Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2
2
Uploaded by
J JohnsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2
2
Uploaded by
J JohnsCopyright:
Available Formats
Working memory, which is the ability to hold and manipulate information in mind, is essential for
various cognitive tasks, such as mental arithmetic or following multi-step instructions. The frontal
lobes, particularly the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, play a critical role in working memory.
Attentional processes are also regulated by the frontal lobes. They enable individuals to selectively
focus on relevant information while filtering out distractions. The anterior cingulate cortex, a part of
the frontal lobes, is involved in monitoring and adjusting attentional control.
Cognitive flexibility, another important function of the frontal lobes, allows individuals to switch
between tasks, adapt to changing situations, and think creatively. This flexibility relies on the
prefrontal cortex's ability to reconfigure neural networks and shift attentional resources.
Inhibition, or the ability to inhibit impulsive responses and resist distractions, is crucial for self-
control and decision-making. The frontal lobes, particularly the ventrolateral prefrontal cortex, play a
significant role in inhibitory control, helping individuals regulate their behavior and make thoughtful
choices.
The frontal lobes are also involved in emotional regulation and social behavior. The ventromedial
prefrontal cortex is associated with processing emotions and integrating emotional information into
decision-making. It helps individuals evaluate risks and rewards and make judgments based on
emotional context. The frontal lobes also contribute to social cognition, including understanding
others' intentions, empathy, and moral reasoning.
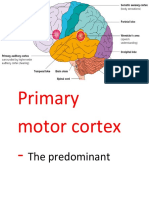
Motor control is yet another function associated with the frontal lobes. The primary motor cortex,
located in the posterior part of the frontal lobes, is responsible for initiating and executing voluntary
movements. The prefrontal cortex plays a role in planning and coordinating complex movements and
integrating sensory feedback.
In summary, the frontal lobes are crucial for a wide range of cognitive processes and behaviors. They
are involved in executive functions such as decision-making, problem-solving, planning, reasoning,
and social behavior. Additionally, the frontal lobes play a role in emotional regulation, attention,
working memory, cognitive flexibility, inhibition, and motor control. Impairments in the frontal lobes,
such as through brain injury or neurological disorders, can lead to deficits in these cognitive and
behavioral functions.
You might also like
- Olly Richards - Alex Rawlings - Short Stories in German For Beginners-John Murray Press (2018)Document224 pagesOlly Richards - Alex Rawlings - Short Stories in German For Beginners-John Murray Press (2018)Rameez Malik100% (4)
- PSYP 610 Practical 2 ReportDocument6 pagesPSYP 610 Practical 2 Reportshahbaz shahid67% (3)
- Test Bank For Understanding Motivation and Emotion 7th Edition Johnmarshall Reeve DownloadDocument13 pagesTest Bank For Understanding Motivation and Emotion 7th Edition Johnmarshall Reeve Downloadjacquelineparkprtfoxgcqd100% (22)
- 3Document1 page3J JohnsNo ratings yet
- Gale Researcher Guide for: The Frontal Lobe and Executive FunctionsFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: The Frontal Lobe and Executive FunctionsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Unit 4Document53 pagesUnit 4saima mubarakNo ratings yet
- Writen - Work - Albino GutierrezDocument3 pagesWriten - Work - Albino GutierrezCarlos AlbinoNo ratings yet
- 5Document2 pages5J JohnsNo ratings yet
- Neuroplasticity: How to Boost Neurogenesis and Rewire Your Brain (Active Pain Management That Helps You Get Back to the Life You Love)From EverandNeuroplasticity: How to Boost Neurogenesis and Rewire Your Brain (Active Pain Management That Helps You Get Back to the Life You Love)No ratings yet
- 6Document2 pages6rockNo ratings yet
- Brain Enhancement. How to Optimize Your Brain for a Fuller Life.From EverandBrain Enhancement. How to Optimize Your Brain for a Fuller Life.No ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument9 pagesResearch Paperapi-282381441No ratings yet
- Assignment NeuroDocument2 pagesAssignment Neuroyashika durejaNo ratings yet
