Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Priscila AlvaradoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
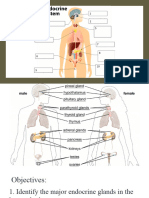
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Priscila AlvaradoCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine System
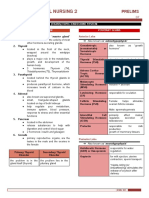
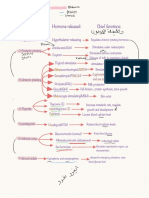
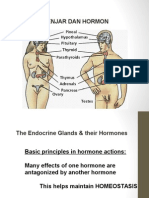
Gland Hormones Hormone functions
Pineal gland 1. Melatonin → Melatonin: promotes sleep by inducing drowsiness and lowering temperature
Hypothalamus 1. Thyrotropin releasing hormone → signals release of TSH
2. Corticotropin releasing hormone → signals release of ACTH
3. Growth hormone releasing hormone → signals release GH
4. Prolactin releasing hormone → signals release of prolactin
5. Gonadotropin releasing hormone → signals release of gonadotropins
Pituitary gland 1. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
2. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
3. Growth hormone (GH) → GH: growth and development
4. Prolactin → Prolactin: milk production
5. Gonadotropins:
-luteinizing hormone (LH)
-follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
6. Oxytocin → Oxytocin: milk ejection and uterine contractions
7. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) → ADH: stops urination; fluid retention
Thyroid gland 1. T3 → T3, T4: metabolism
2. T4: Thyroxine
3. Calcitonin → Calcitonin: decreases calcium in the blood
Parathyroid glands 1. Parathyroid hormone → Parathyroid hormone: increases calcium in the blood
Pancreas 1. Insulin → Insulin: decreases blood sugar
2. Glucagon → Glucagon: increases blood sugar
Adrenal glands Cortex:
1. Aldosterone → Aldosterone: regulates salt and water
2. Cortisol → Cortisol: stress hormone
3. Androgens:
-Testosterone
Medulla:
1. Adrenergic stimulants: → Adrenergic stimulants: stimulate fight or flight
-Epinephrine (adrenaline)
-Norepinephrine (noradrenaline)
-Dopamine
Kidneys 1. Erythropoetin → Erythropoeitin: stimulates bone marrow to produce RBCs
(exocrine, not 2. Renin → Renin: indirectly regulates fluid balance and blood pressure; helps make
endocrine, but it angiotensin
makes hormones) ➢ Angiotensin: promotes aldosterone secretion to raise BP
Ovaries 1. Estrogen → Estrogen: maturation of female sex organs and development of secondary
2. Progesterone sex characteristics
→ Progesterone: regulates menstrual cycle and preps the body for conception
and pregnancy
Testes 1. Testosterone → Testosterone: maturation of male sex organs and development of secondary
sex characteristics
Thymus 1. Thymosin → Thymosin: produce T cells
You might also like
- NMR Spectroscopy As A Characterization Tool Enabling Biologics Formulation Development PDFDocument15 pagesNMR Spectroscopy As A Characterization Tool Enabling Biologics Formulation Development PDFyun baiNo ratings yet
- HSB June 2020Document18 pagesHSB June 2020Osmany MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Theories Related To The Learner's DevelopmentDocument30 pagesTheories Related To The Learner's DevelopmentMichael Moreno83% (36)
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine SystemElaine CalayagNo ratings yet
- Hormones List - NavyaDocument4 pagesHormones List - NavyaNavya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Corticotropins and GonadotropinsDocument39 pagesCorticotropins and GonadotropinsSudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- PNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNDocument4 pagesPNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- Endocrine System Physiology and Pathophysiology (Part 1)Document34 pagesEndocrine System Physiology and Pathophysiology (Part 1)ayaessam392002No ratings yet
- Role of Hormones Endocrine 1Document37 pagesRole of Hormones Endocrine 1zyrle (zayrieeo)No ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument3 pagesChemical Coordination and Integrationakhil01ajNo ratings yet
- 10 Biology 1-16-07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsDocument34 pages10 Biology 1-16-07 Endocrine System Feedback SystemsErivieNo ratings yet
- Endocrine-System Science LessonDocument38 pagesEndocrine-System Science LessonKea BlankyNo ratings yet
- Exercise 13 EditDocument10 pagesExercise 13 EditSamantha De JesusNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Reviewer LecDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Reviewer LecNOELLE LAURAINNE TANZONo ratings yet
