Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English Modal Verbs
Uploaded by
LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
English Modal Verbs
Uploaded by
LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSCopyright:
Available Formats
ACTIVITY TYPE
Reading, Writing, Grammar, After going through your regular review and
Exercises teacher talk, tell the students that they’re going
to learn the English modal verbs.
LANGUAGE FOCUS
English modal verbs
AIM Make one copy of the worksheet for each student
To learn and practice the English
modal verbs
LEVEL
Give one copy of the worksheet to each student.
Beginner, Elementary, Intermediate, Go through the grammar and exercises together.
TIME
30 Minutes
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
Can and could are modal verbs. They are sometimes called modal
auxiliaries because they are generally used with another verb and help us
to understand that verb.
Examples of this auxiliary use are:
ability
permission
asking for something
General characteristics of can and could
They do not add -s in the 3rd person singular:
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
To make a question you don't have to use an auxiliary verb, just invert the
subject and the modal verb:
To make a negative sentence, add not or n't to the modal verb:
As said above, can and could are modal verbs, and modal verbs don't follow
the normal rules for verbs. For example, they don't have an infinitive or an
-ing form.
For this reason can and could are impossible to use when you need to use the
infinitive, the gerund or a continuous tense (though the continuous form
would be impossible anyway!).
Being modal verbs also means they don't necessarily have a form that can
be used for the past or the future, though in very general terms can is used to
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
refer to the present and could is used to refer to the past.
When you can't use can or could, you need to use a form of be able to. This
means exactly the same as can and could. Some examples:
Tense chart
To make things clearer, have a look at the chart below. It shows when you
can use can, could and be able to.
Remember that be able to can always be used, but that English speakers use
can and could whenever they can. Be able to sounds more formal and not
English.
present simple can am/are/is able to
present continuous ------ ------
past simple could was/were able to
past continuous ------ ------
present perfect ------ has/have been able to
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
past perfect ------ had been able to
future ------ will be able to
infinitive ------ (to) be able to
gerund ------ being able to
conditional could would be able to
Notes about tenses
The chart above is only intended as a rough guide. As always with English
verbs, a lot of the time the tense you use depends on what you're talking
about.
For example, can can be used to refer to timetables or schedules in the
future, just as the present simple is used normally:
When talking about the past there's a difference between could and
was/were able to: could is used in a more general sense while was/were
able to is used to talk about more specific occasions:
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
However, when you talk about the past in the negative couldn't and
wasn't/weren't able to are completely interchangeable:
The conditional forms are also interchangeable:
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
We use modal verbs of deduction to express degrees of
certainty about the present and the past - what we are or
are not sure/certain about and what we think may or may
not be true/possible.
1. To express certainty, we use must in the positive and can't in the
negative.
2. To express possibility, we use may, might, could in the positive and
may not, might not (shot forms not usual), in negative.
Modal verbs of deduction with the Present Infinitive
are used for expressing degree of certainty about the
present when we are deducing and supposing about a
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
present event.
Modal verbs of deduction with the Past Participle are
used for expressing degree of certainty about the past when
we are deducing and supposing now about an event in the
past.
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
"Have to" and "must" usually mean the same thing: there is no choice
about something, and you are forced to do it. However, the negatives
of these two modals mean different things. "Don't have to" is different
from "mustn't":
means that something is
Don't not necessary, but you
have to can do it if you want to --
it's up to you.
means that something is
not allowed; it is
Mustn't
forbidden, and you
definitely shouldn't do it.
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
EXERCISE 1.
Write questions using “can”
e.g. Where are my glasses?
Can you see my glasses?
1. Where’s my car? ______________________________
2. Where’s the cat? ______________________________
3. Where’s the door? ______________________________
4. Where are the flowers? ______________________________
5. Where are my shoes? ______________________________
EXERCISE 2.
Write questions using the prompt
e.g. a cup of coffee
Can I have a cup of coffee, please?
1. a beer ______________________________
2. some butter ______________________________
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
3. some fruit ______________________________
4. some salt ______________________________
5. a sausage ______________________________
6. some sugar ______________________________
EXERCISE 3.
Write sentences using the prompt
e.g. drink coffee / smoke
I can drink coffee but I cannot smoke
1. eat some fruit / eat this sausage
____________________________________________
2. remember his face / remember his name
____________________________________________
3. drive a car / drive a bus
____________________________________________
4. ride a bicycle / drive a car
____________________________________________
5. have a shower / have a bath
____________________________________________
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
EXERCISE 4.
