Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Periodic Classification - Mind Maps - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024
Uploaded by
Harsh Singh RajputOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Periodic Classification - Mind Maps - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024
Uploaded by
Harsh Singh RajputCopyright:
Available Formats
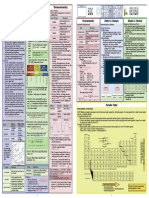
• Law of Triads: Johann Dobereiner (1829) To ease out difficulty in studying •Electronic Configuration is the distribution of electrons into
n studying •Electronic Configuration is the distribution of electrons into subshells
• Law of Octaves: John Alexander Newlands (1865) individually the chemistry of all the of an atom.
• Lothar Meyer plotted a graph between atomic elements and their compounds.
volume and atomic weight. Elements with
•In periods: Number of elements in each period is twice the number of
atomic orbitals available in the energy level that is being filled.
Atomic
similar properties occupied the similar positions _______
Metalloids & Transition metals
on the graph.
Atomic weight
•Group wise: Elements in same group have similar valence shell electronic
• Periodic Law: Dimitri Mendeleev and Lothar Meyer.
It states that the properties of the elements are periodic configurations, hence same number of electrons in outer orbit and
Genesis of
function of their atomic weights. periodic
classification similar properties. These are classified into four blocks i.e., s-block,
·Modern Periodic Law: Henry Moseley (1913)
It states that the physical and chemical properties
Periodic table
classification
p-block, d- block and f-block.
based on electronic
of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic configuration
numbers. ; Horizontal rows - Periods, Vertical columns -
Groups are numbered from 1 to 18.
s-Block Elements d-Block Elements
Derived from the atomic numberof • Group 3-12
element using numerical roots for _
IUPAC
Nomenclature of Classification of Elements and • Group 1 (alkali metals) and Group 2
(alkaline earth metals) • Outer configuration is (n-1 ) d1 - 10 ns 0-2
Periodicity in Properties
elements with
0 and numbers 1-9 and “ium” is atomic • Outermost configuration is ns 1 or ns 2 • Forms coloured ions.
added at the end. • Reactive with low IE. • Exhibit variable valence, paramagneti sm.
• Metallic character and reactivity • Also called as Transition elements.
Down the increases down the group
Properties Group
Period
(Left to Right)
• Some are used as catalysts.
Periodic trends in Periodic table
(a) Atomic Radius properties of classification
elements based on types
Distance from the centre of the Increases p-Block Elements f-Block Elements
Decreases of elements
nucleus to the outermost shell
containing electrons. • Group 13 to 18. • Also called as InnerTransition Elements.
Isoelectronic species
(b) Electron Gain Enthalpy : • Also called as representatives • Contains Lanthanoids and Actinoids.
Becomes Becomes
Energy released when a neutral Atoms and ions with same number of electrons or main group elements • Outer configuration is (n- 2) f1 - 14 (n- 1) d0 -1 ns0 -2
less more
isolated gaseous atom accepts an eg: 0 2,- F-, Na+,Mg2+ have same number of electrons • All are metals.
electron to form anion. negative negative • Outermost configuration varies
l
Size
( +) ve charge
(-) ve charge • Actinoids are radioactive.
(c) Ionization Energy: from ns2 np1 to ns2 np6
The minimum amount of energy • At the end of period are low
required to remove the electron Decreases Increases Q) The increasing order of the ionic radii of the given Q)In the long form of the periodic table, the valence shell
from the outermost orbit of an isoelec tronic species is: reac tive noble gases. electronic configuration of 5s 2 5p4 corresponds to the
element present in
isolated atom in gaseous state. - -
(a) S 2 , Cl , Ca 2+ ,K+ (b) Ca 2+ , K+, Cl-, S 2- •Halogens and Chalcogens have
(a) Group 16 and period 6
(d) Cl , Ca 2+, K+, S 2-
- -
high negative electron gain
2- 2+
(d) Electro-negativity : (c) K , S , Ca , Cl
+
(b) Group 17 and period 5
Tendency of an atom to attract the Decreases Increases enthalpies. (a) Group 16 and period 5
shared pair of electrons towards
itself. Q) Which of the following statements is not correct? •Metallic character increases (b) Group 17 and period 6
(e) Electron Affinity Decreases Increases down the group
(a) Ionisation energy increases on going down a group in the periodic table.
