Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Contemp Reviewer
Uploaded by
John Eric GarciaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Contemp Reviewer
Uploaded by
John Eric GarciaCopyright:
Available Formats
ART FORMS
CONTEMPORARY ★ PICTURE (PAINTING, DRAWING)
ARTS Reviewer ★
★
SCULPTURE
ARCHITECTURE
★ MUSIC
LESSON 1: WHAT IS ART? ★ LITERATURE
★ THEATER
The left brain is more verbal, analytical, and ★ CINEMA
orderly. The right brain is more visual and deals ★ DANCE
in images more than words.
PHILIPPINE ART AS FILIPINO
HUMANITIES
What are the main characteristics of a
- From the Latin word “Humanus” educated Filipino art work?
- Refers to the learning of art
- Humanities is more concerned on how a VILLAGE LANDSCAPE 1958 N.V.M. Gonzales
person expresses his or her feelings
ART
- The expression or application of human
creative skill and imagination, typically in a LANDSCAPE 1969 Edith Tiempo
visual form such as painting or sculpture.
- Art is something we do, a verb. Art is an
expression of our thoughts, emotions, intuitions,
and desires.
❖ `Arts improve your creativity skills - Speculation on the FILIPINO-NESS
❖ Art gives you the opportunity to - Spanish, American, Asian Countries
showcase your own talent - Influenced Philippine Culture
❖ Arts helps you to express your emotion - Filipinos adapted to foreign culture
❖ Art can never be possible without the
knowledge of its basic concepts *When a Filipino Artist paints a farmer casting
❖ Art is a tangible manifestation and nets, the subject is Filipino. The medium of
product of human activity expression should portray the subject as true to
❖ Art is a means of communicating or what it is in reality.
conveying insights and emotions
*Many regarded the works written in Filipino or
ARISTOTLE regional languages more Filipino than in English.
But as Filipinos learn and adapt, the usage of
- He defined art as, “the realization in the English usage, regardless of language, is truly
external form of a true idea.” Humans love to Filipino.
imitate. Art, however, is not limited to just mere
copying. This idealizes nature and completes its *The Identity of the Filipino arts is constantly
deficiencies. Each person would have a different changing, struggling and evolving.
realization of an idea. For example, the idea is to
“draw an apple”. Two different persons will not
create an output that is EXACTLY ALIKE,
because the mind of one person who realizes
completes the idea according to his LESSON 2: ELEMENTS OF ART
understanding and his hand would create an
external form (drawing/sketch) of his realized - building blocks of composition in art
idea (apple). - stylistic features that are included within an art
piece
LINE ● Implied texture - can be exhibited
ex. Fur/Pebbles
- Also termed as “strokes” distance between two
points which is used for outlines and implied in a
design SPACE
DIFFERENT LINES - the area between the objects
- space in a work of art refers to a feeling of
● Expressive lines - are often the ones depth or three dimensions
we “see in nature”; often composed of
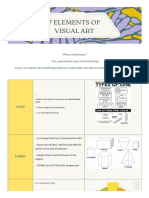
curly, swirly, or wavy lines TYPES OF PERSPECTIVE
● Constructive lines are very measured,
geometric, directional, and angular. LINEAR ATMOSPHERIC
These include horizontal, vertical,
diagonal, zigzag, or jagged, and broken
lines.
TYPES OF LINES
❖ Vertical - Represents dignity, formality,
stability, and strength.
❖ Horizontal - Represents calm, peace,
and relaxation. TYPES OF SPACE
❖ Diagonal - Represents action, activity,
excitement, and movement. ● Shallow space – objects seem really
❖ Curved - Represents freedom, the close to the viewer
natural, having the appearance of ● Deep space – objects may look close to
softness and creates a soothing feeling the viewer, but some objects are shown
or mood. as far away
SHAPE COLOR
- made when lines are enclosed PROPERTIES OF COLOR
DIFFERENT SHAPES ● HUE - the color itself
● INTENSITY - opacity
● Geometric ● VALUE - lightness and darkness
● Organic
“Every child is an artist”
- Pablo Picasso
FORM
COLOR THEORY
- Three dimensional, perceived volume, mass,
depth, width or height. ● Monochromatic - involves using the
same color but with different value
● Analogous - use of three or four color
TEXTURE adjacent to the color wheel
● Complementary - colors that is located
- denotes the smoothness, ruggedness of the in the opposite sides of the color wheel
image or object ● Split complementary - 2 colors
adjacent to the complement
TYPES OF TEXTURE ● Triadic - 3 colors that are equal
distance with each other
● Actual texture - can be felt tangibly
● Tetradic - 2 pairs of complementary
colors in the color wheel
GREAT WAVE OF KANAGAWA
Kasushika Hokusai
BAYANIHAN NORTH ROSE WINDOW
Fernando Amorsolo Notre Dame
LESSON 3: PRINCIPLES OF ART
The elements of art are fundamental tools to
better understand the complexities of the
principles of art. The integration of the elements
and principles of art is vital in producing or
understanding a contemporary piece of art.
UNITY AND HARMONY
The principles of design are the rules a designer
must follow to create an effective and attractive - the feeling of being, or looking like the
composition. The fundamental principles of elements are “put together”. A lack thereof
design are Emphasis, Balance and Alignment, makes an image “chaotic”, or “unreadable”.
Contrast, Repetition, Proportion, Movement. - Unity in design occurs when the elements in a
space work together in such a way that the
resulting look is balanced and harmonious.
BALANCE - Harmony is the principle of art that creates
cohesiveness by stressing the similarities of
- the distribution of the elements of art in a separate but related parts.
picture plane to achieve a visual equilibrium; the
way the elements are arranged to create a
sense of “stability” in the composition. RHYTHM
● Symmetrical – creates a “mirror-effect”; - A continuance, a flow, or a feeling of
happens when all elements are movement achieved by the repetition of
identically distributed regulated visual information.
● Asymmetrical – happens when the - Rhythm is created when one or more elements
elements are unevenly distributed in the of design are used repeatedly to create a feeling
composition but still achieves a “felt” of organized movement.
equilibrium - Rhythm creates a mood like music or dancing.
● Approximate – often confused as To keep rhythm exciting and active, variety is
symmetrical; “almost, but not quite”; one essential.
or more elements are seemingly or
similarly looking the same. ● Regular – has an identical motif or
● Radial – the elements radiate in/out visual beats; has an equal amount of
from a central point to all the quadrants space between motifs
of the plane ● Alternating – achieved by changing
motifs at regular intervals
TAJ MAHAL TAHITIAN WOMEN ● Random – motif is repeated in no
AGRA, INDIA Paul Gauguin particular order; unpredictable. The
motif is repeated in no apparent order.
You can not predict exactly where the
next motif will be.
● Progressive – there is a regular change in - The size relationship of objects; comparison of
motif every time it is repeated. In dimensions or distribution of forms.
progressive rhythm there is a change in - Refers to the relative size and scale of the various
motif or visual beat each time it is elements in a design.
repeated. - It is the feeling of unity created when all parts
● Flowing – uses curly, swirly, wavy, or (sizes, amounts, or numbers) relate well with each
expressive lines other.
MOVEMENT
VARIETY
- used to create the look and feel of action; the
path that our eyes follow - the principle of art that adds interest to an
artwork. Variety works through juxtaposition and
It can be created by: contrast. When an artist places different visual
elements next to one another, he/she is using
- Overlapping objects/elements variety.
- Aligning the edges to produce a feeling of
continuous movement SUBJECTIVE AND OBJECTIVE ART
- Create a path between objects
- Emphasizing/exaggerating elements Art can be evaluated according to its objective
- Blurry outlines qualities and the subjective perception of the one
- Multiple images who makes or appreciates it.
