Professional Documents
Culture Documents
28 PDFsam Al Manu
28 PDFsam Al Manu
Uploaded by
fordownload useOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
28 PDFsam Al Manu
28 PDFsam Al Manu
Uploaded by
fordownload useCopyright:
Available Formats
.
.
.
.
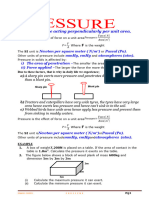
dissipated by. the pile at greater depth. For 100% load supported, the entire
. by the pile cap.
load is supported
Note: To be .conservation using 0% is recommended.
.
Step 5 .
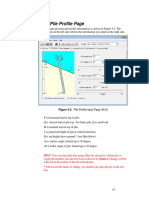
Distributed lateral loads
To distribute load along the length of the pile press the [Input Load] button
to open the panel shown in Figure 4-7. In the Distributed Load table, enter the
following information:
Z The starting point of the distributed load, z is the distance
from the pile top.
Pq Pq is distributed load along pile length at the z location.
B B is the width of the pressure.
Note: To apply the distributed load, the check box above the [Input Load]
button must be checked. You cannot only apply distributed load without a
shear load on pile top. You can move some load to top as shear load.
The following examples illustrate how data are to
be inputted in the table:
Example 1:
A signal post is 6ft wide and 8ft high above
ground. A pile 1.2 ft in diameter supports it
below ground. Wind pressure is 1.5 ksf. You can
input z=0 ft, pq=1.5ksf, B=6 ft in the first row,
and z=8 ft, Pq=0, and B=1.2ft in the second row.
Example 2:
If a lateral pressure load of 1 kip per square foot
(1 ksf or 1 kip/ft2) acting on a 2ft high pile shaft
(dia = 1.5 ft), you can input z=2ft Pq=1ksf and
B=1.5ft.
Example 3:
If a lateral load of 1kip per linear foot (1 kip/ft) is
Figure 4-7. Distributed Load acting on the pile diameter (diameter = 1.5 feet),
you should input Pq=1 ksf and B=1.
4.5.2 Group Piles
Group analysis lets you select two head conditions under compressive, shear,
moment, and torsion loading with unlimited number of piles. The analysis
provides settlement, rotation, and lateral movement of the pile cap under
these loadings. You can select the head condition that best fits your
condition.
27
You might also like
- Lat Pile PYDocument38 pagesLat Pile PYMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Shallow FoundationsDocument29 pagesChapter 3 - Shallow FoundationsBuoyancyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 Flow Over Broad Crested WeirDocument5 pagesExperiment 5 Flow Over Broad Crested WeirKelly Obrien75% (4)
- AllPile 05Document7 pagesAllPile 05Tony Hartono BagioNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering - Ii (Foundation Engineering) : Prepared By: Mc-Lloyd G. SarateDocument39 pagesGeotechnical Engineering - Ii (Foundation Engineering) : Prepared By: Mc-Lloyd G. SaratePascasio Pascasio100% (2)
- Transmission Line Supports.Document37 pagesTransmission Line Supports.ninadpujara2007No ratings yet
- Pile Load CapacityDocument2 pagesPile Load CapacityAziz ul HakeemNo ratings yet
- Pile Lateral Load Analysis Using Finite Difference Method Latpile FunctionDocument29 pagesPile Lateral Load Analysis Using Finite Difference Method Latpile FunctionSomamemory DaelyNo ratings yet
- The Bearing Capacity of Soils: DR Omar Al HattamlehDocument23 pagesThe Bearing Capacity of Soils: DR Omar Al HattamlehPro BookNo ratings yet
- Suelos Con TriangularesDocument61 pagesSuelos Con TriangularesYrcs IngcivilNo ratings yet
- Lec-5 Settlement of Pile GroupsDocument19 pagesLec-5 Settlement of Pile Groupsdereje werkuNo ratings yet
- Ge 420113Document4 pagesGe 420113y zhaoNo ratings yet
- 3 Bearing Capacity Part1Document56 pages3 Bearing Capacity Part1Haider Yousef0% (1)
- Geotechnics: Model Tests On Passive Piles in Soft ClayDocument13 pagesGeotechnics: Model Tests On Passive Piles in Soft ClayscegtsNo ratings yet
- A Review On Assessment of Settlement in Pile Foundation: AbstractDocument6 pagesA Review On Assessment of Settlement in Pile Foundation: Abstractمحمد المصطفى محمد حنتوش اسدNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Sheetpile Converted 181116160255Document61 pagesUnit1 Sheetpile Converted 181116160255Dr-Hany HashishNo ratings yet
- Chapter-Ii-Bearing Capacity of Foundation SoilDocument24 pagesChapter-Ii-Bearing Capacity of Foundation Soilabyalew b.No ratings yet
- Lecture15 Analysis of Single PilesDocument32 pagesLecture15 Analysis of Single PilesJulius Ceasar SanorjoNo ratings yet
- Principle of Geotechnical EngineeringDocument61 pagesPrinciple of Geotechnical EngineeringMhwae Mhwae Kyaing KyaingNo ratings yet
- Problems On PressureDocument4 pagesProblems On Pressurevinod kumarNo ratings yet
- Effects o F Ground Movements On PilesDocument1 pageEffects o F Ground Movements On PilesFernando FanteNo ratings yet
- Pile Cuttack-1Document4 pagesPile Cuttack-1KANHA100% (1)
- HPW Archive: A Clear-Cut Guide To Helical Pier SpacingDocument5 pagesHPW Archive: A Clear-Cut Guide To Helical Pier SpacingSalvatore LombardoNo ratings yet
- Spread Footing DesignDocument12 pagesSpread Footing DesignNikka ToledoNo ratings yet
- 88 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page88 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 1 (B) - Laterally Loaded PilesDocument6 pages1 (B) - Laterally Loaded PilesMinilik Tikur SewNo ratings yet
- Foundation Analysis: Ultimate Bearing Capacity: Shallow FoundationDocument21 pagesFoundation Analysis: Ultimate Bearing Capacity: Shallow FoundationShiela Marie Cruz100% (1)
