Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Manual Lab 2 (Electrical Wiring) F
Uploaded by
Ahmad KhaidirOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Manual Lab 2 (Electrical Wiring) F
Uploaded by
Ahmad KhaidirCopyright:
Available Formats
KEE2353/A221
KEE2353
ENGINEERING PRACTICE
(AMALAN KEJURUTERAAN)
SEMESTER I ACADEMIC SESSION 2022/2023
DATE: OCTOBER 2022 ASSESSMENT: LAB 2
ELECTRICAL WIRING
PROGRAMME ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
GROUP ID GB1
STUDENT'S NAME AHMAD KHAIDIR BIN SALIHUDIN
STUDENT'S ID 1202075
STUDENT'S NAME LUQMAN HAKIM BIN JAMALUDIN
STUDENT'S ID 1202085
STUDENT'S NAME MUHAMMAD ANWAR HAIQAL BIN EMRAN
STUDENT'S ID 1202079
HAKCIPTA TERPELIHARA USIM
1
KEE2353/A221
Title: Electrical Wiring
Objective:
1. Recognize the electrical wiring diagram and installation procedure.
2. Connect cables/wires to connected devices (e.g., fuse, switches, sockets,
lights, fans, etc.) and the main distribution board to demonstrate the electrical
wiring technique.
List of devices:
NO DEVICES FUNCTION SIZE IMAGE
1 Wiring tools Used to do the electrical
(Pliers,scre work like electrical wiring
wdriver,test installations by using this
pen,tape, tool we can do the -
Screw) installation of electrical
wire properly and quickly.
2 Wiring Provides a compact
board location/space for wiring
and the components.
-
3 Related Main devices that want to
devices use in the wiring.
(fluorescent 1.Fluorescent lamp- Used -
lamp, in lighting houses, shops,
switch, offices & the underground
socket, lamp
HAKCIPTA TERPELIHARA USIM
2
KEE2353/A221
holder) metro
2.Switch- Disconnect or
connect the conducting
path in an electrical circuit
3.Socket- Allow us to plug
in appliances to attach
them to the electrical grid
and provide power for
them to run
4.Lamp holder- To hold
the lamp
4 Cables/ To transfer electrical
wires energy to the point where
we want to connect the
load
-
5 Digital A digital multimeter, or
Multimeter DMM, measures and
verifies multiple electrical -
stimuli, including voltage,
current and resistance.
HAKCIPTA TERPELIHARA USIM
3
KEE2353/A221
Introduction:
The electrical installation of cabling and associated equipment in a structure, such as
switches, distribution boards, sockets, and light fittings, is known as wiring. A wiring
diagram is a graphical representation of an electric circuit in which the loop
components and signal connections between devices and the power source are
depicted as simplified shapes using established procedures. Understanding basic
wiring terminology and recognising the most prevalent types of wire and cable will
aid in the study and selection of wiring for new installation and remodelling projects.
During this lab session, students will be able to study various forms of electrical wire
networks, switching, electrical devices, and so on.This lab involves with one-way
switch,two-way switch,one outlet socket(radial connection) and one outlet
socket(ring connection) using of live wire,neutral and earth.
Procedures:
1. Before beginning the assignment, complete the Hazard Identification, Risk
Assessment, and Risk Control (HIRARC) form.
2. Before you begin circuit 1,2,3 and 4,make sure turn off the power to the
distribution box (DB) and any circuits that were previously active.
Figure 1
Circuit 1: Fluorescent Lamp
HAKCIPTA TERPELIHARA USIM
4
KEE2353/A221
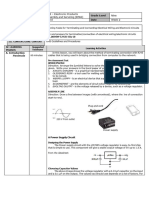
1. Connect a red wire (with a diameter of 1.5mm) from the fluorescent lamp to
the one-way switch. Connect the switch to the DB with another red wire.
Figure 1.1
2. Connect the green PVC insulated cable (earth wire) to any section of the light
casing as well as the DB/main switch. Because fluorescent lights have a
metal shell, they must have an earth wire. If there is a leak and no ground
wire, we may be shocked by electricity.