Write short answers with can
e.g. Can you come alone? No, …
No, I can’t
1. Can I read this book? Yes, ____________________________
2. Can they use the computer? No, ________________________
3. Can I ask you a question? No, __________________________
4. Can you hear me? Yes. _______________________________
5. Can I have your telephone number? No, __________________
6. Can he spell his name? Yes, ___________________________
EXERCISE 5.
Write true sentences about yourself using the following information.
Speak English run fast swim 1km drive a
car
Ride a motorbike ride a horse
play the piano
e.g. I can drive a car
I can’t ride a motorbike.
1.
_______________________________________________________
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
2.______________________________________________________
3.______________________________________________________
4.______________________________________________________
5.______________________________________________________
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
CAN + VERB OF SENSE
The human body has 5 senses; touch, taste, sight, hearing, and smell. The
corresponding verbs are to feel, to taste, to see, to hear, and to smell. These
verbs are combined with can to tell another person what our senses are
doing.
EXERCISE 1.
Use can and a verb of sense to complete the following sentences.
e.g. I can smell gas! The oven hasn’t been turned off properly.
1. I with my eyes.
2. I with my nose.
3. I with my ears.
4. I with my tongue.
5. I something when I touch it or it touches me.
EXERCISE 2.
Complete the following sentences by using can/can’t and the correct verb
of sense.
e.g. I can taste salt when I swim in the sea.
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
1. When I sit in Hyde Park, I the birds chirping in the trees.
2. If Trevor walks in the dark he anything.
3. From the top of the Empire State building I the
skyline of New York.
4. She the roses because she is ill and has a runny nose.
5. you the heat of the sun on your skin?
6. This apple pie is very good! I the cinnamon in it.
7. There is so much noise here that I what you are saying.
8. I burning! Is the cake still baking in the oven?
9. Her arm is asleep. She anything in her fingers.
10. you the rosemary I put in this recipe?
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
EXPLANATION
Maybe is an adverb and it can be considered a synonym of perhaps. It
transmits the idea of possibility, the idea that something is probable, that
something can happen.
EXERCISE 1
e.g. They (to like) her.
Maybe they’ll like her, maybe they won’t.
1. She (to tell) her.
_____________________________________________________
2. He (to ask) her out.
_____________________________________________________
3. They (to go) to the seaside.
_____________________________________________________
4. She (to marry) Peter.
_____________________________________________________
5. It (to explode).
_____________________________________________________
6. We (to sing) together.
_____________________________________________________
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
7. You (to go) to London next week.
_____________________________________________________
8. They (to have) children.
_____________________________________________________
9. Steve (to win) the race.
_____________________________________________________
10. You (to pass) your Level Test.
_____________________________________________________
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
We use must when we are sure that something is true.
e.g. That French restaurant over there must be very good. It’s always full of
people.
We use might when we are sure that something is possible.
EXERCISE 1.
Complete the sentences with “must” or “might”.
e.g. She might have arrived. I’m not sure.
The doorbell has just rung. I’m expecting my mother now, so it must be her.
1. We haven’t got enough food, we _______ go shopping.
2. I don’t have any plans for tonight, so I ________ go to the theatre
this evening.
3. My room is dirty. I ________ clean it.
4. Paul is not at home, he ________ be working.
5. I ________ see you tomorrow, but I’m not sure, because I
_________ have to go to Frankfurt on business.
6. She ________ go to the bank today. She hasn’t got any money.
7. I’m not sure but for my holiday I __________ go to Spain.
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
8. It’s a fantastic movie. You ______ see it!
9. It’s cloudy. It ______ rain.
10. If you want to go to university you _______ pass the last exam!
11. Where is Ann? We have a meeting now! She __________ be in her
office.
12. What happened to Peter? I thought he would be at home by now,
he promised that he would be here by 8.30. He _________ have had an
accident!
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
EXERCISE 1.
Use MUST CAN’T or MIGHT
e.g. She speaks Italian with English accent. She might be Irish
1.She has been studying all day. She……………………..be very tired.
2.Your pub ……………………….be good. It’s usually full of people.
3.You haven’t lived in Rome for long . You………………know many people.
4. He always wears a uniform. He ………………………… be a nurse
5. Mark isn’t at work today. He…………………be sleeping.
6.Jim knows a lot about literature. He……………………..read a lot.
