Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Módulo 8 - Bascula
Módulo 8 - Bascula
Uploaded by
Lucas GonçalvesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Módulo 8 - Bascula
Módulo 8 - Bascula
Uploaded by
Lucas GonçalvesCopyright:
Available Formats
GLOBAL MANPOWER DEVELOPMENT
773G / 775G OFF-HIGHWAY TRUCK
HOIST SYSTEM
MODULE 8 - TEXT REFERENCE
SERV1921
Print Instructor Pages Print Participant Pages
© 2011 Caterpillar Inc.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -2- Module 8 - Hoist System
2
3
2_1
INTRODUCTION
• Hoist system main components The hoist system on the 773G/775G trucks is electronically controlled by the
Transmission/Chassis ECM. The hoist control system operates the same as the
773F/775F trucks.
The main components of the hoist system are:
• Hoist control lever and position sensor (in cab)
• Hydraulic oil tank (1)
• Hoist pump (2)
• Hoist control valve (3)
• Hoist cylinders (4)
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -3- Module 8 - Hoist System
3_1
HOIST SYSTEM COMPONENTS
• Hoist lever positions The operator controls the hoist lever (arrow). The four positions of the hoist lever are
RAISE, HOLD, FLOAT, and LOWER. The hoist valve has a fifth position referred to
• Explain SNUB position as the SNUB position. The operator is unaware of the SNUB position because a
corresponding lever position is not provided. When the body is being lowered, just
before the body contacts the frame, the Transmission/Chassis ECM signals the hoist
lower solenoid to move the hoist valve spool to the SNUB position. In the SNUB
position, the body float speed is reduced to prevent the body from making hard
contact with the frame.
The hoist system can be enabled or disabled using Cat ET. All trucks shipped from
the factory without bodies installed are set at the DISABLED mode. The DISABLED
mode is a test mode only and will prevent the hoist cylinders from accidentally being
activated. After the body is installed, change the hoist system to the ENABLED
mode for the hoist system to function properly.
The truck should normally be operated with the hoist lever in the FLOAT position.
Traveling with the hoist in the FLOAT position will make sure the weight of the body
is on the frame and body pads and not on the hoist cylinders. The hoist control valve
will actually be in the SNUB position.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -4- Module 8 - Hoist System
If the transmission is in REVERSE when the body is being raised, the hoist lever
sensor sends a signal to the Transmission/Chassis ECM to shift the transmission to
NEUTRAL. The transmission will remain in NEUTRAL until the hoist lever is moved
into the HOLD or FLOAT position and the shift lever has been cycled into and out of
NEUTRAL.
NOTE: If the truck is started with the body raised and the hoist lever in FLOAT,
the lever must be moved into HOLD and then FLOAT before the body will
lower.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -5- Module 8 - Hoist System
2
5_1
• Hoist system components: The hoist lever (1) controls a position sensor (2). The PWM sensor sends duty cycle
input signals to the Transmission/Chassis ECM. The hoist lever position sensor is a
- Hoist lever Hall effect position sensor that receives 24 VDC from the machine electrical system.
- Position sensor Depending on the position of the sensor and the corresponding duty cycle, one of the
two solenoids located on the hoist valve is energized.
The four positions of the hoist lever are RAISE, HOLD, FLOAT, and LOWER, but
since the sensor provides a duty cycle signal that changes for all positions of the
hoist lever, the operator can modulate the speed of the hoist cylinders.
The hoist lever sensor performs three functions:
• Raises and lowers the body
• Neutralizes the transmission in REVERSE
• Starts a new Truck Payload Management System (TPMS) cycle
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -6- Module 8 - Hoist System
4 5
1
6
6_1
• Hydraulic tank on right side of Shown is the hoist and brake hydraulic tank. The upper sight gauge (1) is used to
machine: check the oil when the truck bed is down. The oil level should first be checked with
cold oil and the engine stopped. The level should again be checked with warm oil
- Upper sight gauge and the engine running.
- Lower sight gauge
- Hydraulic tank fill tube cover The lower sight gauge (2) can be used to fill the tank when the hoist cylinders are in
the RAISED position. When the hoist cylinders are lowered, the hydraulic oil level
- Hydraulic tank breather cover will increase. After the hoist cylinders are lowered, check the hydraulic tank oil level
- Brake accumulators with the upper sight gauge as explained above.
- Autolube tank (if equipped)
The hydraulic tank oil fill tube is shown with a protective cover (3) installed. The
hydraulic tank breather (not visible) is mounted on top of the tank and is enclosed
by a cover (4).