Figure 1.2
3. Finally, connect the natural wire, which is the black PVC-insulated cable, to
the lamp and the DB/main power supply and test the complete wiring as the
HAKCIPTA TERPELIHARA USIM
5
KEE2353/A221
figure 1.3.If the buzzer at multimeter make sound,that means our wire
connected.Test the complete wiring as per testing procedure.
Figure 1.3
Circuit 2: Two-way switch with two bulb
1. Connect a red wire (with a diameter of 1.5mm) between the L2 and L3 and
carry on with the connection to S2 and S3 to make junction.Then live wire
from S2 connected to DB as shown in figure 2.1
HAKCIPTA TERPELIHARA USIM
6
KEE2353/A221
Figure 2.1 Figure 2.2
Figure 2.1
2. Next, connected the earth wire(green wire) to E port of L2 and L3 to DB.It is
important to have earth wire to prevent electrical shocked if there was any
leakage happen.
3. Lastly, connected the natural wire(black wire) between the L2 and L3 to the
main supply.After that, test the complete wiring as per testing procedure.
Circuit 3: Socket Wiring (Radial connection)
1. Connect a red PVC insulated wire (diameter 2.5mm) from the L port inside S1 to
the miniature circuit breaker (MCB) inside the DB/main switch as the Live Wire.
Connect a wire of the same type between S1 and S2 in the L port.
Figure 3.1
HAKCIPTA TERPELIHARA USIM
7
KEE2353/A221
2. Next, connect the green PVC insulated cable (earth wire) to the E port of S1 and
to the DB/main switch. If there is any leakage and there is no earth wire, we
might get electricity shocked. Connect a same type wire between S1 and S2 in
E port.
3. Lastly, tie the natural wire which is the black PVC insulated cable to the N port
of S1 and S2 to the DB/main supply.Test the complete wiring as per testing
procedure.
Circuit 4: Socket Wiring (Ring connection)
1. Connect a red PVC insulated wire (diameter 2.5mm) which is live wire from L
port inside the S1 to the miniature circuit breaker (MCB) inside the
DB.Connected a same typed wire between the S1,S2,S3 and S4 in L port to
make junction.
2. After that, connected the earth wire(green wire) to the E port of S1 and the
DB.Connected a same type wire between the S1,S2,S3 and S4 in E port to
also make junction.
Figure 4.1
3. Lastly, tie the natural wire(black wire) to the N port of S1,S2,S3 and S4 to
make junction as the figure 4.1 to the main supply(DB).Test the wiring with
multimeter as the figure 1.3 to make sure the wire connected.Test the
complete wiring as per testing procedure.
HAKCIPTA TERPELIHARA USIM
8
KEE2353/A221
Testing procedure:
1. Make sure all the connections were connected and the wire were placed
correctly as figure 5 shown.
Figure 5
2. Switch off the electrical plug to avoid any bad incident happen.
3. Connected the wiring board to the 240V AC supply and turn on the DB.(This
procedure conducted by assistant engineers)
Figure 6
4. Checked the all devices that used such as lamp,buld and socket are works or
not.
HAKCIPTA TERPELIHARA USIM
9
KEE2353/A221
Figure 7
5. Switch off all electrical the switch/plug after checked all the wires are connected
and in good condition.
Data Acquisition:
Diameter of cable Colour Function
1.5mm Red(live),green(earth),black(neutral) To connect the
devices(lamp,plug,switc
h) to the main supply
1.5mm Red(live),green(earth),black(neutral) To connect the
devices(lamp,plug,switc
h) to the main supply
Electrical wiring standard:
MS IEC 60038
- IEC standard voltages as the nominal voltage for the new low voltage supply
system in Malaysia which is 230/400V with a range of +10% and -6% at a frequency
of 50 Hz with a range of ± 1%, replacing the existing supply voltage which is
240/415V with a range of +5 % and -10% at the same frequency.
HAKCIPTA TERPELIHARA USIM
10
KEE2353/A221
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
CIRCUIT RESULT DISCUSSION
A one-way switch is the one
One-way switch which has two terminals and
allows the current to flow
only in one direction,For
example in the figure 8.1, a
one-way switch makes or
breaks an electric circuit by
using two terminals. When
the one-way switch makes
the connection, it is said to
be in ON state and the
Figure 8.1 current flows through it.
