Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mixtures
Uploaded by
Maria BachilleratoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mixtures
Uploaded by
Maria BachilleratoCopyright:
Available Formats
W
''f;jiá
Wfú. The air in a room is a large homogeneous mass of A soft drink is composed of the following:
gas. Answer the questions in your exercise book. (100/o) | carbon dioxide (14.9o/o)
I sugar
o) Where does the oxygen we breathe in come from? I water (450lo) I preservatives and
bJ Where does the carbon dioxide that we breathe out I orange juice (300/o) colourings
(0'010/o)
9o?
a,l Which one of the above is the solvent and which are
c) Where can we find nitrogen gas and oxygen gas?
the solutes?
d) What do we mean when we say that the air is'too b) What state is each of them in?
humid'?
e) ls air composed of one gas or of several gases? V;tffi Lookatthe san o
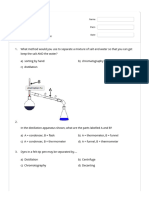
illustration.
filter paper
W.,%" Answer the questions with a partner. Then discuss a) Which separation funnel
your answers with the rest of your class. technique for
a) ls the most lmportant characteristic of a pure mixtures is shown
substance the fact that it looks homogeneous? here?
ó) lf we see different coloured grains in wood, does b) When is this war
that mean that it is a mixture? Why? technique usedT
c) Why is it necessary to analyse matter before 'f*sffi
W Put the steps of distillation in order. Listen and
determining its composition? check,
d) What technique is used to get salt from salt mines? a) Liquid boils, and its vapour rises out of the flask and
What physical change is it based on? into a condenser.
T.ffi,, Name three materials found in the home that look ó) The distillate is collected in a beaker.
homogeneous. Are they mixtures or pure substances? c) The vapour cools down and condenses inside the
How do you know? condenser.
Put some sugar into a glass of water. Then, stir the
'új...............!#, dl The solution is then heated up.
water well with a spoon. e) A solution is put into a flask.
,fu.ffi
W Listen and say which separation technique the
speaker is describing.
a) distillation / sifting
ó) magnetic attract¡on / sifting
cJ crystallisation / filtration
d,l crystallisation / filtration
e) decanting / distillation
fJ magnetic attraction / distillation
'gf:& You distil a solution containing the following
W
liquids: water, ethanol, vinegar and acetone. In what
order are the various distillates collected? Listen and
aJ ls the final mixture homogeneous or
check. Use the information in the table to answer the
heterogeneous? question.
b) How do you know the sugar is still in the water even
though you can't see it?
rl;ffi ldentify the solutes in the following solutions (all of Substance Temperature ("C)
them have water as solvent): Water 100
aJ mineral water Ethanol 78.5
Vinegar 118
ó) milky coffee
Acetone 56.5
cJ shampoo
,\\irr¡'e: ard pr-e rrbr,r..", ffi
ffi
fl Look at the graphs showing the changes of state of b) Oo solutions and mixtures have fixed melting and
distilled water and of the pure substance X. boiling points? And pure substances?
a) At what temperature does ice melt? And substance X? c) How can we distinguish between a pure substance
b) Do water and substance X boil at the same and a homogeneous mixture?
temoerature?
{ IE With a partner decide if the sentences are true or
c) During the changes of state, does either ofthese false.
substances change into a different substance? a) Hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water.
d) ls it correct to say that substance X is not distilled bJ Water is a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen.
water? Why?
c) A compound is not a pure substance.
distilled water
d) Elements are pure substances.
temperature ("C)
ffi Hydrogen and oxygen combine in the following
ratio to form water:
grams of oxygen / grams of hydrogen : 8
How many grams of oxygen combine with 2 g of
hydrogen?
IEI A solid substance is heated for 10 minutes.The
different temperatures are shown here:
Time(min) 0 'l 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Temperature ('C) 25 30 40 40 40 55 75 80 80 80 90
a) Use the data to draw a graph showing the changes
of state of this substance.
ó) What is its melting point?
c) What is its boiling point?
d) lndicate at which point there is a mixture of solid
and liquid.
E A Read and listen to the text. Then answer the
e) Indicate at which point there is a mixture of liquid
questions with your partner.
and gas.
lce melts at 0'C and pure liquid water boils at 100 "C.
