0% found this document useful (0 votes)
406 views1 pageEarth Potential Rise Test
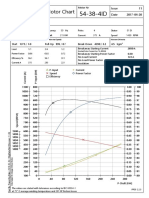
1. The Earth Potential Rise test determines the maximum potential of an earthing installation relative to remote earth under fault conditions. This is done by measuring the voltage between the installation and a remote earth point using the Fall of Potential method.
2. The test injects an off-frequency current into a remote earth and measures the voltage between that earth and the installation earth at increasing distances. A plateau in the voltage readings indicates the maximum Earth Potential Rise.
3. Factors like cable separation, injection point distance, and earthing system impedance must be considered to minimize induced voltages from the injection current and obtain accurate readings.
Uploaded by
nitinrajuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
406 views1 pageEarth Potential Rise Test
1. The Earth Potential Rise test determines the maximum potential of an earthing installation relative to remote earth under fault conditions. This is done by measuring the voltage between the installation and a remote earth point using the Fall of Potential method.
2. The test injects an off-frequency current into a remote earth and measures the voltage between that earth and the installation earth at increasing distances. A plateau in the voltage readings indicates the maximum Earth Potential Rise.
3. Factors like cable separation, injection point distance, and earthing system impedance must be considered to minimize induced voltages from the injection current and obtain accurate readings.
Uploaded by
nitinrajuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd