Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth and Life Sci Q2 W3 - W4 - Law RTP
Uploaded by
Raibern Christian LeeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Earth and Life Sci Q2 W3 - W4 - Law RTP
Uploaded by
Raibern Christian LeeCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
National Capital Region
Schools Division Office of Las Piñas City
Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW)
Earth and Life Science
Grade 11
Name: _____________________________ Date: _________ Rating/Score_________
ANIMAL REPRODUCTION
Activity 1: MODIFIED TRUE OR FALSE
Directions: Read the statement carefully. Write TRUE if the statement is correct, if
not, change the underlined word/s in order to make the sentence proper.
______1. Budding occurs when a new individual grows on the body of the parents
like hydra and yeast.
______2. The organism that split into two then separate into two or more organisms
undergo fission as the mode of reproduction.
______3. Flat worms (planarians) divides into two, leaving one piece headless and
the other tailless, each piece grows the missing parts in a fragmentation
type of reproduction.
______4. The development of embryos without fertilization is possible in
parthenogenesis.
______ 5. Animals that undergo sexual reproduction produces offspring genetically
same to itself.
Activity 2: One Parent or Two!
Directions: Classify which animals reproduce sexually, asexually or both. Write S for
sexual, A for asexual and B for both type of reproduction on the space
provided.
1. 5.
dolphin squirrel
Image Source: https://www.flickr.com/photos/odalaigh/741574234 Image Source: https://www.pinterest.ph/pin/291397038382831396/
Q2 Week 3 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 1 of 8
Target Competency: Describe the different ways of how representative animals reproduce.
(S11/12L-IIa-3)
2. 6.
Horse carabao
Image Source: http://www.gomoodboard.com/boards/DRzQWtP5/share Image Source: https://www.pinterest.ph/pin/174936766748032735/
3. 7.
cockroach deer
Image Source: https://www.familyhandyman.com/list/cockroach-facts/ Image Source: https://www.washingtonpost.com/science/2019/10/24/hunter-believed-his-kill-was-
dead-then-buck-launched-fatal-attack/
4. _______8.
butterfly land snails
Image Source: https://www.pinterest.ph/pin/843580573931862900/ Image Source: https://www.pinterest.ph/pin/59883870031634965/
Activity 3: Finding the Difference!
Directions: Fill up the table below with the appropriate description that best describe
the two types of fertilization. Choose your answer from the box below.
Inside fertilization of
Less number of gametes
Outside fertilization of egg cell
is released egg cell
Numerous gametes are Both male and femaleMale gametes are
released discharged in the
gametes are discharged
Cow, goat, horse, dolphin, cat, in the external female body.
bees, dragonfly, tortoise surrounding. More chances of
Offspring produced are higher Development occurs offspring survival
in number outside the body.
It occurs inside the
Few chances of survival, no body and of three
Requires high energy to
parental care, get preyed find a mate, larger types.
upon, many do not get contribution of
Frog, toad, newts, shark
fertilized. female parent only.
Q2 Week 3 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 2 of 8
Target Competency: Describe the different ways of how representative animals reproduce.
(S11/12L-IIa-3)
BASIS FOR INTERNAL EXTERNAL
COMPARISON FERTILIZATION FERTILIZATION
DESCRIPTION
GAMETES
RELEASED
PROCESS
INVOLVES
ADVANTAGES
DISADVANTAGES
EXAMPLES
Activity 4: Knowing & Understanding Animals!
Directions: Complete the details needed by filling in a word or phrase that best
describe the given animals.
Example: Dolphin; Type of Animal: Mammal
Development of time: 12 months
No. of offspring:1
After Care: 4 to 18 months; 3 to 6 years
Fertilization: Internal
Development: Internal
Survival Rate: 97%
Q2 Week 3 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 3 of 8
Target Competency: Describe the different ways of how representative animals
reproduce.(S11/12L-IIa-3)
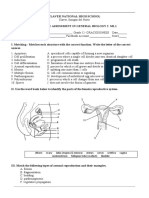
Activity 5: Know Me More... How do I reproduce?
Directions: Name the type of internal development that takes place in the given
animals below. Write oviparous, viviparous, ovoviviparous on the blanks. Briefly
explain the development of the offspring inside the box.
Name of Animal Development of Offspring (young animal)
1. Diamondback rattle snake
https://www.pinterest.ph/pin/436356651365625593/
2. Hen
https://info.mannapro.com/homestead/considering-age-differences-when-feeding-
your-flock
3. Tarsier
https://www.pinterest.ph/pin/205687907968521108/
Q2 Week 3 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 4 of 8
Target Competency: Describe the different ways of how representative animals reproduce.
(S11/12L-IIa-3)
Genetic Engineering and GMOs
Activity 1. Are you Genetically Engineered Animals?
Directions: Identify the animals whether genetically engineered or not. Choose the
animals given on the box below and write your answer on the space provided.
Sheep Cockroach Chicken Dogs Lion Fish Rats Cow Mice Goats
Genetically Engineered Animals Not Genetically Engineered Animals
Activity 2. Process of Generic Engineering
Directions: Arrange the process of genetic engineering. Use numbers 1 to 5, number 1
will serve as the first process and number 5 is the last process.
_____ 1. Introduction of cloning vector into host strain
_____ 2. Selection of recombinant progeny
_____ 3. Splicing and insertion of DNA into cloning vector
_____ 4. Extraction and purification of total cellular DNA
_____ 5. Replication and expression of recombinant DNA
Activity 3: Benefits and Risks of Genetic Engineering
Directions: Identify whether the following are benefits or risks of genetic engineering.
Put an (X) in the correct column.
Benefits Risks
1. Enhancing food production
2. Optimizing animal health and welfare
3. Risky pathogens, viruses and bacteria adapt to environment
4. Unfavorable diversity
5. Advancing human health
6. Reducing environmental impacts
7. Production of cutting-edge industrial applications
8. Less Nutritional value
9. Synthesizing human insulin
10. Resistance to antibiotics
Q2 Week 4 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 5 of 8
Target Competency: Describe the process of genetic engineering. (S11/12LT-1lej-17)
Activity 4: Facts on Genetic Engineering
Directions: Read and analyze each statement. Underline the correct answer in the
parenthesis.
1. DNA segment or (chromosomes, gene, plasmid) is isolated from a source
organism by extracting and purifying the total cellular DNA.
2. Transformation (nonviral, viral, midviral) for bacteria and lower eukaryotes.
3. (Transduction, Conjugation, Transformation) cell-to-cell, for bacteria are all
commonly used method for gene delivery and DNA transfer.
4. DNA serves as a template for (replication, duplication, deletion) and gene
expression, and therefore, harnesses the genetic instruction required for the
functioning of all living organism.
5. In the latter part of the 20th century, the term genetic engineering refers more
specifically to methods of recombinant DNA technology or gene (transmission,
cloning, expression).
6. Genetic engineering refers to the direct manipulation of DNA to alter an organism’s
characteristic (phenotype, genotypes, genes) in a particular way.
7. Genetic engineering, sometimes called genetic modification, is the process of
altering the DNA in an organism’s (genes, cloning, genome).
8. Genetic engineering can be applied to any organism, from a (virus, bacteria,
microorganisms) to a sheep.
9. To help explain the process of genetic engineering we have taken the example of
(Protein, insulin, DNA) that helps regulate the level of sugar in our blood.
10. A small piece of circular DNA called a (genes, plasmid, RNA) is extracted from
the bacteria or yeast cell.
Activity 5: Current Trends of Genetic Engineering
Directions: Research at least 3 current trends of genetic engineering. Write your answer
on the space below.
Q2 Week 4 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 6 of 8
Target Competency: Describe the process of genetic engineering. (S11/12LT-1lej-17)
Activity 6. Multiple Choice Questions
Directions: Analyze the questions and write the letter of the best answer.
______1. What does GMO stand for?
A. Genetically Mutated Organism C. Genetics Modified Organism
B. Genetically Modified Organism D. Genetics Modified Organism
______2. Which of these animals have been genetically engineered to grow faster,
becoming the first animal to be modified specially for human consumption?
A. chicken B. pig C. milk fish D. salmon
______3. What causes the genetic alternations in Bt corn?
A. growth faster C. produces nutritional value
B. drought resistance D. produces a toxin that kills pests
______4. GM crops were created due to the following reasons, except?
A. Reduce food waste C. Good nutritional value
B. Disease resistance D. Insect resistance
______5. How long does it take to develop a new genetically modified crop?
A. Twenty years B. Ten years C. Five years D. One year
Activity 7: History of GMOs
Directions: Match Column A and Column B. Write the correct letter before each
number.
COLUMN A COLUMN B
_____ 1. The first GMOs in agriculture introduced in marketplace A. 2017
_____ 2. GM canola becomes commercial B. 2016
_____ 3. Human begin crop domestication using selective breeding C. 2006
_____ 4. GM apples become commercial D. 1999
_____ 5. GM papaya becomes commercial E. 1997
_____ 6. GM potatoes becomes commercial F. 1996
_____ 7. GM squash and soybeans becomes commercial G. 1995
_____ 8. GM alfalfa and sugar beets become commercial H. 1990
_____ 9. Farmers and scientist begin crossbreeding plants I. late 1800s
and species J. 1982
_____ 10. GM cotton and corn becomes commercial K. 10,000 years ago
Activity 8. Identifying GMOs
Directions: Identify the benefits and risks of Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs).
Put (X) on the space provided.
Benefits Risks
1. Crops limit biodiversity of local environment
2. Solve the hunger issues in developing countries
3. Harmful to the environment
4. Modifying crops to have higher nutritional value
5. To be drought Resistant
6. Removal of traits could have unknown effects
7.Crops can produce herbicides to kill pests
8. Have a higher harvest yield
9. Cross pollination could lead to super weeds
10.Help to end the starvation
Q2 Week 4 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 7 of 8
Target Competency: Evaluate the benefits and risks of using GMOs. (S11/12LT-1lej-19)
Activity 9: Explain Me
Directions: Explain the following questions and write your answer on space below.
1. Why are GM foods produced?
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
2. How GM foods differ from traditional foods?
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
3. Are GM foods safe? Yes or No. Why?
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
4. What are the potential risks of GM foods to human health?
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
Q2 Week 4 (Learning Activity Worksheet) Page 8 of 8
Target Competency: Evaluate the benefits and risks of using GMOs. (S11/12LT-1lej-19)
You might also like
- Science5 - q2 - Mod3 - Modes of Reproduction in Animals - v4Document23 pagesScience5 - q2 - Mod3 - Modes of Reproduction in Animals - v4Nellen Grace Ortiz84% (25)
- Natural Selection Webquest AnswersDocument2 pagesNatural Selection Webquest AnswersLidia Baratas100% (1)
- Science: Department of EducationDocument11 pagesScience: Department of EducationPeterson Dela Cruz EnriquezNo ratings yet
- ELS Q2 M4 How-Representative... 15pDocument15 pagesELS Q2 M4 How-Representative... 15pRachel Ann Canlas100% (1)
- ELS Q2 - WEEK 2 Mod3 PDFDocument16 pagesELS Q2 - WEEK 2 Mod3 PDFALEXZANDRA EBRIEGANo ratings yet
- SHS - LAS - Earth & Life Science - MELC - 3 - Q2 - Week-3 (1) - RemovedDocument6 pagesSHS - LAS - Earth & Life Science - MELC - 3 - Q2 - Week-3 (1) - RemovedNini VillezaNo ratings yet
- LAS Science-5 Q2Document9 pagesLAS Science-5 Q2Gui FawkesNo ratings yet
- Cot 4Document7 pagesCot 4Jerwin Sarcia RemocalNo ratings yet
- W4 ScienceDocument69 pagesW4 ScienceAngie Lea Serra-YlardeNo ratings yet
- SIM LectureDocument17 pagesSIM LectureRaymond BunsoyNo ratings yet
- Learner's Activity Sheet: Earth & Life Science (Quarter II - Week 3)Document6 pagesLearner's Activity Sheet: Earth & Life Science (Quarter II - Week 3)Chenee TanNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument17 pagesScienceBryl MedrozoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 4Document19 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 4Kath Tan Alcantara90% (10)
- Earth Science ModulesDocument14 pagesEarth Science ModulesAlphaNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1643037284745 6891397855556482261Document20 pagesOrca Share Media1643037284745 6891397855556482261JA SonNo ratings yet
- Science5 q2 Mod3 Modes of Reproduction in Animals v4Document24 pagesScience5 q2 Mod3 Modes of Reproduction in Animals v4Charmine Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1643037284720 6891397855452503284Document20 pagesOrca Share Media1643037284720 6891397855452503284JA SonNo ratings yet
- ELS Q2 Week-3Document17 pagesELS Q2 Week-3Adam HinampasNo ratings yet
- Science G7 Q2 W5 MODDocument8 pagesScience G7 Q2 W5 MODAveCorpuz BioCornerNo ratings yet
- Science5 q2 Mod3of7 Howdoanimalsreproduce v2Document26 pagesScience5 q2 Mod3of7 Howdoanimalsreproduce v2notursunshine.syaigNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science ViDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science Vicherkarlo100% (5)
- Science Quarter 2 Module 5Document13 pagesScience Quarter 2 Module 5Zerreitug Elppa100% (2)
- LT Adm 15.2Document11 pagesLT Adm 15.2KristineNo ratings yet
- SHS - LAS - Earth & Life Science - MELC - 3 - Q2 - Week-3Document9 pagesSHS - LAS - Earth & Life Science - MELC - 3 - Q2 - Week-3Jane Hembra100% (3)
- Els q2 Las Week 3 1Document11 pagesEls q2 Las Week 3 1SeanNo ratings yet
- Science-7 Mod5 Reproduction Second GradingDocument19 pagesScience-7 Mod5 Reproduction Second GradingAnna Marie ArguellesNo ratings yet
- Science5 Q2 Mod5 DescribingtheDifferentModesofReproductioninAnimalsSuchasButterfliesMosquitoesFrogsCatsandDogs v3Document23 pagesScience5 Q2 Mod5 DescribingtheDifferentModesofReproductioninAnimalsSuchasButterfliesMosquitoesFrogsCatsandDogs v3DanielMatsunagaNo ratings yet
- EARTHLIFE SCIENCE Q2 Week 3 4aDocument28 pagesEARTHLIFE SCIENCE Q2 Week 3 4aEinjhel Gaverielle ReyesNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-5-Q2-Module 3Document16 pagesSCIENCE-5-Q2-Module 3Mary Ann Gabion80% (5)
- D-3 - 4 What Is SpeciesDocument26 pagesD-3 - 4 What Is SpeciesmanojNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science SHS 3.3 Asexual Reproduction in AnimalsDocument18 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 3.3 Asexual Reproduction in AnimalsZaldy Emmanuel MendozaNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 2 - Module 5: "Where Do I Begin?"Document28 pagesScience: Quarter 2 - Module 5: "Where Do I Begin?"Freya Joy Mercado - Santos90% (10)
