Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anterior Pituitary
Uploaded by
VishalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anterior Pituitary
Uploaded by
VishalCopyright:
Available Formats
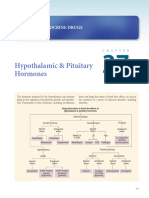
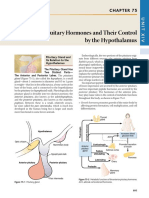
Endocrine Glands & Functions I
Pathophysiology Course
Pituitary Gland
Think of the pituitary as the testis of the brain, since they look like a set of
testicles & similarly release hormones that help the body do many functions.
Separated into 2 lobes:
- Anterior pituitary
The largest part of the pituitary responsible for synthesis & release of Anterior pituitary
most pituitary hormones
Posterior pituitary
- Posterior pituitary
Stores & secretes hormones produced by the hypothalamus right
above the pituitary
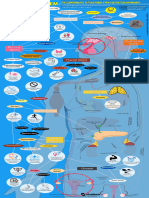
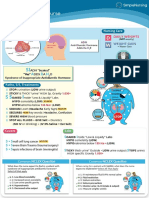
Anterior Pituitary
HORMONE EFFECT ON TARGET STIMULUS FOR RELEASE HORMONE EFFECT ON TARGET STIMULUS FOR RELEASE
ACTH: Stimulates adrenal cortex to Stress FSH: Men: sperm production GnRH
Adrenocorticotropic hormone release aldosterone & cortisol Follicle-stimulating hormone Women: ovarian follicles for eggs Gonadotropin-releasing
hormone
ACTH Aldosterone
FSH Hypothalamus
& cortisol. GnRH
Anterior
pituitary
FSH
LH: Men: testicular GnRH GH: Increased during anabolic metabolism, Normal growth
Luteinizing hormone Women: ovulation (release of the egg) Growth hormone cartilage growth & catabolism of fat. & development
Blood glucose & insulin effects
LH GnRH
Hypothalamus
GH Glycogen
Glucose
Anterior
pituitary
Lipids
LH
Amino acids
PRL: Stimulates production of milk Estrogen, pregnancy TSH: Simulates thyroid to release Thyroid needs
Prolactin in the breast & nursing Thyroid-stimulating hormone T3 & T4
PRL TSH
T3 & T4
TSH
Estrogen Pregnancy
T3 & T4
Nursing
Notes
Notes
You might also like
- 5-HTP - The Complete Guide - Exploring Its Therapeutic Potential In Depression, Anxiety, Insomnia, And Much More - Benefits, Side Effects, And Scientific Evidence For Human HealthFrom Everand5-HTP - The Complete Guide - Exploring Its Therapeutic Potential In Depression, Anxiety, Insomnia, And Much More - Benefits, Side Effects, And Scientific Evidence For Human HealthNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and The Pituitary LectureDocument51 pagesHypothalamus and The Pituitary LecturealkalicharanNo ratings yet
- PUBERTY: THE STAGES OF HUMAN DEVELOPMENTDocument62 pagesPUBERTY: THE STAGES OF HUMAN DEVELOPMENTvaluevaNo ratings yet
- Anterior Pituitary GlandDocument33 pagesAnterior Pituitary Glandmarianne.erdooNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary - Physiology and Pathophysiology: Eric J. Epstein, MD Disclosures: NoneDocument49 pagesHypothalamus and Pituitary - Physiology and Pathophysiology: Eric J. Epstein, MD Disclosures: NoneSøren KierkegaardNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Endocrine SystemDocument43 pagesDrugs Affecting The Endocrine SystemJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamic & Pituitary SHORTDocument9 pagesHypothalamic & Pituitary SHORTa.muhsinNo ratings yet
- Pcol Lec Book FinalsDocument61 pagesPcol Lec Book FinalsMarco Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument2 pagesControl and Coordinationcoolsk2580No ratings yet
- Amended Endocrine System SummerDocument41 pagesAmended Endocrine System SummerKatherineVoNo ratings yet
- HY EndocrineDocument61 pagesHY EndocrineKiranNo ratings yet
- HY EndocrineoeDocument62 pagesHY EndocrineoebrownsmilansNo ratings yet
- Care of The Patient With Complex Endocrine Disorders Endocrine SystemDocument11 pagesCare of The Patient With Complex Endocrine Disorders Endocrine SystemgoodgoNo ratings yet
