Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Law Vmicronotes
Uploaded by
Fakkiresh M GOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Law Vmicronotes
Uploaded by
Fakkiresh M GCopyright:
Available Formats
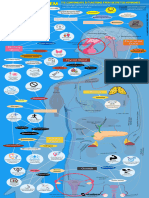
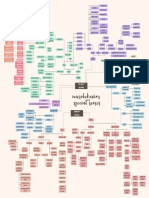
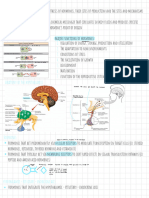
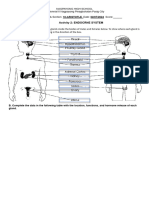
Chemical Coordination & Integration
neural system
gonadotrophins
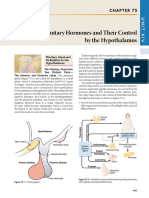
Hypothalamus
..
LH & FSH stimulate gonadal activity
basal part of diencephalon, forebrain
neurosecretory cells( nuclei) produce hormones. In males In females Hypothyroidism during pregnancy
point-to-point rapid coordination among organs.
fast but short-lived.
nerve fibres do not innervate all body cells & cellular functions
regulate synthesis & secretion
of pituitary hormones.
1. Endocrine Glands and Hormones LH stimulates LH induces
ovulation fully graafian follicles
defective development ,
stunted growth (cretinism),
mental retardation,
Hypothalamus 2 types Hormones
releasing hormones inhibiting hormones 2. Human Endocrine System synthesis & secretion
androgens from testis.
maintains corpus luteum, low intelligence quotient,
abnormal skin,
deaf-mutism, etc.
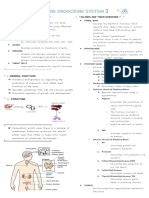
endocrine system
stimulate secretion of
pituitary hormones
inhibit secretions of
pituitary hormones 3. Hormones of Heart, Kidney and FSH & androgens FSH stimulates
adult women, hypothyroidism
irregular menstrual cycle .
Gonadotrophin releasing regulate spermatogenesis
coordination and integration by hormones.
hormone (GnRH)
stimulates pituitary synthesis &
somatostatin
inhibits growth release
hormone from pituitary. Gastrointestinal Tract growth & development
ovarian follicles
release of gonadotrophins.
hyperthyroidism (affects body physiology )
neural system + endocrine system jointly coordinate and regulate
anterior pituitary
4. Mechanism of Hormone Action MSH Due to cancer or nodules in thyroid glands,
body physiological functions acts on melanocytes (melanin containing cells) rate of synthesis abnormal increased high levels
. regulates skin pigmentation
hypothalamic neurons axons nerve endings
hormones
Oxytocin Graves' disease.
hyperthyroidism,
Endocrine Glands and Hormones
acts on body smooth muscles ( s!mulates c"trac!") enlargement thyroid gland,
regulate anterior portal
pituitary gland circulatory system protrusion eyeballs,
pituitary functions In females child birth time (uterus vig#$s c"trac!") increased basal metabolic rate
& weight loss,
milk ejection from mammary gland.
Ductless glands. secretions posterior pituitary
Vasopressin Exopthalmic goitre
under direct neural regulation of hypothalamus
hormone definitions acts on kidney {s!mulates water, electrolytes res#p!"}
classical definition current scientific definition
anti-diuretic hormone (ADH). (No diuresis) Thyroid hormones
growth hormone (GH) regulation of basal metabolic rate.
gigantism dwarfism
If no ADH red blood cell formation.
chemical produced by non-nutrient chemicals act as Diabetes Insipidus ( water lo% and dehydra!" ) control metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, fats.
intercellular messengers & produced in Over-secretion low secretion Maintenance of water & electrolyte balance
endocrine glands & released thyrocalcitonin (TCT) regulates blood calcium levels.
The Pineal Gland
into blood & transported to trace amounts.
distantly target organ
New definition
covers new molecules + hormones
The Pituitary Gland abnormal growth stunted growth
dorsal side of forebrain Parathyroid Gland
secreted
24-hour (diurnal) 4 parathyroid glands
t Acromegaly
Invertebrates body rhythm back side of thyroid gland,
simple endocrine systems +few hormones
pars nervosa Excess secretion GH (adults) middle age
vertebrates stores & releases serious complications,
large number of hormones & provide coordination stalk oxytocin & vasopressin hormones premature death if unchecked.
synthesised by hypothalamus hard to diagnose in early stages,
often undetected for many years hormone (Melatonin)
Human Endocrine System &transported axonally here
until changes noticeable. maintaining normal rhythms of sleep-wake cycle,
body temperature. peptide hormone (parathyroid hormone (PTH)
endocrine glands & hormone influences metabolism, pigmentation,
- severe disfigurement menstrual cycle
secrete by regulated by
defense capability.
producing
Prolactin
↓
diffused tissues/cells
↓
regulates growth of mammary glands & formation of milk
Thyroid Gland parathyroid glands circulating levels of Ca+
Located in diff body parts
TSH ACTH Parathyroid h#m"e (PTH)
Pituitary, pineal, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, parathyroid,
thymus gonads (testis ,ovary) stimulates synthesis &secretion thin flap of connective tissue increases Ca2+ levels in blood.
