Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The DC Power Supply Converts The Standard 120 V
Uploaded by
Ebrahem Shahein0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesOriginal Title
The dc power supply converts the standard 120 V
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views6 pagesThe DC Power Supply Converts The Standard 120 V
Uploaded by
Ebrahem ShaheinCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
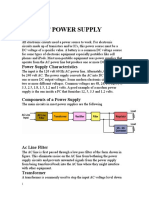
The dc power supply converts the standard 120 V, 60 Hz ac
voltage available at wall outlets into a constant dc voltage.
The dc power supply is one of the most common circuits
you will find, so it is important to understand how it
works.
The voltage produced is used to power all types of
electronic circuits including consumer electronics
(televisions, DVDs, etc.), computers, industrial
con trollers, and most laboratory instrumentation systems
and equipment.
The dc voltage level required depends on the application,
but most applications require relatively low voltages.
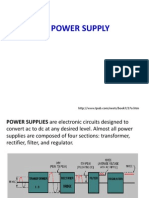
I. Transformer:
changes ac voltages based on the turns ratio between the
primary and sec ondary. If the secondary has more turns than
the primary, the output voltage across the secondary will be
higher and the current will be smaller. If the secondary has
fewer turns than the primary, the output voltage across the
secondary will be lower and the current will be higher.
II. The rectifier :
converts the ac input voltage to a pulsating dc voltage, called a
half-wave rectified voltage, The rectifier can be either a half-
wave rectifier or a full-wave rectifier .A full-wave rectifier
allows unidirectional (one-way) current through the load during
the entire of the input cycle, whereas a half-wave rectifier
allows current through the load only during one-half of the
cycle. The result of full-wave rectification is an output voltage
with a frequency twice the input frequency and that pulsates
every half-cycle of the input
III. The filter:
eliminates the fluctuations in the rectified voltage and
produces a relatively smooth dc voltage
The filter is a capacitor connected from the rectifier output to
ground. It is used to eliminate the fluctuations in the output
voltage of half wave or full wave rectifier and produces a
constant-level DC voltage but with some ripples
In most power supply applications, the standard 60 Hz ac
power line voltage must be converted to an approximately
constant dc voltage. The 60 Hz pulsating dc output of a half-
wave rectifier or the 120 Hz pulsating output of a full-wave
rectifier must be filtered to reduce the large voltage variations.
the filtering concept showing a nearly smooth dc output
voltage from the filter. The small amount of fluctuation in the
filter output voltage is called ripple.
IV. The regulator:
Is a circuit that maintains a constant dc voltage for variations in
the input line voltage or in the load . Regulators vary from a
single semiconductor device to more complex integrated
circuits.
A voltage regulator is connected to the output of a filtered
rectifier and maintains a constant output voltage (or current)
despite changes in the input, the load current, or the
temperature. The capacitor-input filter reduces the input ripple
to the regulator to an acceptable level. The combination of a
large capacitor and a voltage regulator helps produce an
excellent power supply.
Most regulators are integrated circuits and have three
terminals—an input terminal, an output terminal, and a
reference (or adjust) terminal. The input to the regulator is first
filtered with a capacitor to reduce the ripple to The regulator
reduces the ripple to a negligible amount. In addition, most
regulators have an internal voltage reference, short circuit
protection, and thermal shutdown circuitry. They are available
in a variety of voltages, including positive and negative outputs,
and can be designed for variable outputs with a minimum of
external components. Typically, voltage regulators can furnish a
constant output of one or more amps of current with high
ripple rejection. Three-terminal regulators designed for fixed
output voltages require only external capacitors to complete
the regulation portion of the power supply, Filtering is
accomplished by a large-value capacitor between the input
voltage and ground. An output capacitor (typically ) is
connected from the output to ground to improve the transient
response. 0.1 mF t
V. The load:
Is a circuit or device connected to the output of the power
supply and operates from the power supply voltage and
current.