Also visible are the brake accumulators (5). The Autolube tank (6), if equipped,
mounts onto the hydraulic tank in front of the brake accumulators.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -7- Module 8 - Hoist System
3
2
1
5
4 6
7 7_1
• Rear of hoist and brake hydraulic Shown is the rear of the hoist and brake hydraulic tank. The hydraulic oil level is
tank monitored by three sensors that each send a signal to the Transmission/Chassis
ECM indicating the hydraulic tank oil level. The hydraulic oil level sensors are:
- Low hydraulic oil level sensor
- Add hydraulic oil level sensor • LOW (1)
- Full hydraulic oil level sensor
• ADD (2)
- Brake cooling port
- Front brake manifold valve • FULL (3)
return
- Towing valve and secondary Brake cooling oil returns to the hydraulic tank through the brake cooling port (4).
brake valve return Other ports located on the rear of the hydraulic tank are:
- ARC/TCS valve return
• Front brake manifold valve return (5)
• Towing valve and secondary brake valve return (6)
• Automatic Retarding Control (ARC)/Traction Control System (TCS)
valve return (7)
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -8- Module 8 - Hoist System
1
3
4 2
8_1
• Rear of engine: The hoist pump (1) is a gear type pump that is attached to the drive gear at the rear
of the engine. The hoist pump pulls oil from the hydraulic tank and sends the oil to
- Hoist pump the hoist valve through the supply hose (2). Mounted to the hoist pump is the brake
- Supply hose (to hoist valve) charging pump (3) and the brake cooling pump (4).
- Brake charging pump
NOTE: The brake cooling pump is NOT installed on the LRC model trucks.
- Brake cooling pump
- Hoist supply pressure port The body up switch must be in the RAISE position before the LOWER relief valve
setting can be tested. Move a magnet past the body up switch until the body up alert
indicator on the dash turns ON. If the body up switch is in the LOWER position, the
Transmission/Chassis ECM will hold the hoist valve in the SNUB position and the
LOWER relief valve will not open.
In the HOLD, FLOAT, and SNUB positions, a pressure gauge connected to the
supply pressure port (5) will show the brake cooling system pressure, which is a
result of the restriction in the coolers, brakes, and hoses (normally much lower than
the actual oil cooler relief valve setting). The maximum pressure is limited by the oil
cooler relief valve.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -9- Module 8 - Hoist System
4
2
5
2 1
9_1
• Hoist valve location (inside right The hoist control valve (1) is located to the rear of the torque converter mounted on
frame rail): the inboard side of the right frame rail. The hoist valve is the same as the hoist
control valve on the 773F/775F trucks.
- Hoist control valve
- Hydraulic actuators The hoist valve uses brake charging pump oil from the pressure reducing valve in the
- Supply hose (from pump) towing valve as the pilot oil to shift the directional spool inside the hoist valve. Pilot
oil enters the hydraulic actuators (2) on both ends of the hoist valve.
- Return hose (to tank)
- Tube (to brake oil cooler) Oil from the hoist pump flows through the supply hose (3) to the hoist valve. Oil from
the hoist valve returns to the tank through the return hose (4). Oil from the hoist
valve flows to the brake oil cooler though the tube (5) connected to the top of the
hoist valve.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -10- Module 8 - Hoist System
6
1 4
5
3
10_1
• Hoist valve components: Pilot oil pressure is always present at both ends of the directional spool when the
engine is running. Two solenoid valves are used to drain the pilot oil from the ends
- RAISE solenoid valve of the directional spool, which then allows the spool to move. The solenoid on the
- LOWER solenoid valve right is the RAISE solenoid valve (1), and the solenoid on the left is the LOWER
solenoid valve (2).
- Left pressure port
- Right pressure port The left pressure port (3) is used to check the pilot pressure of the hoist lower
- Oil cooler relief valve plug solenoid. The right pressure port (4) is used to check the pilot pressure of the hoist
- RAISE relief valve raise solenoid.
- LOWER relief valve
When the Transmission/Chassis ECM receives an input signal from the hoist lever
sensor, the ECM sends an output signal current between 0 and 1.9 amps to one of
the solenoids. The amount of current sent to the solenoid determines how much
pilot oil is drained from the end of the directional spool and, therefore, how far the
directional spool travels toward the solenoid.
An oil cooler relief valve is located in the hoist control valve behind the large plug (5).
The relief valve limits the brake oil cooling pressure when the hoist valve is in the
HOLD, FLOAT, or SNUB position.