When the switch is in OFF
state, it breaks the circuit
and no current flows through
it.
A two-way switch is a type of
Two-way switch switch which has three
terminals. Basically, a two-
way switch is a combination
of two one-way switches in a
single unit as the figure 8.2
shown. The two-way switch
can conduct in either
directions.
When a two-way switch
conducts, one terminal is
Figure 8.2 connected to another, but
the third terminal has a
broken connection, i.e. all
the three terminals of a two-
way switch cannot be
connected together
HAKCIPTA TERPELIHARA USIM
11
KEE2353/A221
simultaneously.
A single cable (including live,
One outlet neutral, and earth wires)
socket(Plug) runs from the consumer unit
13A(Radial or fusebox to each socket
connection) outlet in turn. Each socket
outlet is powered by the one
before it.
The final plug outlet is easily
recognisable because it only
has one cable connecting to
Figure 8.3 it as shown in figure 8.3.
Radial circuit faults are
simple to locate. If a break
occurs anywhere along the
cable, all of the socket
outlets following the break
will no longer function.
A ring circuit begins similarly
One outlet to a radial circuit, but a cable
socket(Plug) from the last socket outlet
13A(Ring links back to the consumer
connection) unit. There are two cables
linked to each of the socket
outlets, and there is no 'end'.
They are a good technique
to save cable because the
cables can be smaller than
an equivalent radial and
share the load.
The main issue occurs when
the ring is broken, either due
Figure 8.4 to weak connections or faulty
circuit adjustments. This can
cause the cable to become
overloaded because all of
the socket outlets will
continue to function normally
while being powered by a
single wire.This circuit
shown in figure 8.4
HAKCIPTA TERPELIHARA USIM
12
KEE2353/A221
Safety and Health issues
Electricity has the potential to kill or severely harm individuals as well as inflict
property damage. However, you may dramatically reduce the danger of injury to
yourself, your workers, and others by taking simple measures when working with or
around electricity and electrical equipment. These precautions are summarised in
this section.
The main hazards of working with electricity are:
electric shock and burns from contact with live parts
injury from exposure to arcing, fire from faulty electrical equipment or
installations
explosion caused by unsuitable electrical apparatus or static electricity
igniting flammable vapours or dusts, for example in a spray paint booth
Electric shocks can also lead to other types of injury, for example by causing a fall
from ladders or scaffolds and others.
You must ensure an assessment has been made of any electrical hazards, which
covers:
who could be harmed by them
how the level of risk has been established
the precautions taken to control that risk
The risk assessment should examine the type of electrical equipment utilised, how it
is used, and the environment in which it is used.
You must ensure that the electrical installation and equipment are both:
suitable for its intended use and the operating conditions
only used for its intended purpose
Unsuitable equipment can become alive in damp environments, causing its
surrounds to become alive as well. Fuses, circuit breakers, and other devices must
be properly rated for the circuit they are supposed to protect. Keep isolators and
fuse-box enclosures closed and, if feasible, locked.
HAKCIPTA TERPELIHARA USIM
13
KEE2353/A221
Conclusion:
In conclusion, this practical teaches you how to construct a 13A plug outlet socket
circuit (radial circuit connection),ring connection a one-way switch and two-way
switch. Furthermore, we distinguish three sorts of cables: live (red), neutral (black),
and earth (green). We can also employ equipment appropriate for the purpose.
Among the tools are a test pen, a wire cutter, and pliers. We can also learn
something new about wiring in an efficient and safe manner. We also understand
how the socket works.Aside from that, we learned about the safety precautions that
must be taken in the lab to avoid any unintended consequences. We can also use
proper instruments to read the findings and determine the presence of electricity.