Components:
1. AC Source
2. Simple transformer
3. Bridge rectifier ( 4 Diodes )
4. 3 capacitors with different values
5. Voltage regulator
6. Resistance
7. Led
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Essential Components of DC Power SuppliesDocument4 pagesEssential Components of DC Power SuppliesSyed Hassan Abbas RizviNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- DC Power SupplyDocument8 pagesDC Power Supplyweaam raedNo ratings yet
- DC Power SupplyDocument8 pagesDC Power Supplyweaam raedNo ratings yet
- Swtched - Mode Power SupplyDocument13 pagesSwtched - Mode Power Supplynitinhanda100% (1)
- Experiment 3 Eng NaderDocument7 pagesExperiment 3 Eng Naderياسر العويطيNo ratings yet
- Power Supply and Zener Diode (Canvas)Document95 pagesPower Supply and Zener Diode (Canvas)Aaron Jacob ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document18 pagesUnit 4H. ShekharNo ratings yet
- DC Power SupplyDocument4 pagesDC Power SupplySohaib Ahmed100% (1)
- List of ComponentsDocument13 pagesList of ComponentsBenita AgbagwaraNo ratings yet
- Uday Edition 03Document12 pagesUday Edition 03Gulani Sai TejANo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply CircuitDocument7 pagesDC Power Supply CircuitEhtasham Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Bridge Rectifier Circuit Over CenterDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Bridge Rectifier Circuit Over CenterLemuel C. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Reduction of AC MainsDocument3 pagesReduction of AC MainsFaizan NaeemNo ratings yet
- Regulated DC Power SupplyDocument15 pagesRegulated DC Power SupplynalumilanimeNo ratings yet
- DC Regulated Power Supply ExplainedDocument14 pagesDC Regulated Power Supply ExplainedMegha Projects100% (2)
- 5v DC SupplyDocument19 pages5v DC SupplyDev Agarwal100% (1)
- Circuit Diagram and Description of Power Supply UnitDocument14 pagesCircuit Diagram and Description of Power Supply Unitreddyece402No ratings yet
- Filtered Power SupplyDocument39 pagesFiltered Power SupplyAngelo Mark Ordoña Porgatorio0% (1)
- Introduction To Switched-Mode Power Supply (SMPS) CircuitsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Switched-Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Circuits9chand3100% (1)
- Regulated DC Power Supply GuideDocument15 pagesRegulated DC Power Supply GuideMuhammad Omer IshfaqNo ratings yet
- 2010 Me 105Document11 pages2010 Me 105Omer NadeemNo ratings yet
- Rectifier: The Basic DC Power SupplyDocument1 pageRectifier: The Basic DC Power SupplyRina AbayNo ratings yet
- How An Smps Works: Rectifier StageDocument7 pagesHow An Smps Works: Rectifier StageImran AshrafNo ratings yet
- How An SMPS WorksDocument7 pagesHow An SMPS WorksĐorđe PopovićNo ratings yet
- Line 6 Flextone 2 HD Service ManualDocument86 pagesLine 6 Flextone 2 HD Service Manualrnrmf2082No ratings yet
- ANE 620S Course Notes 2015Document177 pagesANE 620S Course Notes 2015TimothyShapamNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 Buck ConverterDocument3 pagesLab 2 Buck ConverterShah VinodNo ratings yet
- DC Regulated Power SupplyDocument2 pagesDC Regulated Power Supplysean ballocanagNo ratings yet
- Early Radio Receivers, Called Crystal Radios, Used A "Cat's Whisker" of Fine Wire Pressing On A Crystal ofDocument4 pagesEarly Radio Receivers, Called Crystal Radios, Used A "Cat's Whisker" of Fine Wire Pressing On A Crystal ofPoonam bhavsarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: 18Cs206 Basic of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument21 pagesUnit 1: 18Cs206 Basic of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringAJAY SNo ratings yet
- HVDC StationDocument26 pagesHVDC StationmeraatNo ratings yet