Movement can apply to a single component in a OBJECTIVE ART
composition or the whole composition at once.
Visual movement is dependent on the other - This is dependent on the physical attributes of the
elements and principles of art. Rhythm, line, color, art composition itself. The evaluation is based on
balance, and space are all examples of elements the usage of the elements and the principles of art.
and principles of art that can play a major role in It shall be devoid of personal thoughts, feelings, or
developing movement in a work of art. emotions. It may answer the question/s:
What shapes are used?
CONTRAST What colors are present?
What image is there?
- The way how the elements are arranged to point
out differences in the composition For this one, it is NOT going to base on one’s
- Contrast refers to the arrangement of opposite interpretation but on what the eyes can see, and
elements (light vs. dark colors, rough vs. smooth which depicts something that is easily recognized
textures, large vs. small shapes, etc.) in a piece to by people who view it. Is it a house? A running
create visual interest, excitement and drama. horse? A child crying?
- Contrast is most associated with readability,
legibility, and accessibility. Art that is easily recognized because of the
“objects” (thus, the term objective) included in it are
EMPHASIS also called objective art, representational art, or
figurative art.
- the focus or the focal point of the artwork;
happens when one area stands out the most and SUBJECTIVE ART
the remaining part of the composition becomes
subordinated. - Subjectivity in art is the word we use to explain
how different people can respond to a work of art in
- Usually the artist will make one area stand out by different ways
contrasting it with other areas. The area could be - Subjectivity is based on personal opinions and
different in size, color, texture, shape, etc. feelings rather than on agreed facts. A painting
might be “beautiful” to one person and “ugly” to
another, but the material object remains
PROPORTION unchanged.
LESSON 4: ART NOUVEAU have used video and the internet as a way of
propagating art.
- Art nouveau is a French term that translates as - Examples: Youtube
"new art" in English.
- Art Nouveau, an ornamental style of art that
flourished between about 1890 and 1910 LESSON 5: PHILIPPINE CONTEMPORARY
throughout Europe and the United States. ART
- Art Nouveau is characterized by its use of a
long, sinuous, organic line and was employed Ang Kiukok (1931-2005)
most often in architecture, interior design,
jewelry and glass design, posters, and - was a renowned Filipino expressionist whose
illustration. colorful and striking paintings portrayed a variety
of cubist-like figures such as a mother
Because art is produced by people who are embracing her infant, grisly crucifixions, tables
influenced by time, contemporary art is a holding on array of fish and fruit, stray dogs, and
continuing practice that has evolved with the screaming subjects.
following new elements or principles:
“The feeling (is) that all is possible in the
● Appropriation contemporary, and conceived as a constantly
● Performance extending and deepening constellation of art.”
● Space
● Technology -Dr. Patrick Flores, Metropolitan Museum
Curator
APPROPRIATION
- By appropriation, the contemporary artist ● Filipinos are becoming more aggressive
revives interest in existing forms of art. ● Arts that express themselves
- Example: The use of prints, images, and icons - Mural in EDSA, graffiti walls
to produce another art form, combining the past
with the present . ARCHITECTURE
PERFORMANCE CARLOS ANTONIO SANTOS-VIOLA
- Performance of contemporary artist has - Architect in the Philippines
evolved to "emphasize spontaneous, - Best known for designing and building
unpredictable elements of chance" -Walker Art churches for the Iglesia ni Cristo
Center
JASON BUENSALIDO
SPACE
“I believe that we need to rediscover, assert, and
- A site-specific art form wherein the art form is claim our own identity if we want to compete,
performed and positioned in a specific spot. converse, and be recognized globally. I started
- Examples: Flash mobs, Sculpture installation
HYBRIDITY LESSON 6: ARTS PROMOTION AND
PRESERVATION
- Hybridity in contemporary art is the mixing of
unlikely materials to produce an artwork. - Art is a national heritage that is essential
- Examples: using coffee for painting using in building the nation and ensuring democracy.
crayons for sculpture - Paintings, sculptures, songs, dances,
poetry,and other art forms remind people of
TECHNOLOGY the origins, histories, struggles, and triumphs of
the nation.
