Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BIOLOGY-Animal Tissues
Uploaded by
Silver0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageThis document summarizes the main tissue types found in animal bodies: epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissue. It describes the composition, function and locations of each tissue type. The four basic tissue types are further divided into subtypes based on their microscopic structure and function. For example, epithelial tissue includes simple squamous, simple cuboidal and stratified squamous tissues; connective tissue includes loose and dense connective tissues. The summary provides an overview of the key animal tissue types and their characteristics.
Original Description:
Tissue Types
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes the main tissue types found in animal bodies: epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissue. It describes the composition, function and locations of each tissue type. The four basic tissue types are further divided into subtypes based on their microscopic structure and function. For example, epithelial tissue includes simple squamous, simple cuboidal and stratified squamous tissues; connective tissue includes loose and dense connective tissues. The summary provides an overview of the key animal tissue types and their characteristics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageBIOLOGY-Animal Tissues
Uploaded by
SilverThis document summarizes the main tissue types found in animal bodies: epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous tissue. It describes the composition, function and locations of each tissue type. The four basic tissue types are further divided into subtypes based on their microscopic structure and function. For example, epithelial tissue includes simple squamous, simple cuboidal and stratified squamous tissues; connective tissue includes loose and dense connective tissues. The summary provides an overview of the key animal tissue types and their characteristics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
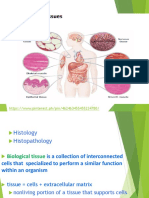
CHAPTER 23: ANIMAL TISSUES AND ORGAN SYSTEMS Dense
o Composition: cells in dense matrix of elastin
Tissue – group of specialized cells that interact and provide and collagen fibers (harder and stronger)
special function o Function: connects muscle to bone;
All animal tissues’ cells are embedded in an connects bone to bone
extracellular matrix (mixture of water, carb, lipids o Locations: tendons (b-m) and ligaments (b-
and protein fiber) b) [strain: tendon; sprain: ligaments]
o When cells are removed, body cells can’t Adipose
survive or replicate o Composition: fat cells in minimal matrix
(thicker)
Organ – consists of two or more interacting tissues that o Function: stores fats for energy and
function as a unit insulation
o Locations: beneath skin, between muscles,
Organ System – consists of two or more organs that are around heart and joints
physically or functionally joined Blood
o Composition: red, white, platelets in plasma
Tissue Types matrix
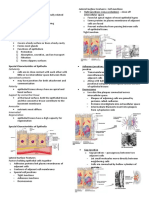
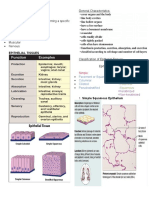
1. Epithelial o Function: transport gases, nutrients, wastes
o Coats the body’s internal and external o Locations: arteries, veins and capillaries
surfaces with tightly packed cells Cartilage
Simple Squamous o Composition: cells in matrix of fine collagen
o Composition: single layer of flattened cells fibers
o Function: allows substances to pass by o Function: flexible support
diffusion and osmosis o Location: Ears, joints, bone ends,
o Locations: Lining of blood vessels, alveoli of respiratory
lungs Bone
Simple Cuboidal o Composition: cells in matrix of collagen and
o Composition: single layer of cube-shaped minerals (strongest part but is limited by
cells pressure)
o Function: stores, secretes and absorbs o Function: firm support
substances o Location: Skeleton
Water is stored to prevent
dehydration 3. Muscle
o Locations: glands, lining of kidney tubules o Consists of cells that contract (become
