Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diffusion and Osmosis Problems
Uploaded by
notthealt 42Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diffusion and Osmosis Problems
Uploaded by
notthealt 42Copyright:
Available Formats
Diffusion and Osmosis Problems
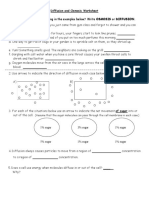
Directions:
beaker containing substances dissolved in water. Draw a blue arrow to show the movement of water. Draw a black
arrow to show movement of any other materials. Answer each question based on the diagram provided.
The membrane is permeable to: glucose, K+, Na+, water, iodine, and the imaginary substances X and Z.
The membrane is impermeable to: starch and imaginary substance Y.
When iodine and starch mix, a bluish/black color will be seen.
Helpful Hint: The problems have been broken down into parts for your benefit. Look at one substance at a time!
Where is the substance more concentrated?
What direction will the substance move?
What direction does the water move?
(Diffusion says it will go from an area of _______________concentration to ______________concentration)
Is the membrane permeable to the substance?
Problem 1:
1) Is the membrane permeable to glucose?
2) Will glucose diffuse? ___________
90% glucose
If so, in what direction?
10 % glucose
3) What is the % water inside the cell? __________
What is the % water outside the cell? __________
4) Will osmosis occur? __________
If so, in what direction?
5) The movement of WATER will cause changes in cell shape and size.
Will this cell shrink or swell? _____________________________ Why?
6) Is the solution in the beaker hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic?
Problem 2:
1) Will glucose diffuse? ___________ 60% glucose
If so, in what direction? 10% glucose 10 % starch
60% starch
2) Will starch diffuse? __________
If so, in what direction?
3) What is the % water inside the cell? ___________
What is the % water outside the cell? ___________
4) Will osmosis occur? _______
If so, in what direction?
5) Is the solution in the beaker hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic?
Problem 3:
1) What is the % water inside the cell? ___________
2) Will potassium (K+) diffuse? ___________
If so, in what direction? 100% water
10% K+
10% Na+
3) Will sodium (Na+) diffuse? __________ 10% starch
If so, in what direction?
4) Will starch diffuse? __________
If so, in what direction?
5) Will osmosis occur? __________
If so, in what direction?
6) Will the cell swell or shrink? _________________________ Why?
7) Is the solution in the beaker hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic?
Problem 4:
1) Will osmosis occur? If so, in what direction?
2) Will any other substances diffuse across the membrane? 40% glucose
Which ones? 20% Na+
1% K+
38% glucose
15% Na+
3% K+
5% starch
3) What direction will each substance diffuse?
4) Will the cell swell or shrink? _________________________
5) Is the solution in the beaker hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic?
6) Iodine is a yellowish solution. A starch solution is white. A starch solution turns purplish-black in the presence
of iodine. If you wait a few hours, then add iodine to the beaker, what color would the beaker solution be? Explain
your answer.
Problem 5:
1) Will osmosis occur? If so, in what direction?
2) Will any other substances diffuse across the membrane? 20% glucose
Which ones? 20% K+
10% iodine
5% glucose
3) What direction will each substance diffuse? 25% starch
4) Is the solution in the beaker hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic?
5) What will be the initial color of the solution (immediately
in the cell? __________________________ in the beaker? ________________________
s)
in the cell? __________________________ in the beaker? ________________________
Problem 6:
2) What substance(s) show net movement into the beaker? 3% glucose
2% starch
5% X
5% Y
5% Z
3) Does osmosis occur? If so, in what direction?
4) If you were told that one of the molecules X, Y, or Z
was the polysaccharide, glycogen, which would you guess
to be the glycogen? Why?
Hint start with the definition of a polysaccharide (HINT: Look at your Chemistry of Life notes)
Problem 7:
2) What substance(s) show net movement into the beaker? 13% iodine
2% starch
5% Y
5% starch
3) Does osmosis occur? If so, in what direction?
