with ER.
What is the function of Golgi?
1. Packaging and shipping station of the cell.
2. Modifying, storing and releasing products from endoplasmic reticulum.
What are the components of cytoskeleton?
1. Microfilaments. 2. Intermediate filaments. 3. Microtubules.
What is the function of Cytoskeleton?
1. Provides mechanical support 2. Maintains shape of the cell. 3. Anchors many organelles.
4. Helps in cell motility.
What is Centrosome?
Centrosome consists of two centrioles. Function in cell division.
What is Lysosome?
Sac of hydrolytic enzymes digests molecules Synthesized by RER and transferred to Golgi.
What are the functions of Lysosome?
1. Help cell renewal by breaking down old cell parts.
2. Digest food found in food vacuoles.
3. Play a big role in programmed cell death.
What are the types of Vacuoles?
1. Food vacuoles: transport food from cell membrane
2. Contractile vacuoles: found in freshwater protists, pump excess water out of the cell.
3. Central vacuoles: found in many mature plant cells.
You might also like
- 2 Cell and TissueDocument45 pages2 Cell and Tissuemandefro2No ratings yet
- Gen Zoology ReviewerDocument19 pagesGen Zoology ReviewerDarey ApostolNo ratings yet
- Cell Physiology-1Document32 pagesCell Physiology-1yoga karsendaNo ratings yet
- Draw A Neat and Clean Diagram of Eukaryotic Cell. Write Down An Exhaustive Note On The Functions of CellDocument3 pagesDraw A Neat and Clean Diagram of Eukaryotic Cell. Write Down An Exhaustive Note On The Functions of CellPratik SagarNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM-LAB ACTIVITY 1 (Caminos, Keen Jude)Document3 pagesBIOCHEM-LAB ACTIVITY 1 (Caminos, Keen Jude)Keen Jude CaminosNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYFINALanswers (1stedition)Document61 pagesBIOLOGYFINALanswers (1stedition)Abhinav VermaNo ratings yet
- Acad Fall08 ThecellDocument13 pagesAcad Fall08 Thecellhassanmusahassan81No ratings yet
- Protoplasm Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles Cell WallDocument9 pagesProtoplasm Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles Cell WallJiaRenTeohNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry (Powerpoint PresentationDocument39 pagesBiochemistry (Powerpoint PresentationAnonymous Person100% (1)
- Biol 101 - GRQ 3Document6 pagesBiol 101 - GRQ 3Damaris Santos-MartinezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologykernelkobieNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMDocument14 pagesBIOCHEMLyhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-The CellDocument43 pagesLecture 2-The CellMatende husseinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CellsDocument19 pagesChapter 3 CellsEuniece AnicocheNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Short Notes (2.1)Document1 pageBiology Form 4 Short Notes (2.1)incognito278No ratings yet
- The CellDocument36 pagesThe CellSam MumoNo ratings yet
- Cell, Cellular Components and Their FunctionDocument6 pagesCell, Cellular Components and Their FunctionSyed Adzha Al-ShahabudinNo ratings yet
- Cells Revision NotesDocument6 pagesCells Revision NotesmarzybarNo ratings yet
- What Are Cells?: Biology Form 4 Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation Subtopic 2.1: Cell Structure & FunctionDocument13 pagesWhat Are Cells?: Biology Form 4 Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation Subtopic 2.1: Cell Structure & FunctionyayeetNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument6 pagesCell Biologyakash kumarNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument6 pagesBIOLOGYKiana BNo ratings yet
- THE CELL I: Cytoplasm and Cytoplasmic Components: by Dr. Taiwo-OlaDocument16 pagesTHE CELL I: Cytoplasm and Cytoplasmic Components: by Dr. Taiwo-OlaJoshua DorisNo ratings yet
- Bio - UNIT 1 - Organisms and Life ProcessesDocument18 pagesBio - UNIT 1 - Organisms and Life ProcessesMuhammad Mahi Nurul IslamNo ratings yet
- Introductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02Document34 pagesIntroductiontophysiologylecture 101020230212 Phpapp02DR KARSHAN NANDANIYANo ratings yet
- CellsDocument1 pageCellshl69962731No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 A Tour of The CellDocument4 pagesChapter 4 A Tour of The Cellmzunl254760% (1)
- 4.1 Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument9 pages4.1 Cell As A Unit of Lifehola adiosNo ratings yet
- A221 Module 1 Cell and Tissue PDFDocument10 pagesA221 Module 1 Cell and Tissue PDFAkmal Danish100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument72 pagesAnatomy and Physiologykins petetNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument37 pagesNotesDaideepya SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Nature of CellsDocument7 pagesNature of CellsAdrian Lee VannorsdallNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in BiologyDocument8 pagesReviewer in BiologyMikaela EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Centro, MF. Module - 5Document9 pagesCentro, MF. Module - 5jessa marie marevilesNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesCell Structure and FunctionYeshua Dan BigasaNo ratings yet
- Hum, An CellDocument6 pagesHum, An CellQlife KlinikNo ratings yet