Simple Columnar shorter) when electrically stimulated
o Composition: single-layer of column-shaped Skeletal Muscle
cells o Composition: elongated cells, each
o Function: stores, secretes and absorbs containing many nuclei, striated
substances; sweeps embryo along uterine o Function: moves the bones of the skeleton;
tube voluntary
o Locations: lining of digestive tract, bronchi o Location: attached to bones
of lungs, uterine tubes (fallopian) Cardiac
Stratified Squamous o Composition: short, branched cells, each
o Composition: multiple layers of flattened containing one nucleus, striated
cells o Function: contraction of atria and ventricles
o Function: protects areas subject to in heart, involuntary
abrasion, prevents water loss and infection Involuntary
o Locations: outer layer of skin o Location: Walls of the Heart
Smooth
2. Connective o Composition: spindle-shaped cells, each
o Consists of cells scattered within an containing one nucleus
extracellular matrix o Functions: Slow, involuntary movement
Occupies more space o Location: Digestive tract, arteries
Loose
o Composition: cells in loose matrix of elastin 4. Nervous
and collagen fibers o Uses electrical signals to convey
o Function: holds organs in place; attaches information rapidly within an animal’s
epithelial tissue to underlying tissue; body
maintain structure (ex: intestine) Other cells then transmit that
o Locations: under skin, between organs information along nerves to the
central nervous system (brain and
spinal cord)
You might also like
- BiologyDocument7 pagesBiologySilverNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 4: HistologyDocument4 pagesHuman Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 4: HistologySuperjunior8No ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue: Absorption, Transport, Excretion, Protection, SecretionDocument7 pagesEpithelial Tissue: Absorption, Transport, Excretion, Protection, SecretionKenneth Rodriguez HerminadoNo ratings yet
- NURANAPC TissuesDocument5 pagesNURANAPC TissuesAlloiza CaguiclaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andDocument5 pagesChapter-6 Tissues Animal Tissues: Tissue Is A Cellular Organizational Level Intermediate Between Cells andMonika MehanNo ratings yet
- 4 Types of TissueDocument3 pages4 Types of TissueAdaNo ratings yet
- The Tissues: The Four Primary Tissue TypesDocument10 pagesThe Tissues: The Four Primary Tissue TypesgilissaNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes 5Document5 pagesConcept Notes 5Yuann AranjuezNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganizationDocument8 pagesCell OrganizationKiele Nicole Calansingin100% (1)
- UntitledDocument32 pagesUntitledMikael ShinnNo ratings yet
- General Biology R Q3Document16 pagesGeneral Biology R Q3Maysheil GalarceNo ratings yet
- Tissues Part 2Document4 pagesTissues Part 2Monika Mehan100% (1)
- Epithelium Tissues: CellularityDocument6 pagesEpithelium Tissues: CellularityErika VerastigueNo ratings yet
- Structural Organization in Animals Animal TissuesDocument3 pagesStructural Organization in Animals Animal TissuesHadiya FatimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cells and TissuesDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Cells and TissuesClarisse Anne QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology (Tissue)Document21 pagesAnatomy and Physiology (Tissue)kimashleymandronNo ratings yet
- Genzoo Reviewer 1st SemDocument4 pagesGenzoo Reviewer 1st SememilpauloquibilanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Points To RememberDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Points To RememberNANDA KISHORE S X A AD : 1 0 6 4 4100% (1)
- Assignment AnaphyDocument7 pagesAssignment Anaphyysa.antonio12No ratings yet
- 10 TissueDocument60 pages10 Tissuebeyonduck100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricDocument23 pagesChapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricMariaNo ratings yet
- BIOL223-Lab 9Document53 pagesBIOL223-Lab 9chicken fries100% (1)
- Animal TissuesDocument2 pagesAnimal TissuesMami AmihanNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissue & Organ System: SMA Pradita DirgantaraDocument30 pagesAnimal Tissue & Organ System: SMA Pradita Dirgantarahafiz amriNo ratings yet
- BIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1Document53 pagesBIO122 - CHAPTER 7 Part 1lili100% (1)
- TissuesDocument46 pagesTissuesericaNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsDocument4 pagesTissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsRyan Cadorna FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Amity International School, Noida Class-Ix Biology Handout Topic-Animal TissuesDocument4 pagesAmity International School, Noida Class-Ix Biology Handout Topic-Animal TissuesL.C. GOYALNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document9 pagesCH 7Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956100% (1)
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Document10 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Saurav Soni100% (1)
- Genbio ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenbio ReviewerAbayan, Elaine Jewel L.No ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Tissues (Human Anatomy and Physiology)Document53 pagesLesson 2 Tissues (Human Anatomy and Physiology)Dump Acc 2No ratings yet
- Tissue Gen Bio ReviewerDocument9 pagesTissue Gen Bio ReviewerAlfred CariñoNo ratings yet
- Human Tissues - 1Document43 pagesHuman Tissues - 1Angel Diadem ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Simple Epithelium-Found in Areas That Require Stratified Epithelium - More Than One Layer of CellsDocument4 pagesSimple Epithelium-Found in Areas That Require Stratified Epithelium - More Than One Layer of CellsDimple Lexiry Gloria100% (1)
- التشريح نظري م 2 غير مترجمةDocument10 pagesالتشريح نظري م 2 غير مترجمةبايNo ratings yet
- Human TissueDocument6 pagesHuman TissueRence GuerraNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument7 pagesEpithelial TissueJoan PaulineNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Connective Tissues Lecture Notes Lectures 1 5Document47 pagesEpithelial Connective Tissues Lecture Notes Lectures 1 5stephenalfa7No ratings yet
- Basic Tissues of The Body: General CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesBasic Tissues of The Body: General CharacteristicsAngela Kate BautistaNo ratings yet
- Tissues - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesTissues - Anatomy and PhysiologyHan CallejaNo ratings yet
- Tissue (Notes) (1) 6roDocument4 pagesTissue (Notes) (1) 6romljnura3No ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec NotesDocument14 pagesAnaphy Lec NotesJohn Rick OrineNo ratings yet
- A P Topic 5 SummaryDocument9 pagesA P Topic 5 SummaryMax Delvalle100% (1)
- 7 Structural Organisation in Animals - Notes - SampleDocument2 pages7 Structural Organisation in Animals - Notes - SampleManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Overview 1Document44 pagesLecture 10 Overview 1mariam tarek100% (1)
- CH 7 - Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument8 pagesCH 7 - Structural Organisation in AnimalsLaxmiNo ratings yet
- ANAT 100 - Module 1 Summary NotesDocument6 pagesANAT 100 - Module 1 Summary NotesRahul BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheets Animal Cell TypesDocument4 pagesFact Sheets Animal Cell Typessamsung picturesNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument3 pagesAnimal TissuesSalman HaiderNo ratings yet
- Humantissue 140314123401 Phpapp01Document30 pagesHumantissue 140314123401 Phpapp01Athar Habib ShahaniNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument31 pagesStructural Organisation in AnimalsVenom Gaming YTNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesKenken MijaresNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 TissuesDocument6 pagesLesson 2 TissuesRodefe AmitNo ratings yet
- BIOL 1409 - Animal - Tissues - LR - Lab Report 4Document11 pagesBIOL 1409 - Animal - Tissues - LR - Lab Report 4Tonya Oliver100% (1)
- Handout Animal Tissues 2023 2024Document4 pagesHandout Animal Tissues 2023 2024reece sayamNo ratings yet
- Histology Lec 1 & 2Document22 pagesHistology Lec 1 & 2Asma Ghazy100% (1)