7. Robert is in a very difficult situation. It…………………….be easy for him.
8.Their restaurant ………………………….be very good. It’s often empty.
9. Mary failed her exam. She ………………… have studied very much
10. Robert is a little pale. He ……………………… have health problems
EXERCISE 2.
Use the words in brackets to write sentences with MUST HAVE
1. I haven’t seen my neighbours for ages. (They / go away)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
2. I can’t find my glasses. (I /leave/them in my office yesterday)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
3. They knew everything about our holiday in France. ( They / listen / to
our conversation)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
4. Tom has rung the doorbell several times but nobody has answered .
(They/ go out)
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
5. I’ve lost my keys. (I / drop / them somewhere)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
EXERCISE 1.
Complete the sentences by using the correct form of could or be able to.
e.g. I could run very fast when I was a schoolboy.
1. Tom_______________ play football very well some years ago.
2. Jenny was an excellent player but that day Susan ______________
beat her.
2. Ask me about your problem. I should_______________ give you a
hand.
3. My secretary ________________type 100 words a minute .
4. His father _________________speak five languages.
5. My brother _______________sing very well and studied to become an
opera singer.
6. During the flight, the pilot had a heart attack. None of the
passengers______pilot a plane but Mary____________ land safely.
7. Did you enjoy the concert? Oh… unfortunately I____________ hear
very well.
9. Jodie _________________repair cars, so she _______________start
the engine again after the accident.
10. As a child, Sally ____________ write with her left hand.
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
EXERCISE 1.
Complete the sentences by putting in must, may or might.
e.g. You’ve been working all day. You must be very tired.
1. James isn’t answering the phone. He __________ be out.
2. “I can’t find Tom. Have you seen him?” – “He __________ be in the
canteen”.
3. It’s very cloudy. It __________ rain.
4. “Whose pen is this?” – “I don’t know. It __________ belong to Maggie”.
5. That pub __________ be very good. It’s always full of people.
6. “Where’s Jack?” – “He __________ be in his office”.
7. Don’t make too much noise. You __________ wake the baby.
8. You didn’t have lunch. You __________ be hungry.
9. Jim’s work __________ be very boring. He does the same things every
day.
10. “Who is that girl with Bob?” – “Ask Sheila. She __________ know.
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
EXERCISE 2.
Read the situations and use the words in brackets to write sentences with
must have, may have and might have.
e.g. I can’t find my keys anywhere.
(I / leave / them /at work). I might have left them at work.
1. It’s 6.30. Sarah was supposed to meet us at 6.00.
(Something / delay / her).
_______________________________________
2. Susan and Paul are not at home.
(They / go / away / for the weekend).
______________________________
3. A woman phoned for you, but she didn’t give her name.
(She / be/ Emma).
_____________________________________________
© 2021 Language Advisor. All Rights Reserved
You might also like
- Modules For Week 1 5Document15 pagesModules For Week 1 5shenahmaecrisbarrogaNo ratings yet
- Expressing Ability in EnglishDocument15 pagesExpressing Ability in EnglishOlivia BoboNo ratings yet
- Guidelines English II Task 2 (Local Issues and Possible Solutions) Semestre 2020-IIDocument4 pagesGuidelines English II Task 2 (Local Issues and Possible Solutions) Semestre 2020-IIAnitaAvilaNo ratings yet
- English 9-Q1-W1-W2-M1Document13 pagesEnglish 9-Q1-W1-W2-M1Maristel C. RebuyasNo ratings yet
- Section 2 GrammerDocument13 pagesSection 2 GrammerAhlamRahoumaNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs Semana 1Document11 pagesModal Verbs Semana 1IvanNo ratings yet
- Learn About Modal Verbs and Their UsesDocument4 pagesLearn About Modal Verbs and Their UsesericNo ratings yet
- English Booklet 7° Fourth Term (2022)Document15 pagesEnglish Booklet 7° Fourth Term (2022)Alberto ConstruyeNo ratings yet
- Test English - Prepare For Your English ExamDocument1 pageTest English - Prepare For Your English Examchaneld708No ratings yet