- Biology Class Notes: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument2 pagesBiology Class Notes: Cell Structure and FunctionAndre WelsNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life: Q 1 .State Cell Theory - Who Proposed It?Document10 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life: Q 1 .State Cell Theory - Who Proposed It?Justin RajanNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument6 pagesCell TopicUbaid Ur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 March 2009Document36 pagesLecture 1 March 2009api-19824406No ratings yet
- Grade 12-General Biology (Cells)Document11 pagesGrade 12-General Biology (Cells)angeliaNo ratings yet
- Cell Anatomy: Lab Exercise 2Document2 pagesCell Anatomy: Lab Exercise 2Eshiebel OrganistaNo ratings yet
- The Cell Theory of BiologyDocument10 pagesThe Cell Theory of BiologyFrezelVillaBasiloniaNo ratings yet
- MIC 311 Lecture NoteDocument107 pagesMIC 311 Lecture NotesiwetwakuNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Cells: Characteristics of The CellDocument4 pagesCells: Characteristics of The CellRashidah R. DisomaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument4 pagesCellscalustre2016No ratings yet
- Key Notes For Chapter-The Fundamental Unit of Life, Are: CellDocument14 pagesKey Notes For Chapter-The Fundamental Unit of Life, Are: CellShweta ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Ollanas - Exercise No.3 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesOllanas - Exercise No.3 Cell Structure and FunctionALETHEA KIRSTEN OLLANASNo ratings yet
- Education NotesDocument5 pagesEducation NotesRwynn MemoryNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument7 pagesCell PhysiologyReslie Joy Serrano100% (1)
- Cell AssignmentDocument3 pagesCell AssignmentDreamy AspirationsNo ratings yet
- Bio Ncert GistDocument96 pagesBio Ncert GistrrphysicsinstituteNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument14 pagesGeneral BiologybonNo ratings yet
- Bio Long NoteDocument12 pagesBio Long Notejacob guerreroNo ratings yet
- CH 6 A Tour of The CellDocument7 pagesCH 6 A Tour of The Cellwil7verNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesLesson 2 - Cell OrganellesAly FayeNo ratings yet
- 1 Bio 102 CELL THEORY AND FUNCTIONDocument6 pages1 Bio 102 CELL THEORY AND FUNCTIONOlamide KoleNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument6 pagesCell Organelles Worksheeteve kidonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Biochemical Characteristics of Living MatterDocument69 pagesChapter 1 Biochemical Characteristics of Living MatterJoyce Jimenez0% (1)
- Z (H) IV GE Human Growth HormoneDocument18 pagesZ (H) IV GE Human Growth HormoneAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument6 pagesCell DivisionAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Anatomy & HistologyDocument7 pagesDigestive System Anatomy & HistologyAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System (Lungs) : Excretes Carbon Dioxide 3. Integumentary System (Skin) : Excretes Water, SaltsDocument2 pagesRespiratory System (Lungs) : Excretes Carbon Dioxide 3. Integumentary System (Skin) : Excretes Water, SaltsAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland: General Principles of Endocrine DiagnosisDocument13 pagesThe Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland: General Principles of Endocrine DiagnosisKiprono Keitany TimothyNo ratings yet
- Anemia NevinDocument69 pagesAnemia NevinAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesCardiovascular SystemAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 5-2data and EpidemiologyDocument27 pages5-2data and EpidemiologyAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The Lymphatic and Immune SystemsAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesEndocrine SystemAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 9program EvaluationDocument10 pages9program EvaluationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 4-1pulmonary DisordersDocument38 pages4-1pulmonary DisordersAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Analytical Studies in Epidemiology:advanced DesigneDocument50 pagesAnalytical Studies in Epidemiology:advanced DesigneAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 2 - SterilizationDocument4 pages2 - SterilizationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 1-Lab SafetyDocument22 pages1-Lab SafetyAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document3 pagesAssignment 1Abdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Summary of Positive Vs Negative FeedbackDocument1 pageSummary of Positive Vs Negative FeedbackAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 3 Using Pulse OximeterDocument2 pages3 Using Pulse OximeterAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Diagnosis of DMDocument28 pages4.3 Diagnosis of DMAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Lipids MetabolismDocument31 pages5.1 Lipids MetabolismAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- علم تشريحDocument58 pagesعلم تشريحAbdallah Alasal100% (1)