- ENDOCRINOLOGYDocument8 pagesENDOCRINOLOGYshaairatogleNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Agents PharmacologyDocument64 pagesHormonal Agents Pharmacologynica velanoNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus Pituitary and Gonad AxisDocument6 pagesHypothalamus Pituitary and Gonad Axisalok nayakNo ratings yet
- Hormones Synthesized and Secreted by The Anterior Pituitary and Their EffectsDocument15 pagesHormones Synthesized and Secreted by The Anterior Pituitary and Their EffectsAaron James RuedasNo ratings yet
- PPT-Endocrine-SystemDocument56 pagesPPT-Endocrine-SystemNoreen BengoNo ratings yet
- 1st Lecture - Hypothalamus Pituitary Gonadal Axis - Reproductive PhysiologyDocument8 pages1st Lecture - Hypothalamus Pituitary Gonadal Axis - Reproductive PhysiologyBHUWAN BASKOTANo ratings yet
- Gland Stimulation of Hormones Produced Action Gland: Fsh/Lh-Gonads ActhDocument2 pagesGland Stimulation of Hormones Produced Action Gland: Fsh/Lh-Gonads ActhshirleyNo ratings yet
- MUST To KNOW in BacteriologyDocument3 pagesMUST To KNOW in BacteriologySam CatanghalNo ratings yet
- Presentation. Lec 11. Animal and Function 2Document42 pagesPresentation. Lec 11. Animal and Function 2diolechiNo ratings yet
- Gland: - Types of Glands:: EndocrinologyDocument45 pagesGland: - Types of Glands:: EndocrinologyCec DfNo ratings yet
- Endocrine WorksheetDocument7 pagesEndocrine WorksheetBrenda Zaragoza63% (8)
- Hipotalamus dan HipofisisDocument1 pageHipotalamus dan HipofisisLiana DaniellaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Infographic PosterDocument1 pageEndocrine System Infographic PosterVohn Archie EdjanNo ratings yet
- On The Posterior Surface of Thyroid GlandDocument2 pagesOn The Posterior Surface of Thyroid GlandRica Marie G. UyNo ratings yet
- Pituitary and Hypothalamus: The Body's Control Center: Lesson A2.2Document40 pagesPituitary and Hypothalamus: The Body's Control Center: Lesson A2.2Khobie PabilicoNo ratings yet
- Science 10 A2.2 Pituitary and Hypothalamus The Bodys Control CentersDocument40 pagesScience 10 A2.2 Pituitary and Hypothalamus The Bodys Control CentersKhobie PabilicoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Pituitary Gland (Endocrine SystemDocument37 pagesLesson Plan On Pituitary Gland (Endocrine SystemRosalyn Angcay Quintinita100% (1)
- Pituitary and Hypothalamic Hormones 2015Document19 pagesPituitary and Hypothalamic Hormones 2015High EducationNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology: Differences Between Nervous and Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesEndocrinology: Differences Between Nervous and Endocrine SystemRezaul RazibNo ratings yet
- Local Media2182658933713495317Document129 pagesLocal Media2182658933713495317JAYMAYMA ELGARIONo ratings yet
- Phys 6.1 and 6.2 Ant Pituitary GH and Post Pituitary NOTESDocument7 pagesPhys 6.1 and 6.2 Ant Pituitary GH and Post Pituitary NOTESsine summsun PradhanNo ratings yet
- Pineal Gland Regulates Sleep-Wake CycleDocument3 pagesPineal Gland Regulates Sleep-Wake CycleNurAdilaNo ratings yet
- PROTEIN AND POLYPEPTIDE HORMONES (Medicinal Chemistry) By: DR Asif HusainDocument44 pagesPROTEIN AND POLYPEPTIDE HORMONES (Medicinal Chemistry) By: DR Asif Husainjuliana leonNo ratings yet
- Diseases of the Pituitary GlandDocument8 pagesDiseases of the Pituitary GlandSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNo ratings yet
- Pathology Tests ExplainedDocument4 pagesPathology Tests ExplainedFabiola Fuentes RomeroNo ratings yet
- Hormones 2Document4 pagesHormones 2den mNo ratings yet
