Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 9 Body Tissues
Lecture 9 Body Tissues
Uploaded by
louise navorOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 9 Body Tissues
Lecture 9 Body Tissues
Uploaded by
louise navorCopyright:
Available Formats
LECTURE
9: BODY TISSUES
Wednesday, October 12, 2022 9:01 AM
CELL JUNCTIONS
TEST
- GAP JUNCTIONS
- Types and tissue characteristics
- TIGHT JUNCTIONS
- Connective tissue types
- DESMOSOME- ADHERING JUNCTION
- Aerocolar
- Dense regular and irregular
TIGHT JUNCTIONS
- Goblet cell
- no movement between cell-
- Simple squamous epithelium= lung tissue
- Present= anything we want to control
- Cell junction
- No absorption between cells
- Kiss sites= tight
- Ex. Intestines, blood brain barrier, gut wall
GAP JUNCTIONS DESMOSOMES
- Allows for movement= of ions - Structural junction
- Transmission of charge - Withstands stress=
- Ex. Heart, gut mechanical
- Gut= moving food - Ex. Skin, uterus, heart
- Heart=contractions, spread by
gap junctions
TISSUES
- Cells with= similar structure and function
- 4 types
1. Epithelial= everywhere
2. Connective tissue= everywhere
3. Nerve
4. muscle
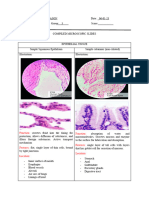
EPITHELIAL TISSUE
EPITHELIAL
FUNCTIONS
- Covering sheets
- Everything is covered by epithelial tissue - Protection
- Ex. Skin - Absorption, secretion
- Ion transport, diffusion
- GLANDS
- Filtration
1. Exocrine
- Form= slippery surfaces= ex
have duct, dump something on the duct or skin
mucus membranes
surface, ex sweat gland, earwax
2. Endocrine
Where we get hormone, dump into the blood
SQUAMOUS
- Ex.lung tissue= a lot of absorption
SIMPLE VS STRATIFIED
- SIMPLE= single layer SIMPLE EPITHELIUM
- STRATIFIED= multiple layers - Epithelium= seen on things we need to
protect
CUBOIDAL, COLUMNAR CELLS
- CUBOIDAL= round shape Simple squamous epithelium
- COLUMNAR= specialized for absorption - Areas= little wear and tear
- Adapted= diffusion and filtration
- Thin walls
- Ex. Lung tissue= easier to diffuse o2
across membrane
STRATIFIED EPITHELIUM
- For wear and tear
Stratified squamous epithelium
- Protect= areas of wear and tear= protection
- Defend= against microbes
- Ex. Outer layer of skin or epidermis , lining of
mouth , vagina
- More outer layer= more flat or squished=
stratified squamous
- Manny cells
Transitional epithelium
- Change shape= depending on what stress it is on
- Areas= subject to stretching
- Ex. Urinary bladder
GLANDS
- Specialized epithelial cells
1. Exocrine glands
Secrete substances into ducts
Ex. Sweat gland's, gut
2. Endocrine glands
Secrete hormones into blood
Ductless
Ex. Thyroid
3. Paracrine gland
Secrete over short distances
EPITHELIEAL TISSUE: TYPES Para= close/ short distance
- Transportign= columnar or cuboidal
- Ciliated= cuboidal to columnar
UNICELLULAR EXOCRINE GLANDS DUCT CLASSIFICATIONS
THE GOBLET CELL (TEST) SIMPLE VS. COMPOUND
- Goblet=produce mucin - Simple= 1 branch
- Mucin+ water= mucus - Compound= multiple branch
- Protects and lubricates = many internal body - Don’t need to study
surfaces
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
- Filler space
- Hold things together
- Functions
1. Connect, support,
strengthens
2. Protect and insulates=
internal organs
3. Compartmentalize
muscle
CONNECTIVE TISSUE
PROTEINS
- Collagen=stiff , string
snap back , ex. Tendon
- Elastin= stretchy, like
elastic, ex. Lung
- Fibroblast= cells that
secrete matrix protein
- Blast= makes something
STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE CONNECTIVE TISSUE
CLASSES OF CONNECTIVE TISSUES
- Extracellular matrix - Difference in structure depends on
- Tissue = Most diverse and abundant
- Collagen and elastin fibres • Type of cells
Main classes
- Viscous= gel like ground substance • Different composition of matrix
- Connective tissue proper= tendons and Ex. Sugar, protein, and water
ligaments, visible