- The internet provides accessibility in
experiencing art forms. Contemporary artists
National Commission for Culture and the Arts love their country and are proud of their cultural
(NCCA) heritage.
- The NHCP carries out its mandate by promoting
- An overall policy-making body, coordinating, and “Philippine history and cultural heritage through
grants giving agency for the development and research, dissemination, conservation, site
promotion of the Philippine Arts and culture. management, and heraldry works.
- Alab ng Haraya (The Flame of Imagination) which - identification, conservation, and restoration of
symbolizes the wellspring of Filipino art and historical sites around the different regions of the
culture.. country.
- The fire is a stylized letter K of Philippine - awareness and appreciation of the noble deeds
indigenous script that stands for kadakilaan or and ideals of our heroes and other illustrious
greatness. The fire represents the highest level of Filipinos to instill pride in the Filipino race and to
imagination and emanates from a three-tiered rekindle the Filipino spirit through the lessons of
censer. history
- The three tiers stand for organization, economic
support, and an orientation rooted on a thorough NATIONAL MUSEUM OF THE PHILIPPINES
grasp of tradition and history, which the NCCA
provides. - the country’s repository of archaeological
- Done in gold to symbolize the immense wealth of artifacts, national treasures, and rare specimens
Philippine culture, it was designed by the late found and produced in the country
Romeo “Boy” Togonon. - solicit, document, preserve, exhibit, and promote
natural and artificial wonders
Six Arts and Cultural Government Agencies
NATIONAL LIBRARY OF THE PHILIPPINES
- serving as a “repository of the printed and
recorded cultural heritage of the country and other
intellectual literary and information sources”
- providing “access to these resources for our
people’s intellectual growth, citizenship building,
lifelong learning, and enlightenment.”
CULTURAL CENTER OF THE PHILIPPINES NATIONAL ARCHIVES OF THE PHILIPPINES
(CCP)
- goes back to as early as the Treaty of Paris in
- Sentrong Pangkultura ng Pilipinas 1898 stipulated the relinquishment or cession of
- National center for performing arts documents from Spanish to American authorities
- Promote Excellence in the arts through the and provided for the preservation of documents.
initiation and implementation of activities that aim - guardian to over 400 documents from the
to improve and elevated standards among Filipino Spanish era dating from 1552–1900 and various
artist records from the American period to the Republic.
- Home of Nine Artistic resident Companies Such
as National MUsic Competition for young Artist KOMISYON SA WIKANG FILIPINO
Foundation (NAMCYA), Ballet Philippines,
Philippine Madrigal Singers, Philippine Ballet - "shall undertake, coordinate and promote
Theater, UST Symphony Orchestra, Tanghalang research for the development, propagation, and
Pilipino, Bayanihan Philippine National Folk Dance preservation of Filipino and other Philippine
Company, Ramon Obusan Folkloric Group languages.”