The hoist system relief pressures are controlled by the two relief valves located on
top of the hoist valve. The RAISE relief valve (6) limits the pressure in the hoist
system during RAISE. The 775G RAISE relief valve is set slightly higher than the
773G RAISE relief valve. The LOWER relief valve (7) limits the pressure in the hoist
system during LOWER.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -11- Module 8 - Hoist System
NOTE: The hoist valve LOWER position (snub adjustment) is an adjustable
parameter in the Transmission/Chassis ECM using Cat ET. The slight adjustment
provides a means to compensate for valve differences.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -12- Module 8 - Hoist System
4
3
6
1
2
12_1
• Hoist valve to hoist cylinder The hoist cylinder lower circuit pressure port (1) and raise circuit pressure port (2)
connections: are located on a manifold (3), which connects the hoist valve (4) and the hoist
cylinders (5).
- Hoist cylinder lower circuit
pressure port The relief valve pressure setting is tested with the engine at HIGH IDLE and the hoist
- Hoist cylinder raise circuit valve in the RAISE or LOWER position.
pressure port
- Manifold The body up switch at the frame near the body pivot pin must be in the RAISE
position before the LOWER relief valve setting can be tested. Move a magnet past
- Hoist valve
the body up switch until the body up alert indicator on the dash turns ON. If the body
- Hoist cylinders up switch is in the LOWER position, the Transmission/Chassis ECM will hold the
- Raise supply hose hoist valve in the SNUB position and the LOWER relief valve will not open.
An orifice plate is installed between the upper hose and the rod end port on both
hoist cylinders. The orifice plate restricts the flow of oil from the rod end of the hoist
cylinders. The orifice plate also prevents cavitation of the cylinders when the body
raises faster than the pump can supply oil to the cylinders (caused by a sudden shift
of the load).
An orifice plate is also installed at the front of the manifold where the raise supply
hose (6) is connected to the manifold. The orifice plate prevents excessive hoist oil
flow retuning to the tank via the hoist valve during bed float down.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -13- Module 8 - Hoist System
NOTE: If the snub feature is not adjusted correctly, residual pressure will exist
in the head end side of the cylinders and the body will not rest on the frame. The
raise circuit pressure port should be used to ensure there is no residual pressure
in the head end side of the cylinders. Otherwise, when checking the raise (high)
circuit pressure, the pressure port on the hoist pump is easier to access.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -14- Module 8 - Hoist System
(6) Brake Oil
(7) Raise Cooler
Solenoid Relief Valve
(11) Low
Pressure (9) Towing Valve
Relief Valve
(13) Main
Relief
(12) High Dump Valve (3) Brake
Pressure Oil Cooler
Relief Valve
(2) Dual Stage (4) Hoist Cylinder
Relief Valve Rod End
Signal Stem
(10) Load (5) Hoist Cylinder
Check Head End
Valve
(1) Directional
Spool
HOIST CONTROL VALVE
HOLD
(9) Towing Valve
(8) Lower
Solenoid
14_1
• Hoist control valve - HOLD This illustration shows a sectional view of the hoist control valve in the HOLD position.
Pilot oil pressure is present at both ends of the directional spool (1). The spool is
held in the centered position by the centering springs and the pilot oil. Passages in
the directional spool vent the dual stage relief valve signal stem (2) to the tank. All
the hoist pump oil flows through the brake oil coolers (3) to the front and rear
brakes.
The position of the directional spool blocks the oil in the hoist cylinder head end (5)
and the hoist cylinder rod end (4).
A gauge connected to a pressure port at the pump, while the hoist valve is in the
HOLD position, will show the brake cooling system pressure, which is a result of the
restriction in the coolers, brakes, and hoses. The maximum pressure in the circuit
should correspond to the setting of the brake oil cooler relief valve (6).
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -15- Module 8 - Hoist System
ON
(6) Brake Oil
(7) Raise Cooler
Solenoid Relief Valve
(11) Low
Pressure (9) Towing Valve
Relief Valve
(13) Main
Relief
(12) High Dump Valve (3) Brake
Pressure Oil Cooler
Relief Valve
(4) Hoist Cylinder
(2) Dual Stage
Rod End
Relief Valve
Signal Stem
(10) Load (5) Hoist Cylinder
Check Head End
Valve
HOIST CONTROL VALVE (1) Directional
RAISE Spool
(9) Towing Valve
(8) Lower
Solenoid
15_1
• Hoist control valve - RAISE In the RAISE position, the raise solenoid (7) is ENERGIZED and drains pilot oil from
the upper end of the directional spool (1). The directional spool moves up. Pump oil
flows past the load check valve (10) and the directional spool to the head end of the
hoist cylinders (5).
When the directional spool is initially shifted, the load check valve remains closed
until the supply pressure is higher than the pressure in the hoist cylinders. The
load check valve prevents the body from dropping before the RAISE pressure
increases.