- Cushions and protects body structure
- Cartilage Ex. Cartilage
- Bone tissue
- Blood
- Fat
CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER
- Has 2 subclasses
1. Loose connective tissue= low fibre= low
structure
• Areolar
• Adipose
2. Dense connective tissue= high fibre
• Regular = organized
• Irregular = not organized
LOOSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE (TEST)
AREOLAR
- Filler= hold stuff in place
- Gel like matrix= with a 3 fibres= not arranged
- Contains
• Fat cells
• White blood cells
• Mast cells
• Fibroblasts
- Underlies= epithelial tissue
- Surrounds blood vessels and organs
- Borders= all other tissue in the organ
- Hold skin to muscle
DENSE IRREGULAR CONNECTIVE TISSU E
IRREGULAR (TEST)
- Have fibres= every direction
- Withstands tension/ pulling
- Collagen= every direction= can take force at
any direction
- - Location= skin, gut, fibrous capsules of joints
and organs
SPECIALIZED
CONNECTIVE TISSUE-
DENSE REGULAR CONNECTIVE TISSUE SERVE SPECIAL
REGULAR (TEST) FUNCTIONS
- Arranged= to take the tension= where you get the most tension BONE
- Parallel collagen fibres - Forms the
- 95%= collagen skeleton
- Some elastin - Spongy vvs.
- Poorly vascularized= colour white= low blood flow=low tim to Compact
repair
- Muscle and bone attachment= withstand stress= in 1 direction
- Ex. Tendons, ligament's
BLOOD
- Transport materials= glucose
and oxygen
Cells
- Fluid matrix of
1. Osteoblast= make bone
• Plasma= fluid
2. Osteoclast= resorb bone,
• Red blood cells
breaking down bone
• White blood cells
3. Osteocytes= mature cells
• Platelets
BONE TYPES
COMPACT
- Harder= harvesian systems
- Forms= shafts and ends, contains marrow space
- Yellow bone marrow= mostly fat= in marrow space\
SPONGY TISSUE
- Trabeculae=form lattice- like support
- Spaces= may contain red bone marrow
BONES- THE HARD ELEMENTS OF SKELETON
BONE
- 10 % cells
- 90% matrix
- Extra cellular matrix:
1. Calcium and phosphate (hydroxyapatite)
2. Collagen
3. Proteins
4. Water
- Cells
1. Osteoblast= make bone
2. Osteoclast= resorb bone, breaking down bone
3. Osteocytes= mature cells
SPECIALIZED CONNECTIVE TISSUE
GROWTH PLATES SERVE SPECIAL FUNCTION
- Epiphyseal plate= calcify- hard bone
CARTILAGE
- transitional issue= from which bone develops
- Maintains shapes= of certain body parts ex. Nose, ears
- Cushion vertebrae= vertebral disks, lines joint cavities
ADIPOSE TISSUE
- Fat cells
- Functions= insulation, protection, and energy storage
CARTILAGE LENDS SUPPORT (DONT NEDD TO STUDY)
- Provides structure and support under compression
CONNECTIVE TISSUES: TYPES
(TEST)
- Loose connective tissue
TYPES - Dense irregular tissue
1. FIBROCARTILAGE= CUSHION - Dense regular tissue
Intervertebral disks= between vertebrae - Connective tissue=
Menisci= in knee joint blood and adipose
2. HYALINE= EPIPHYSEAL PLATE
Forms= embryonic structure= forms bone
Covers and protects ends ogf long bone in joints
3. ELASTIC CARTILAGE
Flexible, outer ear, tip of nose SMOOTH
- Involuntary
- Ex. Gut, blood
vessels
MUSCLE TISSUES
- Contractile=
create force SKELETAL CARDIAC
and movement
- volutary= moves skeleton - Heart
- 3 types
- Can control - Involuntary
1. Cardiac
- Pace maker
2. Smooth
3. Skeletal
TISSUE CHARACTERISTICS
- Bspecigfic connective and
epithelial types
- Epithelial, connective,
muscle, tissue
NERVOUS TISSUE
SIGNAL TRANSMISSION
- Brain
- Nerves= made up of = lots of neurons
- Brain, spinal cord, and nerves= transmit electrical REPAIR
signals - REGENERATION= of damage sithe with the
- 2 types of cells same type of tissue, lay extra tissue= faster
1. Neurons= excitatory cells regeneration
2. Supporting cells- neuroglia cells, most of what - FIBROSIS= proliferation of scar tissue
we have - ORGANIZATION= clot is replaced by
granulation tissue= lay down
- Ex. Heart= has 4 types of tissue
CAPACITY FOR REGENERATION
- Some tissue regenerate better than other