B/w 2 lobes
gastrointestinal tract, liver, kidney, heart thyroid hormones steroid hormones( glucocorticoids) acts on bones, ( s!mulates b"e res#p!" (di%olu!"/de&neralisa!").
from thyroid gland. from adrenal cortex. s!mulates reabs#p!" of Ca2+ by renal tubules
follicles
Each thyroid gland stromal tissues. increases Ca2+ abs#p!" from digested food.
secretes
only 1 hormone
-
follicles tissue
follicular cells
tetraiodothyronine or thyroxine (T4)
Along with TCT, calcium body balance.
triiodothyronine (T3).
melanocyte stimulating lodine For normal rate of thyroid hormone synthesis.
hormone (MSH). If iodine Deficiency (hypothyroidism)
Produces
V
growth hormone (GH),
prolactin (PRL),
thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH),
adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH),
luteinizing hormone (LH)
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH).
Thymus gland emergency hormones or hormones of Fight or Flight. Leydig cells or interstitial cells
Location Peptide hormones Function
increase alertness,
pupilary dilation,
piloerection (raising of hairs),
E Function
Location intertubular spaces
produce androgens mainly testosterone. gastro-intestinal tract gastrin
sweating HCL & pepsinogen
heart beat, gastric glands secretions
heart contraction Androgens act on CNS influence
rate of respiration. male sexual behaviour (libido). regulate development,
maturation & functions of male accessory sex organs water &
epididymis, exocrine pancreas secretin, bicarbonate ions
Catecholamines vas deferens, secretions
seminal vesicles,
lobular structure b/w lungs behind sternum on ventral aorta side also stimulate breakdown of glycogen prostate gland, secretion of pancreatic
breakdown of lipids &proteins. both pancreas and
major role in immune system development urethra etc. enzymes , bile
stimulate muscular growth,
gall bladder cholecystokinin (CCK)
secretes peptide hormones (thymosins)
cortisol main Aldosterone main juice.
growth of facial & axillary hair,
glucocorticoid. mineralocorticoid
aggressiveness,
differentiation of T-lymphocytes, low pitch of voice etc.
carbohydrate metabolism regulate balance of water & inhibits gastric
cell-mediated immunity. spermatogenesis (formation of spermatozoa).
electrolytes Small intestine gastric inhibitory secretion & motility.
produce anabolic (synthetic) effects on protein &
promote production of antibodies to peptide (GIP).
carbohydrate metabolism #
provide humoral immunity. glucocorticoid
Old Child
Increases inhibit
Ovary Several other non-
endocrine tissues
normal growth of
tissues & their
Adrenal Gland
pair of ovaries located in abdomen repairing/regeneration.
gluconeogenesis, cellular uptake
lipolysis amino acids utilisation
primary sex organ &
proteolysis; dual functions I endocrine gland.
Cortisol
anteri# part
Ovary
Mechanism of Hormone Action
maintaining cardio-vascular system& kidney functions. Hormones 7 specific hormone receptors
target tissues
ovarian follicles. stromal tissues.
produces anti-inflammatory reactions
suppresses immune response.
- estrogen -
Pancreas
/
membrane-bound intracellular receptors,
receptors mostly (nuclear receptors)
composite gland > both endocrine gland & exocrine
generate second messengers (e.g., steroid hormones,
V
1 to 2 million Islets of Langerhans -> 1 to 2 % of pancreatic tissue. (e.g. cyclic AMP,Ip3, Ca++ etc) iodothyronines, etc.)
1
L V
Alpha cells & beta cells. 7
secretes mainly progesterone
pep!de h#m"es I in turn regulate cellular regulate gene expression or
metabolism
↓
glucagon. insulin. chromosome function
hyperglycemic hypoglycemia
Estrogens
acts on hepatocytes Acts on hepatocytes and adipocytes
stimulates glycogenolysis , gluconeogenesis enhances cellular glucose uptake and utilisation. stimulation of growth & activities of female secondary sex organs,
also stimulates glycogenesis in target cells. development of growing ovarian follicles,
reduces cellular glucose uptake & utilisation. female secondary sex characters (e.g., high pitch of voice, etc.)