The directional spool also sends hoist cylinder raise pressure to the dual stage relief
valve signal stem (2). The dual stage relief valve signal stem moves down and
blocks the supply pressure from opening the low pressure relief valve (11).
Oil flowing from the rod end of the hoist cylinders (4) flows freely through the brake
oil coolers (3) to the brakes.
If the pressure in the head end of the hoist cylinders exceeds the relief valve settings,
the high pressure relief valve (12) will open. When the high pressure relief valve
opens, pump oil flows to the tank.
The high pressure hoist relief valve setting is checked at the hoist pump pressure
port or the head end pressure port. Check the relief pressure with the hoist lever in
the RAISE position and the engine at HIGH IDLE.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -16- Module 8 - Hoist System
(6) Brake Oil
(7) Raise Cooler
Solenoid Relief Valve
(11) Low
Pressure (9) Towing Valve
Relief Valve
(13) Main
Relief
(12) High Dump Valve (3) Brake
Pressure Oil Cooler
Relief Valve
(4) Hoist Cylinder
(2) Dual Stage
Rod End
Relief Valve
Signal Stem
(10) Load (5) Hoist Cylinder
Check Head End
Valve
(1) Directional
Spool
HOIST CONTROL VALVE
LOWER
(9) Towing Valve
(8) Lower
Solenoid
ON
16_1
• Hoist control valve - LOWER/ In the LOWER (power down) position, the LOWER solenoid (8) is energized and
POWER DOWN drains pilot oil from the lower end of the directional spool (1). The directional spool
moves down.
Supply oil from the pump flows past the load check valve (10) and the directional
spool to the rod end of the hoist cylinders (4). Oil in the head end of the hoist
cylinders (5) flows to the tank through holes in the directional spool. The supply oil
in the rod end of the cylinders and the weight of the body move the cylinders to their
retracted positions.
Just before the body contacts the frame, the body up switch sends a signal to the
Transmission/Chassis ECM to move the directional spool to the SNUB position. In
the SNUB position, the directional spool moves slightly to restrict the flow of head
end oil through only some of the holes in the spool, which allows the body to lower
gradually.
The directional spool also vents the passage to the dual stage relief valve signal
stem (2). The dual stage relief valve signal stem allows supply pressure to be limited
by the low pressure relief valve (11).
If the pressure in the rod end of the hoist cylinders is too high, the low pressure relief
valve will open. When the low pressure relief valve opens, pump oil flows to the
tank.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -17- Module 8 - Hoist System
The low pressure hoist relief valve setting is checked at the rod end pressure port.
Check the relief pressures with the hoist lever in the LOWER position and the engine
at HIGH IDLE.
The body up switch must be in the RAISE position before the LOWER relief valve
setting can be tested. Move a magnet past the body up switch until the body up alert
indicator on the dash turns ON. If the body up switch is in the LOWER position, the
Transmission/Chassis ECM will hold the hoist valve in the SNUB position and the
LOWER relief valve will not open.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -18- Module 8 - Hoist System
(6) Brake Oil
(7) Raise Cooler
Solenoid Relief Valve
(11) Low
Pressure (9) Towing Valve
Relief Valve
(13) Main
Relief
(12) High Dump Valve (3) Brake
Pressure Oil Cooler
Relief Valve
(2) Dual Stage (4) Hoist Cylinder
Relief Valve Rod End
Signal Stem
(10) Load (5) Hoist Cylinder
Check Head End
Valve
(1) Directional
Spool
HOIST CONTROL VALVE
FLOAT
(9) Towing Valve
(8) Lower
Solenoid
ON
18_1
• Hoist control valve - FLOAT In the FLOAT position, the LOWER solenoid (8) is partially energized and drains
some of the pilot oil at the lower end of the directional spool (1) to the tank. The
directional spool moves down. Because the pilot oil is only partially drained, the
directional spool does not move down as far as during LOWER (power down).
Pump supply oil flows past the load check valve (10) and the directional spool to
the rod end of the hoist cylinders (4). Oil in the head end of the hoist cylinders (5)
flows to the tank. The position of the directional spool permits the pressure of the oil
flowing to the brake oil coolers (3) to be felt at the rod end of the hoist cylinders.
The truck should normally be operated with the hoist lever in the FLOAT position.