GOOD
- Et, bone, areolar, ct, dense irregular ct, blood forming
ct
MODERATE
- Smooth muscle
WEAK
- Skeletal mt= muscle tears, because always using
muscles
- Cartilage, dense regular ct= no blood flow
NONE OR ALMOST NONE
- Cardiac mt, nervous tissue
- Tissue= dead= permanent
You might also like
- The Nomad Lore 1.31Document57 pagesThe Nomad Lore 1.31Rui HuNo ratings yet
- Zygote Embryo: TissuesDocument3 pagesZygote Embryo: TissuesChelsea NacinoNo ratings yet
- Animal Histology: 4 Types of Animal TissuesDocument12 pagesAnimal Histology: 4 Types of Animal TissuesJanlyn Ricci S. TañoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesIntegumentary SystemDelosreyes Joy Ann ANo ratings yet
- EPITHELIUMDocument2 pagesEPITHELIUMALEXIS MOIRAH CALIGAGANNo ratings yet
- Epithelial: Type of Tissue CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesEpithelial: Type of Tissue CharacteristicsGlanela ManalotoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 - THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Chapter 4Document23 pagesLESSON 1 - THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Chapter 4Abegail Ashley PenoniaNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument7 pagesConnective TissueSaif AliNo ratings yet
- Bimed 09Document11 pagesBimed 09api-3706483No ratings yet
- HistologyDocument16 pagesHistologyJeong song parkNo ratings yet
- Thermoregulation Protection Vitamin D. Synthesis Excretion IdentificationDocument5 pagesThermoregulation Protection Vitamin D. Synthesis Excretion IdentificationLorraine CayamandaNo ratings yet
- Fit Closely Has 1 Free Surface Epithelium Rests On A Basement Membrane Have No Blood Supply of Their Own From CapillariesDocument3 pagesFit Closely Has 1 Free Surface Epithelium Rests On A Basement Membrane Have No Blood Supply of Their Own From CapillariesCaithlyn KirthleyNo ratings yet
- ZooLec Reviewer February 27Document6 pagesZooLec Reviewer February 27Charles GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Genbio ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenbio ReviewerAbayan, Elaine Jewel L.No ratings yet
- T I S S U E: 4 Major Types of TissueDocument6 pagesT I S S U E: 4 Major Types of TissueMarla TurquezaNo ratings yet
- NG Tin Wing, Cheung TSZ Yau, Yeung Chi Ching, Lam ChingDocument2 pagesNG Tin Wing, Cheung TSZ Yau, Yeung Chi Ching, Lam ChingMartin NgNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Chap4 Tissues TransesDocument4 pagesAnaPhy Chap4 Tissues TransesSophia Margarette CawalingNo ratings yet
- WEEK 4 TissuesDocument15 pagesWEEK 4 TissuesMarjorie Lyka LingatNo ratings yet
- Module 2 TissuesDocument3 pagesModule 2 TissuesRaphael SevillaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesIntegumentary SystemHannah SchwartzNo ratings yet
- Simple Squamous Epithelium: VRMM2023Document5 pagesSimple Squamous Epithelium: VRMM2023VERONICA ROSE MAGPOCNo ratings yet
- BSCI 4001 Transcript MidtermDocument4 pagesBSCI 4001 Transcript MidtermLynell Caraang BarayugaNo ratings yet
- Ex 6 - HistologyDocument9 pagesEx 6 - HistologyCarl Johnave Manigbas MonzonNo ratings yet
- Tissues: Cell ConnectionsDocument3 pagesTissues: Cell ConnectionsRalph AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Genzoo Reviewer 1st SemDocument4 pagesGenzoo Reviewer 1st SememilpauloquibilanNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals Mind MapDocument3 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals Mind MapAstha AgrawalNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument1 pageTissueGrace HernandezNo ratings yet
- L2 EpitheliumDocument4 pagesL2 EpitheliumGlysa MaeNo ratings yet
- 2-Bone and Cartilage Best NiteDocument11 pages2-Bone and Cartilage Best Niteamandagnaw19No ratings yet