4) At the end of your experiment, what color
BONUS: Are these problems examples of active or passive transport? Explain your answer.
You might also like
- Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet: (Assume That The Sugar Molecules Can Pass Through The Cell Membrane in Each Case.)Document2 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis Worksheet: (Assume That The Sugar Molecules Can Pass Through The Cell Membrane in Each Case.)Cavene Scott100% (1)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsNo ratings yet
- BotanyDocument98 pagesBotanyMikhail Landicho100% (1)
- Cell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementDocument5 pagesCell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementMargie OpayNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport WorksheetDocument2 pagesCell Transport WorksheetVictoria Niño D100% (1)
- Cell Trasport Worksheet ANSWER KEYDocument3 pagesCell Trasport Worksheet ANSWER KEYFatima Al sharifNo ratings yet
- Dilute Solution & Colligative Properties-Assignment PDFDocument25 pagesDilute Solution & Colligative Properties-Assignment PDFggk201375% (4)
- CardDocument2 pagesCardAngeline EspinasNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions-Diffusion and Osmosis-02.11Document3 pagesPractice Questions-Diffusion and Osmosis-02.11vishiNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 1 Hkdse Mock Exam V: New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition)Document55 pagesBiology Paper 1 Hkdse Mock Exam V: New Senior Secondary Mastering Biology (Second Edition)Alex ChowNo ratings yet
- Handout - Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesHandout - Cell Transport Review Worksheetapi-502781581No ratings yet
- Gummy Bear Lab 2Document4 pagesGummy Bear Lab 2api-233187566No ratings yet
- Cellular - Transport - Study - Guide - Answer KeyDocument6 pagesCellular - Transport - Study - Guide - Answer KeyJohn Kevin NocheNo ratings yet
- HANDOUT - Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesHANDOUT - Cell Transport Review WorksheetDenis Martinez100% (1)
- Cell Processes Blank ReviewDocument4 pagesCell Processes Blank ReviewDr-Qussai ZuriegatNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Osmosis Dialysis LabDocument5 pagesDiffusion Osmosis Dialysis LabAnthony100% (1)
- GCE A - AS Level Biology A Topic Test - Foundations in BiologyDocument26 pagesGCE A - AS Level Biology A Topic Test - Foundations in Biologyarfaat shah100% (1)
- ExperimentDocument38 pagesExperimentNicolette BingtanNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Tonicity WorksheetDocument2 pagesOsmosis Tonicity WorksheetSean StewartNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review Worksheet 1Document4 pagesCell Transport Review Worksheet 1api-4218765530% (3)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Movement of substancesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Movement of substancesNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Worksheet g8Document4 pagesCell Transport Worksheet g8Ariane DionisioNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review WorksheetsDocument8 pagesCell Transport Review WorksheetsD50% (2)
- Cell - Transport - HW - Packet - JR - 10-11 - Key Finalized MGDocument24 pagesCell - Transport - HW - Packet - JR - 10-11 - Key Finalized MGRodel AzaresNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 FA2Document4 pagesGrade 7 FA2Ali DokmakNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Osmosis Lab Activity PDFDocument8 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis Lab Activity PDFHaris KhanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Cell Membrane - Review WorksheetDocument3 pagesWorksheet - Cell Membrane - Review Worksheetapi-270403367No ratings yet