However, water takes longer to boil if it contains salt. Salt *W é Put the words in order to make questions. Listen
increases the boiling point of water. As we add more and and check. Ask and answer the questions with a partner.
more salt, the boiling point increases and the melt¡ng d) the characteristic properties / What / of / a pure
point decreases. substance /are/?
ó) between / is / What / physical change and chemical
,í-? change / the difference / ?
c) an element / is / between / and a compound / the
difference /What / ?
d) water /Why / a pure substance / is / ?
e,l are / and helium / used / hydrogen / What / for / ?
tII Study the Key words in this unit. Then take turns to
test your partner in one of the following ways:
1. A says the word in English. B says the word in
Spanish.
a) What happens to the boiling point of water when a 2. A says the word in English. B gives a definition in
solute is dissolved in it? And to its freezing point? English or in Spanish.
Mixtures and pure substances fll
You might also like
- CSEC Integrated Science June 2013 P1Document11 pagesCSEC Integrated Science June 2013 P1Tia GreenNo ratings yet
- Orifice and Jet FlowDocument8 pagesOrifice and Jet FlowEngr Arafat Qubati75% (4)
- Sullair 185 CFM Compressor Operation & Maintenance & Parts ListDocument131 pagesSullair 185 CFM Compressor Operation & Maintenance & Parts Listjheinerperez93% (15)
- User Manual: PVL Cutting TorchDocument18 pagesUser Manual: PVL Cutting TorchWriteNo ratings yet
- Tank Farm OperationsDocument13 pagesTank Farm OperationsRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Minevent 2006 PDFDocument12 pagesMinevent 2006 PDFJosé Manuel Berrospi CruzNo ratings yet
- Science Annual 21Document9 pagesScience Annual 21VIMLA BNo ratings yet
- Science Paper 7 - SolvedDocument10 pagesScience Paper 7 - SolvedRavi KumarNo ratings yet
- AS Biology Paper 1Document16 pagesAS Biology Paper 1wegdan100% (2)
- Assignment 01 - FullDocument12 pagesAssignment 01 - FullDivya PritamNo ratings yet
- Science RT 4Document9 pagesScience RT 4Neha GobinathNo ratings yet
- 2020 2021 Class IX Chemistry Part 3 AWDocument8 pages2020 2021 Class IX Chemistry Part 3 AWShiv GorantiwarNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice. Read Each Question Carefully and Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The SpaceDocument5 pagesMultiple Choice. Read Each Question Carefully and Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The SpaceLouie Jane EleccionNo ratings yet
- S4 Questions112Document16 pagesS4 Questions112munyanezaolivier422No ratings yet
- Yishun Town Secondary School: End of Year Examination 2009 Secondary 1 Express Lower Secondary ScienceDocument23 pagesYishun Town Secondary School: End of Year Examination 2009 Secondary 1 Express Lower Secondary ScienceQuinella TuitionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 62 Structured QuestionsDocument23 pagesChapter 62 Structured QuestionsytNo ratings yet
- Chemistry1 F4 2020Document5 pagesChemistry1 F4 2020Yusra . sNo ratings yet
- New Chemistry Pamphlet Volume 1Document17 pagesNew Chemistry Pamphlet Volume 1AstoneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15-16 Test Review AnswersDocument7 pagesChapter 15-16 Test Review AnswersBryce CireNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Examination 2017-2018Document5 pagesFirst Quarter Examination 2017-2018Erwin RelucioNo ratings yet
- Jescspss11 PDFDocument12 pagesJescspss11 PDFVarun DubeyNo ratings yet
- USO Sample Papers For Class 8Document5 pagesUSO Sample Papers For Class 8Fikri DwiNo ratings yet
- 2 Is-Matter-Around-Us-Pure-2Document7 pages2 Is-Matter-Around-Us-Pure-2sciencee2009No ratings yet