- 4-Pile FoundationDocument10 pages4-Pile FoundationRajratna MadhaleNo ratings yet
- Shallow FD 2 and Pile 2Document26 pagesShallow FD 2 and Pile 2Mapoho TlaliNo ratings yet
- The Bearing Capacity of Soils: DR Omar Al HattamlehDocument64 pagesThe Bearing Capacity of Soils: DR Omar Al HattamlehHusam Adnan HamoutaNo ratings yet
- Simple Machines The Lever, The Inclined Plane, and The Pulley - 2440060742 - Jeffrey Liandi - A71Document18 pagesSimple Machines The Lever, The Inclined Plane, and The Pulley - 2440060742 - Jeffrey Liandi - A71Jeffrey LiandiNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Spread Footing AnalysisDocument9 pagesRectangular Spread Footing AnalysisJudy TanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document6 pagesExperiment 4Majdy gamingNo ratings yet
- Francis Turbine-Performance Characteristics ofDocument6 pagesFrancis Turbine-Performance Characteristics ofKaleab TekabeNo ratings yet
- Design of Cantilever Retaining WallDocument38 pagesDesign of Cantilever Retaining WallGajula Pavan100% (1)
- SpsiDocument33 pagesSpsiAnup ShirhattiNo ratings yet
- Laterally Loaded Piles PDFDocument16 pagesLaterally Loaded Piles PDFriad10No ratings yet
- PressureDocument12 pagesPressuretrojanfrpNo ratings yet
- Ijsrdv1i8004 140806073858 Phpapp02 PDFDocument3 pagesIjsrdv1i8004 140806073858 Phpapp02 PDFAlexNo ratings yet
- Foundation DesignDocument6 pagesFoundation DesignBalamuruganNo ratings yet
- The 10xi in The Element Spliced Plus 5 Percent But in Nocase Shouldthe Strength Developed Be Less Than 50percent ofDocument5 pagesThe 10xi in The Element Spliced Plus 5 Percent But in Nocase Shouldthe Strength Developed Be Less Than 50percent ofRaj MeenaNo ratings yet
- @2الاحتكاك السلبي السطحي لمجموعة الركائز@@Document7 pages@2الاحتكاك السلبي السطحي لمجموعة الركائز@@جحاNo ratings yet
- Calc Explaination 05312020Document15 pagesCalc Explaination 05312020immanuel izaniNo ratings yet
- Simple MachinesDocument15 pagesSimple MachinesMHNo ratings yet
- 1516sem2 Ce5107Document5 pages1516sem2 Ce5107winminthetgeoNo ratings yet
- Suggestions To Improve Method of Installation of Cast-In-situ Driven and Bored Concrete PilesDocument4 pagesSuggestions To Improve Method of Installation of Cast-In-situ Driven and Bored Concrete PilesRajen KoleyNo ratings yet
- Term Exam 1 - QuestionsDocument8 pagesTerm Exam 1 - Questionsamadeus135No ratings yet
- Solution Manual TE VOL-IDocument26 pagesSolution Manual TE VOL-IRajesh KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Pressure RevisedDocument5 pagesPressure ReviseddanielNo ratings yet
- Settlement of FoundationDocument11 pagesSettlement of FoundationShane BondNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 11a PilotesDocument34 pagesCapitulo 11a PilotesEdu D. Bocanegra LopezNo ratings yet
- Ps 1Document1 pagePs 1amor Bagon0% (2)
- Floor Loading ScenariosDocument2 pagesFloor Loading ScenariosДончо МацкоскиNo ratings yet
- GuoZhu ISFOG2005 28marchDocument7 pagesGuoZhu ISFOG2005 28marchroshNo ratings yet
- 0143-0807 31 4 014 Ball Bounce Thump and RingingDocument9 pages0143-0807 31 4 014 Ball Bounce Thump and RingingmannefrimanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Pile Foundation Subjected To Lateral and Vertical LoadsDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Pile Foundation Subjected To Lateral and Vertical LoadsEhab ElsharnobiNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910From EverandPressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910No ratings yet
- 87 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page87 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 81 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page81 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 83 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page83 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 78 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page78 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 84 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page84 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 73 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page73 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 72 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page72 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 45 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page45 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 71 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page71 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 63 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page63 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 66 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page66 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 67 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page67 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 58 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page58 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 64 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page64 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 54 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page54 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 57 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page57 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 60 