HAKCIPTA TERPELIHARA USIM
14
You might also like
- Group 4 ReportDocument5 pagesGroup 4 ReportMacrey BwaleiNo ratings yet
- Det1022 PW3Document9 pagesDet1022 PW3Muhammad FaissalNo ratings yet
- Electrical WiringDocument11 pagesElectrical WiringRasydan AliNo ratings yet
- LO 1:-Plan and Prepare To Construct/ Electrical/electronic CircuitsDocument36 pagesLO 1:-Plan and Prepare To Construct/ Electrical/electronic CircuitsLeta SKNo ratings yet
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Module 24 SAHITA Electrical InstallationDocument16 pagesModule 24 SAHITA Electrical InstallationLungisaniNo ratings yet
- Emw Final ReportDocument25 pagesEmw Final ReportOm BankarNo ratings yet
- Domestic InstallatiuonDocument10 pagesDomestic InstallatiuonJoseph MvurachenaNo ratings yet
- Broken Wire Detector Circuit Using IC CD4069Document40 pagesBroken Wire Detector Circuit Using IC CD4069olawale gbadebo100% (1)
- Lab ReportDocument11 pagesLab Report10. Amni DamiaNo ratings yet
- List of Experiments: Ge8261-Engineering Practices Laboratory - Group BDocument57 pagesList of Experiments: Ge8261-Engineering Practices Laboratory - Group BJeeva RathnamNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL INSTALLATIONS Task1Document7 pagesELECTRICAL INSTALLATIONS Task1Akmal HazimNo ratings yet
- Bài 2,3 Thí Nghiệm Trang Bị ĐiệnDocument37 pagesBài 2,3 Thí Nghiệm Trang Bị ĐiệnNguyen TrongNo ratings yet
- Eet Sum NotesDocument4 pagesEet Sum NotesshondelB 5No ratings yet
- SRM IST, Kattankulathur - 603 203: Sub Code & Name: 18EES102L WORKSHOP LABDocument7 pagesSRM IST, Kattankulathur - 603 203: Sub Code & Name: 18EES102L WORKSHOP LABgautam KrishnaNo ratings yet
- SRM IST, Kattankulathur - 603 203: Sub Code & Name: 18EES102L WORKSHOP LABDocument7 pagesSRM IST, Kattankulathur - 603 203: Sub Code & Name: 18EES102L WORKSHOP LABgautam KrishnaNo ratings yet
- North South University: Lab 1: Ohm's Law, KVL, and Voltage Divider Rule Using Series CircuitDocument12 pagesNorth South University: Lab 1: Ohm's Law, KVL, and Voltage Divider Rule Using Series CircuitNazmul Hasan 1911742042No ratings yet
- Domestic Electrical WiringDocument4 pagesDomestic Electrical WiringSyed Showkath AliNo ratings yet
- Shri G.S. Institute of Technology & Science: Dept. of Electronics and Instrumentation EnggDocument20 pagesShri G.S. Institute of Technology & Science: Dept. of Electronics and Instrumentation EnggMUFADDAL MURABBI gs0801ei191039No ratings yet
- House Wiring ReportDocument9 pagesHouse Wiring ReportCovid VirusNo ratings yet
- BSD - M Odule 5Document38 pagesBSD - M Odule 5M MNo ratings yet
- 1901208-Engineering Practices Laboratory - EEE PDFDocument24 pages1901208-Engineering Practices Laboratory - EEE PDFSuryaraj C.KNo ratings yet
- Electrical House WiringDocument27 pagesElectrical House WiringMary JennyNo ratings yet
- EEE 141 Lab ManualsDocument45 pagesEEE 141 Lab Manualsjazz popNo ratings yet
- Wireless Ac Power Detector 1Document27 pagesWireless Ac Power Detector 1belacheweshetu222No ratings yet
- WS 1020Document44 pagesWS 1020Sunil Sree NathNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8&9-Electric and LightningDocument62 pagesLecture 8&9-Electric and LightningMuhammad FakhriNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Part-I Wiring Materials and Accessories - 094901Document45 pagesChapter-2 Part-I Wiring Materials and Accessories - 094901SegniNo ratings yet
- Electrical Wiring InstallationDocument11 pagesElectrical Wiring InstallationDurrahKhazalle100% (26)
- Chapter 3 - Wiring System and DistributionDocument65 pagesChapter 3 - Wiring System and DistributionMohamad Syahmi100% (1)