- The logo, derived from the Baybayin character Ka - promote and develop our national language
and styled based on a Katipunan design, - KWF has annually given the Talaang Ginto:
represents Katotohanan, Kagandahan at Makata ng Taon for Filipino poetry, Aklat ng
Kabutihan(Truth, Beauty and Goodness) Bayan, and other grants or programs on
funding, awards, and project
NATIONAL HISTORICAL COMMISSION OF THE
PHILIPPINES (NHCP)
- The NHCP was created with a vision of a Filipino
society with citizens informed of their history, who
You might also like
- Contemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionsDocument26 pagesContemporary Philippine Arts From The RegionsPaulajean Almarez De CastroNo ratings yet
- CJ20N Change Create Additional WBS-Hierarchy GraphicsDocument9 pagesCJ20N Change Create Additional WBS-Hierarchy Graphicssatheesh408No ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument6 pagesArt Appreciationleannanicole.bustamanteNo ratings yet
- CPAR NotesDocument4 pagesCPAR NotesJahzara Daveigh BolivarNo ratings yet
- Con Arts Reviewer Gate Keep EditionDocument16 pagesCon Arts Reviewer Gate Keep EditionBenNo ratings yet
- A Moorish Woman With Her Maid Felix Jacques Moulin 1856: Form, Subject and Content Lesson 2Document2 pagesA Moorish Woman With Her Maid Felix Jacques Moulin 1856: Form, Subject and Content Lesson 2Vianca June LouiseNo ratings yet
- CPAR ReviewerDocument10 pagesCPAR ReviewerKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- What are the key elements and subjects of artDocument1 pageWhat are the key elements and subjects of artJamaica Haduca BalleraNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Power of ArtDocument6 pagesUnderstanding the Power of ArtMariz TrajanoNo ratings yet
- Art Appre. ReviewerDocument5 pagesArt Appre. ReviewerJunabelle Jaculbe ClementeNo ratings yet
- Bpe 224Document21 pagesBpe 224Plutonium MeowkNo ratings yet
- Presented by Magbanua, Rhean Miranda, Sigen Marc Novales, Leslie Ann GrapesDocument66 pagesPresented by Magbanua, Rhean Miranda, Sigen Marc Novales, Leslie Ann GrapesGrapes NovalesNo ratings yet
- Integrative ArtsDocument2 pagesIntegrative ArtsangelanatifayNo ratings yet
- Subject of ArtDocument41 pagesSubject of ArtThal ThalNo ratings yet
- Daily Planner Doc in Pastel Purple Pastel Yellow Teal Fun Patterns Illustrations StyleDocument3 pagesDaily Planner Doc in Pastel Purple Pastel Yellow Teal Fun Patterns Illustrations StyleMax GrantozaNo ratings yet
- Finals PDFDocument3 pagesFinals PDFAngela BarcebalNo ratings yet
- Art Ap 2nd Exam CoverageDocument3 pagesArt Ap 2nd Exam CoverageArnold LuayonNo ratings yet
- MAPEHDocument5 pagesMAPEHALLISONNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in CparDocument2 pagesReviewer in CparAlaine Chloe Bondoc AlvaroNo ratings yet
- Why Is Art Important To Our Society? Characteristics of Contemporary ArtDocument2 pagesWhy Is Art Important To Our Society? Characteristics of Contemporary ArtGroovy모니카No ratings yet
- Gen EdDocument27 pagesGen EdChristian TaladtadNo ratings yet
- ArtsDocument3 pagesArtslheagomezsisonNo ratings yet
- GEC 6 UNIT I Chapter 5Document74 pagesGEC 6 UNIT I Chapter 5RoseAnne Joy Robelo CabicoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Arts ReviewerDocument4 pagesLesson 1: Arts ReviewerFaith MarasiganNo ratings yet
- CPARDocument9 pagesCPARAina kate BayucanNo ratings yet
- ART APPRECIATION HANDOUT FOR EDIT ReviewerDocument6 pagesART APPRECIATION HANDOUT FOR EDIT ReviewerHanifa NorodinNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument139 pagesArt AppreciationOwangkid TvNo ratings yet