- Science 4 Misosa - Animals Hatched From Eggs and Born AliveDocument6 pagesScience 4 Misosa - Animals Hatched From Eggs and Born AliveMA. KRISTINA MANLANGIT JUATON,No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanLara Michelle Sanday Binudin50% (2)
- Reproduction in Animals: Plants" in Class Seventh. Now You WillDocument18 pagesReproduction in Animals: Plants" in Class Seventh. Now You WillvenkataNo ratings yet
- Science 3 DLP 18 - Identifying Animals in The LocalityDocument10 pagesScience 3 DLP 18 - Identifying Animals in The LocalityMa Isabella T Ballesteros100% (1)
- "Wanted: Dead or Alive?": Department of EducationDocument16 pages"Wanted: Dead or Alive?": Department of EducationJonathan YambaoNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Guide: Learning Plan in Science 5 Plan 26Document30 pagesTeacher's Guide: Learning Plan in Science 5 Plan 26Castle GelynNo ratings yet
- Clitoris Ovary Labia (Majora & Minora) Uterus Cervix Urethra Vagina Endometrium Fallopian Tube (Oviduct) BladderDocument5 pagesClitoris Ovary Labia (Majora & Minora) Uterus Cervix Urethra Vagina Endometrium Fallopian Tube (Oviduct) BladderQueng ElediaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 5 WEEK 4 (2nd Quarter by Sir Ray Marasigan)Document5 pagesSCIENCE 5 WEEK 4 (2nd Quarter by Sir Ray Marasigan)Renge Taña100% (1)
- Science DLPDocument7 pagesScience DLPVanessa RamosNo ratings yet
- Week 5: Day 1Document31 pagesWeek 5: Day 1bessie lorzanoNo ratings yet
- Shs Els-Lp q2-w3Document4 pagesShs Els-Lp q2-w3Kim Arrieta GaudianoNo ratings yet
- S10 Q3 Week-7bDocument11 pagesS10 Q3 Week-7bPatricia TanasasNo ratings yet
- Sci7 Q2 M5 EditedaftercontentlayoutlanguageevaluationDocument22 pagesSci7 Q2 M5 EditedaftercontentlayoutlanguageevaluationNena TabayayNo ratings yet
- Activity VertebratesDocument6 pagesActivity VertebratesAbegail Ilocso-DomingoNo ratings yet
- Science Worksheet Reproduction in Animals Class 4 CDocument3 pagesScience Worksheet Reproduction in Animals Class 4 CLOUIE ESTRADANo ratings yet
- Earth-and-Life-Science Q2 Mod11 Animal-Reproduction Version1Document15 pagesEarth-and-Life-Science Q2 Mod11 Animal-Reproduction Version1ivanjade627No ratings yet
- LP TemplateDocument10 pagesLP TemplategedreleneNo ratings yet
- Q2 Science 5 Summative TestDocument1 pageQ2 Science 5 Summative Testpot pooot83% (23)
- Earth and Life Science SHS 17. Asexual Reproduction in AnimalsDocument16 pagesEarth and Life Science SHS 17. Asexual Reproduction in AnimalsAlbert BonggotNo ratings yet
- RBI Script 13Document3 pagesRBI Script 13Mary-Ann SanchezNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed LP q2Document6 pagesSemi Detailed LP q2mercy paduaNo ratings yet
- Minimum Learning Capsule Biology Xii 2018Document88 pagesMinimum Learning Capsule Biology Xii 2018Aryan JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Classification Worksheet: Name: Duru Metin DateDocument5 pagesClassification Worksheet: Name: Duru Metin DateDuru MetinNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningDocument7 pagesCurriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningMerce Tojino ManigosNo ratings yet
- Ste Biotech Q4M4 Animal Biotechnology AjsnhDocument30 pagesSte Biotech Q4M4 Animal Biotechnology AjsnhKRIELYN VILLADOSNo ratings yet
- ELS Q2 Module-3 Perpetuation-Of-Life v2Document10 pagesELS Q2 Module-3 Perpetuation-Of-Life v2Rosalie OlaliaNo ratings yet
- Science7 - q2 - slk5 - Reproductionbeingbothasexual and Sexual - v1Document36 pagesScience7 - q2 - slk5 - Reproductionbeingbothasexual and Sexual - v1alain presillasNo ratings yet