- Scientific American Biology For A Changing World With Core Physiology 3rd Edition Shuster Test BankDocument34 pagesScientific American Biology For A Changing World With Core Physiology 3rd Edition Shuster Test Bankbrittanysummerstrkayoizcj100% (8)
- AP Bio Lab1Document10 pagesAP Bio Lab1Eva DesireeNo ratings yet
- TALAGTAG JOHN ANDREI Cell Transport Worksheet 1Document7 pagesTALAGTAG JOHN ANDREI Cell Transport Worksheet 1Malachi LamaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Part A June 2009Document12 pagesFinal Exam Part A June 2009Ms Ratna Lestyana DewiNo ratings yet
- CHALLENGENaked PotatoesDocument3 pagesCHALLENGENaked PotatoesFernando NicastriNo ratings yet
- Diffusion and Osmosis Lab Answer Sheet Lab 5Document9 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis Lab Answer Sheet Lab 5BlonDeAmBitionTouRNo ratings yet
- PP1 - Potato OsmolarityDocument4 pagesPP1 - Potato OsmolarityLejla RedžovićNo ratings yet
- AP 5069 L04 DiffusionAndOsmosisDocument10 pagesAP 5069 L04 DiffusionAndOsmosisChinyere Igwe0% (1)
- Cell Transport ActivityDocument2 pagesCell Transport ActivityascanobraverichmondNo ratings yet
- Osmosis LabDocument3 pagesOsmosis LabMutuluShakurNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport ReviewDocument2 pagesCell Transport ReviewRizza MoradaNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Diffusion Worksheet 2Document2 pagesOsmosis and Diffusion Worksheet 2Kayla HNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Transport WorksheetJackielyn RavinaNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementDocument2 pagesCell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementJaniya KellyNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review WorksheetsDocument6 pagesCell Transport Review WorksheetsRyan De AlloNo ratings yet
- Cell - Transport Chapter SummaryDocument3 pagesCell - Transport Chapter SummaryAlfredo Mandia IIINo ratings yet
- HANDOUT - Cell Transport Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesHANDOUT - Cell Transport Review Worksheet7qvxkqqhs7No ratings yet
- Cell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementDocument3 pagesCell Transport Review Worksheet: Complete The Table by Checking The Correct Column For Each StatementMa.Janice GarciaNo ratings yet
- Bmjopen 2021 January 11 1 Inline Supplementary Material 3Document6 pagesBmjopen 2021 January 11 1 Inline Supplementary Material 3Diana AvramNo ratings yet
- Klasa Xi GR CDocument5 pagesKlasa Xi GR CgertaNo ratings yet
- Bio Osmosis Lab Write UpDocument8 pagesBio Osmosis Lab Write Upapi-345751834No ratings yet
- Worksheet No.2 - Cell ProcessesDocument4 pagesWorksheet No.2 - Cell ProcessesLaureen BarbsNo ratings yet
- Biology: (Effective Alternative Secondary Education)Document27 pagesBiology: (Effective Alternative Secondary Education)Jarven SaguinNo ratings yet
- Biology 9th 10-Feb-24 Full BookDocument2 pagesBiology 9th 10-Feb-24 Full BookCRO TJSSNo ratings yet
- Quiz Bio Cell Membrane TransDocument35 pagesQuiz Bio Cell Membrane TransJamaela BulajaoNo ratings yet
- Question 1Document3 pagesQuestion 1Fatima FaizanNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET NO. 3cell Transport WorksheetDocument3 pagesWORKSHEET NO. 3cell Transport WorksheetLaureen BarbsNo ratings yet
- Final WorksheetDocument26 pagesFinal WorksheetAmr SaadNo ratings yet
- Snail Eloda Virtual Lab 2015Document2 pagesSnail Eloda Virtual Lab 2015Daniel De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Enzyme F22 WorksheetDocument8 pagesDiffusion Enzyme F22 WorksheetVy TranNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Lab ReportDocument10 pagesOsmosis Lab Reportapi-345335976No ratings yet
- Module 3 Movement of Materials Through The Cell MembraneDocument24 pagesModule 3 Movement of Materials Through The Cell MembraneDon FreecsNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Study GuideDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Study GuideJose MendietaNo ratings yet