(f) Valency: Increase (b) Among alkaline earth metals, reducing character increases down the group.
Number of univalent atoms from 1 to 4
which combine with an No Change and then (c) Fluorine is the most electronegative element.
decrease from
PHYSICS
atom of given element 4 to 0. (d) Metallic character increases on going down a group in the periodic table.
(g) Metallic Character Increases Decreases
(h) Non-Metallic Character Decreases Increases
WALLAH
You might also like
- 13.periodic Table and Periodicity PDFDocument20 pages13.periodic Table and Periodicity PDFP. E. I. AcademicsNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Concept & Titrations Ontents: JEE (Advanced) SyllabusDocument44 pagesEquivalent Concept & Titrations Ontents: JEE (Advanced) SyllabussharkrameshNo ratings yet
- P Block Elements Notes Class 12Document45 pagesP Block Elements Notes Class 12NeerajNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Periodic TableDocument44 pagesUnit 1 Periodic TablePratik ParkaleNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes ThermodynamicsDocument11 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes ThermodynamicsAivenNo ratings yet
- Periodicity (Chemistry) PDFDocument13 pagesPeriodicity (Chemistry) PDFMarga AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology Notes Chapter 2 Studyguide360Document10 pagesClass 11 Biology Notes Chapter 2 Studyguide360ANo ratings yet
- 26 E19 20 Respiration in Plants Enzyme 1589118408Document43 pages26 E19 20 Respiration in Plants Enzyme 1589118408Allen Chryso67% (3)
- Study Material 12 PhysicsDocument117 pagesStudy Material 12 PhysicsVaishu UparkarNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 12 - Test Paper - Lakshya NEET 2024Document17 pagesPractice Test 12 - Test Paper - Lakshya NEET 2024Pandey 14No ratings yet
- Neet Booster Test Series (NBTS) For Neet-2021 Test - 1: PhysicsDocument17 pagesNeet Booster Test Series (NBTS) For Neet-2021 Test - 1: PhysicsMangesh VeerNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Concept TheoryDocument13 pagesEquivalent Concept TheoryDIPESH100% (1)
- 4 - Chemical Kinetics & RadioactivityDocument19 pages4 - Chemical Kinetics & RadioactivityNimeshNo ratings yet
- Class 11 CH 1 Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument6 pagesClass 11 CH 1 Some Basic Concepts of ChemistrySai Kotian50% (2)
- Classplusapp - NEET CHEM-Ch 4Document37 pagesClassplusapp - NEET CHEM-Ch 4Muhammad Ali100% (1)
- Spectrum Biology - September 2016 PDFDocument84 pagesSpectrum Biology - September 2016 PDFMarco MarcogambaNo ratings yet
- Quick Revision CapsuleDocument18 pagesQuick Revision CapsuleRacsGamer100% (1)
- Arihant Chemistry Class 12 Term 1 - WWW - jeebOOKS.inDocument161 pagesArihant Chemistry Class 12 Term 1 - WWW - jeebOOKS.inSrishti PathakNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Magnetism & MatterDocument12 pagesCH 5 Magnetism & MatterAkash KoulNo ratings yet
- Chapter Contents: Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument34 pagesChapter Contents: Chemical Thermodynamicskrish masterjee100% (2)
- Class XI NEET Mock TestDocument5 pagesClass XI NEET Mock TestkalloliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter Physics Cbse Class 12Document16 pagesChapter 5 Magnetism and Matter Physics Cbse Class 12HemnathpalaniNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra HSC Physics Paper 2 PDFDocument37 pagesMaharashtra HSC Physics Paper 2 PDFSWAPNILNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: CheatDocument22 pagesChemistry: CheatKashish UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Aufbau Principle PDFDocument4 pagesAufbau Principle PDFcrbruma100% (2)
- SRG Physics Question Bank - SolutionDocument147 pagesSRG Physics Question Bank - SolutionUtkarsh DimriNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Support Material Part-ADocument117 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Support Material Part-ANIRUPAMA VNo ratings yet
- 12 Std. IMPORTANT QUESTIONS & PROBLEMS - 2022 - 2023 PDFDocument16 pages12 Std. IMPORTANT QUESTIONS & PROBLEMS - 2022 - 2023 PDFUdhayaNo ratings yet