- Axial Skeleton: Skull Hyoid Vertebral Column Thoracic Cage Parietal BoneDocument5 pagesAxial Skeleton: Skull Hyoid Vertebral Column Thoracic Cage Parietal BoneGabriel Joseph CabreraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Anatomy of The Nasal Cavity and PharynxDocument22 pagesLecture 2 - Anatomy of The Nasal Cavity and PharynxAmelia RoziantyNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals - Mind Maps - Yakeen 3.0 2024Document3 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals - Mind Maps - Yakeen 3.0 2024thakur.shrish.singhNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument27 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyFaithNo ratings yet
- I Am An Exam Question: Pre-Operative Physical Examination of A Surgical PatientDocument9 pagesI Am An Exam Question: Pre-Operative Physical Examination of A Surgical PatientMyrtle Yvonne RagubNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter4Document10 pagesAnaphy Chapter4justin mendiazNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue or Epithelium: FunctionsDocument10 pagesEpithelial Tissue or Epithelium: FunctionsJOAN KLAIRE I. LIBOTNo ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy of The Skin: Integument: Chordate Epidermis / Dermis Function of Integument 1. Agnathans / JawlessDocument7 pagesComparative Anatomy of The Skin: Integument: Chordate Epidermis / Dermis Function of Integument 1. Agnathans / JawlessHugh WeinerNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Digestive System - HandoutDocument11 pagesAnaphy Digestive System - HandoutAEGEL DARO TORRALBANo ratings yet
- Tissue Histology Types of Tissues: Kylie Jan C. SilvaDocument3 pagesTissue Histology Types of Tissues: Kylie Jan C. SilvaKert trocioNo ratings yet
- Histology Lab Practicals - AY 2021-2022Document15 pagesHistology Lab Practicals - AY 2021-2022H TNo ratings yet
- Botany and Zoology (Grade 12-Biology Reviewer)Document12 pagesBotany and Zoology (Grade 12-Biology Reviewer)Patricia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Tissue LocationsDocument4 pagesTissue Locationsrenee belle isturisNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2: Abdominal: Stomach, Liver, Pelvic: Reproductive OrgansDocument6 pagesAnatomy 2: Abdominal: Stomach, Liver, Pelvic: Reproductive OrgansPHILYP EPHRAIM PARANGALANNo ratings yet
- Biological Organization: B) Stratified Epithelial TissueDocument8 pagesBiological Organization: B) Stratified Epithelial TissueShane V. TabalbaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy MidtermDocument14 pagesAnaphy MidtermKatherine bundalianNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues - Micro Notes by Seep PahujaDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissues - Micro Notes by Seep Pahujahh100% (1)
- Animal Tissues - Micro Notes by Seep PahujaDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissues - Micro Notes by Seep PahujaKazi AkibNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ReviewerDocument10 pagesChapter 4 ReviewerrizzamaegomezoctavianoNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument4 pagesTissuesMicth Laica BetoyaNo ratings yet
- Embryology TimelineDocument3 pagesEmbryology Timelinesayeda.raza24No ratings yet
- Pentason CompiledTissues (HHIS)Document18 pagesPentason CompiledTissues (HHIS)Danelyn PentasonNo ratings yet
- OPD Surgery Complete PDFDocument22 pagesOPD Surgery Complete PDFPeter Paul RecaboNo ratings yet
- Ch1 XI Animal Kingdom Zlgy Minhad Hsslive PDFDocument9 pagesCh1 XI Animal Kingdom Zlgy Minhad Hsslive PDFBrilliant Cloudprint100% (1)
- MC 1 Midterm Notes (Anatomy and Physiology)Document14 pagesMC 1 Midterm Notes (Anatomy and Physiology)Aiza CereighneNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 - Epithelial TissueDocument4 pagesActivity 4 - Epithelial TissueMay Ann EnoserioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Epithelial TissuesDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Epithelial TissuesAngelNo ratings yet