- EpitheliumDocument25 pagesEpitheliumAsmita BhattNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue ReportDocument29 pagesConnective Tissue ReportSheina UdaundoNo ratings yet
- Disorders: By: Nur Hanisah Binti ZainorenDocument53 pagesDisorders: By: Nur Hanisah Binti ZainorenJœnríčk AzueloNo ratings yet
- Training of War Dogs 1962 0 PDFDocument132 pagesTraining of War Dogs 1962 0 PDFjens_hermesmeyer100% (1)
- Immediate DenturesDocument35 pagesImmediate DenturesPrince AhmedNo ratings yet
- Significance of Personal Grooming and Hygenic Practice Followed As A ProfessionalDocument10 pagesSignificance of Personal Grooming and Hygenic Practice Followed As A ProfessionalSuhelica RoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ATLSDocument27 pagesChapter 5 ATLSUlfaa MutiaaNo ratings yet
- Anaemia: What Is Anemia?Document21 pagesAnaemia: What Is Anemia?Rashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Kinesia ParadoxaDocument7 pagesKinesia ParadoxaArcenciel26No ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome Hmd-Ttnb-Mas-Neonatal PneumoniaDocument65 pagesRespiratory Distress Syndrome Hmd-Ttnb-Mas-Neonatal PneumoniaBLOBLOBNo ratings yet
- Crestal Bone: The Maintenance of Around Dental ImplantsDocument5 pagesCrestal Bone: The Maintenance of Around Dental ImplantsJing XueNo ratings yet
- Sensory Evaluation of Bitter Gourd Momordica Charantia DoughnutDocument66 pagesSensory Evaluation of Bitter Gourd Momordica Charantia DoughnutMary Angelie BaguinNo ratings yet
- Finance Research Letters: John W. Goodell TDocument5 pagesFinance Research Letters: John W. Goodell TRuhma ZainabNo ratings yet
- Consti and Juris Cases Compilation 3Document169 pagesConsti and Juris Cases Compilation 3MG DangtayanNo ratings yet
- Girish Kumar - Cell Tower Radiation Hazards - 12 May 2011Document62 pagesGirish Kumar - Cell Tower Radiation Hazards - 12 May 2011Neha KumarNo ratings yet
- Spinal Curves ScoliosisDocument22 pagesSpinal Curves ScoliosisJennifer Mann100% (1)
- Embrace SP Version Bi TC 201612 FinalDocument9 pagesEmbrace SP Version Bi TC 201612 Finalka yat ngaiNo ratings yet
- Care of Patient With Liver Cirrhosis For Nursing Process Related Nursing CareDocument89 pagesCare of Patient With Liver Cirrhosis For Nursing Process Related Nursing CareMohamed Anwer Naleef100% (3)
- Aravind Eye Care SystemDocument5 pagesAravind Eye Care SystemArpit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing MCQsDocument4 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing MCQssivakamasundari pichaipillai90% (10)
- Enzymes: Clinical ChemistryDocument16 pagesEnzymes: Clinical ChemistryLauter Manaloto FrancoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION PDFDocument16 pagesChapter 7 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION PDFAngelene PelayoNo ratings yet
- Emergency Nursing Post TestDocument25 pagesEmergency Nursing Post TestAngie RelosNo ratings yet
- Romberg's Test: Neurological FunctionDocument4 pagesRomberg's Test: Neurological FunctionAlfa RidziNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility ComplexDocument16 pagesMajor Histocompatibility ComplexnikitaNo ratings yet
- MULTIPLE CHOICE. Read The Following Questions and Choose The Best Answer by Shading TheDocument14 pagesMULTIPLE CHOICE. Read The Following Questions and Choose The Best Answer by Shading ThePrince Mark BadilloNo ratings yet
- PHARMA 06. Introduction To Autonomic PharmacologyDocument6 pagesPHARMA 06. Introduction To Autonomic PharmacologyCindy Mae MacamayNo ratings yet
- 1955Document801 pages1955Anonymous GwfFuFYq4ZNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation ImDocument15 pagesCase Presentation ImZakwan ZainalNo ratings yet
- Writing Silviculture PrescriptionsDocument29 pagesWriting Silviculture PrescriptionsJason BrownNo ratings yet
- Establishing The Place of Health Social Work: Sarah Gehlert, Christina Andrews, and Teri BrowneDocument3 pagesEstablishing The Place of Health Social Work: Sarah Gehlert, Christina Andrews, and Teri BrowneSintia SetiawatiNo ratings yet
- Ass 1Document14 pagesAss 1Kenneth WongNo ratings yet