- Enfghdocrine Sfghstem Infogrhgfaphic Vihgfsual PohgfsterDocument1 pageEnfghdocrine Sfghstem Infogrhgfaphic Vihgfsual PohgfsterRăzvan RoșcaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemZennith AngawaNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Trans EndoDocument6 pagesPediatrics Trans EndoyayayanizaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandsDocument36 pagesEndocrine GlandsnasyitahnorzlanNo ratings yet
- Ciclo Mestrual - ApostilaDocument27 pagesCiclo Mestrual - ApostilaIsabella GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- 5M: Care of Clients With Hormonal Disturbances: Endocrine SystemDocument19 pages5M: Care of Clients With Hormonal Disturbances: Endocrine SystemEmmanuelle Soroño AmoresNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesEndocrine SystemYashwinieNo ratings yet
- A&P Lec NotesDocument2 pagesA&P Lec NotesShum ChanNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis: - Oleh: - I Dewa Made RuspawanDocument33 pagesHypothalamic-Pituitary Axis: - Oleh: - I Dewa Made RuspawanherlinaNo ratings yet
- Hormonii Axei Reproductive Andra CaragheorgheopolDocument70 pagesHormonii Axei Reproductive Andra CaragheorgheopolMadalina PavelNo ratings yet
- Unit IV. Endocrine SystemDocument44 pagesUnit IV. Endocrine Systemtajuddin shaikNo ratings yet
- Endocrinedisorders Study 20session 201 1Document39 pagesEndocrinedisorders Study 20session 201 1Yehuda Gelar PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Q3 S10 Week 1 Lecture or NotesDocument5 pagesQ3 S10 Week 1 Lecture or NotesJuben OdalNo ratings yet
- 9F. Endokrin 2Document53 pages9F. Endokrin 2Irfan Maulana AjiNo ratings yet
- ENDORCRINE SYSTEM - Review Anaphy NotesDocument10 pagesENDORCRINE SYSTEM - Review Anaphy NotesJae TyNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer LT1 - Q4Document2 pagesScience Reviewer LT1 - Q4Cara IsabelNo ratings yet
- Hypothalamus and HypophysisDocument32 pagesHypothalamus and HypophysisAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- Doc1 2797957740485071Document1 pageDoc1 2797957740485071Ramon W Muscat JuniorNo ratings yet
- Endocrine GlandDocument12 pagesEndocrine GlandMikee PaningbatanNo ratings yet
- GH Chap 2Document12 pagesGH Chap 2Shellz2428No ratings yet
- HypothalamusDocument4 pagesHypothalamusLeanderVoetsNo ratings yet
- Growth Hormone DisordersDocument1 pageGrowth Hormone DisordersVishalNo ratings yet
- Siadh - Patho, Signs, Causes, TreatmentDocument1 pageSiadh - Patho, Signs, Causes, TreatmentVishalNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Patho & SignsDocument1 pagePneumonia Patho & SignsVishalNo ratings yet
- Thyroid (Hyper & Hypo) - Patho, Causes, LabsDocument1 pageThyroid (Hyper & Hypo) - Patho, Causes, LabsVishalNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Failure & ARDSDocument1 pageAcute Respiratory Failure & ARDSVishalNo ratings yet
- Asthma - Pathom, Signs & ComlicationsDocument1 pageAsthma - Pathom, Signs & ComlicationsVishalNo ratings yet
- Asthma II Pathophysiology Course - PFTs, Triggers, and Patho Test TipsDocument1 pageAsthma II Pathophysiology Course - PFTs, Triggers, and Patho Test TipsVishalNo ratings yet
- TonsillitisDocument1 pageTonsillitisVishalNo ratings yet
- Basic Chart 2 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesDocument1 pageBasic Chart 2 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesVishal100% (1)
- Respiratory Key TermsDocument1 pageRespiratory Key TermsVishalNo ratings yet