- KMT#4Document5 pagesKMT#4RomanHerreraNo ratings yet
- Build a regulated power supply in 40 stepsDocument7 pagesBuild a regulated power supply in 40 stepsAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument4 pagesRectifierAngellicaNo ratings yet
- 3 Level InverterDocument63 pages3 Level InverterThirumal ValavanNo ratings yet
- A Power Supply UnitDocument11 pagesA Power Supply UnitShin Jae JiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics 1st ExamDocument34 pagesIndustrial Electronics 1st ExamJomar Bonje100% (1)
- HVAC Control Boards 01Document11 pagesHVAC Control Boards 01Osama AhmedNo ratings yet
- Half Wave and Full Wave RectifierDocument10 pagesHalf Wave and Full Wave RectifiersunilsathishNo ratings yet
- Summary 3-117 Till 3-120: FiltersDocument2 pagesSummary 3-117 Till 3-120: FiltersVandervock RomelusNo ratings yet
- A Technical Guide To Smps AdaptersDocument28 pagesA Technical Guide To Smps AdaptersHitesh MehtaNo ratings yet
- RectifierDocument11 pagesRectifierasislakhaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractDocument20 pagesEmergency Lighting Fluorescent Lamp: AbstractAakash SheelvantNo ratings yet
- Switch Mode Power Supply and Switching RegulatorsDocument10 pagesSwitch Mode Power Supply and Switching Regulatorsmarcoms75No ratings yet
- Components Required - : Block DiagramDocument8 pagesComponents Required - : Block DiagramJethro MolenoNo ratings yet
- AC to DC Power SupplyDocument12 pagesAC to DC Power SupplyMadhu Mathi ErNo ratings yet
- Regulated Power SupplyDocument6 pagesRegulated Power Supplypandadillipkumar26No ratings yet
- Switch Mode Power Supply and Switching RegulatorsDocument13 pagesSwitch Mode Power Supply and Switching Regulatorsyuj oNo ratings yet
- Cep Problem ElectricalDocument7 pagesCep Problem ElectricalZaid HassanNo ratings yet
- 5.LDR Based Highways Road Light Failed Intimation Using GSMDocument44 pages5.LDR Based Highways Road Light Failed Intimation Using GSMfotronichs velloreNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Components and System: Engr - Kashif IqbalDocument21 pagesSupplementary Components and System: Engr - Kashif IqbalHassan Bin QasimNo ratings yet
- Load Inverter Solar Panel: Chapter ThreeDocument13 pagesLoad Inverter Solar Panel: Chapter ThreeMakesh MäKzNo ratings yet
- Wi-Fi Home AutomationDocument23 pagesWi-Fi Home Automationchandru_8No ratings yet
- Signal Conditioning and Power SuppliesDocument10 pagesSignal Conditioning and Power SuppliesPrashant LochamNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Switched Mode Power Supply TopologiesDocument21 pagesAn Introduction to Switched Mode Power Supply Topologiesseahate100% (1)
- Lab Report 2 Phy547: Experiment 2: Zener Diode and Power SupplyDocument8 pagesLab Report 2 Phy547: Experiment 2: Zener Diode and Power SupplyAtikah IzzatiNo ratings yet
- Unit-I: 1. What Is An Inverter?Document12 pagesUnit-I: 1. What Is An Inverter?Gnanaseharan ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- How a 500-watt modified sine wave inverter worksDocument5 pagesHow a 500-watt modified sine wave inverter worksmongiagoldyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Problems: CW 3.4, 3.6, 3.7, 3.9, 3.24 HW 3.1, 3.3, 3.5 Now Let's Begins Solving Chapter 3 Classwork ProblemsDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Problems: CW 3.4, 3.6, 3.7, 3.9, 3.24 HW 3.1, 3.3, 3.5 Now Let's Begins Solving Chapter 3 Classwork ProblemsEbrahem ShaheinNo ratings yet
- CH 4 PHY 101Document14 pagesCH 4 PHY 101Ebrahem ShaheinNo ratings yet