- Eapp Week1Document6 pagesEapp Week1Ian Jay Enriquez CamanayNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument157 pagesPDFSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- English 5: Let's Distinguish Them!Document10 pagesEnglish 5: Let's Distinguish Them!janine mancanesNo ratings yet
- English 5: Let's Distinguish Them!Document11 pagesEnglish 5: Let's Distinguish Them!Vhalerie MayNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 1 - Module 2Document14 pagesEnglish: Quarter 1 - Module 2GLORIFIE PITOGONo ratings yet
- Modal VerbsDocument10 pagesModal Verbsana marques100% (1)
- ENGLISH_GR.6_ADM_Q4_M9_MODULE5Document4 pagesENGLISH_GR.6_ADM_Q4_M9_MODULE5Vangie SolanoNo ratings yet
- Emphasis Words and ExpressionsDocument4 pagesEmphasis Words and ExpressionsMae Ann PiorqueNo ratings yet
- ENG9Quarter1Week1 2Document6 pagesENG9Quarter1Week1 2Nelle SndvlNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 1: Module in Modal Verbs, Nouns, and AdverbsDocument10 pagesEnglish: Quarter 1: Module in Modal Verbs, Nouns, and AdverbsJoy OcampoNo ratings yet
- Workbook Kids Level 8Document19 pagesWorkbook Kids Level 8Maritza arteaga100% (1)
- Modals: Composing Clear Sentences Using Appropriate Grammatical StructureDocument6 pagesModals: Composing Clear Sentences Using Appropriate Grammatical Structurepot poootNo ratings yet
- Cohesive DevicesDocument5 pagesCohesive DevicesMargielyn Tiburcio Marte - AngayNo ratings yet
- 5-Day Vocabulary Teaching Plan: Introduce Target Vocabulary in ContextDocument29 pages5-Day Vocabulary Teaching Plan: Introduce Target Vocabulary in ContextAlina RadescuNo ratings yet
- Verb Patterns: Student's InformationDocument5 pagesVerb Patterns: Student's InformationLUIS RAMSES RAMIREZ CRUZ100% (1)
- Eng10 Q1 Mod10 Discourse Markers Generalization Version 3 PDFDocument56 pagesEng10 Q1 Mod10 Discourse Markers Generalization Version 3 PDFEdzNo ratings yet
- Learn how to use the modal verb CAN for abilityDocument2 pagesLearn how to use the modal verb CAN for abilityDAVID ROMERONo ratings yet
- Modal Auxiliary VerbsDocument6 pagesModal Auxiliary VerbsKhg XmanxNo ratings yet
- 43 Exam B2.1 December 2021Document5 pages43 Exam B2.1 December 2021Pedro GarcíaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 - Present - Present ContinuousDocument21 pagesUNIT 1 - Present - Present ContinuousOliver TorresNo ratings yet
- Assessment Upper IntermediateDocument5 pagesAssessment Upper IntermediateRed AmoresNo ratings yet
- Eng101 Extra WorksheetDocument4 pagesEng101 Extra WorksheetбулбулNo ratings yet
- Module Enriching Your VocabularyDocument15 pagesModule Enriching Your VocabularyJhon Renren LogatocNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris..Document12 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris..Sintiya Yunisyah SiregarNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs ExplainedDocument12 pagesModal Verbs ExplainedSintiya Yunisyah SiregarNo ratings yet
- Anthology 2ND SemesterDocument138 pagesAnthology 2ND SemesterJuana GómezNo ratings yet
- Paraphrasing Nominalization SS.Document7 pagesParaphrasing Nominalization SS.Ahmet AtakanNo ratings yet
- Can-Modal Explanationtosha PDFDocument9 pagesCan-Modal Explanationtosha PDFCamila Moreno RomeroNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide Eng 9 Week 2Document8 pagesLearning Guide Eng 9 Week 2Juvelyn Abugan LifanaNo ratings yet
- English With Fluency Academy PlansDocument10 pagesEnglish With Fluency Academy PlansnearhirumaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-4 Test Listening and Reading AssessmentDocument10 pagesUnit 3-4 Test Listening and Reading AssessmentNGÂN HUỲNH TƯỜNGNo ratings yet
- EAPP SHS Module 1Document6 pagesEAPP SHS Module 1Hanna Theresa Frias RamosNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Strategies for Academic SuccessDocument110 pagesReading Comprehension Strategies for Academic SuccessAinun MaksuraNo ratings yet
- G8 ACTIVITIES Week 6-7Document4 pagesG8 ACTIVITIES Week 6-7danica baguiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1Munjaroh Dwi SNo ratings yet