- Lecture 14 - Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma L0 COPD - EditedDocument42 pagesLecture 14 - Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma L0 COPD - EditedAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- ICU NursingDocument9 pagesICU NursingAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Lectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationDocument27 pagesLectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Lec 10 Feeding Patients Oral Diets and Enteral and Parenteral NutritionDocument39 pagesLec 10 Feeding Patients Oral Diets and Enteral and Parenteral NutritionAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Health 25-10-2022.Document29 pagesGeriatric Health 25-10-2022.Abdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- 200-Protein Quantification BCA™, Modified Lowry and Bradford AssaysDocument5 pages200-Protein Quantification BCA™, Modified Lowry and Bradford AssaysMusa LooNo ratings yet
- Test 1 - APQ Model Answers-1Document14 pagesTest 1 - APQ Model Answers-1Matsiri ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- Bio 3rd ExamDocument4 pagesBio 3rd ExamavinmanzanoNo ratings yet
- 6 Enzymes and Cellular Regulation-SDocument5 pages6 Enzymes and Cellular Regulation-Sapi-502781581No ratings yet
- Lecture NotesDocument32 pagesLecture Noteslira shresthaNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 S 13Document10 pagesExam 1 S 13Asad Javed MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Biology of SNU Cell LinesDocument19 pagesBiology of SNU Cell Lineshari_iyer16No ratings yet
- Laboratory Diagnosis of HIV InfectionDocument26 pagesLaboratory Diagnosis of HIV Infection12. Akshit Atwal100% (1)
- Dual Glo Luciferase Assay System TM058Document26 pagesDual Glo Luciferase Assay System TM058cfibanezNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Molecular Biology: Lisabeth A. AllisonDocument89 pagesFundamental Molecular Biology: Lisabeth A. AllisonJu noNo ratings yet
- St. Xavier's Senior Secondary School, Pant Nagar Gonda Class-Ix (Science) Set-A Mm:20Document4 pagesSt. Xavier's Senior Secondary School, Pant Nagar Gonda Class-Ix (Science) Set-A Mm:20Noor Fatima KhanNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland and Its Rule in Human BodyDocument9 pagesThyroid Gland and Its Rule in Human BodyDrFarah Emad AliNo ratings yet
- Research in Lecture "All About Nucleic Acid": Bicol University College of Nursing Legazpi City 2015-2016Document27 pagesResearch in Lecture "All About Nucleic Acid": Bicol University College of Nursing Legazpi City 2015-2016Kim GoNo ratings yet
- Separation of Proteins Using (NH4) 2SO4 PrecipitationDocument8 pagesSeparation of Proteins Using (NH4) 2SO4 PrecipitationAnura BandaraNo ratings yet
- Liposome Drug Delivery SystemDocument28 pagesLiposome Drug Delivery SystemNelsi Fitri HayatyNo ratings yet
- Light Dependent ReactionsDocument2 pagesLight Dependent ReactionsDuaa Saqri RamahiNo ratings yet
- MBB231 Chapter 9 Cytoskeleton Introduction 1197Document28 pagesMBB231 Chapter 9 Cytoskeleton Introduction 1197nathanNo ratings yet
- MSM Health Benefits PDFDocument11 pagesMSM Health Benefits PDFRocco LamponeNo ratings yet
- Enzymatic Cleavage and The Creation of Heteroduplex DNA: Holliday ModelDocument10 pagesEnzymatic Cleavage and The Creation of Heteroduplex DNA: Holliday ModelAshwini PillaiNo ratings yet
- Mcqs in Physiology: Collected By: Professor Bassam Talib Al-Gailani (M.B.CH.B., PHD)Document417 pagesMcqs in Physiology: Collected By: Professor Bassam Talib Al-Gailani (M.B.CH.B., PHD)khywh2qnsrNo ratings yet
- Cancer Anorexia and CachexiaDocument5 pagesCancer Anorexia and CachexiaWildan Satrio WemindraNo ratings yet
- Development of An Immuno-Based Colorimetric Assay For White Spot Syndrome VirusDocument6 pagesDevelopment of An Immuno-Based Colorimetric Assay For White Spot Syndrome VirusendorengasNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: DNA Base Pairing WorksheetDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: DNA Base Pairing Worksheetphil tolentinoNo ratings yet
- Pemisahan Dan Analisis ProteinDocument77 pagesPemisahan Dan Analisis ProteinEricka PutriNo ratings yet
- Expression of RAD6, DDB2 and Cancer Stem Cell _ CSC Protein (CD44 _sup_+__sup__CD24 _sup_-__sup_) on Therapy Response to the Administration of Chemotherapy in Ovarian Cancer_ A Prospective Flow Cytometry Study by Unedo H.M. Sihombing, Andrijono , GatoDocument11 pagesExpression of RAD6, DDB2 and Cancer Stem Cell _ CSC Protein (CD44 _sup_+__sup__CD24 _sup_-__sup_) on Therapy Response to the Administration of Chemotherapy in Ovarian Cancer_ A Prospective Flow Cytometry Study by Unedo H.M. Sihombing, Andrijono , GatoKristabella GianinaNo ratings yet
- Atp Cloze NotesDocument4 pagesAtp Cloze Notesapi-260690009No ratings yet
- Semester 1 Rev 2019Document33 pagesSemester 1 Rev 2019Anthony WilsonNo ratings yet
- Degradasi Karbohidrat 1Document32 pagesDegradasi Karbohidrat 1Bryan AswNo ratings yet
- Create A Concept Map of BiomoleculesDocument1 pageCreate A Concept Map of BiomoleculesMarivic Bernardo GalvezNo ratings yet
- DR Linda Molecular BiosDocument73 pagesDR Linda Molecular BiosValency BathoNo ratings yet