- FINALS (Art Appreciation)Document28 pagesFINALS (Art Appreciation)King Sigue100% (1)
- Elements and Principles of ArtDocument4 pagesElements and Principles of ArtjunquelalaNo ratings yet
- Visual Elements of ArtsDocument5 pagesVisual Elements of ArtsJan Mae EstaresNo ratings yet
- ART FORMS AND FUNCTIONSDocument4 pagesART FORMS AND FUNCTIONSChocochip100% (1)
- Art Elements and Principles Visual GuideDocument2 pagesArt Elements and Principles Visual GuideSANGALANG , Patricia Elena J.No ratings yet
- Lesson 8Document4 pagesLesson 8Aliyah PlaceNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument4 pagesUntitled DocumentTrishNo ratings yet
- Elements in Arts1Document56 pagesElements in Arts1Leian MenorNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation ReviewerDocument5 pagesArt Appreciation Reviewersarah gonzagaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary-Philippine-Arts-from-the-Regions-Module-2-Q1 - DESIGNED FOR 12 HUMSS A, B, C, D, E and 12 EPAS BOOKLET FORMDocument25 pagesContemporary-Philippine-Arts-from-the-Regions-Module-2-Q1 - DESIGNED FOR 12 HUMSS A, B, C, D, E and 12 EPAS BOOKLET FORMroy oraaNo ratings yet
- Artapp ReviewerDocument7 pagesArtapp ReviewerCarl PalicteNo ratings yet
- Arts ReviewerDocument3 pagesArts ReviewerJerome MagdaongNo ratings yet
- LESSON-1Document32 pagesLESSON-1Princess Camille dela PenaNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation 1st ShiftingDocument9 pagesArt Appreciation 1st ShiftingRica UyNo ratings yet
- 01 Art Appreciation IntroductionDocument34 pages01 Art Appreciation IntroductionCaladhiel100% (1)
- Art Appreciation ElementsDocument6 pagesArt Appreciation ElementsConstantine RebmemerNo ratings yet
- AA ReviewerDocument6 pagesAA ReviewerbrylleNo ratings yet
- The Elements and Principles of ArtDocument96 pagesThe Elements and Principles of Artave sambranaNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation NotesDocument13 pagesArt Appreciation NotesMitchie FaustinoNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Philippine Art in 40 CharactersDocument23 pagesContemporary Philippine Art in 40 Charactersphoebe porrasNo ratings yet
- Philippine Contemporary Arts - Integrative Art-Elements and Principles of ArtDocument6 pagesPhilippine Contemporary Arts - Integrative Art-Elements and Principles of Art030. Mozo, Athena Chelsea c.No ratings yet
- CONPHI 3Q Exam ReviewerDocument3 pagesCONPHI 3Q Exam Reviewervince.ortegaNo ratings yet
- Art Elements Principles PlaylistDocument30 pagesArt Elements Principles PlaylistNavarro, Jherwin F.No ratings yet
- ArtappDocument57 pagesArtappVI DALAGAN RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Reviewing Contemporary Philippine ArtsDocument6 pagesReviewing Contemporary Philippine ArtsMadelaine MendozaNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer For Visual Arts REVIEW 1Document9 pagesLET Reviewer For Visual Arts REVIEW 1Joy Erica LeoNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation - Prelim ReviewerDocument9 pagesArt Appreciation - Prelim ReviewerSab Sadorra100% (1)
- GEC ART - Finals ReviewerDocument11 pagesGEC ART - Finals ReviewerUrsula Grace LucaNo ratings yet
- What is Art? Understanding Elements, Forms and MeaningDocument5 pagesWhat is Art? Understanding Elements, Forms and MeaningMichiiee BatallaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Contempt Arts - LG1 4Document8 pagesReviewer Contempt Arts - LG1 4Nicole Gonzales RagaasNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument7 pagesArt Appreciationprincess.pinedaNo ratings yet
- ART APP ReviewerDocument2 pagesART APP ReviewerVincent AsiborNo ratings yet