- Block 3 HistologyDocument8 pagesBlock 3 HistologyjungsoonistNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: YANES, Myngelle C. Anaphy Bmls 02Document4 pagesChapter Four: YANES, Myngelle C. Anaphy Bmls 02cheewyyyyNo ratings yet
- Module # Epitheleal TransDocument5 pagesModule # Epitheleal TransLara VanessNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- Chapter 18 - SkinDocument29 pagesChapter 18 - SkinMohammad Riovaldo Radja NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Dermatology - 3rd EdDocument137 pagesDermatology - 3rd Edalexweiyan.97No ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument7 pagesEpithelial TissueJoan PaulineNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Patton Solutions ManualDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Patton Solutions Manualashleyjamesdbfpajsegr100% (24)
- The Extracellular Matrix in Development PDFDocument16 pagesThe Extracellular Matrix in Development PDFMaura HokamaNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Janeways Immunobiology 9th Edition Murphy Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Janeways Immunobiology 9th Edition Murphy Test Bank PDFsiennaclimatal1bk6t6100% (13)
- MammaryglandDocument3 pagesMammaryglandMARTINEZ JUSTINENo ratings yet
- (PATHO A) Colloid GoiterDocument7 pages(PATHO A) Colloid GoiterPaulene RiveraNo ratings yet
- Histology Mock ExamDocument73 pagesHistology Mock ExamRozen GaiserNo ratings yet
- Histopathological Insight of An Adenomatoid Odontogenic Lesion - A Cyst, Tumor or Hamartoma?Document6 pagesHistopathological Insight of An Adenomatoid Odontogenic Lesion - A Cyst, Tumor or Hamartoma?gunawan121982No ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument14 pagesIntegumentary SystemVert MochiNo ratings yet
- MCQ Question BankDocument102 pagesMCQ Question BankdrmadaanpiyushNo ratings yet
- Nursing OncologyDocument131 pagesNursing Oncologyapi-3818438100% (5)
- ANAPHY111Document60 pagesANAPHY111Gerlyn MortegaNo ratings yet
- Eye and Ear HistologyDocument96 pagesEye and Ear HistologyErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MD100% (1)
- GINGIVADocument41 pagesGINGIVADENTALORG.COM0% (2)
- PDF of ProtectionDocument28 pagesPDF of ProtectionAROOJ ASLAMNo ratings yet
- 2014-15 Department Annual ReportDocument9 pages2014-15 Department Annual ReportPramodNo ratings yet
- 2 Anatomy 2021 Cells and TissuesDocument87 pages2 Anatomy 2021 Cells and TissuesMJ Jomoc ArejolaNo ratings yet
- Nsg241 Study Guide Exam 5Document76 pagesNsg241 Study Guide Exam 5NatalieAndersonNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument127 pagesPDFSamir ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Development of Human PeriodontiumDocument117 pagesDevelopment of Human PeriodontiumvsdeepsNo ratings yet
- Histologyoftracheaandlung 160315034320Document65 pagesHistologyoftracheaandlung 160315034320MUBEEN SHAIKHNo ratings yet
- CH - 04 Skin and Body MembraneDocument64 pagesCH - 04 Skin and Body MembraneDavid Jasher AbadNo ratings yet
- Biology - Tissue - Animals Revision Notes - askIITiansDocument7 pagesBiology - Tissue - Animals Revision Notes - askIITiansAbhinav PandeyNo ratings yet
- Zikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsDocument37 pagesZikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsZikriAimanNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument116 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 1 - Module 1 Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeNoraine Princess TabangcoraNo ratings yet
- Histology AssignmentDocument4 pagesHistology AssignmentNico LokoNo ratings yet
- 1) Pathology: Myasthenia Gravis Is An Autoimmune Disease Associated With Antibodies Directed To TheDocument49 pages1) Pathology: Myasthenia Gravis Is An Autoimmune Disease Associated With Antibodies Directed To TheAhmad HassanNo ratings yet