- Taller Clase 6 y 7 TerminadoDocument11 pagesTaller Clase 6 y 7 TerminadoJIMMY ALBERTO CASTANEDA HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- Activity Type: Reading, Writing, Grammar, ExercisesDocument16 pagesActivity Type: Reading, Writing, Grammar, ExercisesMinh Lý TrịnhNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Inglés II Task 1 (What Is Coming in 10 Years) INGLÉS.Document3 pagesGuidelines Inglés II Task 1 (What Is Coming in 10 Years) INGLÉS.jhon jairo ortega monteroNo ratings yet
- Level 1 6.2 Lesson Plan: Session 1Document8 pagesLevel 1 6.2 Lesson Plan: Session 1RebeccaSulivanNo ratings yet
- Using Adverbs of Manner EffectivelyDocument18 pagesUsing Adverbs of Manner EffectivelyDom Ricafranca CuetoNo ratings yet
- Can Could SpecialDocument4 pagesCan Could SpecialShameerNo ratings yet
- CELTA Assignment 1 - Focus On The Learne NatalieDocument10 pagesCELTA Assignment 1 - Focus On The Learne NatalieNatalie TaoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English 10aDocument20 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English 10aMelbayne AglugubNo ratings yet
- Level I Unit 1 Personal Info ExchangeDocument6 pagesLevel I Unit 1 Personal Info ExchangePaula MendozaNo ratings yet
- Week 16 - Basic EnglishDocument24 pagesWeek 16 - Basic EnglishFederico Alberto Campos SotoNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs Guide for Ability, Requests & ObligationsDocument10 pagesModal Verbs Guide for Ability, Requests & ObligationskandaomenaiNo ratings yet
- Grade5 English Q2 W2 GLAKDocument12 pagesGrade5 English Q2 W2 GLAKBe MotivatedNo ratings yet
- Workbook ENGLISH CLASSDocument71 pagesWorkbook ENGLISH CLASSNilbia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Starfall's Sing-Along Volume TwoDocument27 pagesStarfall's Sing-Along Volume TwoLUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Addition and Counting On For Our Brilliant Kids 10Document3 pagesAddition and Counting On For Our Brilliant Kids 10LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- 5280 Magazine - October 2021Document138 pages5280 Magazine - October 2021LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Starfall's Sing-Along Volume 1 and 2Document50 pagesStarfall's Sing-Along Volume 1 and 2LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- 800 Operational MathematicsDocument57 pages800 Operational MathematicsLUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Australian Bartender - March 2021Document70 pagesAustralian Bartender - March 2021LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Archaeology - November-December 2021Document72 pagesArchaeology - November-December 2021LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOS100% (1)
- Amateur Photographer - 02 October 2021Document70 pagesAmateur Photographer - 02 October 2021LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- American Fine Art - September-October 2021Document102 pagesAmerican Fine Art - September-October 2021LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Aesthetic Medicine - July-August 2021Document88 pagesAesthetic Medicine - July-August 2021LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Airsoft International - Volume 17 Issue 6 - 23 September 2021Document82 pagesAirsoft International - Volume 17 Issue 6 - 23 September 2021LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Australian Bartender - March 2021Document70 pagesAustralian Bartender - March 2021LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Airsoft International - Volume 17 Issue 6 - 23 September 2021Document82 pagesAirsoft International - Volume 17 Issue 6 - 23 September 2021LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- American Fine Art - September-October 2021Document102 pagesAmerican Fine Art - September-October 2021LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Troy Thomas Poussin S Women Sex and Gender in The Artist S Works 2020Document387 pagesTroy Thomas Poussin S Women Sex and Gender in The Artist S Works 2020LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Aesthetic Medicine - July-August 2021Document88 pagesAesthetic Medicine - July-August 2021LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- 5280 Magazine - October 2021Document138 pages5280 Magazine - October 2021LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Archaeology - November-December 2021Document72 pagesArchaeology - November-December 2021LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOS100% (1)