- Oel Lab Report Front Page - Level 2Document13 pagesOel Lab Report Front Page - Level 2Noradila RoslanNo ratings yet
- Commercial and Residential Electrical InstallationDocument15 pagesCommercial and Residential Electrical InstallationCovid VirusNo ratings yet
- CH-12 Electricity & Circuits PPT-2Document22 pagesCH-12 Electricity & Circuits PPT-2SUHANEERIYANo ratings yet
- Eim-9 Quarter IVDocument25 pagesEim-9 Quarter IVmanolito mercado jr.No ratings yet
- Iec Lab Report 1Document12 pagesIec Lab Report 1mahrabhasanchowdhury1No ratings yet
- Terminating, Connecting and Testing Electrical Wirings and Electronic CircuitsDocument4 pagesTerminating, Connecting and Testing Electrical Wirings and Electronic CircuitsCyril Joy N. Fernando50% (2)
- Department of Electronics and InstrumentationDocument15 pagesDepartment of Electronics and InstrumentationRajeshwariNo ratings yet
- Electrical System: Submitted By: Sumit Kumar 12BAC-022 Achal Gupta 12BAC043Document25 pagesElectrical System: Submitted By: Sumit Kumar 12BAC-022 Achal Gupta 12BAC043bharat vermaNo ratings yet
- Workshop Training Manual COURSE: WS1020: Central Workshop Indian Institute of Technology Madras CHENNAI - 600036, INDIADocument44 pagesWorkshop Training Manual COURSE: WS1020: Central Workshop Indian Institute of Technology Madras CHENNAI - 600036, INDIAhariharanhemanthNo ratings yet
- Electric Shock Proof Houses: C. PrabhakarDocument2 pagesElectric Shock Proof Houses: C. PrabhakarerpublicationNo ratings yet
- Det1022 PW2Document9 pagesDet1022 PW2Muhammad FaissalNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document12 pagesLab 1Sazid MohsinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Project: 1.1 AbstractDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Project: 1.1 AbstractTrupti WaghNo ratings yet
- Fire Alarm 09Document15 pagesFire Alarm 09Supriya Kolekar75% (4)
- Electronics 2 Lecture NotesDocument13 pagesElectronics 2 Lecture NotesRex LeopardNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - LEC CercuitDocument21 pagesUnit 1 - LEC CercuitBusico Aivan Kent NatsuNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 1Document9 pagesExperiment # 1majorskNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 Ist Circuit and ElectronicsDocument14 pagesLab 01 Ist Circuit and ElectronicsHammad GillNo ratings yet
- College of Information Technology Dmmmsu-Mluc City of San FernandoDocument9 pagesCollege of Information Technology Dmmmsu-Mluc City of San FernandoZoilo BagtangNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Introduction To Industrial Arts Part 2 (IEIAT - TLEHE8)Document8 pagesUnit 3 - Introduction To Industrial Arts Part 2 (IEIAT - TLEHE8)Vendivel KristineNo ratings yet
- Yildiz Technical University Department of Marine EngineeringDocument9 pagesYildiz Technical University Department of Marine EngineeringAyberk ArdıçNo ratings yet
- Electrical WiringDomest 8310585Document20 pagesElectrical WiringDomest 8310585Berry KasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 4 8 Watt Power AmplifierDocument15 pagesChapter 1 4 8 Watt Power AmplifierRonn Albert GabucayNo ratings yet
- TLE IA EP9 Week 2 RecoveredDocument4 pagesTLE IA EP9 Week 2 Recovereddainegarano64No ratings yet
- Electrical EquipmentDocument10 pagesElectrical EquipmentRica Jewel VistaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 2021Document66 pagesLab Manual 2021Rsarath KumarNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual Course Code: Ece 130 Course Title: Electrical and Electronics WorkshopDocument36 pagesLaboratory Manual Course Code: Ece 130 Course Title: Electrical and Electronics WorkshopDebashis PaulNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power Distribution & Utilization: Lab ManualDocument40 pagesElectrical Power Distribution & Utilization: Lab ManualUzair HussainNo ratings yet
- Dirty Dozen List of Endocrine DisruptorsDocument4 pagesDirty Dozen List of Endocrine DisruptorsMariuszNo ratings yet
- Technician's Instructions Estetica E30Document142 pagesTechnician's Instructions Estetica E30виктор100% (1)
- Minimum Number of Thermocouples-Local PWHTDocument5 pagesMinimum Number of Thermocouples-Local PWHTPradip Goswami100% (1)
- MoRTH 1000 Materials For StructureDocument18 pagesMoRTH 1000 Materials For StructureApurv PatelNo ratings yet
- Learnership AgreementDocument10 pagesLearnership Agreementkarl0% (1)
- MLT IMLT Content Guideline 6-14Document4 pagesMLT IMLT Content Guideline 6-14Arif ShaikhNo ratings yet
- DM - BienAir - CHIROPRO 980 - EngDocument8 pagesDM - BienAir - CHIROPRO 980 - Engfomed_twNo ratings yet
- What Is An Engineering Change OrderDocument3 pagesWhat Is An Engineering Change OrderKundan Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Rest Pfas Appendix g1 31097 enDocument51 pagesRest Pfas Appendix g1 31097 endasfNo ratings yet
- Electronic Fetal MonitoringDocument4 pagesElectronic Fetal MonitoringMauZungNo ratings yet
- CASE 1. Non-Cash Assets Are Sold For P 580,000Document3 pagesCASE 1. Non-Cash Assets Are Sold For P 580,000Riza Mae AlceNo ratings yet
- Giardiasis PDFDocument14 pagesGiardiasis PDFSaad Motawéa0% (1)
- Building Technology (CE1303) : Window: Lecturer: Madam FatinDocument19 pagesBuilding Technology (CE1303) : Window: Lecturer: Madam FatinRazif AjibNo ratings yet
- BrainPOP Nutrition Quiz242342Document1 pageBrainPOP Nutrition Quiz242342MathableNo ratings yet
- Melancholic PersonalityDocument5 pagesMelancholic PersonalityChris100% (1)
- தமிழ் உணவு வகைகள் (Tamil Cuisine) (Archive) - SkyscraperCityDocument37 pagesதமிழ் உணவு வகைகள் (Tamil Cuisine) (Archive) - SkyscraperCityAsantony Raj0% (1)
- Labor EstimateDocument26 pagesLabor EstimateAngelica CabreraNo ratings yet
- Unsaturated HydrocarbonsDocument84 pagesUnsaturated HydrocarbonsHey itsJamNo ratings yet
- MPX-200 Service Manual PDFDocument90 pagesMPX-200 Service Manual PDFvivijaNo ratings yet
- Shawarma Refers To The Middle Eastern Method Cooking Where Thin Slices of MeatDocument3 pagesShawarma Refers To The Middle Eastern Method Cooking Where Thin Slices of MeatColai's BcdNo ratings yet
- ReclosersDocument28 pagesReclosersSteven BeharryNo ratings yet
- HOME (2021) - Fransivan MacKenzieDocument21 pagesHOME (2021) - Fransivan MacKenzieFransivan MacKenzie100% (1)
- Fora Active Plus P 30 ManualDocument32 pagesFora Active Plus P 30 ManualBvcNo ratings yet
- T103 InstructionsDocument1 pageT103 Instructionsjtcool74No ratings yet
- Guarantor Indemnity For Illness or DeathDocument2 pagesGuarantor Indemnity For Illness or Deathlajaun hindsNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument17 pagesAmino AcidsSiddharth Rohilla100% (2)
- Unit 5.4 - Incapacity As A Ground For DismissalDocument15 pagesUnit 5.4 - Incapacity As A Ground For DismissalDylan BanksNo ratings yet
- NASA Corrosion of SS TubingDocument14 pagesNASA Corrosion of SS TubingClaudia Mms100% (1)
- Copy of HW UMTS KPIsDocument18 pagesCopy of HW UMTS KPIsMohamed MoujtabaNo ratings yet
- Radial Lead Varistors LA Varistor SeriesDocument13 pagesRadial Lead Varistors LA Varistor SeriesLeman SihotangNo ratings yet