- S3 Level 2 Assessment 1 Term 2 2009: Section A: MCQ (1 Mark Each)Document5 pagesS3 Level 2 Assessment 1 Term 2 2009: Section A: MCQ (1 Mark Each)Zna101No ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Acid Base Titration - in Lab Evaluation - Print - QuizizzDocument4 pagesExperiment 2 - Acid Base Titration - in Lab Evaluation - Print - Quizizzaishu25No ratings yet
- Matter WorksheetDocument4 pagesMatter WorksheetShikha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper-4 - Science Science Time: 3Hrs Max - Marks: 80 InstructionsDocument9 pagesSample Question Paper-4 - Science Science Time: 3Hrs Max - Marks: 80 Instructionskan PadmasreeNo ratings yet
- Fish-Kill Self Directed LabDocument10 pagesFish-Kill Self Directed Labapi-253772243No ratings yet
- Chemistry AssignmentDocument12 pagesChemistry AssignmentE.LOKESH NAIKNo ratings yet
- Sample PaperDocument12 pagesSample PaperKashika KocharNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Secondary Checkpoint - Science (1113) October 2016 Paper 1Document16 pagesCambridge Secondary Checkpoint - Science (1113) October 2016 Paper 1Chinmay LimayeNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument5 pagesIs Matter Around Us PureLazyBrain /No ratings yet
- CSSC Science QP Set 2 1Document8 pagesCSSC Science QP Set 2 1tivokaf268No ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us Pure: 1. Ncert Intext QuestionsDocument11 pagesIs Matter Around Us Pure: 1. Ncert Intext QuestionsKumar AbhishantNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 1 2 3 4 Revision Questions and AnswersDocument88 pagesChemistry Form 1 2 3 4 Revision Questions and AnswersOdero BravinNo ratings yet
- Separation Techniques - QuizizzDocument8 pagesSeparation Techniques - QuizizzMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 End Assessment TestDocument3 pagesChapter 3 End Assessment TestEden AceNo ratings yet
- P6 Science CA1 2017 Nanyang Exam PapersDocument47 pagesP6 Science CA1 2017 Nanyang Exam PapersKui LiuNo ratings yet
- Alston Worksheet Solid, Liquid, GasDocument9 pagesAlston Worksheet Solid, Liquid, GasHazron Anderson Pandiangan100% (3)
- PRE-MID TERM EXAM (2022 - 23) Subject: Science Class: Ix Time: 1.30 Hour M.M - 40Document3 pagesPRE-MID TERM EXAM (2022 - 23) Subject: Science Class: Ix Time: 1.30 Hour M.M - 40VatsalyaNo ratings yet
- Monthly Test 1 Term 1 Chemistry Grade 9Document4 pagesMonthly Test 1 Term 1 Chemistry Grade 9Ria MandasariNo ratings yet
- Chem Test Chap 4Document1 pageChem Test Chap 4Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- Carb & Compound &light Answer KeyDocument15 pagesCarb & Compound &light Answer KeyHarshit BajajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - 2Document5 pagesChapter 1 - 2Sureshkumar DevanNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Ismatterarounduspure 01Document6 pages09 Science Ismatterarounduspure 01sureshabcdNo ratings yet
- 5ad9ad59e4b0330dfab77595 PDFDocument18 pages5ad9ad59e4b0330dfab77595 PDFMehtab AnsariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 15 and 16Document5 pagesChemistry Chapter 15 and 16Zohaib AsgharNo ratings yet
- 7TH CPP Set 2Document9 pages7TH CPP Set 2Swati AshtakeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1 Nine Weeks Review 2020 Use Loose-Leaf Paper To Write Out Answer ResponsesDocument2 pagesChemistry 1 Nine Weeks Review 2020 Use Loose-Leaf Paper To Write Out Answer ResponsesAtiah GillamNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 2 - Is Matter Around Us Pure Important Questions 2023-24Document13 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 2 - Is Matter Around Us Pure Important Questions 2023-24IX17-41 Suvayu ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Study Questions P. 5Document31 pagesStudy Questions P. 5Kazi Farhan MahiNo ratings yet
- Tional: EdulabzDocument4 pagesTional: Edulabzbhaskar51178No ratings yet