- Visual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesDocument1 pageVisual Chart 1 - Developmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Visual Chart 2 - Developmental MilestonesDocument1 pageVisual Chart 2 - Developmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Basic Chart 1 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesDocument1 pageBasic Chart 1 of 2 - Delopmental MilestonesVishalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine, Reproductive Block ObjectivesDocument22 pagesEndocrine, Reproductive Block Objectiveshur-azmi-1154No ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument7 pagesPathophysiologyAko Si Vern ÖNo ratings yet
- Kak UkkDocument4 pagesKak UkksantiNo ratings yet
- GP Balance Themethod PaginaDocument163 pagesGP Balance Themethod PaginaPedro100% (1)
- How I Stopped SweatingDocument14 pagesHow I Stopped Sweatingscribd_acount01No ratings yet
- Parathyroid Disorders GuideDocument2 pagesParathyroid Disorders GuideJan Uriel OicalegNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Endocrinology: Dr. Jehad Al-ShuneigatDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Endocrinology: Dr. Jehad Al-Shuneigatyousef sarairehNo ratings yet
- MCQS On PHYSIOLOGY OF LACTATIONDocument6 pagesMCQS On PHYSIOLOGY OF LACTATIONnighatkhanNo ratings yet
- Analytical Method For Cleaning Validation of Levothyroxine Sodium inDocument9 pagesAnalytical Method For Cleaning Validation of Levothyroxine Sodium inDidarulNo ratings yet
- HyperthyroidismDocument2 pagesHyperthyroidismZane ZyraNo ratings yet
- Nontoxic Nodular GoiterDocument7 pagesNontoxic Nodular GoiterKayshey Christine ChuaNo ratings yet
- Internal Male AnatomyDocument1 pageInternal Male AnatomybabyNo ratings yet
- ROJoson PEP Talk: National Thyroid Cancer Awareness Week - 2022Document75 pagesROJoson PEP Talk: National Thyroid Cancer Awareness Week - 2022rojosonNo ratings yet
- N64.4 Mastodynia: C73 Malignant Neoplasm of Thyroid GlandDocument1 pageN64.4 Mastodynia: C73 Malignant Neoplasm of Thyroid Glanddebby nirmasariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34 The Endocrine SystemDocument39 pagesChapter 34 The Endocrine SystemCarl Agape Davis100% (3)
- GNRH Agonists Et AnatagonistsDocument44 pagesGNRH Agonists Et Anatagonistshoussein.hajj.md100% (1)
- Kriya Sharir Paper 2Document11 pagesKriya Sharir Paper 2Amit PandyaNo ratings yet
- KER48201059583796394Document3 pagesKER48201059583796394fahad fahadNo ratings yet
- Eccrine Sweat GlandsDocument5 pagesEccrine Sweat GlandssakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Assessment of Thyroid Function - UpToDateDocument14 pagesLaboratory Assessment of Thyroid Function - UpToDateFadhli KarimNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 CommunicationIII 1Document30 pagesLecture10 CommunicationIII 1Liana Rose MeregildoNo ratings yet
- SPEED Endocrine e-Dialogues (SEED) Virtual ConferenceDocument7 pagesSPEED Endocrine e-Dialogues (SEED) Virtual ConferenceRajendra ChavanNo ratings yet
- Beyond The Fixed Setpoint of The Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid AxisDocument12 pagesBeyond The Fixed Setpoint of The Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Thyroid AxisJuliany AscanioNo ratings yet
- Introduction Prof IevaDocument39 pagesIntroduction Prof Ievabagus_wandaNo ratings yet
- Oral Manifestations of Thyroid Disorders and Its MDocument4 pagesOral Manifestations of Thyroid Disorders and Its MNike WijayaNo ratings yet
- Cushing - AddisonDocument27 pagesCushing - AddisonMelissa-Andreea Ardeleanu Carvajal OsorioNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology ReportDocument7 pagesEndocrine Physiology ReportLeanne CubarNo ratings yet
- Special Chemistry: Final ReportDocument1 pageSpecial Chemistry: Final ReportAMIRNo ratings yet
- BDBF3 D 01Document3 pagesBDBF3 D 01rendaoNo ratings yet
- THYROID DISORDERS - ENDOCRINOLOGY - Pocket MedicineDocument1 pageTHYROID DISORDERS - ENDOCRINOLOGY - Pocket Medicineعبد السلام الناشريNo ratings yet