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page60 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 52 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page52 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 59 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page59 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 51 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page51 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 40 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page40 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 50 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page50 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 36 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page36 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 16 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page16 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 23 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page23 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 21 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page21 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 22 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page22 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 20 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page20 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 18 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page18 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- 19 PDFsam Al ManuDocument1 page19 PDFsam Al Manufordownload useNo ratings yet
- Damage Tolerance Design: Bernardo Vilhena Gavinho LourençoDocument10 pagesDamage Tolerance Design: Bernardo Vilhena Gavinho LourençoLekh SoniNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis: Diagnosis Using Warning Light (Including Diag-Nosis Memory)Document3 pagesDiagnosis: Diagnosis Using Warning Light (Including Diag-Nosis Memory)александрNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes-IIT Bombay PDFDocument379 pagesLecture Notes-IIT Bombay PDFSumesh SpankoNo ratings yet
- Estandard Sepecifications:: 600x900mm RECI W6 130W-160W Glass Laser Tube (12 Months Warranty)Document5 pagesEstandard Sepecifications:: 600x900mm RECI W6 130W-160W Glass Laser Tube (12 Months Warranty)Oswaldo LópezNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation On Out-Of-Plane Behavior of Masonry Panels Strengthened With CFRP SheetsDocument13 pagesExperimental Investigation On Out-Of-Plane Behavior of Masonry Panels Strengthened With CFRP Sheetsjai kumarNo ratings yet
- Mock Test Class 11 PhysicsDocument4 pagesMock Test Class 11 PhysicsANITA CHOUHANNo ratings yet
- Sawan Kumar Rawat, Himanshu Upreti, Manoj KumarDocument20 pagesSawan Kumar Rawat, Himanshu Upreti, Manoj KumarShafqat HussainNo ratings yet
- Answer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 MarksDocument2 pagesAnswer Any Three Full Questions, Each Carries 10 MarksVarsha SreekumarNo ratings yet
- Technical Terms Chapter 80Document5 pagesTechnical Terms Chapter 80thena MartinNo ratings yet
- QCM HydraulicDocument6 pagesQCM HydraulicAdil KhNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's EquationDocument8 pagesBernoulli's EquationOkay Printing100% (1)
- Eckerle EIPH2 - 3 - 6 Series PDFDocument12 pagesEckerle EIPH2 - 3 - 6 Series PDFOleg080No ratings yet
- Ventilador CSPDocument2 pagesVentilador CSPJuan Jose RobalinoNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Dimension InspectionDocument17 pagesPressure Vessel Dimension InspectionEqubal KhanNo ratings yet
- Model h25 Service ManualDocument34 pagesModel h25 Service ManualKaique MelloNo ratings yet
- 247224540-Seal-Drum-CalcDocument1 page247224540-Seal-Drum-Calchwang2No ratings yet
- Structural Tank Instructions 11967-ADocument22 pagesStructural Tank Instructions 11967-Aiftikhar_khalid_1No ratings yet
- 0708-Q-CC-004 Pipe Stress Calculation From KO Drum To Flare Rev ADocument9 pages0708-Q-CC-004 Pipe Stress Calculation From KO Drum To Flare Rev AElias EliasNo ratings yet
- Electric Tool Parts List: Hitachi Power ToolsDocument4 pagesElectric Tool Parts List: Hitachi Power ToolsCamila LopezNo ratings yet
- Heat Pumps Up To 2000 KWDocument42 pagesHeat Pumps Up To 2000 KWanon_411130333No ratings yet
- Camshaft Bearings - Remove and Install (SENR5547-04)Document2 pagesCamshaft Bearings - Remove and Install (SENR5547-04)Muhammad Danang MadhribieNo ratings yet
- Mechancial Piping, Valve and Steam Trap BOQDocument4 pagesMechancial Piping, Valve and Steam Trap BOQAnonymous uLAATWpfNo ratings yet
- L36GL Data Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesL36GL Data Sheet PDFManuel ValdiviesoNo ratings yet
- Cable Blowing, Handheld Blower and Microduct InstallationDocument15 pagesCable Blowing, Handheld Blower and Microduct InstallationComstar SupplyNo ratings yet
- Coil On Plug IgnitionDocument4 pagesCoil On Plug IgnitionFabricio LimaNo ratings yet
- Bridge Engg-Live Load Moment and Shear in BridgesDocument38 pagesBridge Engg-Live Load Moment and Shear in BridgesAdithya SKNo ratings yet
- Niederer1990 - Sobre MotocicletasDocument8 pagesNiederer1990 - Sobre MotocicletasAlexandre FontouraNo ratings yet
- S36X Boom Pump Jan 2022Document11 pagesS36X Boom Pump Jan 2022Sinamm Engineering LimitedNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer-Distillation DesignDocument47 pagesMass Transfer-Distillation DesignMeera PatelNo ratings yet