" mammary gland development.
treated with regulate female sexual behaviour.
diabetes mellitus ↓
Prolonged hyperglycemia insulin therapy.
associated with glucose loss by urine
ketone bodies formed. Progesterone Protein hormone Steroid hormone
Underproduction of hormones by adrenal cortex Testis supports pregnancy.
acts on mammary glands & stimulates alveoli formation
alters carbohydrate metabolism pair of testis in scrotal sac (outside abdomen) of male (sac-like structures which store milk) and milk secretion.
causing acute weakness & fatigue
primary sex organ &
dual functions I endocrine gland. Hormones of Heart, Kidney, Gastrointestinal Tract
Adrenal medulla Testis
hormones > endocrine glands
hormones. > some tissues.
Mr
Location Function
seminiferous stromal or
tubules interstitial tissue. Peptide hormones
hormone + receptor = hormone-receptor complex
heart atrial natriuretic factor blood vessels dilation
atrial wall (ANF), blood pressure decreases
biochemical changes
metabolism
kidney
physiological functions regulated
erythropoietin
juxtaglomerular cells stimulates erythropoiesis
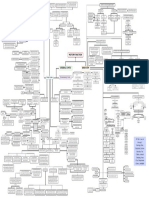
hormones divided On basis of chemical nature
hormones Examples
insulin, glucagon, pituitary
peptide, polypeptide, protein hormones hormones, hypothalamic
hormones, etc.
cortisol, testosterone,
7 adrenaline steroids
estradiol and progesterone)
adrenal medulla
secretes (epinephrine)
iodothyronines thyroid hormones
2 hormones noradrenaline
epinephrine
amino-acid derivatives
(norepinephrine)
You might also like
- NeuroSuccess: Your Brain Retraining Guide to Wealth and AccomplishmentFrom EverandNeuroSuccess: Your Brain Retraining Guide to Wealth and AccomplishmentNo ratings yet
- Post-Traumatic Stress DisorderDocument1 pagePost-Traumatic Stress DisorderJoan MonzonesNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System - SheepDocument1 pageEndocrine System - SheepmilumvzNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Diencephalon Basal Ganglia Brain VentriclesDocument12 pagesWeek 7 Diencephalon Basal Ganglia Brain Ventriclessuen sarahNo ratings yet
- Global Report On Birth Defects The Hidden Toll ofDocument1 pageGlobal Report On Birth Defects The Hidden Toll ofvolNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Infographic PosterDocument1 pageEndocrine System Infographic PosterVohn Archie EdjanNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Gland: A Two-Component Endocrine Organ Under the HypothalamusDocument6 pagesPituitary Gland: A Two-Component Endocrine Organ Under the Hypothalamusمحمد القرنيNo ratings yet
- Hormones 2Document4 pagesHormones 2den mNo ratings yet
- WA10004-Directed Differentiation Pluripotent Stem CellsDocument1 pageWA10004-Directed Differentiation Pluripotent Stem CellsJorge Mario “Jorge” Gamboa CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Concept Map PT 1Document1 pageConcept Map PT 1api-657741346No ratings yet
- GH Chap 2Document12 pagesGH Chap 2Shellz2428No ratings yet
- Enfghdocrine Sfghstem Infogrhgfaphic Vihgfsual PohgfsterDocument1 pageEnfghdocrine Sfghstem Infogrhgfaphic Vihgfsual PohgfsterRăzvan RoșcaNo ratings yet
- Kidney AmatomyDocument1 pageKidney AmatomyCarlotta ranalliNo ratings yet
- CEREBELLUMDocument1 pageCEREBELLUMOscar Orengo AlbertorioNo ratings yet
- Judo Is The BestDocument1 pageJudo Is The BestAnkit MohantaNo ratings yet
- Almanda Gitta PuspaDocument1 pageAlmanda Gitta PuspaAlmanda Gitta PuspaNo ratings yet
- PDF Crash Course Endocrinology 4e Pdftahir99 VRG CompressDocument60 pagesPDF Crash Course Endocrinology 4e Pdftahir99 VRG CompressNabila Azahara PutriNo ratings yet
- Coordination: GlandsDocument11 pagesCoordination: Glandskashish joshiNo ratings yet
- Anterior PituitaryDocument1 pageAnterior PituitaryVishalNo ratings yet
- Responsible For The Direct Control of The Endocrine System Through The Pituitary GlandDocument4 pagesResponsible For The Direct Control of The Endocrine System Through The Pituitary GlandJessa Mae BanquirigNo ratings yet
- Psywar PDFDocument1 pagePsywar PDFmrelfeNo ratings yet