- Medical VMC Medical Revision Test-03 (VRTS-03) 10PMT20 & 11PMT20Document22 pagesMedical VMC Medical Revision Test-03 (VRTS-03) 10PMT20 & 11PMT20Keshav ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Physics XII Concept Maps PDFDocument15 pagesPhysics XII Concept Maps PDFcbsegirlsaipmt100% (1)
- P - Block PDFDocument60 pagesP - Block PDFSubham roushanNo ratings yet
- Margolis, Emil - J. - Formulation and Stoichiometry PDFDocument230 pagesMargolis, Emil - J. - Formulation and Stoichiometry PDFOscar Perez RosalesNo ratings yet
- Physics Exam Quick Revision NotesDocument40 pagesPhysics Exam Quick Revision NotesPinky Ann DanielNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties (@Document20 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties (@LONE WOLFNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of AtomsDocument51 pagesElectronic Structure of AtomsEng AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Neet Physics FormulasDocument26 pagesNeet Physics Formulasvishwanathvt9993No ratings yet
- Reaction Mechanism IIDocument21 pagesReaction Mechanism IIFilmode100% (2)
- Emailing Chemical Kinetics (Class 12)Document12 pagesEmailing Chemical Kinetics (Class 12)roceniNo ratings yet
- Study Material Term 2 Xi Physics 2021-22Document176 pagesStudy Material Term 2 Xi Physics 2021-22Rudresh Kalasannavar100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry - Class 12th - Practice MCQsDocument22 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Class 12th - Practice MCQsLiza DahiyaNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Shiv Das First TermDocument29 pages12 Chemistry Shiv Das First TermRaj AgamNo ratings yet
- AIPMT-NEET Previous Year Solved Paper 2002Document16 pagesAIPMT-NEET Previous Year Solved Paper 2002Aakash KashyapNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids NotesDocument74 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Notessamay gujratiNo ratings yet
- NCERT Maps PhysicsDocument55 pagesNCERT Maps PhysicsSagnik BhuniaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 3 Electrochemistry PDFDocument15 pagesChemistry 3 Electrochemistry PDFinfinilifeNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordination Compounds Scan Aug 31, 2022 - 26037590Document24 pagesCo-Ordination Compounds Scan Aug 31, 2022 - 26037590Anonymous Jr.No ratings yet
- NEET UG Physics Electrostatics MCQsDocument52 pagesNEET UG Physics Electrostatics MCQsAmit SutarNo ratings yet
- NEET Chemistry Chapter Wise Mock Test - General Chemistry - CBSE TutsDocument25 pagesNEET Chemistry Chapter Wise Mock Test - General Chemistry - CBSE Tutssreenandhan 2017No ratings yet
- MLL Chemistry 2024Document6 pagesMLL Chemistry 2024prembabumahawar782No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument82 pagesChemistrySobana JoyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Study NotesDocument355 pagesCBSE Class 12 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Study NotesDharaneesh S.k.100% (1)
- ALLEN - NCERT Based Objective - Physics - Question BankDocument144 pagesALLEN - NCERT Based Objective - Physics - Question Banksamsuzzaman sahin100% (1)
- Chemistry: Cbse (Part-I)Document332 pagesChemistry: Cbse (Part-I)Kartikay RajNo ratings yet
- Emailing Chemical Kinetics (Class 12)Document12 pagesEmailing Chemical Kinetics (Class 12)Bakul ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry: TopicDocument8 pagesSome Basic Concepts in Chemistry: TopicRishabh RanjanNo ratings yet
- 11th Science MHT Cet Triumph Chemistry McqsDocument12 pages11th Science MHT Cet Triumph Chemistry McqsAirtel PrepaidNo ratings yet
- 01 Some Basic Concept of Chemistry Formula Sheets Quizrr PDFDocument7 pages01 Some Basic Concept of Chemistry Formula Sheets Quizrr PDFKalyana ChakravarthiNo ratings yet
- 36 Years Physics Pyq PWDocument316 pages36 Years Physics Pyq PWCat123No ratings yet
- Disha Chemistry Revision (WWW - Crackjee.xyz)Document9 pagesDisha Chemistry Revision (WWW - Crackjee.xyz)Tanmay Morey100% (1)
- HALOALKENES AND HALO ARENES - Chemistry NotesDocument24 pagesHALOALKENES AND HALO ARENES - Chemistry Notesrahul SNo ratings yet