- Week5 Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesWeek5 Endocrine SystemHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine SystemKAUSTUBH SAWANTNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine System: Ilah M, SKPDocument36 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Endocrine System: Ilah M, SKPOmbun FajarNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyDocument28 pagesEndocrine System: School of Laboratory Medicine and Medical Sciences AnatomyHumaira BadatNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesThe Endocrine Systemheyraheyra70No ratings yet
- AP1 Lab16 Endocrine System FA2021Document11 pagesAP1 Lab16 Endocrine System FA2021daleng subNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesDocument35 pagesThe Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesEtta Sagita Leonora100% (1)
- The Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesDocument35 pagesThe Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesRizky PratamaNo ratings yet
- Q3 1 EndocrineDocument42 pagesQ3 1 Endocrineerlamay.valeNo ratings yet
- Padlan, Syra May M. - Endocrine System Assignment PDFDocument3 pagesPadlan, Syra May M. - Endocrine System Assignment PDFSyra May PadlanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System/socialDocument33 pagesEndocrine System/socialrpant3165No ratings yet
- Endocrine NotesDocument1 pageEndocrine NotesShivraj singh RajputNo ratings yet
- ABT Endocrine PPDocument39 pagesABT Endocrine PPABT SchoolNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Physology 2023 SharedDocument121 pagesEndocrine Physology 2023 SharedputracahyaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemDocument34 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Endocrine SystemUzma Khan100% (1)
- Endocrine PhysiologyDocument26 pagesEndocrine Physiologysam bossaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - Class - 10 - Icse.Document2 pagesEndocrine System - Class - 10 - Icse.zoha afshanNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesDocument35 pagesThe Endocrine Glands & Their HormonesShe JocelynNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing 2: PrelimsDocument10 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing 2: PrelimsjoanneNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusDocument9 pagesEndocrine System: Pituitary Gland and HypothalamusRohan Sahu0% (1)
- Endocrine System Short Review Original PDFDocument13 pagesEndocrine System Short Review Original PDFBijay Kumar MahatoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionDocument2 pagesChapter 38 Endocrine System FunctionPaige Nicole GauthreauxNo ratings yet
- 01 EndocrineDocument40 pages01 EndocrineMavi SaldevarNo ratings yet
- Hormones: Hormonal Control Nervous ControlDocument5 pagesHormones: Hormonal Control Nervous Controlvaibhav trivediNo ratings yet
- 22 Chemical Co-OrdinationDocument47 pages22 Chemical Co-OrdinationRachna JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: FunctionDocument24 pagesEndocrine System: FunctionCzyvel KryzNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Endocrine SystemDocument24 pages2018 - Endocrine SystemCzyvel KryzNo ratings yet
- Atar Notes Endorcine SystemDocument12 pagesAtar Notes Endorcine Systembella.wenman6No ratings yet
- Science Reviewer LT1 - Q4Document2 pagesScience Reviewer LT1 - Q4Cara IsabelNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PPT Session 12-13Document35 pagesEndocrine System PPT Session 12-13Lawrence Genelago GamboaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemDocument41 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemJessica Glitter100% (2)
- The Endocrine System:: Chemical Signals in AnimalsDocument13 pagesThe Endocrine System:: Chemical Signals in AnimalsbobNo ratings yet
- Note 17 Dec 2021Document2 pagesNote 17 Dec 2021mNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System LessonDocument47 pagesEndocrine System LessonMA. FRITZIE DE ASISNo ratings yet
- HORMONESDocument2 pagesHORMONESDa HernandezNo ratings yet
- Endokrin 1Document34 pagesEndokrin 1dianpn27No ratings yet
- Endocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Document61 pagesEndocrine System March 5 - 8, 2024Almira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine Systemydnic alykPNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument1 pageEndocrine SystemMaryna KryvenkoNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System NotesDocument6 pagesThe Endocrine System NotesRohit AnthuliaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System PPT Session 12-13Document35 pagesEndocrine System PPT Session 12-13LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Discussion Notes AnaphyDocument36 pagesDiscussion Notes Anaphyjade tanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument60 pagesEndocrine SystemseibdNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NoteDocument4 pagesEndocrine System NoteFumzy AdelakunNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument26 pagesEndocrine DisordersCrisia GungobNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ADRENAL GLANDS AND SIADH & DIDocument9 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of ADRENAL GLANDS AND SIADH & DIAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.No ratings yet
- Thyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!From EverandThyroid Diet : Thyroid Solution Diet & Natural Treatment Book For Thyroid Problems & Hypothyroidism Revealed!Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Thyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedFrom EverandThyroid Health: The Thyroid Solution Diet ExposedRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- DR - Vinay PhagocytosisDocument62 pagesDR - Vinay PhagocytosisVinaykumar HallurNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Review LecDocument5 pagesObstetric Review LecKevin PatrickNo ratings yet
- AE 152 M1 - Soil-Water-Plant RelationshipDocument20 pagesAE 152 M1 - Soil-Water-Plant Relationshipgregorio roa100% (2)
- Bio DegradationDocument6 pagesBio DegradationVictor Fassina BroccoNo ratings yet
- Ecology of The City: A Perspective From ScienceDocument5 pagesEcology of The City: A Perspective From SciencePrajitha Jinachandran T KNo ratings yet
- Westbrook Delamater Psychological and Neural Mechanisms of Extinction 2014Document14 pagesWestbrook Delamater Psychological and Neural Mechanisms of Extinction 2014Harry HuangNo ratings yet
- Evidence LawDocument13 pagesEvidence Lawrashi baksh100% (1)
- Meaning, Definition and Components of EnvironmentDocument15 pagesMeaning, Definition and Components of EnvironmentLarah May DocusinNo ratings yet
- Chem 23.1 Experiment 5 PostLabDocument4 pagesChem 23.1 Experiment 5 PostLabJoshua RomeaNo ratings yet
- Master Thesis Defence PresentationDocument6 pagesMaster Thesis Defence Presentationafloziubadtypc100% (2)
- Impacts of Gmo'S On Genetically Modified Organisms Produced by Philippine ResearchersDocument3 pagesImpacts of Gmo'S On Genetically Modified Organisms Produced by Philippine ResearchersIrish Cheska EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Abstracts INNOHORT2015 PDFDocument56 pagesAbstracts INNOHORT2015 PDFe1596769No ratings yet
- 04 MalasseziaDocument7 pages04 MalasseziaResty Agiastuty Eka PutriNo ratings yet
- Lab Policies Complete Blood Count of Whole Blood On The Sysmex KX 21N - RB Lab 1535Document20 pagesLab Policies Complete Blood Count of Whole Blood On The Sysmex KX 21N - RB Lab 1535tomNo ratings yet
- Porphyromonas Gingivalis in AlzheimerDocument21 pagesPorphyromonas Gingivalis in AlzheimerJhonatan Efrain Lopez CarbajalNo ratings yet
- 002 ARA CCHI Mini - Glossary ENT EarDocument5 pages002 ARA CCHI Mini - Glossary ENT Eartarboosh20146No ratings yet
- Viegas Et Al 2014 - Proof VersionDocument22 pagesViegas Et Al 2014 - Proof VersionDinizViegasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy One Shot DR AshwiniDocument95 pagesAnatomy One Shot DR Ashwinienthusiast383No ratings yet
- Biol - 209 Spring 2021-2022Document3 pagesBiol - 209 Spring 2021-2022charles murrNo ratings yet
- Additional Science BDocument136 pagesAdditional Science Bapi-26229281No ratings yet
- Science Movement Lesson Plan (By Meredith Lane)Document4 pagesScience Movement Lesson Plan (By Meredith Lane)api-308563816No ratings yet
- Agriculture Final SyllabusDocument63 pagesAgriculture Final SyllabusAshish RajNo ratings yet
- La Amígdala: Implicaciones Funcionales: M. Torras, I. Portell, I. MorgadoDocument6 pagesLa Amígdala: Implicaciones Funcionales: M. Torras, I. Portell, I. MorgadoaddagornNo ratings yet
- AFPDocument4 pagesAFPHassan GillNo ratings yet
- Genetika Populasi: Faktor-Faktor Yang Berpengaruh Pada GENPOP???Document13 pagesGenetika Populasi: Faktor-Faktor Yang Berpengaruh Pada GENPOP???Diah kusumanithaNo ratings yet
- Journal of Applied Horticulture 12 (1) 2010Document85 pagesJournal of Applied Horticulture 12 (1) 2010Shailendra RajanNo ratings yet
- Alma VDocument9 pagesAlma VJun MagparoNo ratings yet