Traveling with the hoist in the FLOAT position will make sure the weight of the body
is on the frame and body pads and not on the hoist cylinders. The hoist valve will
actually be in the SNUB position.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -19- Module 8 - Hoist System
(6) Brake Oil
(7) Raise Cooler
Solenoid Relief Valve
(11) Low
Pressure (9) Towing Valve
Relief Valve
(13) Main
Relief
(12) High Dump Valve (3) Brake
Pressure Oil Cooler
Relief Valve
(4) Hoist Cylinder
(2) Dual Stage
Rod End
Relief Valve
Signal Stem
(10) Load (5) Hoist Cylinder
Check Head End
Valve
(1) Directional
Spool
HOIST CONTROL VALVE
SNUB
(9) Towing Valve
(8) Lower
Solenoid
ON
19_1
• Hoist control valve - SNUB As the body is lowered, just before the body contacts the frame, the body up switch
sends a signal to the Transmission/Chassis ECM to move the directional spool (1) to
the SNUB position. In the SNUB position, the directional spool moves slightly to a
position between HOLD and FLOAT. The SNUB position restricts the flow of oil and
lowers the body gradually.
The operator does not control the SNUB position. When the hoist lever is in the
LOWER or FLOAT position and the body up switch is in the DOWN position, the hoist
control valve is in the SNUB position.
A gauge connected to the rod end pressure port while the hoist control valve is in the
SNUB position will show the brake cooling system pressure, which is a result of the
restriction in the coolers, brakes, and hoses. The maximum pressure in the circuit
should correspond to the setting of the brake oil cooler relief valve (6).
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -20- Module 8 - Hoist System
20_1
• Hoist cylinders Two-stage hoist cylinders (arrows) are used to raise the body. Oil flows from the
hoist control valve to the two hoist cylinders when the directional spool in the hoist
control valve is not in HOLD.
Hoist pilot pressure is required to lower the body with a dead engine. The towing
pump can be used to provide the hoist pilot oil.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -21- Module 8 - Hoist System
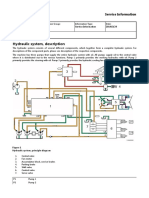
HOIST HYDRAULIC SYSTEM SCHEMATIC
(5) Towing Valve
(15) Main Relief Dump Spool
(12) Raise
Relief Valve
(3) (11) Lower (10)
Brake Oil Coolers (16) Relief Valve Dual Stage
Brake Charge
Signal Spool
Valve
(2) (8)
Hoist Valve Lower
Solenoid
RAISE (13)
(17) Orifice Transmission/
Plate HOLD Chassis ECM
(9) Hoist
Cylinder
SNUB
(1) (14) (6)
Hoist Orifice Directional
FLOAT
Pump Plate Spool
(18)
(9) Hoist LOWER
Manifold (4)
Cylinder
Brake
Cooling
Relief
Valve
(7)
Raise
Solenoid
21_1
• Hoist and brake cooling This illustration shows the hoist hydraulic system in the HOLD position. The hoist
schematic - HOLD pump (1) pulls oil from the hydraulic tank through the suction screen located in the
rear of the tank. Oil flows from the hoist pump to the hoist control valve (2).
When the hoist control valve is in the HOLD, FLOAT, or SNUB position, all the hoist
pump oil flows through the brake oil coolers (3). Oil flows from the oil coolers, through
the brakes, and returns to the hydraulic tank.
• Brake cooling relief valve A brake cooling relief valve (4) is located in the hoist control valve. The relief valve
limits the brake oil cooling pressure when the hoist control valve is in the HOLD,
FLOAT, or SNUB position.
• Pilot oil comes from brake Oil from the brake charging pump flows to a pressure reducing valve inside the
charging pump towing valve (5). The pressure reducing valve decreases the brake pump pressure,
which is used as the pilot oil to shift the directional spool (6) inside the hoist control
valve. Oil flows from the towing valve to both ends of the directional spool.
• Directional spool Pilot pressure is always present at both ends of the directional spool when the engine
is running. The raise solenoid valve (7) and the lower solenoid valve (8) are used to
drain the pilot oil from the ends of the directional spool, which then allows the
centering springs and the pressure on the opposite end of the spool to move the
spool. When the RAISE solenoid is energized, the directional spool will move toward
the RAISE solenoid.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
SERV1921 - 09/11 -22- Module 8 - Hoist System
• RAISE and LOWER solenoid valve The RAISE and LOWER solenoid valves constantly receive approximately 300
millivolts at a frequency of 80 Hz from the Transmission/Chassis ECM (13) when
they are in any position except HOLD. The excitation, referred to as “dither,” is used
to keep the solenoids in a ready state for quick response.
When the Transmission/Chassis ECM receives an input signal from the hoist lever
sensor, the ECM sends an output signal current between 0 and 1.9 amps to one of
the solenoids. The amount of current sent to the solenoid determines how much pilot
oil is drained from the end of the directional spool and, therefore, the distance that
the directional spool travels.