- Trans-Dichlorobis (Ethylenediamine) Cobalt (III) Chloride: The Synthesis ofDocument9 pagesTrans-Dichlorobis (Ethylenediamine) Cobalt (III) Chloride: The Synthesis ofANA MARIA VERA ESCAMILLANo ratings yet
- Al2o3 Material BalenceDocument23 pagesAl2o3 Material BalenceEmgr. Muhammad FahdNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Electronic Theories of Organic ChemistryDocument1 pageAn Introduction To Electronic Theories of Organic ChemistryMuhammad AbdulazizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 The Periodic TableDocument50 pagesChapter 5 The Periodic TableLENETTE ALAGONNo ratings yet
- CBSE - 12 - English - Art Integrated ProjectDocument7 pagesCBSE - 12 - English - Art Integrated ProjectAnusha75% (4)
- Chemistry 1st QTR EXAMDocument3 pagesChemistry 1st QTR EXAMJul RoseNo ratings yet
- 2019 TJC H2 Chem Prelim P1 QPDocument16 pages2019 TJC H2 Chem Prelim P1 QPaliciaNo ratings yet
- Macho Laminador: M DIN 13. ISO 724/965.1 MF DIN 13. ISO 724/965.1 MF DIN 13. ISO 724/965.1 Unc Asme B1.1Document2 pagesMacho Laminador: M DIN 13. ISO 724/965.1 MF DIN 13. ISO 724/965.1 MF DIN 13. ISO 724/965.1 Unc Asme B1.1emerson.mineiro100% (1)
- Coordinate CompoundDocument13 pagesCoordinate CompoundAman KapoorNo ratings yet
- Intertek Minerals Schedule of Services and Charges 2018 AUSDocument48 pagesIntertek Minerals Schedule of Services and Charges 2018 AUSJulian CassablancaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Uses of Organic Compounds Part1Document35 pages2021 Uses of Organic Compounds Part1Rachelle Anne VistalNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen: Navigation SearchDocument503 pagesHydrogen: Navigation Searchp4ukumar1No ratings yet
- Review Questions: Written/Composed By: - SHAHZAD IFTIKHAR Contact # 0313-5665666 WebsiteDocument6 pagesReview Questions: Written/Composed By: - SHAHZAD IFTIKHAR Contact # 0313-5665666 WebsitesohailNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry 3ed TR Eoc Test Answers 2Document1 pageIgcse Chemistry 3ed TR Eoc Test Answers 2Marin PesicNo ratings yet
- Specification Points Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument3 pagesSpecification Points Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- 50 Years of WACKER POLYSILICONDocument13 pages50 Years of WACKER POLYSILICONAndréNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 5 Phd124Document10 pagesLab Report 5 Phd124NUR ALYA BATRISYIA ZUKMINo ratings yet
- Synthesis of PolycaprolactoneDocument21 pagesSynthesis of PolycaprolactoneAdela CezaraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Igcse Atp Important NotesDocument12 pagesChemistry Igcse Atp Important Notesrazan nazeer86% (7)
- Combined Past Paper Questions On StoiciometryDocument27 pagesCombined Past Paper Questions On StoiciometryRamesh Iyer50% (4)
- Chemistry Eoc Study Guide (11x17)Document2 pagesChemistry Eoc Study Guide (11x17)api-254514513No ratings yet
- Indian Standard: Method For Chemical Analysis of SteelsDocument10 pagesIndian Standard: Method For Chemical Analysis of SteelsMuthusamy ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Citrato de Sodio - Weifang EnsignDocument1 pageCitrato de Sodio - Weifang EnsignEmanuel Juan Flores ArbulúNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3: Synthesis of Tris (Acetylacetonato) Manganese (III)Document16 pagesExperiment 3: Synthesis of Tris (Acetylacetonato) Manganese (III)Fatima AhmedNo ratings yet
- 201 L 4 Gravimetric AnalysisDocument24 pages201 L 4 Gravimetric AnalysisJawad AhmadNo ratings yet
- 15 - Amines (New) PDFDocument25 pages15 - Amines (New) PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Transition Metals. Characteristics, Properties and UsesDocument509 pagesTransition Metals. Characteristics, Properties and Useslhphong0211910% (1)
- Fe Analysis by REDOX Titration PDFDocument4 pagesFe Analysis by REDOX Titration PDFarun231187No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lehninger Biochemistry Test BankDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Lehninger Biochemistry Test Bankitskez17 x100% (2)