- Brain ActivityDocument31 pagesBrain ActivityaseshNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Rough NotesDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Rough NotescynthiasenNo ratings yet
- Alternative Ways For Treating The Characteristics of Autism WithoDocument10 pagesAlternative Ways For Treating The Characteristics of Autism WithoAlicia Gabriela Mercado JiménezNo ratings yet
- The Power Of Emotional Intelligence: How To Build A Powerful Emotional Intelligence And Change Your Life With The Best TechniquesFrom EverandThe Power Of Emotional Intelligence: How To Build A Powerful Emotional Intelligence And Change Your Life With The Best TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Active Mind Maintenance: Tools and Tips for Improving Cognitive Thinking: Functional Health SeriesFrom EverandActive Mind Maintenance: Tools and Tips for Improving Cognitive Thinking: Functional Health SeriesNo ratings yet
- Anuvinda P1 TADocument8 pagesAnuvinda P1 TAAnuvinda ManiNo ratings yet
- Temporal LobesDocument5 pagesTemporal LobesGreyed OutNo ratings yet
- Information Processing TheoryDocument6 pagesInformation Processing TheoryJos Van ElzNo ratings yet
- 4 Lobes FunctionDocument4 pages4 Lobes FunctionAcharya PradeepNo ratings yet
- Pocket Handbook For The Brain: Technology To Improve Your Functioning and Emotional Well-BeingDocument22 pagesPocket Handbook For The Brain: Technology To Improve Your Functioning and Emotional Well-BeingArmando GaonaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Psych Module 7Document14 pagesMidterm Psych Module 7Ladybelle GototosNo ratings yet
- Frontal Lobe Plays in Daily Functions Include: Speech and Language Production: Broca'sDocument1 pageFrontal Lobe Plays in Daily Functions Include: Speech and Language Production: Broca'sMarygold SalesNo ratings yet
- Frontal Lobe and Temporal Lobe Functions and SyndromesDocument48 pagesFrontal Lobe and Temporal Lobe Functions and SyndromesShreya Sharma100% (1)
- Adolescent Report Chapter 5Document31 pagesAdolescent Report Chapter 5mark porralNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Correlations of MemoryDocument3 pagesAnatomical Correlations of Memory46tzkswbj8No ratings yet
- Branches of BiopsychologyDocument4 pagesBranches of BiopsychologyPoulomiNo ratings yet
- Detailed Brain FunctionsDocument14 pagesDetailed Brain FunctionsJoeNo ratings yet
- Executive FunctionsDocument9 pagesExecutive FunctionsnieotyagiNo ratings yet
- Semester Reflection Paper-1Document7 pagesSemester Reflection Paper-1Nasir Ali RiazNo ratings yet
- Uecker 2014Document8 pagesUecker 2014yalocim666No ratings yet
- G11 Hope - Per Dev 0402Document2 pagesG11 Hope - Per Dev 0402Roy De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Brain and MindDocument5 pagesBrain and MindMubashir AminNo ratings yet
- Daily QuestionDocument1 pageDaily QuestionkeiramaryhillNo ratings yet
- Fungtion BrainDocument15 pagesFungtion BrainNur NatasyaNo ratings yet
- Behavior As InputDocument1 pageBehavior As InputsuparswaNo ratings yet
- Executive Functions - WikipediaDocument19 pagesExecutive Functions - WikipediafrickinNo ratings yet
- 1 ArticleDocument3 pages1 Articleapi-277929152No ratings yet
- From Very Early On in UteroDocument1 pageFrom Very Early On in Uteromohitnet1327No ratings yet
- Introduction To Cognitive PsychologyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Cognitive PsychologyNI?A MARIE BONTOGNo ratings yet
- 15 Areas of The Brain and Their FunctionsDocument6 pages15 Areas of The Brain and Their Functionslaurahermoza1995No ratings yet
- Brain Health - How to Have a Healthy Memory and a Healthy BrainFrom EverandBrain Health - How to Have a Healthy Memory and a Healthy BrainNo ratings yet
- Functional Areas of BrainDocument8 pagesFunctional Areas of BrainirfanzukriNo ratings yet
- Intelligence and BehaviourDocument1 pageIntelligence and BehaviourDuvNo ratings yet
- Child PsychopathologyDocument6 pagesChild PsychopathologyTanu GowdaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 4 - Brain PDFDocument17 pagesGROUP 4 - Brain PDFJoshua VillarNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 Neural Basis of EmotionsDocument14 pagesModule - 4 Neural Basis of EmotionsErfana ThasnemNo ratings yet
- The Role of Emotion and Reflection in Student Achievement: (The Frontal Lobe/ Amygdala Connection)From EverandThe Role of Emotion and Reflection in Student Achievement: (The Frontal Lobe/ Amygdala Connection)No ratings yet
- Vlog ScriptDocument2 pagesVlog ScriptdelumennikkaNo ratings yet
- Copy CNSDocument2 pagesCopy CNSJesica MarieNo ratings yet