• RAISE position When the hoist control valve is in the RAISE position, pump supply oil flows to the
head end of the hoist cylinders (9). Pump supply oil also flows to the top of the dual
stage signal spool (10) and moves the spool down. When the dual stage signal
spool moves down, pump supply oil is blocked from the LOWER relief valve (11), and
the RAISE relief valve (12) will limit the hoist system pressure.
• LOWER, FLOAT, SNUB positions When the hoist control valve is in the LOWER (power down), FLOAT, or SNUB
position, pump supply oil flows to the rod end of the hoist cylinders. Pump supply oil
is blocked from the dual stage signal spool and the spring holds the spool in the up
position. When the dual stage signal spool is in the up position, pump supply oil can
flow to the LOWER relief valve, and hoist system pressure is controlled by the
LOWER relief valve.
• Orifice plates An orifice plate (14) is installed between the upper hose and the rod end port on both
hoist cylinders. The orifice plate prevents cavitation of the cylinders when the body
raises faster than the pump can supply oil to the cylinders (caused by a sudden shift
of the load).
An orifice plate (17) is also installed at the front of the manifold (18) where the raise
supply hose is connected to the manifold. The orifice plate prevents excessive hoist
oil flow retuning to the tank via the hoist valve during bed float down.
Caterpillar: Confidential Yellow
You might also like
- 8L90 IntroductionDocument66 pages8L90 IntroductionBrandon100% (6)
- Heat Transfer Analysis of Integral-Fin TubesDocument12 pagesHeat Transfer Analysis of Integral-Fin Tubeshermez19No ratings yet
- CFD Methodology For Liquid Pressure Recovery PredictionsDocument9 pagesCFD Methodology For Liquid Pressure Recovery PredictionsAshok SureshNo ratings yet
- 777G M07 HstSys EN TXTDocument23 pages777G M07 HstSys EN TXTpmcisissengueNo ratings yet
- 777g m07 Hstsys en SLDDocument19 pages777g m07 Hstsys en SLDJohnny RubioNo ratings yet
- Catalogo 2 777DDocument79 pagesCatalogo 2 777DEdith RiosNo ratings yet
- Global Service Learning: 777F (JRP) Off-Highway TrucksDocument79 pagesGlobal Service Learning: 777F (JRP) Off-Highway TrucksManuel Pompa Flores100% (3)
- 793f Ac Hoist SystemDocument30 pages793f Ac Hoist SystemJorge Sandro Uribe AguilarNo ratings yet
- R1600G - Load Haul Dump: Operator'S Station and Monitoring SystemDocument26 pagesR1600G - Load Haul Dump: Operator'S Station and Monitoring SystemJORGE QUIQUIJANANo ratings yet
- Módulo 6 - DireçãoDocument23 pagesMódulo 6 - DireçãoLucas GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- 400 Controls and InstrumentsDocument17 pages400 Controls and InstrumentsMrAlbert2009No ratings yet
- Operator'S Station: 994H Wheel LoaderDocument13 pagesOperator'S Station: 994H Wheel LoaderAntony Armando Huaylla QuispeNo ratings yet
- Leveling System Controller Electro-HydraulicDocument5 pagesLeveling System Controller Electro-HydraulicCHRISTIAN LOPEZ FLOREZNo ratings yet
- 336E M10 SwgHydSys EN STUDocument7 pages336E M10 SwgHydSys EN STUKJDNKJZEFNo ratings yet
- 400 RearlinkageDocument27 pages400 RearlinkageMrAlbert2009No ratings yet
- 6060HydMiningShvl M08 SwingSys enDocument20 pages6060HydMiningShvl M08 SwingSys enJonathan José Alvis GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Telemotor Helm OrdersDocument92 pagesUnit 4 - Telemotor Helm Ordersmecete8514No ratings yet
- 988K-834-836K M01 OpSta EN SLDDocument15 pages988K-834-836K M01 OpSta EN SLDZul HermanNo ratings yet
- CPC 20Document98 pagesCPC 20juan david lópez montalegreNo ratings yet
- FTSXX108LL Inst Motorista IngDocument21 pagesFTSXX108LL Inst Motorista IngdomingosNo ratings yet
- CâmbioDocument21 pagesCâmbiopaulojfeitoza100% (1)
- Sistema Hidraulico PilotoDocument6 pagesSistema Hidraulico PilotoRafael RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Operation & Service Manual: Balanceweight Type Forklift Truck With EngineDocument99 pagesOperation & Service Manual: Balanceweight Type Forklift Truck With EngineFaouzi Zorgati100% (2)