- Answer ch4 MTHDocument13 pagesAnswer ch4 MTHEbrahem ShaheinNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Anatomy and Functions of the Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Circulation, and Regulation of Blood Pressure</TITLEDocument85 pagesCardiovascular System: Anatomy and Functions of the Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Circulation, and Regulation of Blood Pressure</TITLEEbrahem ShaheinNo ratings yet
- Assessing Environmental ImpactsDocument23 pagesAssessing Environmental ImpactsEbrahem ShaheinNo ratings yet
- Snc1d U2 Lesson 13 Reducing Electrical Energy ConsumptionDocument25 pagesSnc1d U2 Lesson 13 Reducing Electrical Energy ConsumptionnogmgmggmgNo ratings yet
- PhototransistorsDocument17 pagesPhototransistorskamran amjadNo ratings yet
- Water Saturation From Electric Logs TotalDocument12 pagesWater Saturation From Electric Logs TotalAlfredo SGNo ratings yet
- NDB CV - 16 YearsDocument5 pagesNDB CV - 16 YearsnileshNo ratings yet
- Trisil ProtectionDocument4 pagesTrisil ProtectionShashi Kumar GowdaNo ratings yet
- And8023 DDocument24 pagesAnd8023 Dcititorul53No ratings yet
- F01320en 02Document4 pagesF01320en 02Fahru ZainiNo ratings yet
- Veriflex Intercon 1.8-3kV Cable - 1Document2 pagesVeriflex Intercon 1.8-3kV Cable - 1anastasia abengoaNo ratings yet
- Inventobox InstructionsDocument3 pagesInventobox InstructionsAsep JamaludinNo ratings yet
- Features Description Cutout Details Ordering Information: Trip Circuit Supervision RelayDocument4 pagesFeatures Description Cutout Details Ordering Information: Trip Circuit Supervision RelayDeepak WaikarNo ratings yet
- HT33-TX Series Tower Online UPS: 10-40kVA (380V/400V/415V)Document1 pageHT33-TX Series Tower Online UPS: 10-40kVA (380V/400V/415V)dhaferNo ratings yet
- Celan GT SL enDocument7 pagesCelan GT SL enwosahe3570No ratings yet
- LC08-098-XXX: Technical Data Sheet Cable Assembly N Male / N MaleDocument2 pagesLC08-098-XXX: Technical Data Sheet Cable Assembly N Male / N MaleLão ChuNo ratings yet
- Manual GM1357Document2 pagesManual GM1357Maria DiamantopoulouNo ratings yet
- Electrical Instrumentation Lab ManualDocument35 pagesElectrical Instrumentation Lab ManualAditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- SICAM Q100 Specs PDFDocument3 pagesSICAM Q100 Specs PDFhassan karimiNo ratings yet
- Off Grid With Battery Design Simulation Tool Type2Document8 pagesOff Grid With Battery Design Simulation Tool Type2Balamurugan ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Transformers definedDocument11 pagesTransformers definedAbdul BasitNo ratings yet
- FM TransmitterDocument5 pagesFM TransmitterLiaqat Hussain BhattiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23Document224 pagesChapter 23Vasco SantosNo ratings yet
- Permanent Magnet Brushless Motor Field Oriented Control with Dither Signal InjectionDocument4 pagesPermanent Magnet Brushless Motor Field Oriented Control with Dither Signal InjectionTony starkNo ratings yet
- Ieee Tie - 2Document12 pagesIeee Tie - 2kdm007No ratings yet
- 13 Ec 558Document1 page13 Ec 558Siva KumarNo ratings yet
- Autoplant Irrigation SystemDocument33 pagesAutoplant Irrigation SystemShubam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Elektronik Lab ReportDocument12 pagesElektronik Lab ReportoliverNo ratings yet
- OMS 1600 Boosters-Amps Rev-A 09jan07Document23 pagesOMS 1600 Boosters-Amps Rev-A 09jan07Marcelo MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Samson s2000 ManualDocument12 pagesSamson s2000 ManualpeepoleNo ratings yet
- Static Var CompensatorDocument55 pagesStatic Var CompensatorSuresh Nagulavancha50% (2)
- Mansoor HussainDocument3 pagesMansoor Hussaingmats123No ratings yet
- SOT-363 Plastic-Encapsulate Transistors: Umx1NDocument3 pagesSOT-363 Plastic-Encapsulate Transistors: Umx1Nramon elias hicher leonNo ratings yet