- Day 3 SSC 7 RemedialDocument4 pagesDay 3 SSC 7 RemedialRhodeliza TiotangcoNo ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 25Document11 pagesCbjescpu 25bprkupraveenNo ratings yet
- Science Solved Paper-23Document39 pagesScience Solved Paper-23StudyNo ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures: The Main Question Is: How Will Separate Mixtures Into Their Components?Document4 pagesSeparating Mixtures: The Main Question Is: How Will Separate Mixtures Into Their Components?Simovic AnastasijaNo ratings yet
- 8th Science PP IDocument2 pages8th Science PP IbharathNo ratings yet
- Scih103 QPDocument8 pagesScih103 QPVarsha.V.NairNo ratings yet
- CH 1 PDFDocument12 pagesCH 1 PDFkrishnaNo ratings yet
- PreBoard2 Class10 ScienceDocument3 pagesPreBoard2 Class10 Sciencesusupotty26No ratings yet
- Chem Class 11th & 12th QB and FS PDFDocument742 pagesChem Class 11th & 12th QB and FS PDFAvinash MoreNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemNo ratings yet
- BSABE2 - Blasquez - Lab Report 2Document7 pagesBSABE2 - Blasquez - Lab Report 2Lorenzo Niño BlasquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-Fluid Flow in The Reservoir PDFDocument36 pagesChapter 9-Fluid Flow in The Reservoir PDFMudassir KhanNo ratings yet
- Air Movements: By:Group3 7 - L UnaDocument10 pagesAir Movements: By:Group3 7 - L UnaLean Amara VillarNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger - ThesisDocument120 pagesHeat Exchanger - ThesisZoempek CavaleraNo ratings yet
- Cycloneseparator 1Document15 pagesCycloneseparator 1Chandra Sekar RNo ratings yet
- Exergy Analysis of Thermodynamic CyclesDocument17 pagesExergy Analysis of Thermodynamic CyclesHARSSH MATHHURNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 BoilerDocument66 pagesChapter 4 BoilerAnonymous YSdtimxAbNo ratings yet
- 795 Series Double-Diaphragm Pressure-Balanced Actuator (Obsolete Product)Document17 pages795 Series Double-Diaphragm Pressure-Balanced Actuator (Obsolete Product)gani prayudaNo ratings yet
- Diamec U6 Spare PartDocument3 pagesDiamec U6 Spare PartJairo Boechat JuniorNo ratings yet
- HD23639 5 As P6abDocument1 pageHD23639 5 As P6abWalter SoriaNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Symbols PDFDocument5 pagesVacuum Symbols PDFChris RobNo ratings yet
- V.T Report SailDocument32 pagesV.T Report SailAshish Jha100% (1)
- Calculation of Orifice DiameterDocument4 pagesCalculation of Orifice DiameterNaseer HydenNo ratings yet
- Artificial Lift: Focus On Hydraulic Submersible Pumps: Abhishek Bhatia and Scott A.L. Mcallister, Clydeunion PumpsDocument3 pagesArtificial Lift: Focus On Hydraulic Submersible Pumps: Abhishek Bhatia and Scott A.L. Mcallister, Clydeunion PumpsCarlita SuntaxiNo ratings yet
- A005Document4 pagesA005majid fardniaNo ratings yet
- Hydrovane ControllerDocument5 pagesHydrovane ControllerMark CarterNo ratings yet
- PR LC Lfa e PDFDocument68 pagesPR LC Lfa e PDFmanjappahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics Sheet 1: TemperatureDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics Sheet 1: Temperaturemohammed sallemNo ratings yet
- Menabam Pohon Kamboja HitamDocument1 pageMenabam Pohon Kamboja HitamWisnu BharataNo ratings yet
- Project Department Kuwait National Petroleum Company: Daily Welding Inspection ReportDocument1 pageProject Department Kuwait National Petroleum Company: Daily Welding Inspection ReportMuthazhagan SaravananNo ratings yet
- Validation NitrogenDocument4 pagesValidation NitrogenRohitsahuvapiNo ratings yet
- 6-Absorption Stripping Pt1Document18 pages6-Absorption Stripping Pt1Naufal FasaNo ratings yet
- CABINTOYDocument6 pagesCABINTOYMatt Kristopher DiazNo ratings yet
- Pages From WARMAN PUMP-maintenance-manual 3Document1 pagePages From WARMAN PUMP-maintenance-manual 3mohadeseroustaNo ratings yet
- Viscous Flow in DuctsDocument13 pagesViscous Flow in DuctsLászló CzétányNo ratings yet