- 590 Super R 695 Super R: Section 82 - LoaderDocument12 pages590 Super R 695 Super R: Section 82 - LoaderTeknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- 336E M11 TravelSys EN STUDocument8 pages336E M11 TravelSys EN STUKJDNKJZEFNo ratings yet
- Owners Manual/Operating Instructions: Lift-Rite Titan Series Hand Pallet TruckDocument4 pagesOwners Manual/Operating Instructions: Lift-Rite Titan Series Hand Pallet Trucksrinivasa ReddyNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual Loader 99781 PDFDocument43 pagesInstruction Manual Loader 99781 PDFapostuNo ratings yet
- Testeo TransmisionDocument53 pagesTesteo TransmisionTaller Pahr100% (1)
- 04 OperationDocument10 pages04 OperationJorge GalarceNo ratings yet
- Pilot Hydraulic System Components Hydraulic Lockout (Activation) 1. Lever Hydraulic Activation Crossbar 2. Limit Switch (Behind Gray 3. Housing)Document1 pagePilot Hydraulic System Components Hydraulic Lockout (Activation) 1. Lever Hydraulic Activation Crossbar 2. Limit Switch (Behind Gray 3. Housing)vitaliyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Intermediate Hydraulics - 950G Wheel LoaderDocument45 pagesUnit 2: Intermediate Hydraulics - 950G Wheel LoaderAlha DNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic SystemDocument16 pagesHydraulic Systemluis tocoraNo ratings yet
- Trans Repair Manual 2145-2210 Section 4Document150 pagesTrans Repair Manual 2145-2210 Section 4nunyaNo ratings yet
- Steering System: 777G Off-Highway TruckDocument18 pagesSteering System: 777G Off-Highway TruckFrancisco Ferrer100% (1)
- 9 Hydraulic System, Digging, Handling, Grading Equipment, Misc EquipmentDocument181 pages9 Hydraulic System, Digging, Handling, Grading Equipment, Misc EquipmentDaniel NavasNo ratings yet
- 590 Super R 695 Super R: Section 41 - Steering SystemDocument34 pages590 Super R 695 Super R: Section 41 - Steering SystemTeknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- Techdoc Print Page TEST TRANSMISSIONDocument11 pagesTechdoc Print Page TEST TRANSMISSIONtyok sajaNo ratings yet
- Módulo 1 - Estação OperadorDocument22 pagesMódulo 1 - Estação OperadorLucas GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Manual 3 PDFDocument66 pagesManual 3 PDFciobiiuliNo ratings yet
- 794 Ac m04 Steersys enDocument31 pages794 Ac m04 Steersys enDavidCPNo ratings yet
- ZL 60 H Manual OperationDocument56 pagesZL 60 H Manual OperationRedNo ratings yet
- Testing and AdjustingDocument55 pagesTesting and Adjustingahmad sulaimanNo ratings yet
- McDonnell Douglas DC 10 40 Flight ControlsDocument19 pagesMcDonnell Douglas DC 10 40 Flight ControlsAndrewNo ratings yet
- D-WATCH 322 - Prelim Week 1Document139 pagesD-WATCH 322 - Prelim Week 1Jeth Ro UmbaoNo ratings yet
- 994H Wheel Loader: Global Manpower DevelopmentDocument12 pages994H Wheel Loader: Global Manpower DevelopmentAntony Armando Huaylla QuispeNo ratings yet
- Unitrigmt6500 Hyd Dump SysDocument19 pagesUnitrigmt6500 Hyd Dump Sysnikbeam0% (1)
- D WATCH 322 Prelim Week 1Document80 pagesD WATCH 322 Prelim Week 1Berly FreemanNo ratings yet
- 05 Steering Hydraulic LG958LDocument36 pages05 Steering Hydraulic LG958LGeorge Jhonson100% (1)
- Steering System: 994H Wheel LoaderDocument24 pagesSteering System: 994H Wheel LoaderAntony Armando Huaylla QuispeNo ratings yet
- 994K WHLLDR M04 SteerSys en TXT-ParticipantDocument34 pages994K WHLLDR M04 SteerSys en TXT-ParticipantAngela AllenNo ratings yet
- JKR Basic Lift ComponentsDocument47 pagesJKR Basic Lift ComponentsKayrol Amry0% (1)
- 390D Hydraulic Excavator Operator Station: Global Manpower DevelopmentDocument21 pages390D Hydraulic Excavator Operator Station: Global Manpower DevelopmentLewis NemanangaNo ratings yet
- ArtesDocument28 pagesArtesarturo laosNo ratings yet
- Power Train System Operation 938GDocument48 pagesPower Train System Operation 938Gjvc251100% (4)
- Iefly Describe The Following Steering Gear Control SystemsDocument6 pagesIefly Describe The Following Steering Gear Control Systems1989muhdNo ratings yet