- Hormones and The Endocrine System: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument68 pagesHormones and The Endocrine System: Powerpoint Lectures Forxo_simpledreamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Endocrine SystemDocument38 pagesChapter 10 Endocrine SystemMacthalas QuiazonNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument1 pageCase PresentationGLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBANo ratings yet
- Feb 5 2020 - Endocrine System g10Document5 pagesFeb 5 2020 - Endocrine System g10Lymberth BenallaNo ratings yet
- Empagliflozin Metformin HCL: Jardiance Duo®Document2 pagesEmpagliflozin Metformin HCL: Jardiance Duo®Lord Carlo CabangalNo ratings yet
- Science - LensDocument8 pagesScience - LensAte DannyNo ratings yet
- Guía Health ScienceDocument8 pagesGuía Health ScienceIan Franco ManniNo ratings yet
- Jerry Leung - Enhancing Transfusable Platelets Using mRNA Therapy To Produce Exogenous ProteinsDocument1 pageJerry Leung - Enhancing Transfusable Platelets Using mRNA Therapy To Produce Exogenous ProteinsCBR UBCNo ratings yet
- sci-reviewer (2)Document3 pagessci-reviewer (2)Ice SullezaNo ratings yet
- 5M: Care of Clients With Hormonal Disturbances: Endocrine SystemDocument19 pages5M: Care of Clients With Hormonal Disturbances: Endocrine SystemEmmanuelle Soroño AmoresNo ratings yet
- Case 5 Concept MapDocument1 pageCase 5 Concept MapdreamedyyyNo ratings yet
- Pathology Notes - Endocrine SystemDocument1 pagePathology Notes - Endocrine Systems21514.laiNo ratings yet
- Q3 S10 Week 1 Lecture or NotesDocument5 pagesQ3 S10 Week 1 Lecture or NotesJuben OdalNo ratings yet
- Hsci Lesson 5Document9 pagesHsci Lesson 5Eyvette GoNo ratings yet
- HUMAN REPRODUCTIONDocument2 pagesHUMAN REPRODUCTIONsrishtiNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Jan 13, 2024Document3 pagesAdobe Scan Jan 13, 2024Abhijeet KumarNo ratings yet
- A7 Structural Organization in Animals MinDocument1 pageA7 Structural Organization in Animals MinDME MPonlineNo ratings yet
- PCOL - Hormonal AgentsDocument7 pagesPCOL - Hormonal AgentsTerepe CrimsonNo ratings yet
- Hormones Secreted by Endocrine GlandsDocument5 pagesHormones Secreted by Endocrine Glandsaditya7324100% (1)
- PPT-Endocrine-SystemDocument56 pagesPPT-Endocrine-SystemNoreen BengoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System WorksheetDocument8 pagesEndocrine System WorksheetALLAN JAY D. LAPIZNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System EditedDocument80 pagesEndocrine System EditedKyle Gwyneth BobierNo ratings yet
- Human CD Chart PDFDocument1 pageHuman CD Chart PDFLia WieNo ratings yet
- HGHDocument1 pageHGHThe London Free Press100% (1)
- Alzheimer's Disease Glioblastoma Multiforme: Exploiting Biomarkers To Identify & Monitor Brain DysfunctionDocument2 pagesAlzheimer's Disease Glioblastoma Multiforme: Exploiting Biomarkers To Identify & Monitor Brain DysfunctionAndrei BăcanuNo ratings yet
- Neonatal JaundiceDocument1 pageNeonatal JaundiceinavdaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Ana Lec 2Document53 pagesNervous System Ana Lec 2hey lolNo ratings yet
- Chief Taxonomic Subdivisions and Organ Systems of The Animal PhylaDocument2 pagesChief Taxonomic Subdivisions and Organ Systems of The Animal PhylaL P100% (1)
- An Introduction To Optimal Control Applied To Disease ModelsDocument37 pagesAn Introduction To Optimal Control Applied To Disease ModelsMohammad Umar RehmanNo ratings yet
- Panel Discussion QuestionsDocument2 pagesPanel Discussion QuestionsJoey SanosaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cells and Their StructuresDocument10 pagesProkaryotic Cells and Their Structuresadhit46No ratings yet
- SAFC Biosciences Scientific Posters - Proteomic Analysis of CHO Cells During Recombinant Protein Production in High-Density CultureDocument1 pageSAFC Biosciences Scientific Posters - Proteomic Analysis of CHO Cells During Recombinant Protein Production in High-Density CultureSAFC-Global100% (1)
- CH13 GRP9 HandoutsDocument10 pagesCH13 GRP9 HandoutsアーロンクリスチャンNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrine Systemadrianacasanov199No ratings yet