- Bio Exam 2Document19 pagesBio Exam 2tulldmNo ratings yet
- 2001 - 1995Document170 pages2001 - 1995api-3706564No ratings yet
- Online Quiz 1Document5 pagesOnline Quiz 1heidi_hyun100% (1)
- Eoc Review PacketDocument12 pagesEoc Review Packetapi-293001217No ratings yet
- YSC2023Prelim Problems&AnswersDocument14 pagesYSC2023Prelim Problems&AnswersGAN ZHONG WEN MoeNo ratings yet
- Exercise-Muscle Study GuideDocument3 pagesExercise-Muscle Study Guidenotthealt 42No ratings yet
- Census 2020Document1 pageCensus 2020notthealt 42No ratings yet
- TracksDocument14 pagesTracksnotthealt 42No ratings yet
- 3 1lessonDocument7 pages3 1lessonnotthealt 42No ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Calculation: Yohannes Nigatu (B.PHARM)Document63 pagesPharmaceutical Calculation: Yohannes Nigatu (B.PHARM)temesgen yohannesNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport MechanismsDocument21 pagesCell Transport MechanismsCj CasintoNo ratings yet
- DATE: 23-09-2022 TO 24-09-2022: Two Day Workshop For PGT (Chemistry)Document349 pagesDATE: 23-09-2022 TO 24-09-2022: Two Day Workshop For PGT (Chemistry)Athiya ParveenNo ratings yet
- Transport Mechanism: Lesson 2Document11 pagesTransport Mechanism: Lesson 2JGHUNGERNo ratings yet
- Sy Chemistry Q. Bank Sem 1 2023-24Document7 pagesSy Chemistry Q. Bank Sem 1 2023-24Kia AsherNo ratings yet
- MCC Nursing 111 Lecture Notes - Fall 2016Document94 pagesMCC Nursing 111 Lecture Notes - Fall 2016Marc LaBarberaNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 FinalDocument26 pagesNCM 112 FinalMarielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Trắc nghiệm tiến hóa sinh lý sinh tháiDocument13 pagesTrắc nghiệm tiến hóa sinh lý sinh tháiGia TuệNo ratings yet
- InternalAssessment OsmolarityDocument13 pagesInternalAssessment OsmolaritynsnsnsnsNo ratings yet
- Different Types of IV FluidsDocument6 pagesDifferent Types of IV FluidsnicoleNo ratings yet
- Bio 110 - Chapter 5Document32 pagesBio 110 - Chapter 5moayadNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Calculations Laboratory: IsotonicityDocument6 pagesPharmaceutical Calculations Laboratory: IsotonicityZel BulanonNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5: The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument78 pagesChapter - 5: The Fundamental Unit of LifeRoboNo ratings yet
- Solutions and SolubilityDocument9 pagesSolutions and SolubilityDarrell W. GarwayNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1: Osmosis and Diffusion: Pisan, Marrie Kris Saguid, Reinah Lyn Versoza, Jasmine NikkiDocument7 pagesExperiment No.1: Osmosis and Diffusion: Pisan, Marrie Kris Saguid, Reinah Lyn Versoza, Jasmine NikkiMage San LuisNo ratings yet
- Bio Cornell Notes Cell Transport 2Document3 pagesBio Cornell Notes Cell Transport 2api-335205149No ratings yet
- Biology Notes For o Level HTMLDocument91 pagesBiology Notes For o Level HTML123456789No ratings yet
- OsmosislabDocument8 pagesOsmosislabapi-328190492No ratings yet
- Jawapan: Kertas 1 BiologyDocument9 pagesJawapan: Kertas 1 BiologyNang Maizana Megat YahyaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy 3Document30 pagesAnaphy 3Roan Redyna MariñasNo ratings yet
- Summative Practice 3: Movement of Substances Across A Plasma MembraneDocument14 pagesSummative Practice 3: Movement of Substances Across A Plasma MembraneDewi SallehNo ratings yet
- OrnidazoleDocument16 pagesOrnidazolekannanppharmaNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Class 9 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument4 pagesBiology Notes Class 9 The Fundamental Unit of LifeSai Uday Shankar BommakantiNo ratings yet
- 3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsDocument67 pages3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsThom PaglinawanNo ratings yet