- Master Minds: Creativity in Picasso's & Husain's Paintings (Part - 2): 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, #2From EverandMaster Minds: Creativity in Picasso's & Husain's Paintings (Part - 2): 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, #2No ratings yet
- SALE JA GEC 6 W6 2T Assessment 1Document3 pagesSALE JA GEC 6 W6 2T Assessment 1Jay AnnNo ratings yet
- How to Add Output Variables and Diagnostics to WRF Using the RegistryDocument62 pagesHow to Add Output Variables and Diagnostics to WRF Using the RegistryPutu Agus Dedy PermanaNo ratings yet
- Tyndale 2013-2014 #CatalogDocument73 pagesTyndale 2013-2014 #CatalogjeremeetylerNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy of MelancholyDocument1,186 pagesThe Anatomy of MelancholyBruno Anselmo100% (2)
- The Oral Approach and SituatioanalDocument5 pagesThe Oral Approach and SituatioanalKaka NurNo ratings yet
- What is RhetoricDocument6 pagesWhat is RhetoricBazura BaharuddinNo ratings yet
- 2012 Language DevelopmentDocument7 pages2012 Language DevelopmentJulian Caro MorenoNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary and Grammar Answer Key: Extension 1Document5 pagesVocabulary and Grammar Answer Key: Extension 1Araceli Ramirez VigoNo ratings yet
- PowerShell 4.0 Scheduling, Dynamic Methods, File HashesDocument2 pagesPowerShell 4.0 Scheduling, Dynamic Methods, File Hashesreemreem01100% (3)
- Metric SpacesDocument31 pagesMetric Spacesshamsul arifeenNo ratings yet
- Compound NounsDocument5 pagesCompound NounsVictor Magne ChavesNo ratings yet
- Presentation Week 11 IntProg Structure Pachshenko G.N.Document33 pagesPresentation Week 11 IntProg Structure Pachshenko G.N.Darkhan YermakhanovNo ratings yet
- Useful Information For OS/DB Migration - 1Document15 pagesUseful Information For OS/DB Migration - 1Ofrates SiringanNo ratings yet
- Catholic ApologeticsDocument166 pagesCatholic ApologeticsLeon GuintoNo ratings yet
- Aryans & DravidiansDocument9 pagesAryans & DravidianskdvprasadNo ratings yet
- 5 Choose A, B or C To Complete The SentencesDocument1 page5 Choose A, B or C To Complete The SentencesPaqui Martin AcuñaNo ratings yet
- Test 1 2ms4 22Document2 pagesTest 1 2ms4 22imane hopeNo ratings yet
- Military School ESPDocument5 pagesMilitary School ESPAdachi RenaNo ratings yet
- 21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The World Century Literature From The PhilippinesDocument21 pages21 Century Literature From The Philippines and The World Century Literature From The PhilippinesJoross Sibal Pacturan100% (1)
- Command Quick Guide R12 - 2009Document48 pagesCommand Quick Guide R12 - 2009Marcelito MorongNo ratings yet
- Universal XSS PDF Vulnerability ExplainedDocument11 pagesUniversal XSS PDF Vulnerability ExplainedMaoelana NoermoehammadNo ratings yet
- C Programming Practical ExercisesDocument6 pagesC Programming Practical ExercisesAdvance TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Modal Exercises Lesson 4 PDFDocument27 pagesModal Exercises Lesson 4 PDFJose Guardiola TomásNo ratings yet
- The Call of The Wild EssayDocument3 pagesThe Call of The Wild Essayafibafftauhxeh100% (2)
- Metric Screw Threads: Nissan Engineering StandardDocument90 pagesMetric Screw Threads: Nissan Engineering StandardBea RiveraNo ratings yet
- Music AnalysisDocument15 pagesMusic Analysisapi-457183086No ratings yet
- Semi-Detailed LP 7 - Imperative SentencesDocument2 pagesSemi-Detailed LP 7 - Imperative SentencesAngelo DizonNo ratings yet
- LSM Grade 3 English 1st Trim Exam SY 2009-2010Document6 pagesLSM Grade 3 English 1st Trim Exam SY 2009-2010Mauie FloresNo ratings yet
- Poem - The RavenDocument2 pagesPoem - The RavenValerieNo ratings yet