- Servotransmision 8 Vel (1) CatDocument22 pagesServotransmision 8 Vel (1) Catinsano008No ratings yet
- Diesel Engine Care and Repair: A Captain's Quick GuideFrom EverandDiesel Engine Care and Repair: A Captain's Quick GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Módulo 6 - DireçãoDocument23 pagesMódulo 6 - DireçãoLucas GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Módulo 3 - MotorDocument28 pagesMódulo 3 - MotorLucas GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Módulo 5 - Trem de ForçaDocument32 pagesMódulo 5 - Trem de ForçaLucas GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Módulo 1 - Estação OperadorDocument22 pagesMódulo 1 - Estação OperadorLucas GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Módulo 4 - Sistema EmissãoDocument15 pagesMódulo 4 - Sistema EmissãoLucas GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Pai Nosso - Our Father-OboéDocument1 pagePai Nosso - Our Father-OboéLucas GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Installation Equipment: Sanitary Fittings and ValvesDocument89 pagesInstallation Equipment: Sanitary Fittings and ValvesSebassde0% (1)
- Valves DatasheetDocument1 pageValves DatasheetLuis Acevedo AyalaNo ratings yet
- HazopDocument75 pagesHazopSaima Saima89% (9)
- PIPING Isometric DrawingsDocument8 pagesPIPING Isometric DrawingsKUMAARRRNo ratings yet
- Giotto TOPDocument30 pagesGiotto TOPtycristinaNo ratings yet
- Manual Atl Sauter Oper Inst Ba 695 Disc Tool Turret PDFDocument40 pagesManual Atl Sauter Oper Inst Ba 695 Disc Tool Turret PDFVladimir Colombiano de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Let's Start With: S P EC IA LF E A T U R EDocument15 pagesLet's Start With: S P EC IA LF E A T U R EAndré Faria100% (1)
- Engine Fault Codes: CumminsDocument20 pagesEngine Fault Codes: CumminsCarlosNo ratings yet
- Canalta DBB Product Manual - LOW RESDocument12 pagesCanalta DBB Product Manual - LOW RESFer VFNo ratings yet
- Installation Guide: L31227 (94130007) Rev 6/10Document4 pagesInstallation Guide: L31227 (94130007) Rev 6/10Dime JovanovNo ratings yet
- Valvula Accionamiento Directo Herion 95000Document2 pagesValvula Accionamiento Directo Herion 95000Base SistemasNo ratings yet
- Storm PackerDocument38 pagesStorm PackerJay T. Yong100% (1)
- Sym Mio 50 - 100 (EN)Document215 pagesSym Mio 50 - 100 (EN)manualsym50% (2)
- Technical Specification: 1) Filter Feed Pump With Motor 1 NosDocument4 pagesTechnical Specification: 1) Filter Feed Pump With Motor 1 NosKamatchi NathanNo ratings yet
- Almag Is 150109Document4 pagesAlmag Is 150109alisuseNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts Book: Ity. Mped. OriginalDocument108 pagesSpare Parts Book: Ity. Mped. OriginalSergey MylnikovNo ratings yet
- SWG-22-8571 Ersatzteile Fahrmischer en RZDocument9 pagesSWG-22-8571 Ersatzteile Fahrmischer en RZsantoshNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3b - BUILDING UTILITIES 2 - Fire Protection SystemsDocument89 pagesLecture 3b - BUILDING UTILITIES 2 - Fire Protection SystemsNicole DizonNo ratings yet
- Komatsu AcronymsDocument7 pagesKomatsu Acronymsالمهندسوليدالطويل100% (4)
- FXB00013539 - FXB00001143 - 0814402 PartsListDocument5 pagesFXB00013539 - FXB00001143 - 0814402 PartsListJose Esteem M CamelNo ratings yet
- Operators and ActuatorsDocument11 pagesOperators and ActuatorsNyoman RakaNo ratings yet
- UST - A1100 Guardian Overfill Prevention ValveDocument1 pageUST - A1100 Guardian Overfill Prevention ValvelauraNo ratings yet
- National Oil Corporation: Rev Date Description Checked ApprovedDocument26 pagesNational Oil Corporation: Rev Date Description Checked ApprovedYousab JacobNo ratings yet
- Tata 1109 G LPT BrochureDocument2 pagesTata 1109 G LPT BrochureVishal Karad100% (1)
- Pom Blending SystemsDocument8 pagesPom Blending Systemspablo292No ratings yet
- Air Die Grinder (22000rpm) GP 824Document1 pageAir Die Grinder (22000rpm) GP 824Jhun AquinoNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual SE20SX P3 M01693Document119 pagesInstruction Manual SE20SX P3 M01693Michael OlanrewajuNo ratings yet