- Reeves - Twentieth-Century America - A Brief History (1999) PDFDocument322 pagesReeves - Twentieth-Century America - A Brief History (1999) PDFEn T100% (1)
- Amateur Photographer - 02 October 2021Document70 pagesAmateur Photographer - 02 October 2021LUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Robert Silverberg VenustrapDocument12 pagesRobert Silverberg VenustrapLUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Sara Douglass The Evil WithinDocument33 pagesSara Douglass The Evil WithinLUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Juleen Brantingham PatternsDocument20 pagesJuleen Brantingham PatternsLUIZ ANTONIO DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous Tense ExercisesDocument3 pagesPresent Continuous Tense Exercisesreg4share01No ratings yet
- BK Acx0 152509Document184 pagesBK Acx0 152509AngelNo ratings yet
- Learning Package in English 7: Aint JosephDocument49 pagesLearning Package in English 7: Aint JosephRowinNo ratings yet
- Final Presentation300Document30 pagesFinal Presentation300Aisha RehnumaNo ratings yet
- My English LabDocument95 pagesMy English LabELIZABET SOFIA PEREIRA LONDOãO100% (1)
- More Phrase Structure Rules: The Predicate of A SentenceDocument24 pagesMore Phrase Structure Rules: The Predicate of A SentenceSyr Rubio LptNo ratings yet
- P.3 Grammar NotesDocument19 pagesP.3 Grammar Notesice200mNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Voice, Conditional Sentence & Reported SpeechDocument22 pagesActive and Passive Voice, Conditional Sentence & Reported SpeechTrịnh Quốc HiếuNo ratings yet
- Brain Control American English Upper Intermediate Advanced GroupDocument3 pagesBrain Control American English Upper Intermediate Advanced GroupElio MateusNo ratings yet
- Year 5 Simplified SowDocument34 pagesYear 5 Simplified SowiqadinNo ratings yet
- Students Book Level 6 PDFDocument40 pagesStudents Book Level 6 PDFAlejandro RojasNo ratings yet
- ESOL Bibliography Provides References for Teaching EnglishDocument57 pagesESOL Bibliography Provides References for Teaching EnglishJoelNo ratings yet
- Verb Phrase (VP) : Intransitive: David Smokes Transitive: David Smokes CigarsDocument6 pagesVerb Phrase (VP) : Intransitive: David Smokes Transitive: David Smokes CigarsIvana LeševićNo ratings yet
- INGLÉS Vepre UncpDocument33 pagesINGLÉS Vepre UncpEduardo Manuel Peralta SalomeNo ratings yet
- Guide to English Grammar StructuresDocument224 pagesGuide to English Grammar Structurescantor2000100% (1)
- Grammar Guide to Auxiliary Verbs and NegativesDocument15 pagesGrammar Guide to Auxiliary Verbs and NegativesNawel ZoghlamiNo ratings yet
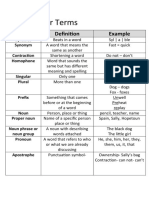
- Grammar Terms Vocab ListDocument3 pagesGrammar Terms Vocab ListMollyNo ratings yet
- Tarea Ingles ValeriaDocument8 pagesTarea Ingles ValeriaJovani Christ Alejo67% (6)
- Past TensesDocument57 pagesPast TensesValentina ValenciaNo ratings yet
- B 1 Student's Book (To Print Out)Document170 pagesB 1 Student's Book (To Print Out)Jorge Sempertegui MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Understand Sentence StructureDocument28 pagesUnderstand Sentence StructureMario AlvaroNo ratings yet
- 100 Golden Rules of English Grammar For Error DetectionDocument13 pages100 Golden Rules of English Grammar For Error DetectionShivamSinghNo ratings yet
- Development of Algorithms and Computational Grammar For UrduDocument262 pagesDevelopment of Algorithms and Computational Grammar For UrduDrJafarRizviNo ratings yet
- Grammar Notes For Lesson 11: 1. Formulations With The Te-FormDocument19 pagesGrammar Notes For Lesson 11: 1. Formulations With The Te-FormGab ServacioNo ratings yet
- Simple Present and Present Progressive Tenses ExplainedDocument69 pagesSimple Present and Present Progressive Tenses ExplainedDaniel Sergio QCNo ratings yet
- Morphology Word FormationDocument34 pagesMorphology Word FormationkrostinichuNo ratings yet
- Understanding English Sentence ConstructionDocument24 pagesUnderstanding English Sentence ConstructionEvinda SulistianiNo ratings yet
- The Time WebDocument2 pagesThe Time WebRita OteroNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan VerbDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan VerbHanna MikangcrzNo ratings yet
- Questions For Reading Text Meeting 3 English For ArchitectureDocument3 pagesQuestions For Reading Text Meeting 3 English For ArchitectureAnonymous CbIIJLUJNo ratings yet