- Brain Overhaul: Upgrading Your Mind for Accelerated Learning and SuccessFrom EverandBrain Overhaul: Upgrading Your Mind for Accelerated Learning and SuccessNo ratings yet
- Sts Cheat Sheet of The BrainDocument28 pagesSts Cheat Sheet of The BrainAdrian GtNo ratings yet
- Human Memory 2024Document33 pagesHuman Memory 2024ezaat.shalbyNo ratings yet
- Psychology PaperDocument15 pagesPsychology PaperTadesse LulitNo ratings yet
- 4.11 Motor SkillsDocument2 pages4.11 Motor Skills薇霍康No ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document6 pagesChapter 13Neus Sangrós VidalNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets - Perssonal DevelopmentDocument6 pagesLearning Activity Sheets - Perssonal DevelopmentLyncel FayeNo ratings yet
- BrainDocument29 pagesBrainRidawati LimpuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document2 pagesChapter 12Neus Sangrós VidalNo ratings yet
- How Important Knowing The Function of The BrainDocument1 pageHow Important Knowing The Function of The BrainAlrevia GunNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 ReadingDocument5 pagesUnit 5 ReadingDilan AdithyaNo ratings yet
- Beattie, G., & Ellis, A. (2017) - The Psychology of Language and Communication. London - RoutledgeDocument312 pagesBeattie, G., & Ellis, A. (2017) - The Psychology of Language and Communication. London - Routledgepaticex241No ratings yet
- Traditional and Modern Methods and Approaches of LanguageDocument100 pagesTraditional and Modern Methods and Approaches of LanguageIldi BeszeNo ratings yet
- CS8691 SyllabusDocument1 pageCS8691 SyllabusArise and ShineNo ratings yet
- How The Mind Comes Into Being: Introducing Cognitive Science From A Functional and Computational Perspective First Edition ButzDocument54 pagesHow The Mind Comes Into Being: Introducing Cognitive Science From A Functional and Computational Perspective First Edition Butzdavid.binger195100% (10)
- Artificial Intelligence To ConvertDocument12 pagesArtificial Intelligence To ConvertMaki ErkuNo ratings yet
- Kartikey QTCV PBLDocument10 pagesKartikey QTCV PBLAYUSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Language Learning TrackerDocument7 pagesLanguage Learning TrackerBruno FilettoNo ratings yet
- Application of Theories of Motivation and LearningDocument31 pagesApplication of Theories of Motivation and LearningAradhana kumariNo ratings yet
- The Science of MemoryDocument6 pagesThe Science of Memorymousti84No ratings yet
- RedundantDocument11 pagesRedundantSuraj RajNo ratings yet
- Students' Lack of Interest, Motivation in Learning, and Classroom Participation: How To Motivate ThemDocument11 pagesStudents' Lack of Interest, Motivation in Learning, and Classroom Participation: How To Motivate ThemPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Human vsArtificialIntelligence - FrontiersinAI 04 622364Document14 pagesHuman vsArtificialIntelligence - FrontiersinAI 04 622364hreshviksewrajNo ratings yet
- OpenAI's Cornerstone in The Pursuit of AGIDocument4 pagesOpenAI's Cornerstone in The Pursuit of AGIzishankamalNo ratings yet
- TuTeach Surigao Cuñado 100 Items TQs No Answer KeysDocument16 pagesTuTeach Surigao Cuñado 100 Items TQs No Answer KeysReview MaterialsNo ratings yet
- T3 Worksheet 3Document6 pagesT3 Worksheet 3gonearly AliNo ratings yet
- History of Psychology Slide ShowDocument20 pagesHistory of Psychology Slide ShowJohn Alldrin Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Psychological Mechanism of The Speech ProcessDocument14 pagesPsychological Mechanism of The Speech ProcessMariia BilovodNo ratings yet
- Share Cognitive Notes Doc-1Document15 pagesShare Cognitive Notes Doc-1GinniNo ratings yet
- RSPMDocument21 pagesRSPMPriyanka KumariNo ratings yet
- Desinterstedness and Desire in Kant's AestheticsDocument13 pagesDesinterstedness and Desire in Kant's AestheticsVNo ratings yet
- Tema 1Document5 pagesTema 1y.lysyanskyy.lsgiNo ratings yet
- May 8 122023Document9 pagesMay 8 122023Jonah BolivarNo ratings yet
- Human Motor Control 2nd Edition Rosenbaum Test BankDocument5 pagesHuman Motor Control 2nd Edition Rosenbaum Test BankKyleFitzgeraldyckas100% (14)
- Adult Learning PriciplesDocument12 pagesAdult Learning PriciplesChiranjib BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Hanky Khoo - Coaching Culture HandoutDocument55 pagesHanky Khoo - Coaching Culture HandoutKennyNo ratings yet
- 180 Abstract and Spatial Reasoning Reviewer PART 1Document12 pages180 Abstract and Spatial Reasoning Reviewer PART 1Ma'am CharryNo ratings yet