- Q3 Activity 2 Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesQ3 Activity 2 Endocrine Systempt09651934948No ratings yet
- Major Endocrine Gland: Cerebrospinal Fluid) - The Pineal Gland Also Produces Another Hormone Called "Serotonin"Document5 pagesMajor Endocrine Gland: Cerebrospinal Fluid) - The Pineal Gland Also Produces Another Hormone Called "Serotonin"Goal Digger Squad VlogNo ratings yet
- 人脑图谱 PDFDocument1 page人脑图谱 PDFzmNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument55 pagesEndocrineKolapo SanusiNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan To Online 5Document522 pagesPembahasan To Online 5vanadiel4No ratings yet
- Post-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesPost-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanCyrus De AsisNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Function TestsDocument29 pagesThyroid Function TestsAkwesaNo ratings yet
- Oral - Medicine Book ListDocument334 pagesOral - Medicine Book ListSrinivas HarikrishnanNo ratings yet
- Thyroid NodulesDocument7 pagesThyroid Noduleshossein kasiriNo ratings yet
- Assesment of NormalDocument5 pagesAssesment of NormalmirazNo ratings yet
- DR Ananta Thyroid SlideDocument73 pagesDR Ananta Thyroid SlideRoshan Kumar PanditNo ratings yet
- Head to Toe Assessment Define Key TermsDocument33 pagesHead to Toe Assessment Define Key TermsBryan Neil Garma100% (1)
- Anaesthesia For Thyroid SurgeryDocument19 pagesAnaesthesia For Thyroid SurgeryPraveen Ramasamy0% (1)
- AP-2 Lab Report - Lab 01 The Endrocine SystemDocument15 pagesAP-2 Lab Report - Lab 01 The Endrocine Systemrcdunfee86% (7)
- Approach To A Patient With "Solitary Thyroid Nodule" (STN)Document6 pagesApproach To A Patient With "Solitary Thyroid Nodule" (STN)Jacob Alexander MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Clinical Biochemistry Part 1 exam questionsDocument14 pagesClinical Biochemistry Part 1 exam questionsكن مع الله100% (1)
- Result of Hyperthyroidism: Sumber: Mayo ClinicDocument9 pagesResult of Hyperthyroidism: Sumber: Mayo ClinicChrisNo ratings yet
- Steps in The Synthesis and Secretion of Thyroid Hormone: Process Diagrams Step-by-StepDocument9 pagesSteps in The Synthesis and Secretion of Thyroid Hormone: Process Diagrams Step-by-Steprambabs369No ratings yet
- Endocrine DisorderDocument5 pagesEndocrine DisorderMenly SusadaNo ratings yet
- Treatment For Benign Thyroid Nodules With A CombinDocument7 pagesTreatment For Benign Thyroid Nodules With A CombindarthjesussithNo ratings yet
- MNLS Daily RoutineDocument8 pagesMNLS Daily RoutinePratibha RamasahayamNo ratings yet
- DEBOLDocument317 pagesDEBOLalehegn belete100% (5)
- Labreportnew - 2022-12-17T172351.750Document1 pageLabreportnew - 2022-12-17T172351.750Himanshu MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Test DocumentDocument156 pagesTest DocumentBob M100% (3)
- Intercollegiate MRCS SyllabusDocument88 pagesIntercollegiate MRCS Syllabuskelly_ann23No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hyperthyroidism and Thyroid StormDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Hyperthyroidism and Thyroid StormPen MontanteNo ratings yet
- Iodine PH Oxygen and CancerDocument4 pagesIodine PH Oxygen and CancerAndrew DuntonNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsDocument16 pagesPharmacology of Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsVikas Viki100% (1)
- Endocrine DisordersDocument77 pagesEndocrine Disordersahmad100% (2)
- Endocrine System Notes - NCERT BasedDocument8 pagesEndocrine System Notes - NCERT Basedpallab mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Immunopath bms3Document31 pagesEndocrine Immunopath bms3Kato CalebNo ratings yet
- Immunology Report: Test Is Carried Out by Maglumi-2000 PlusDocument1 pageImmunology Report: Test Is Carried Out by Maglumi-2000 PlusKH. A. H. M. SAYEF 1706024No ratings yet
- Clinical Endocrinology of Dogs Cats PDFDocument353 pagesClinical Endocrinology of Dogs Cats PDFsanjagruborovicNo ratings yet